Yongzhu Chang
Crafting a Good Prompt or Providing Exemplary Dialogues? A Study of In-Context Learning for Persona-based Dialogue Generation
Feb 17, 2024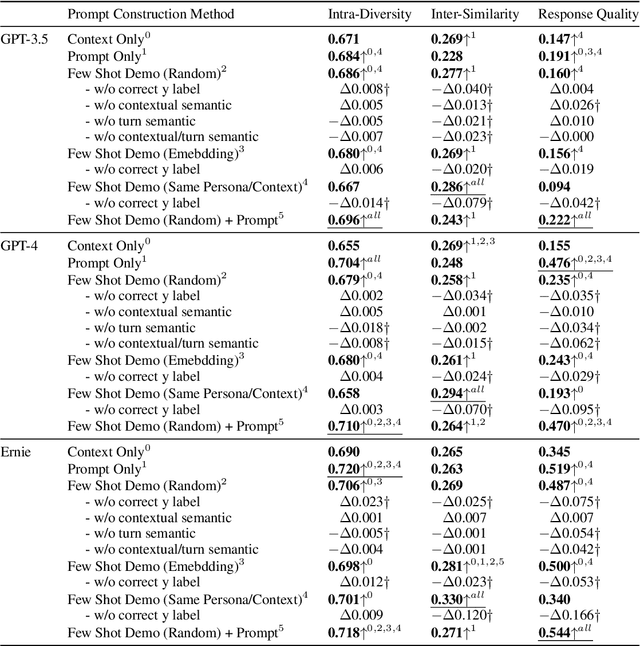
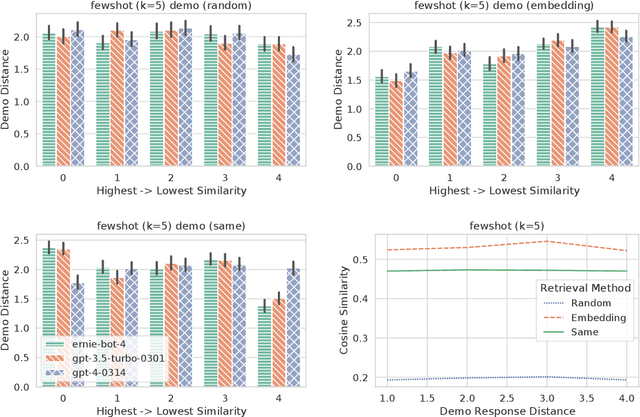
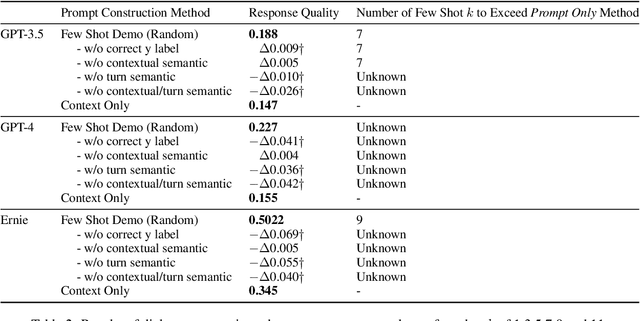
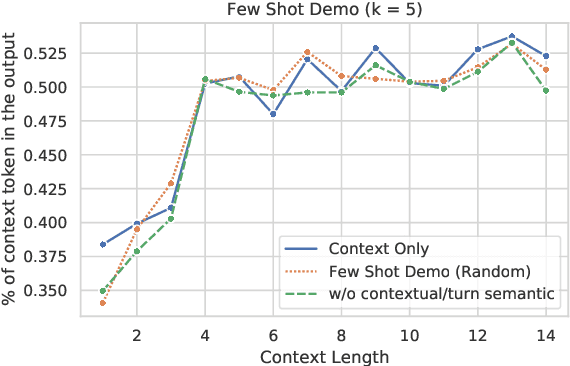
Abstract:Previous in-context learning (ICL) research has focused on tasks such as classification, machine translation, text2table, etc., while studies on whether ICL can improve human-like dialogue generation are scarce. Our work fills this gap by systematically investigating the ICL capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in persona-based dialogue generation, conducting extensive experiments on high-quality real human Chinese dialogue datasets. From experimental results, we draw three conclusions: 1) adjusting prompt instructions is the most direct, effective, and economical way to improve generation quality; 2) randomly retrieving demonstrations (demos) achieves the best results, possibly due to the greater diversity and the amount of effective information; counter-intuitively, retrieving demos with a context identical to the query performs the worst; 3) even when we destroy the multi-turn associations and single-turn semantics in the demos, increasing the number of demos still improves dialogue performance, proving that LLMs can learn from corrupted dialogue demos. Previous explanations of the ICL mechanism, such as $n$-gram induction head, cannot fully account for this phenomenon.
Examining the Effect of Pre-training on Time Series Classification
Sep 11, 2023Abstract:Although the pre-training followed by fine-tuning paradigm is used extensively in many fields, there is still some controversy surrounding the impact of pre-training on the fine-tuning process. Currently, experimental findings based on text and image data lack consensus. To delve deeper into the unsupervised pre-training followed by fine-tuning paradigm, we have extended previous research to a new modality: time series. In this study, we conducted a thorough examination of 150 classification datasets derived from the Univariate Time Series (UTS) and Multivariate Time Series (MTS) benchmarks. Our analysis reveals several key conclusions. (i) Pre-training can only help improve the optimization process for models that fit the data poorly, rather than those that fit the data well. (ii) Pre-training does not exhibit the effect of regularization when given sufficient training time. (iii) Pre-training can only speed up convergence if the model has sufficient ability to fit the data. (iv) Adding more pre-training data does not improve generalization, but it can strengthen the advantage of pre-training on the original data volume, such as faster convergence. (v) While both the pre-training task and the model structure determine the effectiveness of the paradigm on a given dataset, the model structure plays a more significant role.
Sudowoodo: a Chinese Lyric Imitation System with Source Lyrics
Aug 09, 2023Abstract:Lyrics generation is a well-known application in natural language generation research, with several previous studies focusing on generating accurate lyrics using precise control such as keywords, rhymes, etc. However, lyrics imitation, which involves writing new lyrics by imitating the style and content of the source lyrics, remains a challenging task due to the lack of a parallel corpus. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{\textit{Sudowoodo}}, a Chinese lyrics imitation system that can generate new lyrics based on the text of source lyrics. To address the issue of lacking a parallel training corpus for lyrics imitation, we propose a novel framework to construct a parallel corpus based on a keyword-based lyrics model from source lyrics. Then the pairs \textit{(new lyrics, source lyrics)} are used to train the lyrics imitation model. During the inference process, we utilize a post-processing module to filter and rank the generated lyrics, selecting the highest-quality ones. We incorporated audio information and aligned the lyrics with the audio to form the songs as a bonus. The human evaluation results show that our framework can perform better lyric imitation. Meanwhile, the \textit{Sudowoodo} system and demo video of the system is available at \href{https://Sudowoodo.apps-hp.danlu.netease.com/}{Sudowoodo} and \href{https://youtu.be/u5BBT_j1L5M}{https://youtu.be/u5BBT\_j1L5M}.
I-WAS: a Data Augmentation Method with GPT-2 for Simile Detection
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Simile detection is a valuable task for many natural language processing (NLP)-based applications, particularly in the field of literature. However, existing research on simile detection often relies on corpora that are limited in size and do not adequately represent the full range of simile forms. To address this issue, we propose a simile data augmentation method based on \textbf{W}ord replacement And Sentence completion using the GPT-2 language model. Our iterative process called I-WAS, is designed to improve the quality of the augmented sentences. To better evaluate the performance of our method in real-world applications, we have compiled a corpus containing a more diverse set of simile forms for experimentation. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed data augmentation method for simile detection.
* 15 pages, 1 figure
Probing Simile Knowledge from Pre-trained Language Models
Apr 27, 2022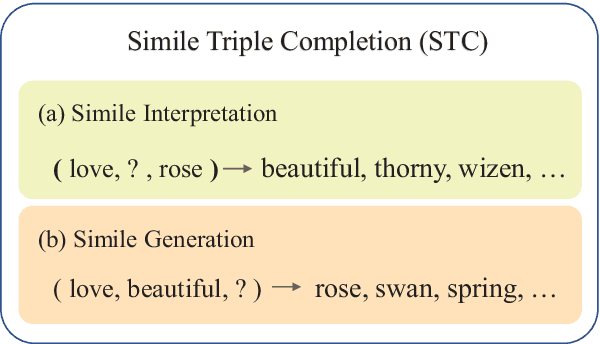
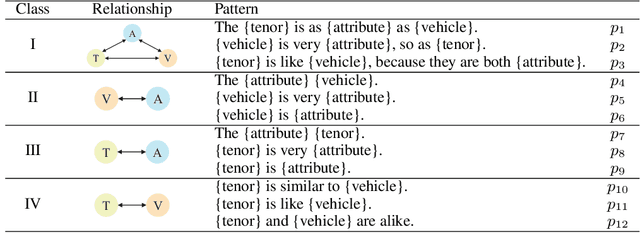
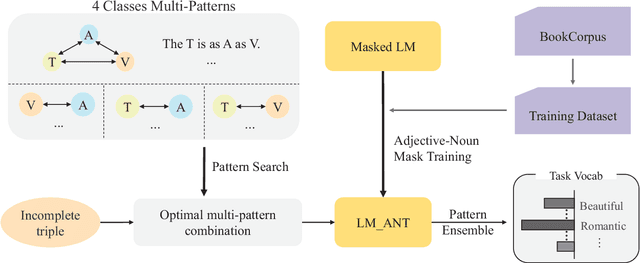
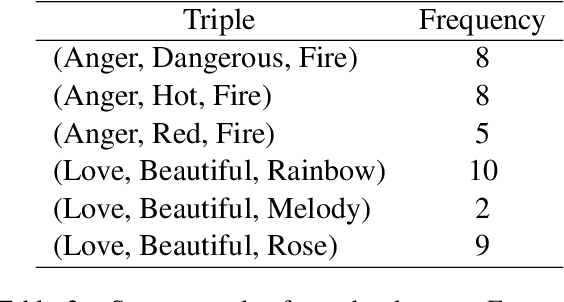
Abstract:Simile interpretation (SI) and simile generation (SG) are challenging tasks for NLP because models require adequate world knowledge to produce predictions. Previous works have employed many hand-crafted resources to bring knowledge-related into models, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. In recent years, pre-trained language models (PLMs) based approaches have become the de-facto standard in NLP since they learn generic knowledge from a large corpus. The knowledge embedded in PLMs may be useful for SI and SG tasks. Nevertheless, there are few works to explore it. In this paper, we probe simile knowledge from PLMs to solve the SI and SG tasks in the unified framework of simile triple completion for the first time. The backbone of our framework is to construct masked sentences with manual patterns and then predict the candidate words in the masked position. In this framework, we adopt a secondary training process (Adjective-Noun mask Training) with the masked language model (MLM) loss to enhance the prediction diversity of candidate words in the masked position. Moreover, pattern ensemble (PE) and pattern search (PS) are applied to improve the quality of predicted words. Finally, automatic and human evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in both SI and SG tasks.
Dialog Intent Induction via Density-based Deep Clustering Ensemble
Jan 18, 2022



Abstract:Existing task-oriented chatbots heavily rely on spoken language understanding (SLU) systems to determine a user's utterance's intent and other key information for fulfilling specific tasks. In real-life applications, it is crucial to occasionally induce novel dialog intents from the conversation logs to improve the user experience. In this paper, we propose the Density-based Deep Clustering Ensemble (DDCE) method for dialog intent induction. Compared to existing K-means based methods, our proposed method is more effective in dealing with real-life scenarios where a large number of outliers exist. To maximize data utilization, we jointly optimize texts' representations and the hyperparameters of the clustering algorithm. In addition, we design an outlier-aware clustering ensemble framework to handle the overfitting issue. Experimental results over seven datasets show that our proposed method significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge