Zhaoning Wang
Unsupervised Model Diagnosis
Oct 08, 2024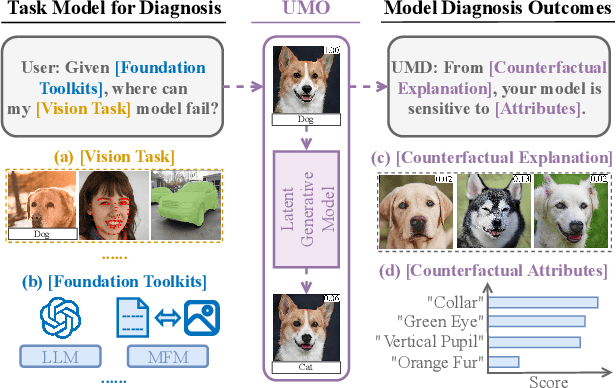
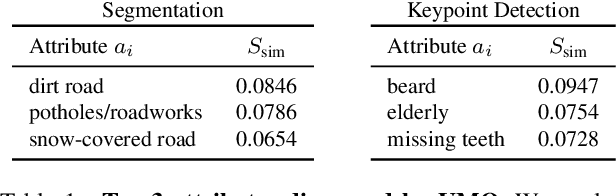
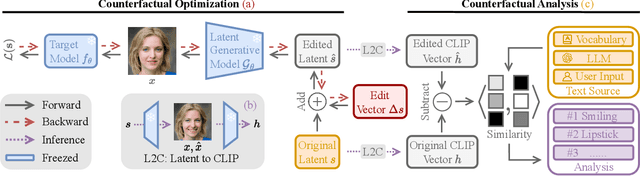
Abstract:Ensuring model explainability and robustness is essential for reliable deployment of deep vision systems. Current methods for evaluating robustness rely on collecting and annotating extensive test sets. While this is common practice, the process is labor-intensive and expensive with no guarantee of sufficient coverage across attributes of interest. Recently, model diagnosis frameworks have emerged leveraging user inputs (e.g., text) to assess the vulnerability of the model. However, such dependence on human can introduce bias and limitation given the domain knowledge of particular users. This paper proposes Unsupervised Model Diagnosis (UMO), that leverages generative models to produce semantic counterfactual explanations without any user guidance. Given a differentiable computer vision model (i.e., the target model), UMO optimizes for the most counterfactual directions in a generative latent space. Our approach identifies and visualizes changes in semantics, and then matches these changes to attributes from wide-ranging text sources, such as dictionaries or language models. We validate the framework on multiple vision tasks (e.g., classification, segmentation, keypoint detection). Extensive experiments show that our unsupervised discovery of semantic directions can correctly highlight spurious correlations and visualize the failure mode of target models without any human intervention.
MeshFormer: High-Quality Mesh Generation with 3D-Guided Reconstruction Model
Aug 19, 2024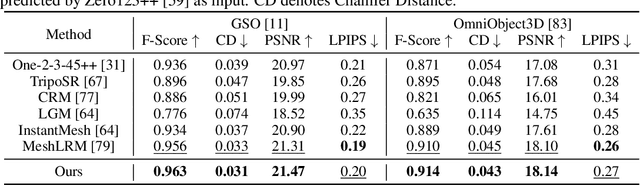
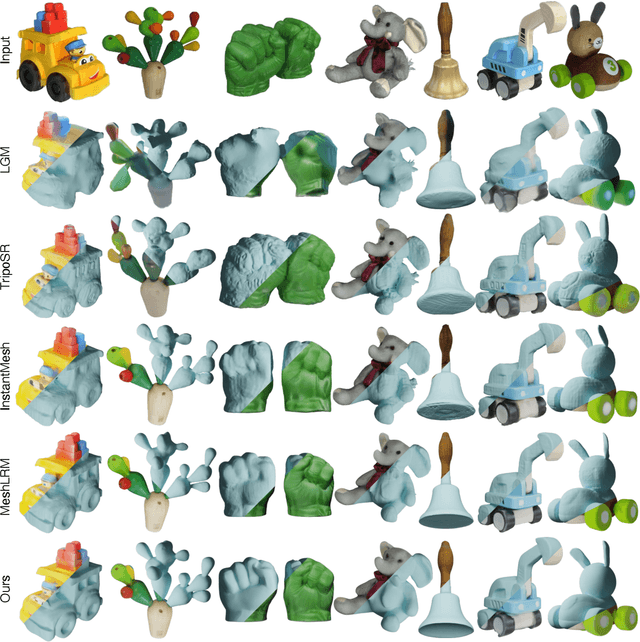
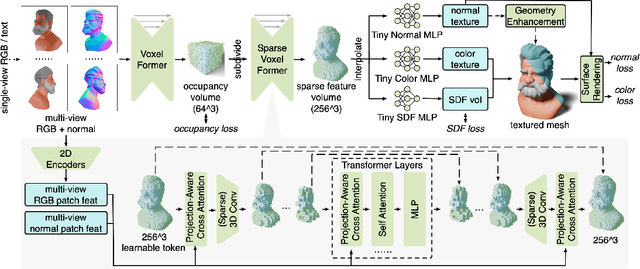
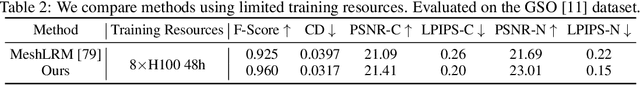

Abstract:Open-world 3D reconstruction models have recently garnered significant attention. However, without sufficient 3D inductive bias, existing methods typically entail expensive training costs and struggle to extract high-quality 3D meshes. In this work, we introduce MeshFormer, a sparse-view reconstruction model that explicitly leverages 3D native structure, input guidance, and training supervision. Specifically, instead of using a triplane representation, we store features in 3D sparse voxels and combine transformers with 3D convolutions to leverage an explicit 3D structure and projective bias. In addition to sparse-view RGB input, we require the network to take input and generate corresponding normal maps. The input normal maps can be predicted by 2D diffusion models, significantly aiding in the guidance and refinement of the geometry's learning. Moreover, by combining Signed Distance Function (SDF) supervision with surface rendering, we directly learn to generate high-quality meshes without the need for complex multi-stage training processes. By incorporating these explicit 3D biases, MeshFormer can be trained efficiently and deliver high-quality textured meshes with fine-grained geometric details. It can also be integrated with 2D diffusion models to enable fast single-image-to-3D and text-to-3D tasks. Project page: https://meshformer3d.github.io
ControlNet++: Improving Conditional Controls with Efficient Consistency Feedback
Apr 11, 2024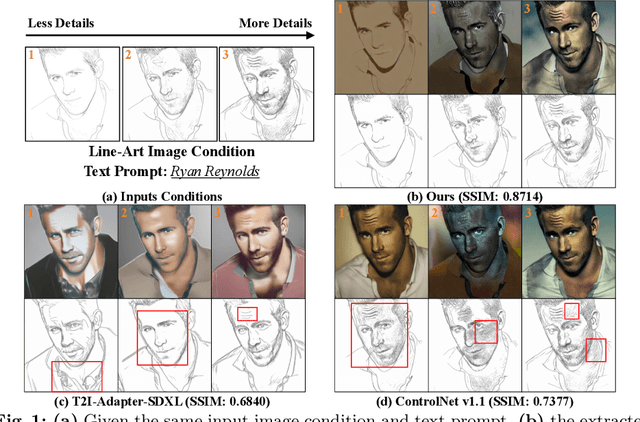
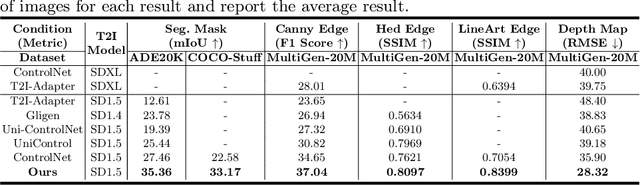
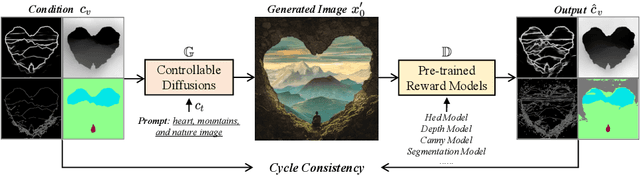
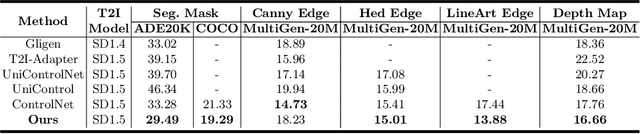
Abstract:To enhance the controllability of text-to-image diffusion models, existing efforts like ControlNet incorporated image-based conditional controls. In this paper, we reveal that existing methods still face significant challenges in generating images that align with the image conditional controls. To this end, we propose ControlNet++, a novel approach that improves controllable generation by explicitly optimizing pixel-level cycle consistency between generated images and conditional controls. Specifically, for an input conditional control, we use a pre-trained discriminative reward model to extract the corresponding condition of the generated images, and then optimize the consistency loss between the input conditional control and extracted condition. A straightforward implementation would be generating images from random noises and then calculating the consistency loss, but such an approach requires storing gradients for multiple sampling timesteps, leading to considerable time and memory costs. To address this, we introduce an efficient reward strategy that deliberately disturbs the input images by adding noise, and then uses the single-step denoised images for reward fine-tuning. This avoids the extensive costs associated with image sampling, allowing for more efficient reward fine-tuning. Extensive experiments show that ControlNet++ significantly improves controllability under various conditional controls. For example, it achieves improvements over ControlNet by 7.9% mIoU, 13.4% SSIM, and 7.6% RMSE, respectively, for segmentation mask, line-art edge, and depth conditions.
LucidDreaming: Controllable Object-Centric 3D Generation
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:With the recent development of generative models, Text-to-3D generations have also seen significant growth. Nonetheless, achieving precise control over 3D generation continues to be an arduous task, as using text to control often leads to missing objects and imprecise locations. Contemporary strategies for enhancing controllability in 3D generation often entail the introduction of additional parameters, such as customized diffusion models. This often induces hardness in adapting to different diffusion models or creating distinct objects. In this paper, we present LucidDreaming as an effective pipeline capable of fine-grained control over 3D generation. It requires only minimal input of 3D bounding boxes, which can be deduced from a simple text prompt using a Large Language Model. Specifically, we propose clipped ray sampling to separately render and optimize objects with user specifications. We also introduce object-centric density blob bias, fostering the separation of generated objects. With individual rendering and optimizing of objects, our method excels not only in controlled content generation from scratch but also within the pre-trained NeRF scenes. In such scenarios, existing generative approaches often disrupt the integrity of the original scene, and current editing methods struggle to synthesize new content in empty spaces. We show that our method exhibits remarkable adaptability across a spectrum of mainstream Score Distillation Sampling-based 3D generation frameworks, and achieves superior alignment of 3D content when compared to baseline approaches. We also provide a dataset of prompts with 3D bounding boxes, benchmarking 3D spatial controllability.
Zero-shot Model Diagnosis
Mar 27, 2023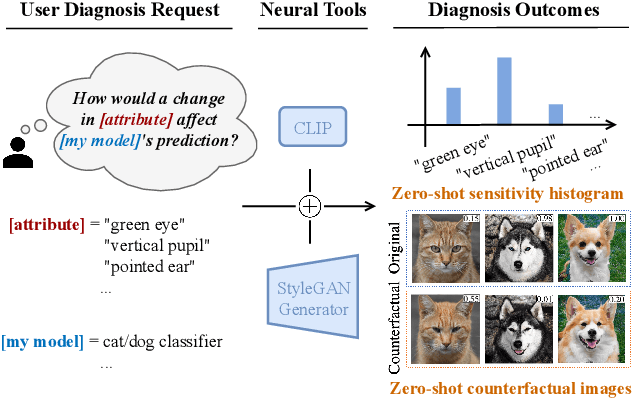
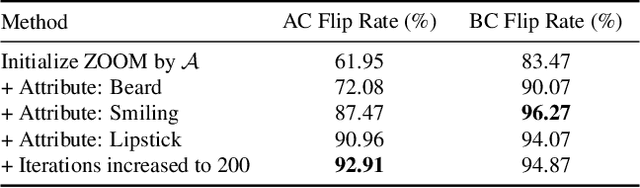
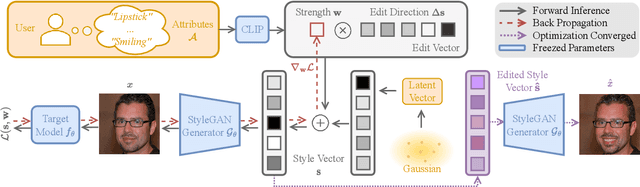
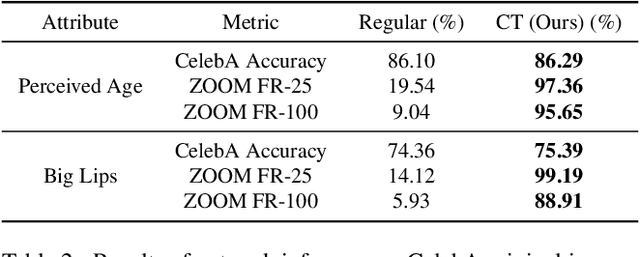
Abstract:When it comes to deploying deep vision models, the behavior of these systems must be explicable to ensure confidence in their reliability and fairness. A common approach to evaluate deep learning models is to build a labeled test set with attributes of interest and assess how well it performs. However, creating a balanced test set (i.e., one that is uniformly sampled over all the important traits) is often time-consuming, expensive, and prone to mistakes. The question we try to address is: can we evaluate the sensitivity of deep learning models to arbitrary visual attributes without an annotated test set? This paper argues the case that Zero-shot Model Diagnosis (ZOOM) is possible without the need for a test set nor labeling. To avoid the need for test sets, our system relies on a generative model and CLIP. The key idea is enabling the user to select a set of prompts (relevant to the problem) and our system will automatically search for semantic counterfactual images (i.e., synthesized images that flip the prediction in the case of a binary classifier) using the generative model. We evaluate several visual tasks (classification, key-point detection, and segmentation) in multiple visual domains to demonstrate the viability of our methodology. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method is capable of producing counterfactual images and offering sensitivity analysis for model diagnosis without the need for a test set.
Semantic Image Attack for Visual Model Diagnosis
Mar 23, 2023



Abstract:In practice, metric analysis on a specific train and test dataset does not guarantee reliable or fair ML models. This is partially due to the fact that obtaining a balanced, diverse, and perfectly labeled dataset is typically expensive, time-consuming, and error-prone. Rather than relying on a carefully designed test set to assess ML models' failures, fairness, or robustness, this paper proposes Semantic Image Attack (SIA), a method based on the adversarial attack that provides semantic adversarial images to allow model diagnosis, interpretability, and robustness. Traditional adversarial training is a popular methodology for robustifying ML models against attacks. However, existing adversarial methods do not combine the two aspects that enable the interpretation and analysis of the model's flaws: semantic traceability and perceptual quality. SIA combines the two features via iterative gradient ascent on a predefined semantic attribute space and the image space. We illustrate the validity of our approach in three scenarios for keypoint detection and classification. (1) Model diagnosis: SIA generates a histogram of attributes that highlights the semantic vulnerability of the ML model (i.e., attributes that make the model fail). (2) Stronger attacks: SIA generates adversarial examples with visually interpretable attributes that lead to higher attack success rates than baseline methods. The adversarial training on SIA improves the transferable robustness across different gradient-based attacks. (3) Robustness to imbalanced datasets: we use SIA to augment the underrepresented classes, which outperforms strong augmentation and re-balancing baselines.
VOS: Learning What You Don't Know by Virtual Outlier Synthesis
Feb 04, 2022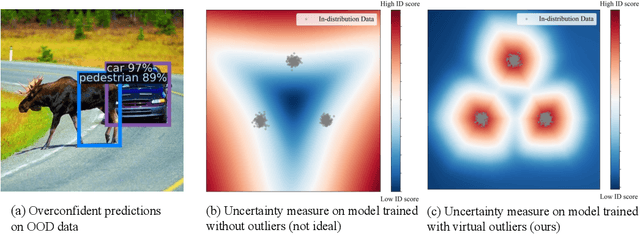
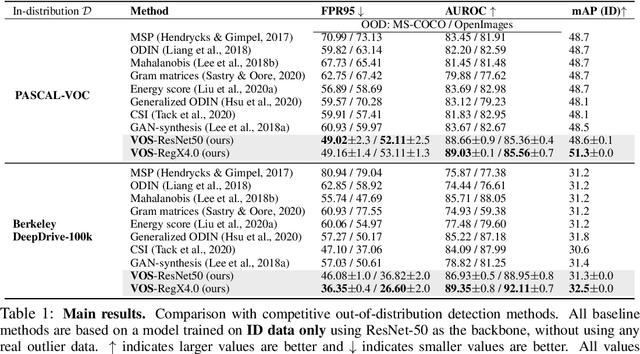
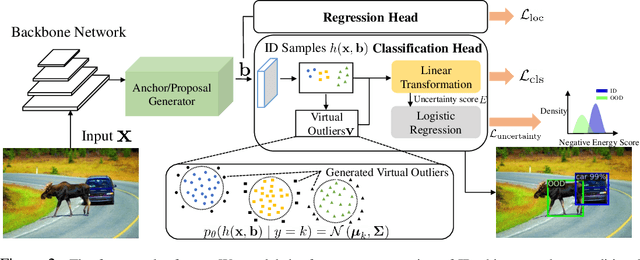
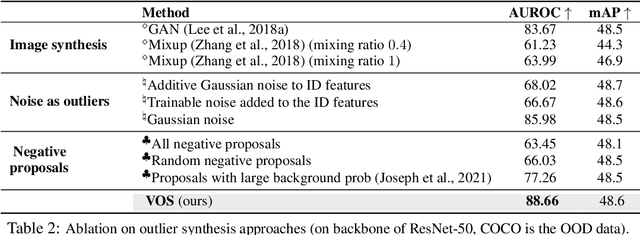
Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection has received much attention lately due to its importance in the safe deployment of neural networks. One of the key challenges is that models lack supervision signals from unknown data, and as a result, can produce overconfident predictions on OOD data. Previous approaches rely on real outlier datasets for model regularization, which can be costly and sometimes infeasible to obtain in practice. In this paper, we present VOS, a novel framework for OOD detection by adaptively synthesizing virtual outliers that can meaningfully regularize the model's decision boundary during training. Specifically, VOS samples virtual outliers from the low-likelihood region of the class-conditional distribution estimated in the feature space. Alongside, we introduce a novel unknown-aware training objective, which contrastively shapes the uncertainty space between the ID data and synthesized outlier data. VOS achieves state-of-the-art performance on both object detection and image classification models, reducing the FPR95 by up to 7.87% compared to the previous best method. Code is available at https://github.com/deeplearning-wisc/vos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge