Boxi Wu
SNR-Edit: Structure-Aware Noise Rectification for Inversion-Free Flow-Based Editing
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Inversion-free image editing using flow-based generative models challenges the prevailing inversion-based pipelines. However, existing approaches rely on fixed Gaussian noise to construct the source trajectory, leading to biased trajectory dynamics and causing structural degradation or quality loss. To address this, we introduce SNR-Edit, a training-free framework achieving faithful Latent Trajectory Correction via adaptive noise control. Mechanistically, SNR-Edit uses structure-aware noise rectification to inject segmentation constraints into the initial noise, anchoring the stochastic component of the source trajectory to the real image's implicit inversion position and reducing trajectory drift during source--target transport. This lightweight modification yields smoother latent trajectories and ensures high-fidelity structural preservation without requiring model tuning or inversion. Across SD3 and FLUX, evaluations on PIE-Bench and SNR-Bench show that SNR-Edit delivers performance on pixel-level metrics and VLM-based scoring, while adding only about 1s overhead per image.
PhyRPR: Training-Free Physics-Constrained Video Generation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Recent diffusion-based video generation models can synthesize visually plausible videos, yet they often struggle to satisfy physical constraints. A key reason is that most existing approaches remain single-stage: they entangle high-level physical understanding with low-level visual synthesis, making it hard to generate content that require explicit physical reasoning. To address this limitation, we propose a training-free three-stage pipeline,\textit{PhyRPR}:\textit{Phy\uline{R}eason}--\textit{Phy\uline{P}lan}--\textit{Phy\uline{R}efine}, which decouples physical understanding from visual synthesis. Specifically, \textit{PhyReason} uses a large multimodal model for physical state reasoning and an image generator for keyframe synthesis; \textit{PhyPlan} deterministically synthesizes a controllable coarse motion scaffold; and \textit{PhyRefine} injects this scaffold into diffusion sampling via a latent fusion strategy to refine appearance while preserving the planned dynamics. This staged design enables explicit physical control during generation. Extensive experiments under physics constraints show that our method consistently improves physical plausibility and motion controllability.
ThinkRL-Edit: Thinking in Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning-Centric Image Editing
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Instruction-driven image editing with unified multimodal generative models has advanced rapidly, yet their underlying visual reasoning remains limited, leading to suboptimal performance on reasoning-centric edits. Reinforcement learning (RL) has been investigated for improving the quality of image editing, but it faces three key challenges: (1) limited reasoning exploration confined to denoising stochasticity, (2) biased reward fusion, and (3) unstable VLM-based instruction rewards. In this work, we propose ThinkRL-Edit, a reasoning-centric RL framework that decouples visual reasoning from image synthesis and expands reasoning exploration beyond denoising. To the end, we introduce Chain-of-Thought (CoT)-based reasoning sampling with planning and reflection stages prior to generation in online sampling, compelling the model to explore multiple semantic hypotheses and validate their plausibility before committing to a visual outcome. To avoid the failures of weighted aggregation, we propose an unbiased chain preference grouping strategy across multiple reward dimensions. Moreover, we replace interval-based VLM scores with a binary checklist, yielding more precise, lower-variance, and interpretable rewards for complex reasoning. Experiments show our method significantly outperforms prior work on reasoning-centric image editing, producing instruction-faithful, visually coherent, and semantically grounded edits.
Any-to-Bokeh: One-Step Video Bokeh via Multi-Plane Image Guided Diffusion
May 27, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion based editing models have enabled realistic camera simulation and image-based bokeh, but video bokeh remains largely unexplored. Existing video editing models cannot explicitly control focus planes or adjust bokeh intensity, limiting their applicability for controllable optical effects. Moreover, naively extending image-based bokeh methods to video often results in temporal flickering and unsatisfactory edge blur transitions due to the lack of temporal modeling and generalization capability. To address these challenges, we propose a novel one-step video bokeh framework that converts arbitrary input videos into temporally coherent, depth-aware bokeh effects. Our method leverages a multi-plane image (MPI) representation constructed through a progressively widening depth sampling function, providing explicit geometric guidance for depth-dependent blur synthesis. By conditioning a single-step video diffusion model on MPI layers and utilizing the strong 3D priors from pre-trained models such as Stable Video Diffusion, our approach achieves realistic and consistent bokeh effects across diverse scenes. Additionally, we introduce a progressive training strategy to enhance temporal consistency, depth robustness, and detail preservation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method produces high-quality, controllable bokeh effects and achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple evaluation benchmarks.
SUDO: Enhancing Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Self-Supervised Direct Preference Optimization
Apr 20, 2025
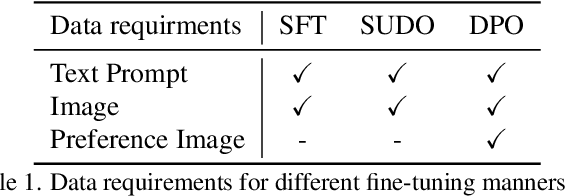


Abstract:Previous text-to-image diffusion models typically employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to enhance pre-trained base models. However, this approach primarily minimizes the loss of mean squared error (MSE) at the pixel level, neglecting the need for global optimization at the image level, which is crucial for achieving high perceptual quality and structural coherence. In this paper, we introduce Self-sUpervised Direct preference Optimization (SUDO), a novel paradigm that optimizes both fine-grained details at the pixel level and global image quality. By integrating direct preference optimization into the model, SUDO generates preference image pairs in a self-supervised manner, enabling the model to prioritize global-level learning while complementing the pixel-level MSE loss. As an effective alternative to supervised fine-tuning, SUDO can be seamlessly applied to any text-to-image diffusion model. Importantly, it eliminates the need for costly data collection and annotation efforts typically associated with traditional direct preference optimization methods. Through extensive experiments on widely-used models, including Stable Diffusion 1.5 and XL, we demonstrate that SUDO significantly enhances both global and local image quality. The codes are provided at \href{https://github.com/SPengLiang/SUDO}{this link}.
Discriminator-Free Direct Preference Optimization for Video Diffusion
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), which aligns models with human preferences through win/lose data pairs, has achieved remarkable success in language and image generation. However, applying DPO to video diffusion models faces critical challenges: (1) Data inefficiency. Generating thousands of videos per DPO iteration incurs prohibitive costs; (2) Evaluation uncertainty. Human annotations suffer from subjective bias, and automated discriminators fail to detect subtle temporal artifacts like flickering or motion incoherence. To address these, we propose a discriminator-free video DPO framework that: (1) Uses original real videos as win cases and their edited versions (e.g., reversed, shuffled, or noise-corrupted clips) as lose cases; (2) Trains video diffusion models to distinguish and avoid artifacts introduced by editing. This approach eliminates the need for costly synthetic video comparisons, provides unambiguous quality signals, and enables unlimited training data expansion through simple editing operations. We theoretically prove the framework's effectiveness even when real videos and model-generated videos follow different distributions. Experiments on CogVideoX demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed method.
MagicID: Hybrid Preference Optimization for ID-Consistent and Dynamic-Preserved Video Customization
Mar 16, 2025
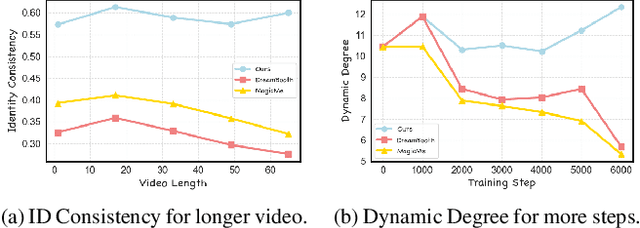

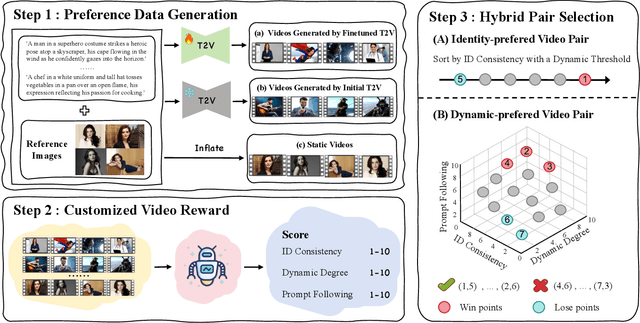
Abstract:Video identity customization seeks to produce high-fidelity videos that maintain consistent identity and exhibit significant dynamics based on users' reference images. However, existing approaches face two key challenges: identity degradation over extended video length and reduced dynamics during training, primarily due to their reliance on traditional self-reconstruction training with static images. To address these issues, we introduce $\textbf{MagicID}$, a novel framework designed to directly promote the generation of identity-consistent and dynamically rich videos tailored to user preferences. Specifically, we propose constructing pairwise preference video data with explicit identity and dynamic rewards for preference learning, instead of sticking to the traditional self-reconstruction. To address the constraints of customized preference data, we introduce a hybrid sampling strategy. This approach first prioritizes identity preservation by leveraging static videos derived from reference images, then enhances dynamic motion quality in the generated videos using a Frontier-based sampling method. By utilizing these hybrid preference pairs, we optimize the model to align with the reward differences between pairs of customized preferences. Extensive experiments show that MagicID successfully achieves consistent identity and natural dynamics, surpassing existing methods across various metrics.
VidSketch: Hand-drawn Sketch-Driven Video Generation with Diffusion Control
Feb 03, 2025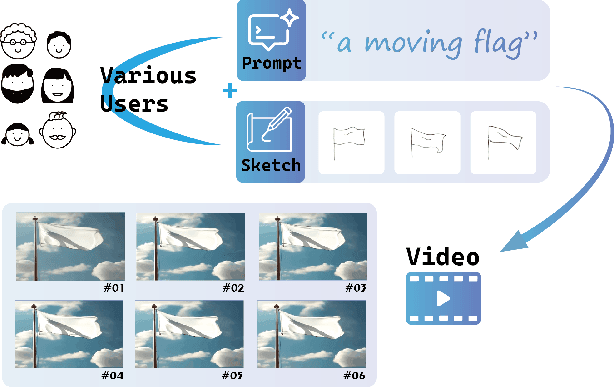
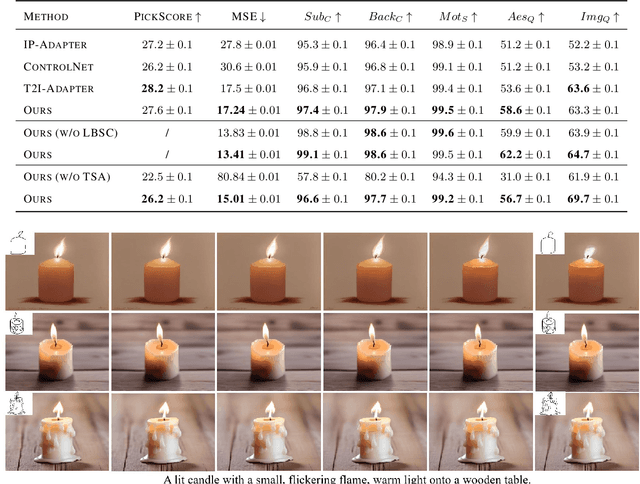

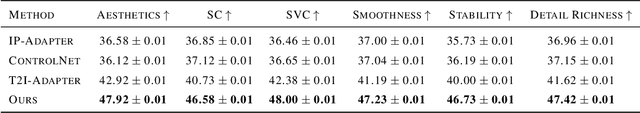
Abstract:With the advancement of generative artificial intelligence, previous studies have achieved the task of generating aesthetic images from hand-drawn sketches, fulfilling the public's needs for drawing. However, these methods are limited to static images and lack the ability to control video animation generation using hand-drawn sketches. To address this gap, we propose VidSketch, the first method capable of generating high-quality video animations directly from any number of hand-drawn sketches and simple text prompts, bridging the divide between ordinary users and professional artists. Specifically, our method introduces a Level-Based Sketch Control Strategy to automatically adjust the guidance strength of sketches during the generation process, accommodating users with varying drawing skills. Furthermore, a TempSpatial Attention mechanism is designed to enhance the spatiotemporal consistency of generated video animations, significantly improving the coherence across frames. You can find more detailed cases on our official website.
HuViDPO:Enhancing Video Generation through Direct Preference Optimization for Human-Centric Alignment
Feb 02, 2025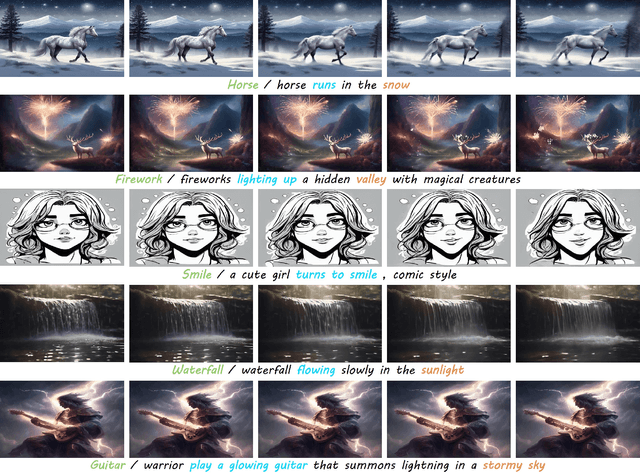
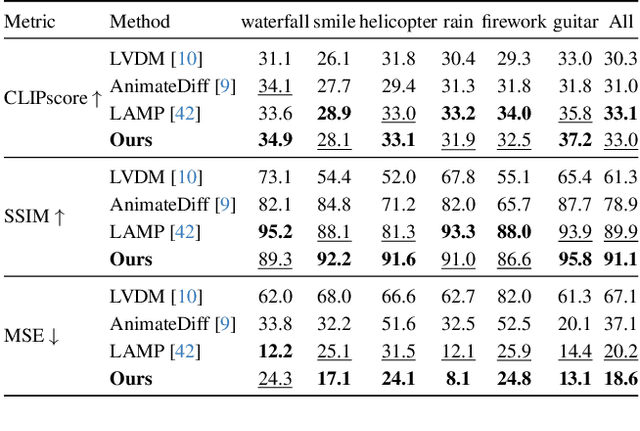
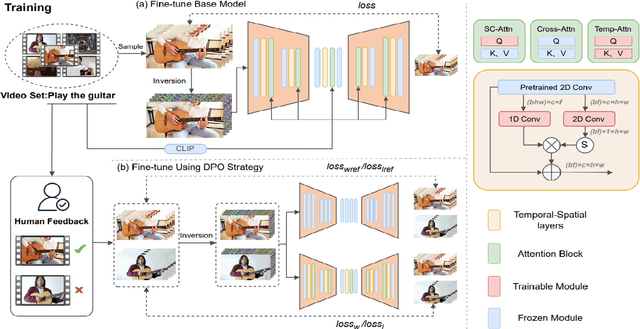
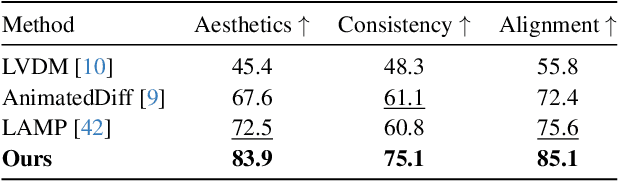
Abstract:With the rapid development of AIGC technology, significant progress has been made in diffusion model-based technologies for text-to-image (T2I) and text-to-video (T2V). In recent years, a few studies have introduced the strategy of Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) into T2I tasks, significantly enhancing human preferences in generated images. However, existing T2V generation methods lack a well-formed pipeline with exact loss function to guide the alignment of generated videos with human preferences using DPO strategies. Additionally, challenges such as the scarcity of paired video preference data hinder effective model training. At the same time, the lack of training datasets poses a risk of insufficient flexibility and poor video generation quality in the generated videos. Based on those problems, our work proposes three targeted solutions in sequence. 1) Our work is the first to introduce the DPO strategy into the T2V tasks. By deriving a carefully structured loss function, we utilize human feedback to align video generation with human preferences. We refer to this new method as HuViDPO. 2) Our work constructs small-scale human preference datasets for each action category and fine-tune this model, improving the aesthetic quality of the generated videos while reducing training costs. 3) We adopt a First-Frame-Conditioned strategy, leveraging the rich in formation from the first frame to guide the generation of subsequent frames, enhancing flexibility in video generation. At the same time, we employ a SparseCausal Attention mechanism to enhance the quality of the generated videos.More details and examples can be accessed on our website: https://tankowa.github.io/HuViDPO. github.io/.
GCA-3D: Towards Generalized and Consistent Domain Adaptation of 3D Generators
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Recently, 3D generative domain adaptation has emerged to adapt the pre-trained generator to other domains without collecting massive datasets and camera pose distributions. Typically, they leverage large-scale pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models to synthesize images for the target domain and then fine-tune the 3D model. However, they suffer from the tedious pipeline of data generation, which inevitably introduces pose bias between the source domain and synthetic dataset. Furthermore, they are not generalized to support one-shot image-guided domain adaptation, which is more challenging due to the more severe pose bias and additional identity bias introduced by the single image reference. To address these issues, we propose GCA-3D, a generalized and consistent 3D domain adaptation method without the intricate pipeline of data generation. Different from previous pipeline methods, we introduce multi-modal depth-aware score distillation sampling loss to efficiently adapt 3D generative models in a non-adversarial manner. This multi-modal loss enables GCA-3D in both text prompt and one-shot image prompt adaptation. Besides, it leverages per-instance depth maps from the volume rendering module to mitigate the overfitting problem and retain the diversity of results. To enhance the pose and identity consistency, we further propose a hierarchical spatial consistency loss to align the spatial structure between the generated images in the source and target domain. Experiments demonstrate that GCA-3D outperforms previous methods in terms of efficiency, generalization, pose accuracy, and identity consistency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge