Saman Motamed
Do generative video models learn physical principles from watching videos?
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:AI video generation is undergoing a revolution, with quality and realism advancing rapidly. These advances have led to a passionate scientific debate: Do video models learn ``world models'' that discover laws of physics -- or, alternatively, are they merely sophisticated pixel predictors that achieve visual realism without understanding the physical principles of reality? We address this question by developing Physics-IQ, a comprehensive benchmark dataset that can only be solved by acquiring a deep understanding of various physical principles, like fluid dynamics, optics, solid mechanics, magnetism and thermodynamics. We find that across a range of current models (Sora, Runway, Pika, Lumiere, Stable Video Diffusion, and VideoPoet), physical understanding is severely limited, and unrelated to visual realism. At the same time, some test cases can already be successfully solved. This indicates that acquiring certain physical principles from observation alone may be possible, but significant challenges remain. While we expect rapid advances ahead, our work demonstrates that visual realism does not imply physical understanding. Our project page is at https://physics-iq.github.io; code at https://github.com/google-deepmind/physics-IQ-benchmark.
InTraGen: Trajectory-controlled Video Generation for Object Interactions
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Advances in video generation have significantly improved the realism and quality of created scenes. This has fueled interest in developing intuitive tools that let users leverage video generation as world simulators. Text-to-video (T2V) generation is one such approach, enabling video creation from text descriptions only. Yet, due to the inherent ambiguity in texts and the limited temporal information offered by text prompts, researchers have explored additional control signals like trajectory-guided systems, for more accurate T2V generation. Nonetheless, methods to evaluate whether T2V models can generate realistic interactions between multiple objects are lacking. We introduce InTraGen, a pipeline for improved trajectory-based generation of object interaction scenarios. We propose 4 new datasets and a novel trajectory quality metric to evaluate the performance of the proposed InTraGen. To achieve object interaction, we introduce a multi-modal interaction encoding pipeline with an object ID injection mechanism that enriches object-environment interactions. Our results demonstrate improvements in both visual fidelity and quantitative performance. Code and datasets are available at https://github.com/insait-institute/InTraGen
Investigating the Effectiveness of Cross-Attention to Unlock Zero-Shot Editing of Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:With recent advances in image and video diffusion models for content creation, a plethora of techniques have been proposed for customizing their generated content. In particular, manipulating the cross-attention layers of Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models has shown great promise in controlling the shape and location of objects in the scene. Transferring image-editing techniques to the video domain, however, is extremely challenging as object motion and temporal consistency are difficult to capture accurately. In this work, we take a first look at the role of cross-attention in Text-to-Video (T2V) diffusion models for zero-shot video editing. While one-shot models have shown potential in controlling motion and camera movement, we demonstrate zero-shot control over object shape, position and movement in T2V models. We show that despite the limitations of current T2V models, cross-attention guidance can be a promising approach for editing videos.
A Unified and Interpretable Emotion Representation and Expression Generation
Apr 01, 2024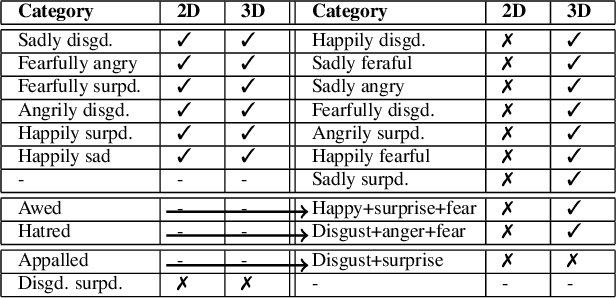
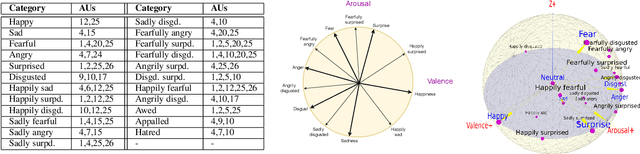
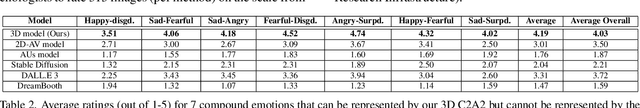
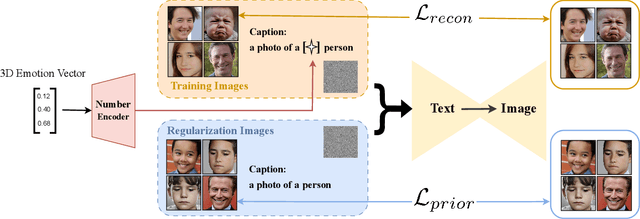
Abstract:Canonical emotions, such as happy, sad, and fearful, are easy to understand and annotate. However, emotions are often compound, e.g. happily surprised, and can be mapped to the action units (AUs) used for expressing emotions, and trivially to the canonical ones. Intuitively, emotions are continuous as represented by the arousal-valence (AV) model. An interpretable unification of these four modalities - namely, Canonical, Compound, AUs, and AV - is highly desirable, for a better representation and understanding of emotions. However, such unification remains to be unknown in the current literature. In this work, we propose an interpretable and unified emotion model, referred as C2A2. We also develop a method that leverages labels of the non-unified models to annotate the novel unified one. Finally, we modify the text-conditional diffusion models to understand continuous numbers, which are then used to generate continuous expressions using our unified emotion model. Through quantitative and qualitative experiments, we show that our generated images are rich and capture subtle expressions. Our work allows a fine-grained generation of expressions in conjunction with other textual inputs and offers a new label space for emotions at the same time.
D3GU: Multi-Target Active Domain Adaptation via Enhancing Domain Alignment
Jan 10, 2024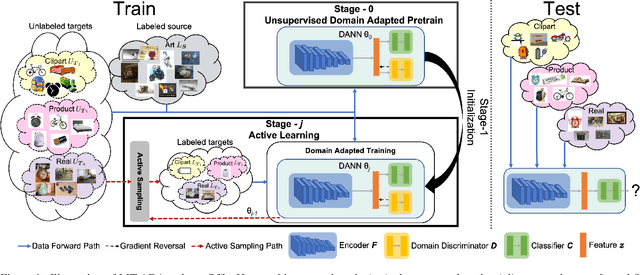
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) for image classification has made remarkable progress in transferring classification knowledge from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain, thanks to effective domain alignment techniques. Recently, in order to further improve performance on a target domain, many Single-Target Active Domain Adaptation (ST-ADA) methods have been proposed to identify and annotate the salient and exemplar target samples. However, it requires one model to be trained and deployed for each target domain and the domain label associated with each test sample. This largely restricts its application in the ubiquitous scenarios with multiple target domains. Therefore, we propose a Multi-Target Active Domain Adaptation (MT-ADA) framework for image classification, named D3GU, to simultaneously align different domains and actively select samples from them for annotation. This is the first research effort in this field to our best knowledge. D3GU applies Decomposed Domain Discrimination (D3) during training to achieve both source-target and target-target domain alignments. Then during active sampling, a Gradient Utility (GU) score is designed to weight every unlabeled target image by its contribution towards classification and domain alignment tasks, and is further combined with KMeans clustering to form GU-KMeans for diverse image sampling. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets, Office31, OfficeHome, and DomainNet, have been conducted to validate consistently superior performance of D3GU for MT-ADA.
Personalized Face Inpainting with Diffusion Models by Parallel Visual Attention
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:Face inpainting is important in various applications, such as photo restoration, image editing, and virtual reality. Despite the significant advances in face generative models, ensuring that a person's unique facial identity is maintained during the inpainting process is still an elusive goal. Current state-of-the-art techniques, exemplified by MyStyle, necessitate resource-intensive fine-tuning and a substantial number of images for each new identity. Furthermore, existing methods often fall short in accommodating user-specified semantic attributes, such as beard or expression. To improve inpainting results, and reduce the computational complexity during inference, this paper proposes the use of Parallel Visual Attention (PVA) in conjunction with diffusion models. Specifically, we insert parallel attention matrices to each cross-attention module in the denoising network, which attends to features extracted from reference images by an identity encoder. We train the added attention modules and identity encoder on CelebAHQ-IDI, a dataset proposed for identity-preserving face inpainting. Experiments demonstrate that PVA attains unparalleled identity resemblance in both face inpainting and face inpainting with language guidance tasks, in comparison to various benchmarks, including MyStyle, Paint by Example, and Custom Diffusion. Our findings reveal that PVA ensures good identity preservation while offering effective language-controllability. Additionally, in contrast to Custom Diffusion, PVA requires just 40 fine-tuning steps for each new identity, which translates to a significant speed increase of over 20 times.
Lego: Learning to Disentangle and Invert Concepts Beyond Object Appearance in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Nov 23, 2023Abstract:Diffusion models have revolutionized generative content creation and text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models in particular have increased the creative freedom of users by allowing scene synthesis using natural language. T2I models excel at synthesizing concepts such as nouns, appearances, and styles. To enable customized content creation based on a few example images of a concept, methods such as Textual Inversion and DreamBooth invert the desired concept and enable synthesizing it in new scenes. However, inverting more general concepts that go beyond object appearance and style (adjectives and verbs) through natural language, remains a challenge. Two key characteristics of these concepts contribute to the limitations of current inversion methods. 1) Adjectives and verbs are entangled with nouns (subject) and can hinder appearance-based inversion methods, where the subject appearance leaks into the concept embedding and 2) describing such concepts often extends beyond single word embeddings (being frozen in ice, walking on a tightrope, etc.) that current methods do not handle. In this study, we introduce Lego, a textual inversion method designed to invert subject entangled concepts from a few example images. Lego disentangles concepts from their associated subjects using a simple yet effective Subject Separation step and employs a Context Loss that guides the inversion of single/multi-embedding concepts. In a thorough user study, Lego-generated concepts were preferred over 70% of the time when compared to the baseline. Additionally, visual question answering using a large language model suggested Lego-generated concepts are better aligned with the text description of the concept.
PATMAT: Person Aware Tuning of Mask-Aware Transformer for Face Inpainting
Apr 12, 2023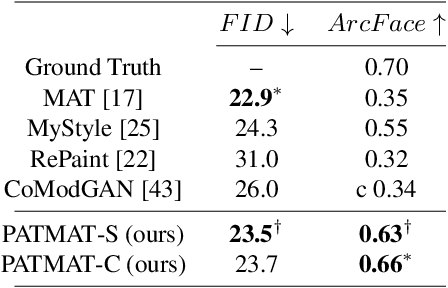
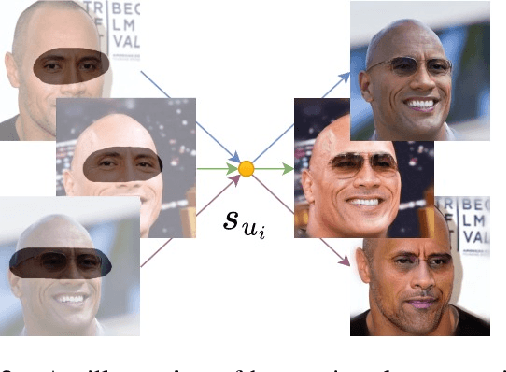

Abstract:Generative models such as StyleGAN2 and Stable Diffusion have achieved state-of-the-art performance in computer vision tasks such as image synthesis, inpainting, and de-noising. However, current generative models for face inpainting often fail to preserve fine facial details and the identity of the person, despite creating aesthetically convincing image structures and textures. In this work, we propose Person Aware Tuning (PAT) of Mask-Aware Transformer (MAT) for face inpainting, which addresses this issue. Our proposed method, PATMAT, effectively preserves identity by incorporating reference images of a subject and fine-tuning a MAT architecture trained on faces. By using ~40 reference images, PATMAT creates anchor points in MAT's style module, and tunes the model using the fixed anchors to adapt the model to a new face identity. Moreover, PATMAT's use of multiple images per anchor during training allows the model to use fewer reference images than competing methods. We demonstrate that PATMAT outperforms state-of-the-art models in terms of image quality, the preservation of person-specific details, and the identity of the subject. Our results suggest that PATMAT can be a promising approach for improving the quality of personalized face inpainting.
Generative Visual Prompt: Unifying Distributional Control of Pre-Trained Generative Models
Sep 14, 2022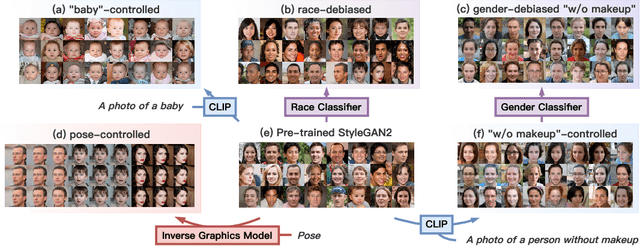
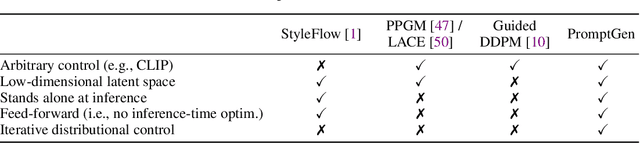

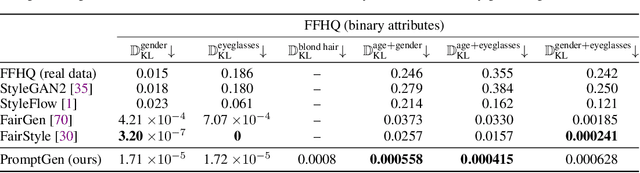
Abstract:Generative models (e.g., GANs and diffusion models) learn the underlying data distribution in an unsupervised manner. However, many applications of interest require sampling from a specific region of the generative model's output space or evenly over a range of characteristics. To allow efficient sampling in these scenarios, we propose Generative Visual Prompt (PromptGen), a framework for distributional control over pre-trained generative models by incorporating knowledge of arbitrary off-the-shelf models. PromptGen defines control as an energy-based model (EBM) and samples images in a feed-forward manner by approximating the EBM with invertible neural networks, avoiding optimization at inference. We demonstrate how PromptGen can control several generative models (e.g., StyleGAN2, StyleNeRF, diffusion autoencoder, and NVAE) using various off-the-shelf models: (1) with the CLIP model, PromptGen can sample images guided by text, (2) with image classifiers, PromptGen can de-bias generative models across a set of attributes, and (3) with inverse graphics models, PromptGen can sample images of the same identity in different poses. (4) Finally, PromptGen reveals that the CLIP model shows "reporting bias" when used as control, and PromptGen can further de-bias this controlled distribution in an iterative manner. Our code is available at https://github.com/ChenWu98/Generative-Visual-Prompt.
Vanishing Twin GAN: How training a weak Generative Adversarial Network can improve semi-supervised image classification
Mar 03, 2021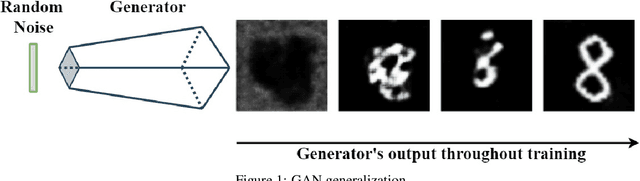
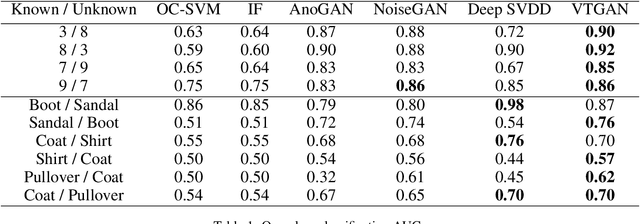

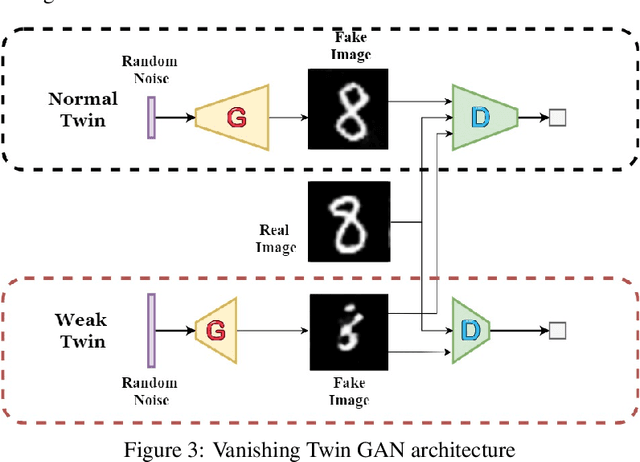
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks can learn the mapping of random noise to realistic images in a semi-supervised framework. This mapping ability can be used for semi-supervised image classification to detect images of an unknown class where there is no training data to be used for supervised classification. However, if the unknown class shares similar characteristics to the known class(es), GANs can learn to generalize and generate images that look like both classes. This generalization ability can hinder the classification performance. In this work, we propose the Vanishing Twin GAN. By training a weak GAN and using its generated output image parallel to the regular GAN, the Vanishing Twin training improves semi-supervised image classification where image similarity can hurt classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge