Yangyi Huang
Symbolic Graphics Programming with Large Language Models
Sep 05, 2025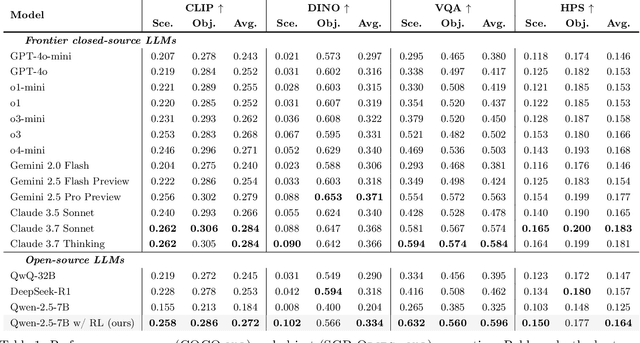
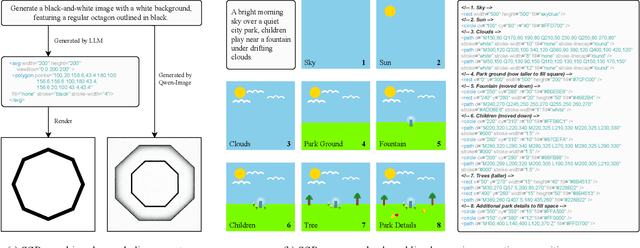
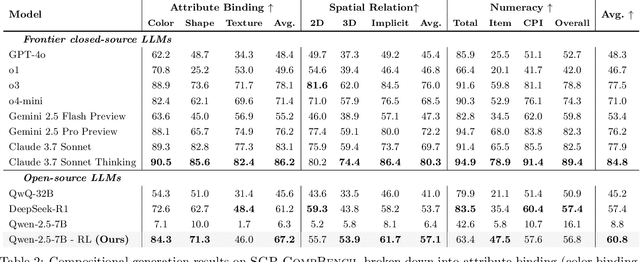
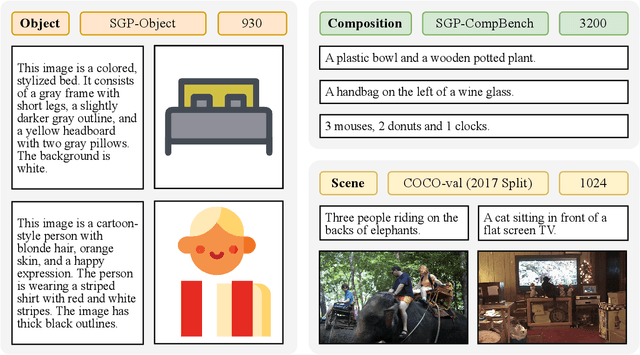
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at program synthesis, yet their ability to produce symbolic graphics programs (SGPs) that render into precise visual content remains underexplored. We study symbolic graphics programming, where the goal is to generate an SGP from a natural-language description. This task also serves as a lens into how LLMs understand the visual world by prompting them to generate images rendered from SGPs. Among various SGPs, our paper sticks to scalable vector graphics (SVGs). We begin by examining the extent to which LLMs can generate SGPs. To this end, we introduce SGP-GenBench, a comprehensive benchmark covering object fidelity, scene fidelity, and compositionality (attribute binding, spatial relations, numeracy). On SGP-GenBench, we discover that frontier proprietary models substantially outperform open-source models, and performance correlates well with general coding capabilities. Motivated by this gap, we aim to improve LLMs' ability to generate SGPs. We propose a reinforcement learning (RL) with verifiable rewards approach, where a format-validity gate ensures renderable SVG, and a cross-modal reward aligns text and the rendered image via strong vision encoders (e.g., SigLIP for text-image and DINO for image-image). Applied to Qwen-2.5-7B, our method substantially improves SVG generation quality and semantics, achieving performance on par with frontier systems. We further analyze training dynamics, showing that RL induces (i) finer decomposition of objects into controllable primitives and (ii) contextual details that improve scene coherence. Our results demonstrate that symbolic graphics programming offers a precise and interpretable lens on cross-modal grounding.
AdaHuman: Animatable Detailed 3D Human Generation with Compositional Multiview Diffusion
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Existing methods for image-to-3D avatar generation struggle to produce highly detailed, animation-ready avatars suitable for real-world applications. We introduce AdaHuman, a novel framework that generates high-fidelity animatable 3D avatars from a single in-the-wild image. AdaHuman incorporates two key innovations: (1) A pose-conditioned 3D joint diffusion model that synthesizes consistent multi-view images in arbitrary poses alongside corresponding 3D Gaussian Splats (3DGS) reconstruction at each diffusion step; (2) A compositional 3DGS refinement module that enhances the details of local body parts through image-to-image refinement and seamlessly integrates them using a novel crop-aware camera ray map, producing a cohesive detailed 3D avatar. These components allow AdaHuman to generate highly realistic standardized A-pose avatars with minimal self-occlusion, enabling rigging and animation with any input motion. Extensive evaluation on public benchmarks and in-the-wild images demonstrates that AdaHuman significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both avatar reconstruction and reposing. Code and models will be publicly available for research purposes.
GAvatar: Animatable 3D Gaussian Avatars with Implicit Mesh Learning
Dec 18, 2023



Abstract:Gaussian splatting has emerged as a powerful 3D representation that harnesses the advantages of both explicit (mesh) and implicit (NeRF) 3D representations. In this paper, we seek to leverage Gaussian splatting to generate realistic animatable avatars from textual descriptions, addressing the limitations (e.g., flexibility and efficiency) imposed by mesh or NeRF-based representations. However, a naive application of Gaussian splatting cannot generate high-quality animatable avatars and suffers from learning instability; it also cannot capture fine avatar geometries and often leads to degenerate body parts. To tackle these problems, we first propose a primitive-based 3D Gaussian representation where Gaussians are defined inside pose-driven primitives to facilitate animation. Second, to stabilize and amortize the learning of millions of Gaussians, we propose to use neural implicit fields to predict the Gaussian attributes (e.g., colors). Finally, to capture fine avatar geometries and extract detailed meshes, we propose a novel SDF-based implicit mesh learning approach for 3D Gaussians that regularizes the underlying geometries and extracts highly detailed textured meshes. Our proposed method, GAvatar, enables the large-scale generation of diverse animatable avatars using only text prompts. GAvatar significantly surpasses existing methods in terms of both appearance and geometry quality, and achieves extremely fast rendering (100 fps) at 1K resolution.
TADA! Text to Animatable Digital Avatars
Aug 21, 2023
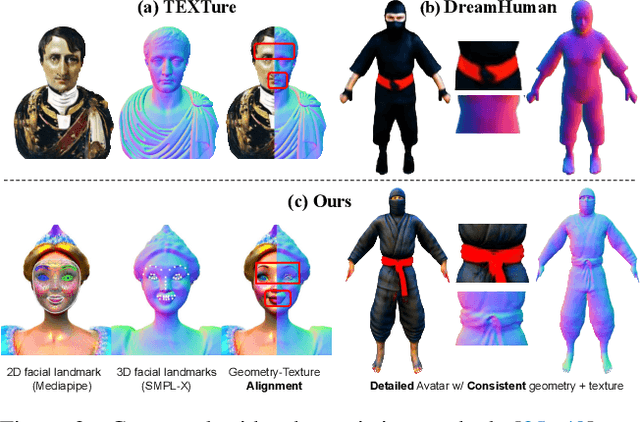
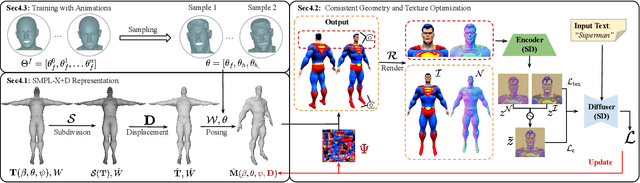

Abstract:We introduce TADA, a simple-yet-effective approach that takes textual descriptions and produces expressive 3D avatars with high-quality geometry and lifelike textures, that can be animated and rendered with traditional graphics pipelines. Existing text-based character generation methods are limited in terms of geometry and texture quality, and cannot be realistically animated due to inconsistent alignment between the geometry and the texture, particularly in the face region. To overcome these limitations, TADA leverages the synergy of a 2D diffusion model and an animatable parametric body model. Specifically, we derive an optimizable high-resolution body model from SMPL-X with 3D displacements and a texture map, and use hierarchical rendering with score distillation sampling (SDS) to create high-quality, detailed, holistic 3D avatars from text. To ensure alignment between the geometry and texture, we render normals and RGB images of the generated character and exploit their latent embeddings in the SDS training process. We further introduce various expression parameters to deform the generated character during training, ensuring that the semantics of our generated character remain consistent with the original SMPL-X model, resulting in an animatable character. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that TADA significantly surpasses existing approaches on both qualitative and quantitative measures. TADA enables creation of large-scale digital character assets that are ready for animation and rendering, while also being easily editable through natural language. The code will be public for research purposes.
TeCH: Text-guided Reconstruction of Lifelike Clothed Humans
Aug 19, 2023Abstract:Despite recent research advancements in reconstructing clothed humans from a single image, accurately restoring the "unseen regions" with high-level details remains an unsolved challenge that lacks attention. Existing methods often generate overly smooth back-side surfaces with a blurry texture. But how to effectively capture all visual attributes of an individual from a single image, which are sufficient to reconstruct unseen areas (e.g., the back view)? Motivated by the power of foundation models, TeCH reconstructs the 3D human by leveraging 1) descriptive text prompts (e.g., garments, colors, hairstyles) which are automatically generated via a garment parsing model and Visual Question Answering (VQA), 2) a personalized fine-tuned Text-to-Image diffusion model (T2I) which learns the "indescribable" appearance. To represent high-resolution 3D clothed humans at an affordable cost, we propose a hybrid 3D representation based on DMTet, which consists of an explicit body shape grid and an implicit distance field. Guided by the descriptive prompts + personalized T2I diffusion model, the geometry and texture of the 3D humans are optimized through multi-view Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) and reconstruction losses based on the original observation. TeCH produces high-fidelity 3D clothed humans with consistent & delicate texture, and detailed full-body geometry. Quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that TeCH outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of reconstruction accuracy and rendering quality. The code will be publicly available for research purposes at https://huangyangyi.github.io/TeCH
One-shot Implicit Animatable Avatars with Model-based Priors
Dec 05, 2022Abstract:Existing neural rendering methods for creating human avatars typically either require dense input signals such as video or multi-view images, or leverage a learned prior from large-scale specific 3D human datasets such that reconstruction can be performed with sparse-view inputs. Most of these methods fail to achieve realistic reconstruction when only a single image is available. To enable the data-efficient creation of realistic animatable 3D humans, we propose ELICIT, a novel method for learning human-specific neural radiance fields from a single image. Inspired by the fact that humans can easily reconstruct the body geometry and infer the full-body clothing from a single image, we leverage two priors in ELICIT: 3D geometry prior and visual semantic prior. Specifically, ELICIT introduces the 3D body shape geometry prior from a skinned vertex-based template model (i.e., SMPL) and implements the visual clothing semantic prior with the CLIP-based pre-trained models. Both priors are used to jointly guide the optimization for creating plausible content in the invisible areas. In order to further improve visual details, we propose a segmentation-based sampling strategy that locally refines different parts of the avatar. Comprehensive evaluations on multiple popular benchmarks, including ZJU-MoCAP, Human3.6M, and DeepFashion, show that ELICIT has outperformed current state-of-the-art avatar creation methods when only a single image is available. Code will be public for reseach purpose at https://elicit3d.github.io .
FuseFormer: Fusing Fine-Grained Information in Transformers for Video Inpainting
Sep 07, 2021



Abstract:Transformer, as a strong and flexible architecture for modelling long-range relations, has been widely explored in vision tasks. However, when used in video inpainting that requires fine-grained representation, existed method still suffers from yielding blurry edges in detail due to the hard patch splitting. Here we aim to tackle this problem by proposing FuseFormer, a Transformer model designed for video inpainting via fine-grained feature fusion based on novel Soft Split and Soft Composition operations. The soft split divides feature map into many patches with given overlapping interval. On the contrary, the soft composition operates by stitching different patches into a whole feature map where pixels in overlapping regions are summed up. These two modules are first used in tokenization before Transformer layers and de-tokenization after Transformer layers, for effective mapping between tokens and features. Therefore, sub-patch level information interaction is enabled for more effective feature propagation between neighboring patches, resulting in synthesizing vivid content for hole regions in videos. Moreover, in FuseFormer, we elaborately insert the soft composition and soft split into the feed-forward network, enabling the 1D linear layers to have the capability of modelling 2D structure. And, the sub-patch level feature fusion ability is further enhanced. In both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, our proposed FuseFormer surpasses state-of-the-art methods. We also conduct detailed analysis to examine its superiority.
Decoupled Spatial-Temporal Transformer for Video Inpainting
Apr 14, 2021



Abstract:Video inpainting aims to fill the given spatiotemporal holes with realistic appearance but is still a challenging task even with prosperous deep learning approaches. Recent works introduce the promising Transformer architecture into deep video inpainting and achieve better performance. However, it still suffers from synthesizing blurry texture as well as huge computational cost. Towards this end, we propose a novel Decoupled Spatial-Temporal Transformer (DSTT) for improving video inpainting with exceptional efficiency. Our proposed DSTT disentangles the task of learning spatial-temporal attention into 2 sub-tasks: one is for attending temporal object movements on different frames at same spatial locations, which is achieved by temporally-decoupled Transformer block, and the other is for attending similar background textures on same frame of all spatial positions, which is achieved by spatially-decoupled Transformer block. The interweaving stack of such two blocks makes our proposed model attend background textures and moving objects more precisely, and thus the attended plausible and temporally-coherent appearance can be propagated to fill the holes. In addition, a hierarchical encoder is adopted before the stack of Transformer blocks, for learning robust and hierarchical features that maintain multi-level local spatial structure, resulting in the more representative token vectors. Seamless combination of these two novel designs forms a better spatial-temporal attention scheme and our proposed model achieves better performance than state-of-the-art video inpainting approaches with significant boosted efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge