Linghao Chen
EasyHeC++: Fully Automatic Hand-Eye Calibration with Pretrained Image Models
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:Hand-eye calibration plays a fundamental role in robotics by directly influencing the efficiency of critical operations such as manipulation and grasping. In this work, we present a novel framework, EasyHeC++, designed for fully automatic hand-eye calibration. In contrast to previous methods that necessitate manual calibration, specialized markers, or the training of arm-specific neural networks, our approach is the first system that enables accurate calibration of any robot arm in a marker-free, training-free, and fully automatic manner. Our approach employs a two-step process. First, we initialize the camera pose using a sampling or feature-matching-based method with the aid of pretrained image models. Subsequently, we perform pose optimization through differentiable rendering. Extensive experiments demonstrate the system's superior accuracy in both synthetic and real-world datasets across various robot arms and camera settings. Project page: https://ootts.github.io/easyhec_plus.
MeshFormer: High-Quality Mesh Generation with 3D-Guided Reconstruction Model
Aug 19, 2024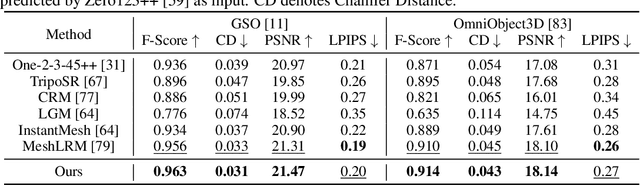
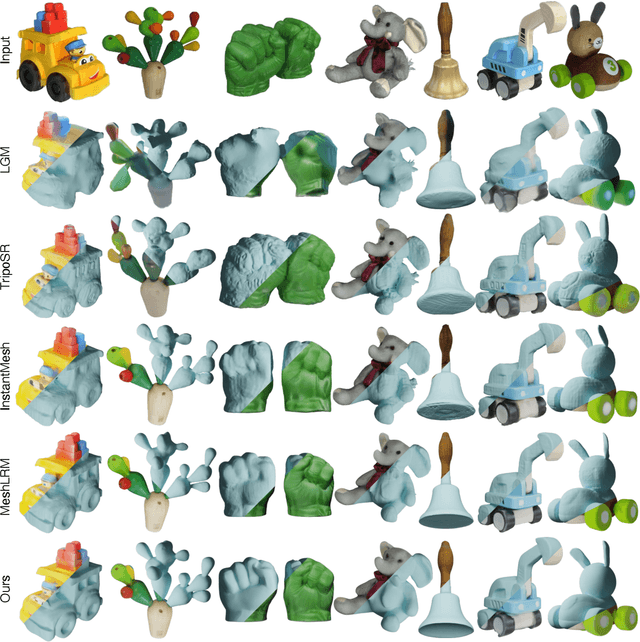
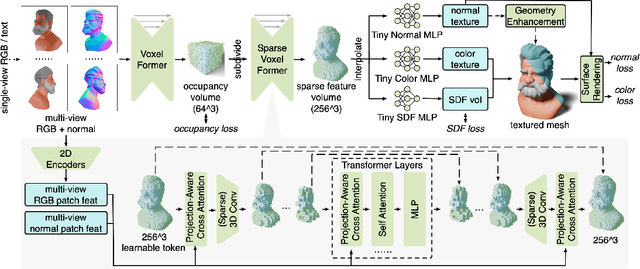
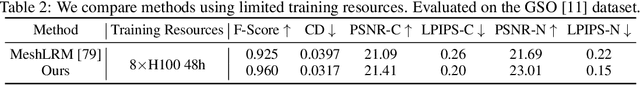

Abstract:Open-world 3D reconstruction models have recently garnered significant attention. However, without sufficient 3D inductive bias, existing methods typically entail expensive training costs and struggle to extract high-quality 3D meshes. In this work, we introduce MeshFormer, a sparse-view reconstruction model that explicitly leverages 3D native structure, input guidance, and training supervision. Specifically, instead of using a triplane representation, we store features in 3D sparse voxels and combine transformers with 3D convolutions to leverage an explicit 3D structure and projective bias. In addition to sparse-view RGB input, we require the network to take input and generate corresponding normal maps. The input normal maps can be predicted by 2D diffusion models, significantly aiding in the guidance and refinement of the geometry's learning. Moreover, by combining Signed Distance Function (SDF) supervision with surface rendering, we directly learn to generate high-quality meshes without the need for complex multi-stage training processes. By incorporating these explicit 3D biases, MeshFormer can be trained efficiently and deliver high-quality textured meshes with fine-grained geometric details. It can also be integrated with 2D diffusion models to enable fast single-image-to-3D and text-to-3D tasks. Project page: https://meshformer3d.github.io
SpaRP: Fast 3D Object Reconstruction and Pose Estimation from Sparse Views
Aug 19, 2024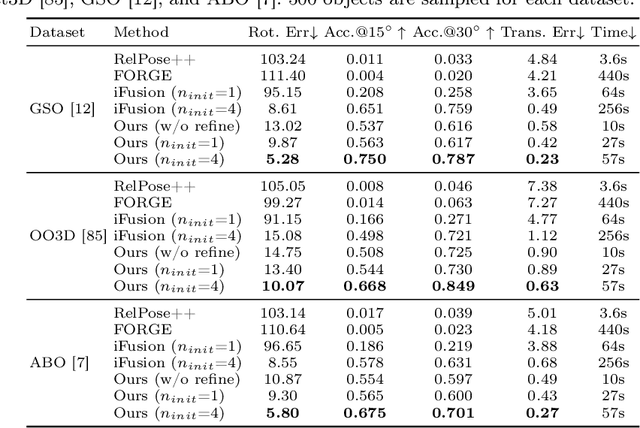
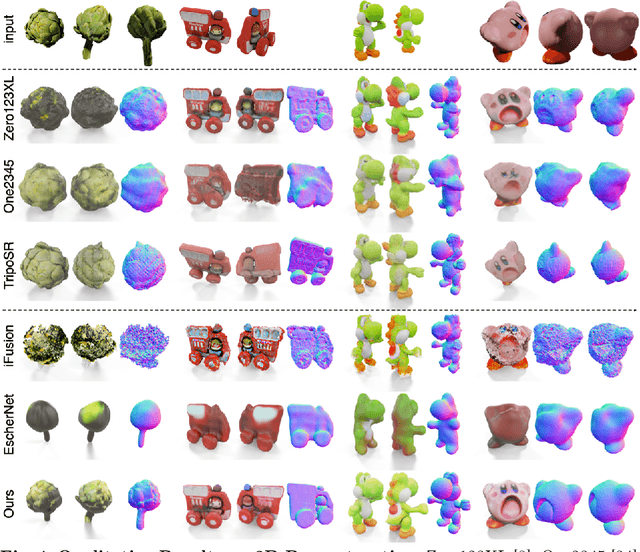

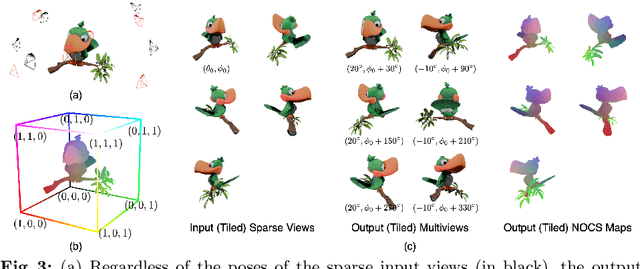

Abstract:Open-world 3D generation has recently attracted considerable attention. While many single-image-to-3D methods have yielded visually appealing outcomes, they often lack sufficient controllability and tend to produce hallucinated regions that may not align with users' expectations. In this paper, we explore an important scenario in which the input consists of one or a few unposed 2D images of a single object, with little or no overlap. We propose a novel method, SpaRP, to reconstruct a 3D textured mesh and estimate the relative camera poses for these sparse-view images. SpaRP distills knowledge from 2D diffusion models and finetunes them to implicitly deduce the 3D spatial relationships between the sparse views. The diffusion model is trained to jointly predict surrogate representations for camera poses and multi-view images of the object under known poses, integrating all information from the input sparse views. These predictions are then leveraged to accomplish 3D reconstruction and pose estimation, and the reconstructed 3D model can be used to further refine the camera poses of input views. Through extensive experiments on three datasets, we demonstrate that our method not only significantly outperforms baseline methods in terms of 3D reconstruction quality and pose prediction accuracy but also exhibits strong efficiency. It requires only about 20 seconds to produce a textured mesh and camera poses for the input views. Project page: https://chaoxu.xyz/sparp.
Robo360: A 3D Omnispective Multi-Material Robotic Manipulation Dataset
Dec 09, 2023
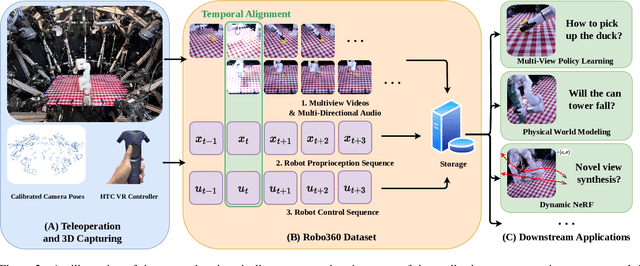
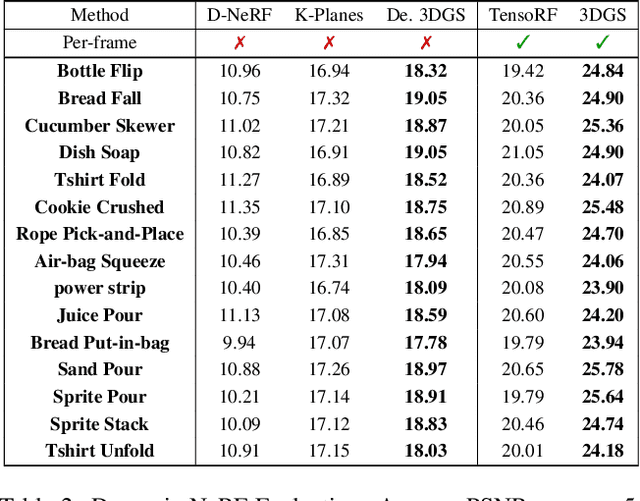
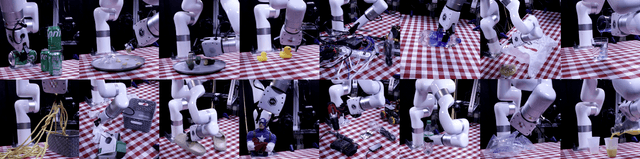
Abstract:Building robots that can automate labor-intensive tasks has long been the core motivation behind the advancements in computer vision and the robotics community. Recent interest in leveraging 3D algorithms, particularly neural fields, has led to advancements in robot perception and physical understanding in manipulation scenarios. However, the real world's complexity poses significant challenges. To tackle these challenges, we present Robo360, a dataset that features robotic manipulation with a dense view coverage, which enables high-quality 3D neural representation learning, and a diverse set of objects with various physical and optical properties and facilitates research in various object manipulation and physical world modeling tasks. We confirm the effectiveness of our dataset using existing dynamic NeRF and evaluate its potential in learning multi-view policies. We hope that Robo360 can open new research directions yet to be explored at the intersection of understanding the physical world in 3D and robot control.
One-2-3-45++: Fast Single Image to 3D Objects with Consistent Multi-View Generation and 3D Diffusion
Nov 14, 2023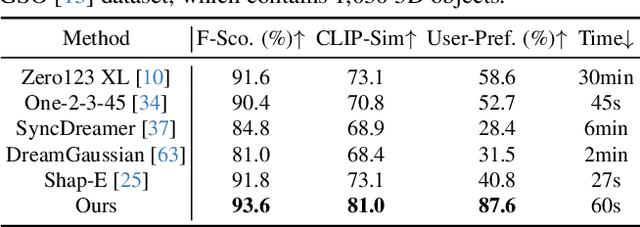
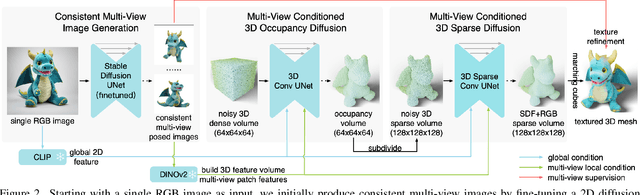
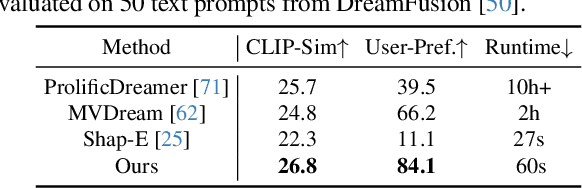
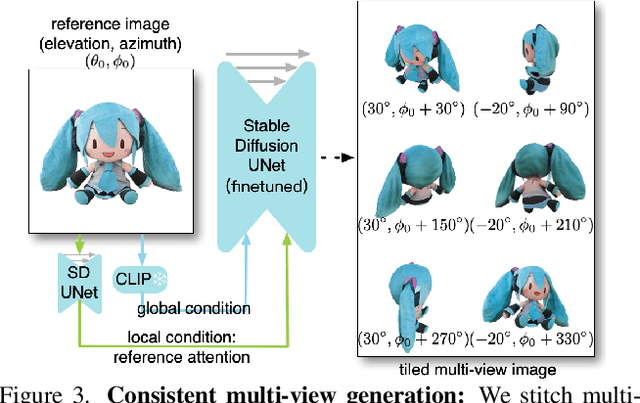
Abstract:Recent advancements in open-world 3D object generation have been remarkable, with image-to-3D methods offering superior fine-grained control over their text-to-3D counterparts. However, most existing models fall short in simultaneously providing rapid generation speeds and high fidelity to input images - two features essential for practical applications. In this paper, we present One-2-3-45++, an innovative method that transforms a single image into a detailed 3D textured mesh in approximately one minute. Our approach aims to fully harness the extensive knowledge embedded in 2D diffusion models and priors from valuable yet limited 3D data. This is achieved by initially finetuning a 2D diffusion model for consistent multi-view image generation, followed by elevating these images to 3D with the aid of multi-view conditioned 3D native diffusion models. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that our method can produce high-quality, diverse 3D assets that closely mirror the original input image. Our project webpage: https://sudo-ai-3d.github.io/One2345plus_page.
Zero123++: a Single Image to Consistent Multi-view Diffusion Base Model
Oct 23, 2023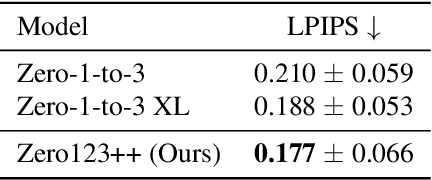
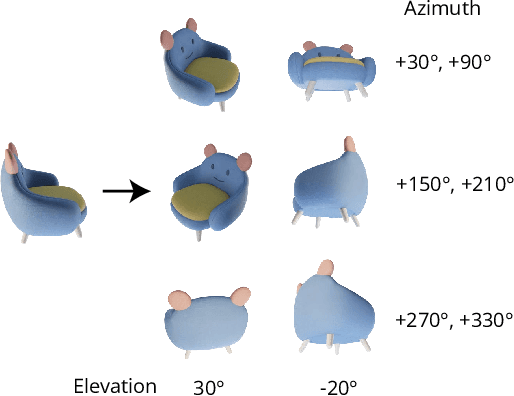
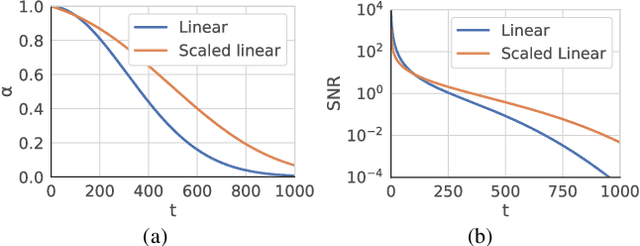

Abstract:We report Zero123++, an image-conditioned diffusion model for generating 3D-consistent multi-view images from a single input view. To take full advantage of pretrained 2D generative priors, we develop various conditioning and training schemes to minimize the effort of finetuning from off-the-shelf image diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion. Zero123++ excels in producing high-quality, consistent multi-view images from a single image, overcoming common issues like texture degradation and geometric misalignment. Furthermore, we showcase the feasibility of training a ControlNet on Zero123++ for enhanced control over the generation process. The code is available at https://github.com/SUDO-AI-3D/zero123plus.
OpenIllumination: A Multi-Illumination Dataset for Inverse Rendering Evaluation on Real Objects
Sep 14, 2023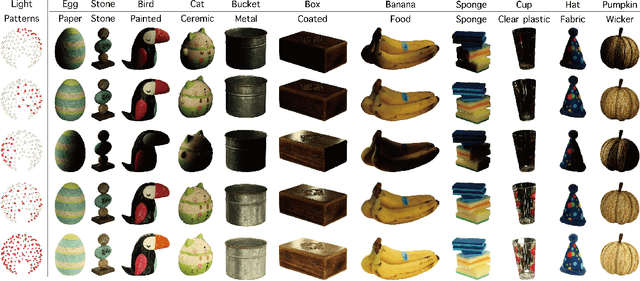
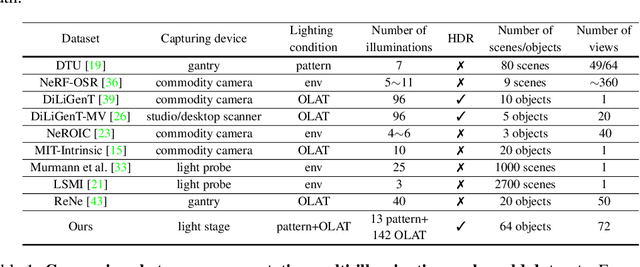

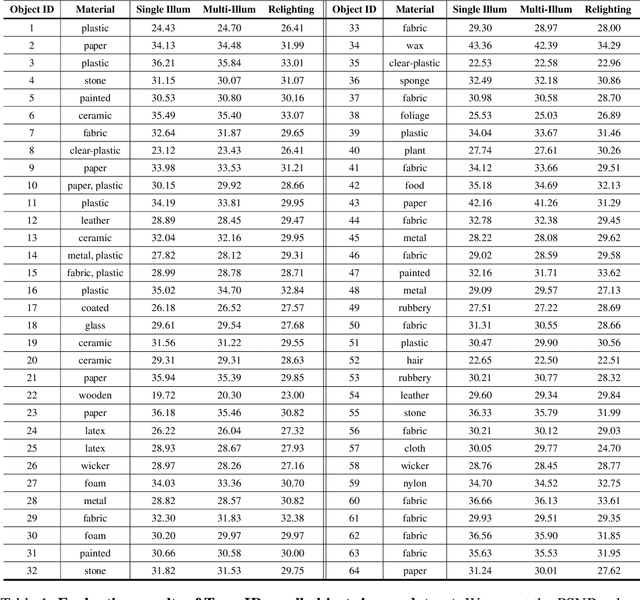
Abstract:We introduce OpenIllumination, a real-world dataset containing over 108K images of 64 objects with diverse materials, captured under 72 camera views and a large number of different illuminations. For each image in the dataset, we provide accurate camera parameters, illumination ground truth, and foreground segmentation masks. Our dataset enables the quantitative evaluation of most inverse rendering and material decomposition methods for real objects. We examine several state-of-the-art inverse rendering methods on our dataset and compare their performances. The dataset and code can be found on the project page: https://oppo-us-research.github.io/OpenIllumination.
One-2-3-45: Any Single Image to 3D Mesh in 45 Seconds without Per-Shape Optimization
Jun 29, 2023
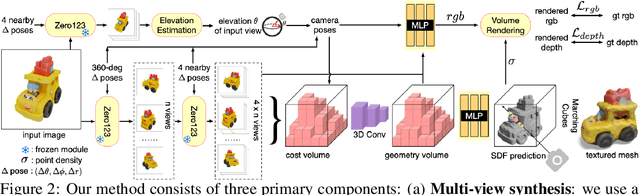
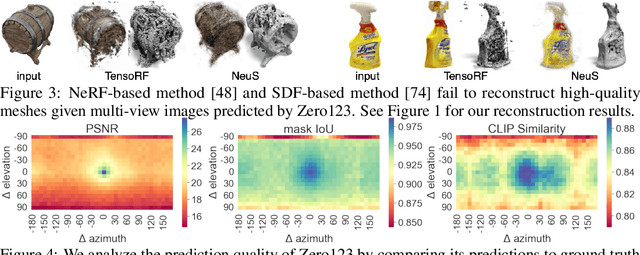

Abstract:Single image 3D reconstruction is an important but challenging task that requires extensive knowledge of our natural world. Many existing methods solve this problem by optimizing a neural radiance field under the guidance of 2D diffusion models but suffer from lengthy optimization time, 3D inconsistency results, and poor geometry. In this work, we propose a novel method that takes a single image of any object as input and generates a full 360-degree 3D textured mesh in a single feed-forward pass. Given a single image, we first use a view-conditioned 2D diffusion model, Zero123, to generate multi-view images for the input view, and then aim to lift them up to 3D space. Since traditional reconstruction methods struggle with inconsistent multi-view predictions, we build our 3D reconstruction module upon an SDF-based generalizable neural surface reconstruction method and propose several critical training strategies to enable the reconstruction of 360-degree meshes. Without costly optimizations, our method reconstructs 3D shapes in significantly less time than existing methods. Moreover, our method favors better geometry, generates more 3D consistent results, and adheres more closely to the input image. We evaluate our approach on both synthetic data and in-the-wild images and demonstrate its superiority in terms of both mesh quality and runtime. In addition, our approach can seamlessly support the text-to-3D task by integrating with off-the-shelf text-to-image diffusion models.
EasyHeC: Accurate and Automatic Hand-eye Calibration via Differentiable Rendering and Space Exploration
May 02, 2023
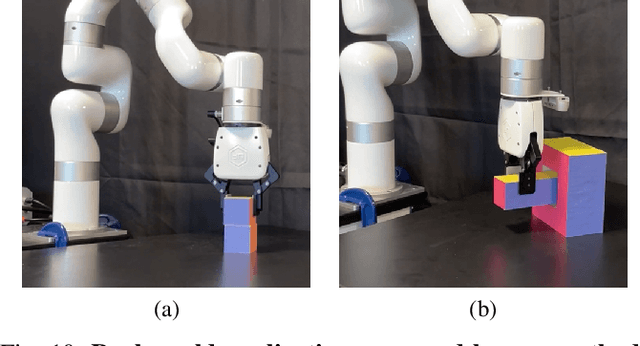
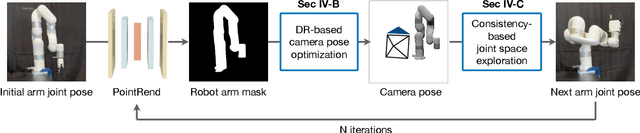
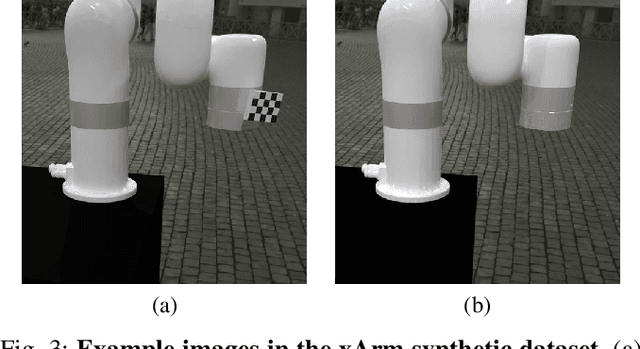
Abstract:Hand-eye calibration is a critical task in robotics, as it directly affects the efficacy of critical operations such as manipulation and grasping. Traditional methods for achieving this objective necessitate the careful design of joint poses and the use of specialized calibration markers, while most recent learning-based approaches using solely pose regression are limited in their abilities to diagnose inaccuracies. In this work, we introduce a new approach to hand-eye calibration called EasyHeC, which is markerless, white-box, and offers comprehensive coverage of positioning accuracy across the entire robot configuration space. We introduce two key technologies: differentiable rendering-based camera pose optimization and consistency-based joint space exploration, which enables accurate end-to-end optimization of the calibration process and eliminates the need for the laborious manual design of robot joint poses. Our evaluation demonstrates superior performance in synthetic and real-world datasets, enhancing downstream manipulation tasks by providing precise camera poses for locating and interacting with objects. The code is available at the project page: https://ootts.github.io/easyhec.
Chain-of-Thought Predictive Control
Apr 03, 2023


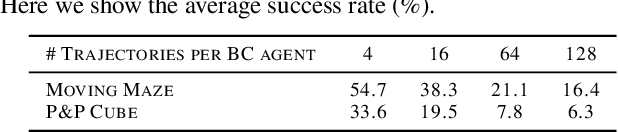
Abstract:We study generalizable policy learning from demonstrations for complex low-level control tasks (e.g., contact-rich object manipulations). We propose an imitation learning method that incorporates the idea of temporal abstraction and the planning capabilities from Hierarchical RL (HRL) in a novel and effective manner. As a step towards decision foundation models, our design can utilize scalable, albeit highly sub-optimal, demonstrations. Specifically, we find certain short subsequences of the demos, i.e. the chain-of-thought (CoT), reflect their hierarchical structures by marking the completion of subgoals in the tasks. Our model learns to dynamically predict the entire CoT as coherent and structured long-term action guidance and consistently outperforms typical two-stage subgoal-conditioned policies. On the other hand, such CoT facilitates generalizable policy learning as they exemplify the decision patterns shared among demos (even those with heavy noises and randomness). Our method, Chain-of-Thought Predictive Control (CoTPC), significantly outperforms existing ones on challenging low-level manipulation tasks from scalable yet highly sub-optimal demos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge