Liang Peng
ExperienceWeaver: Optimizing Small-sample Experience Learning for LLM-based Clinical Text Improvement
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Clinical text improvement is vital for healthcare efficiency but remains difficult due to limited high-quality data and the complex constraints of medical documentation. While Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise, current approaches struggle in small-sample settings: supervised fine-tuning is data-intensive and costly, while retrieval-augmented generation often provides superficial corrections without capturing the reasoning behind revisions. To address these limitations, we propose ExperienceWeaver, a hierarchical framework that shifts the focus from data retrieval to experience learning. Instead of simply recalling past examples, ExperienceWeaver distills noisy, multi-dimensional feedback into structured, actionable knowledge. Specifically, error-specific Tips and high-level Strategies. By injecting this distilled experience into an agentic pipeline, the model learns "how to revise" rather than just "what to revise". Extensive evaluations across four clinical datasets demonstrate that ExperienceWeaver consistently improves performance, surpassing state-of-the-art models such as Gemini-3 Pro in small-sample settings.
RISER: Orchestrating Latent Reasoning Skills for Adaptive Activation Steering
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Recent work on domain-specific reasoning with large language models (LLMs) often relies on training-intensive approaches that require parameter updates. While activation steering has emerged as a parameter efficient alternative, existing methods apply static, manual interventions that fail to adapt to the dynamic nature of complex reasoning. To address this limitation, we propose RISER (Router-based Intervention for Steerable Enhancement of Reasoning), a plug-and-play intervention framework that adaptively steers LLM reasoning in activation space. RISER constructs a library of reusable reasoning vectors and employs a lightweight Router to dynamically compose them for each input. The Router is optimized via reinforcement learning under task-level rewards, activating latent cognitive primitives in an emergent and compositional manner. Across seven diverse benchmarks, RISER yields 3.4-6.5% average zero-shot accuracy improvements over the base model while surpassing CoT-style reasoning with 2-3x higher token efficiency and robust accuracy gains. Further analysis shows that RISER autonomously combines multiple vectors into interpretable, precise control strategies, pointing toward more controllable and efficient LLM reasoning.
SMART: Semantic Matching Contrastive Learning for Partially View-Aligned Clustering
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Multi-view clustering has been empirically shown to improve learning performance by leveraging the inherent complementary information across multiple views of data. However, in real-world scenarios, collecting strictly aligned views is challenging, and learning from both aligned and unaligned data becomes a more practical solution. Partially View-aligned Clustering aims to learn correspondences between misaligned view samples to better exploit the potential consistency and complementarity across views, including both aligned and unaligned data. However, most existing PVC methods fail to leverage unaligned data to capture the shared semantics among samples from the same cluster. Moreover, the inherent heterogeneity of multi-view data induces distributional shifts in representations, leading to inaccuracies in establishing meaningful correspondences between cross-view latent features and, consequently, impairing learning effectiveness. To address these challenges, we propose a Semantic MAtching contRasTive learning model (SMART) for PVC. The main idea of our approach is to alleviate the influence of cross-view distributional shifts, thereby facilitating semantic matching contrastive learning to fully exploit semantic relationships in both aligned and unaligned data. Extensive experiments on eight benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches on the PVC problem.
Refinement Contrastive Learning of Cell-Gene Associations for Unsupervised Cell Type Identification
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised cell type identification is crucial for uncovering and characterizing heterogeneous populations in single cell omics studies. Although a range of clustering methods have been developed, most focus exclusively on intrinsic cellular structure and ignore the pivotal role of cell-gene associations, which limits their ability to distinguish closely related cell types. To this end, we propose a Refinement Contrastive Learning framework (scRCL) that explicitly incorporates cell-gene interactions to derive more informative representations. Specifically, we introduce two contrastive distribution alignment components that reveal reliable intrinsic cellular structures by effectively exploiting cell-cell structural relationships. Additionally, we develop a refinement module that integrates gene-correlation structure learning to enhance cell embeddings by capturing underlying cell-gene associations. This module strengthens connections between cells and their associated genes, refining the representation learning to exploiting biologically meaningful relationships. Extensive experiments on several single-cell RNA-seq and spatial transcriptomics benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in cell-type identification accuracy. Moreover, downstream biological analyses confirm that the recovered cell populations exhibit coherent gene-expression signatures, further validating the biological relevance of our approach. The code is available at https://github.com/THPengL/scRCL.
Finding Time Series Anomalies using Granular-ball Vector Data Description
Nov 15, 2025



Abstract:Modeling normal behavior in dynamic, nonlinear time series data is challenging for effective anomaly detection. Traditional methods, such as nearest neighbor and clustering approaches, often depend on rigid assumptions, such as a predefined number of reliable neighbors or clusters, which frequently break down in complex temporal scenarios. To address these limitations, we introduce the Granular-ball One-Class Network (GBOC), a novel approach based on a data-adaptive representation called Granular-ball Vector Data Description (GVDD). GVDD partitions the latent space into compact, high-density regions represented by granular-balls, which are generated through a density-guided hierarchical splitting process and refined by removing noisy structures. Each granular-ball serves as a prototype for local normal behavior, naturally positioning itself between individual instances and clusters while preserving the local topological structure of the sample set. During training, GBOC improves the compactness of representations by aligning samples with their nearest granular-ball centers. During inference, anomaly scores are computed based on the distance to the nearest granular-ball. By focusing on dense, high-quality regions and significantly reducing the number of prototypes, GBOC delivers both robustness and efficiency in anomaly detection. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method, highlighting its ability to handle the challenges of time series anomaly detection.
OT-Talk: Animating 3D Talking Head with Optimal Transportation
May 03, 2025Abstract:Animating 3D head meshes using audio inputs has significant applications in AR/VR, gaming, and entertainment through 3D avatars. However, bridging the modality gap between speech signals and facial dynamics remains a challenge, often resulting in incorrect lip syncing and unnatural facial movements. To address this, we propose OT-Talk, the first approach to leverage optimal transportation to optimize the learning model in talking head animation. Building on existing learning frameworks, we utilize a pre-trained Hubert model to extract audio features and a transformer model to process temporal sequences. Unlike previous methods that focus solely on vertex coordinates or displacements, we introduce Chebyshev Graph Convolution to extract geometric features from triangulated meshes. To measure mesh dissimilarities, we go beyond traditional mesh reconstruction errors and velocity differences between adjacent frames. Instead, we represent meshes as probability measures and approximate their surfaces. This allows us to leverage the sliced Wasserstein distance for modeling mesh variations. This approach facilitates the learning of smooth and accurate facial motions, resulting in coherent and natural facial animations. Our experiments on two public audio-mesh datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques both quantitatively and qualitatively in terms of mesh reconstruction accuracy and temporal alignment. In addition, we conducted a user perception study with 20 volunteers to further assess the effectiveness of our approach.
SUDO: Enhancing Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Self-Supervised Direct Preference Optimization
Apr 20, 2025
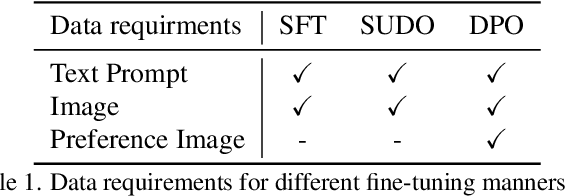


Abstract:Previous text-to-image diffusion models typically employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to enhance pre-trained base models. However, this approach primarily minimizes the loss of mean squared error (MSE) at the pixel level, neglecting the need for global optimization at the image level, which is crucial for achieving high perceptual quality and structural coherence. In this paper, we introduce Self-sUpervised Direct preference Optimization (SUDO), a novel paradigm that optimizes both fine-grained details at the pixel level and global image quality. By integrating direct preference optimization into the model, SUDO generates preference image pairs in a self-supervised manner, enabling the model to prioritize global-level learning while complementing the pixel-level MSE loss. As an effective alternative to supervised fine-tuning, SUDO can be seamlessly applied to any text-to-image diffusion model. Importantly, it eliminates the need for costly data collection and annotation efforts typically associated with traditional direct preference optimization methods. Through extensive experiments on widely-used models, including Stable Diffusion 1.5 and XL, we demonstrate that SUDO significantly enhances both global and local image quality. The codes are provided at \href{https://github.com/SPengLiang/SUDO}{this link}.
Discriminator-Free Direct Preference Optimization for Video Diffusion
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), which aligns models with human preferences through win/lose data pairs, has achieved remarkable success in language and image generation. However, applying DPO to video diffusion models faces critical challenges: (1) Data inefficiency. Generating thousands of videos per DPO iteration incurs prohibitive costs; (2) Evaluation uncertainty. Human annotations suffer from subjective bias, and automated discriminators fail to detect subtle temporal artifacts like flickering or motion incoherence. To address these, we propose a discriminator-free video DPO framework that: (1) Uses original real videos as win cases and their edited versions (e.g., reversed, shuffled, or noise-corrupted clips) as lose cases; (2) Trains video diffusion models to distinguish and avoid artifacts introduced by editing. This approach eliminates the need for costly synthetic video comparisons, provides unambiguous quality signals, and enables unlimited training data expansion through simple editing operations. We theoretically prove the framework's effectiveness even when real videos and model-generated videos follow different distributions. Experiments on CogVideoX demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed method.
EmoFace: Emotion-Content Disentangled Speech-Driven 3D Talking Face with Mesh Attention
Aug 21, 2024
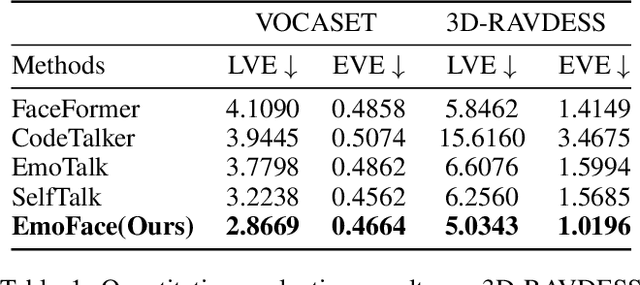
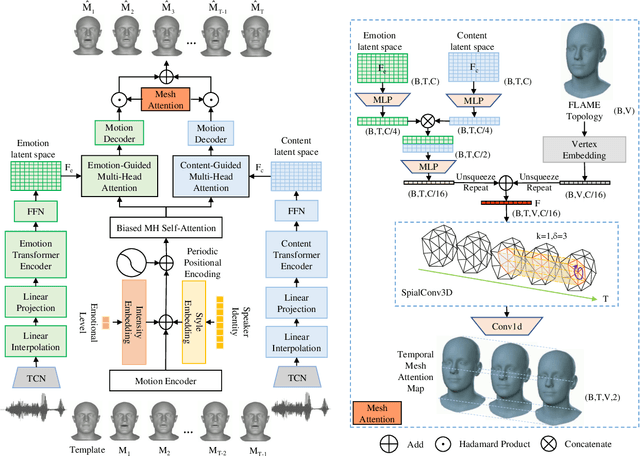

Abstract:The creation of increasingly vivid 3D virtual digital humans has become a hot topic in recent years. Currently, most speech-driven work focuses on training models to learn the relationship between phonemes and visemes to achieve more realistic lips. However, they fail to capture the correlations between emotions and facial expressions effectively. To solve this problem, we propose a new model, termed EmoFace. EmoFace employs a novel Mesh Attention mechanism, which helps to learn potential feature dependencies between mesh vertices in time and space. We also adopt, for the first time to our knowledge, an effective self-growing training scheme that combines teacher-forcing and scheduled sampling in a 3D face animation task. Additionally, since EmoFace is an autoregressive model, there is no requirement that the first frame of the training data must be a silent frame, which greatly reduces the data limitations and contributes to solve the current dilemma of insufficient datasets. Comprehensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations on our proposed high-quality reconstructed 3D emotional facial animation dataset, 3D-RAVDESS ($5.0343\times 10^{-5}$mm for LVE and $1.0196\times 10^{-5}$mm for EVE), and publicly available dataset VOCASET ($2.8669\times 10^{-5}$mm for LVE and $0.4664\times 10^{-5}$mm for EVE), demonstrate that our algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance.
GLDiTalker: Speech-Driven 3D Facial Animation with Graph Latent Diffusion Transformer
Aug 03, 2024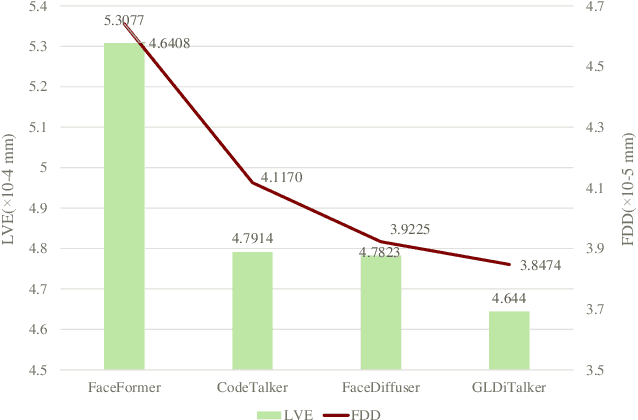
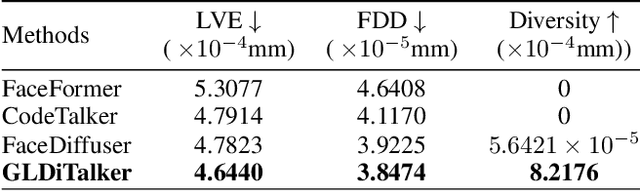
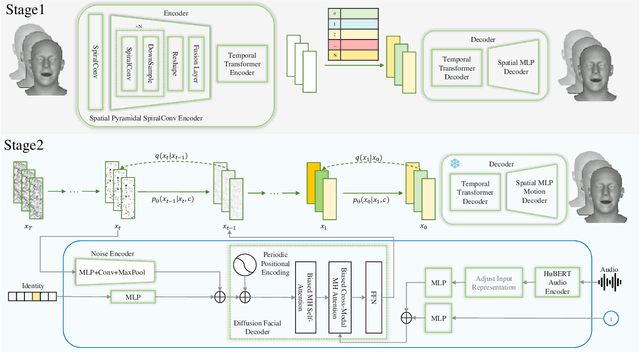
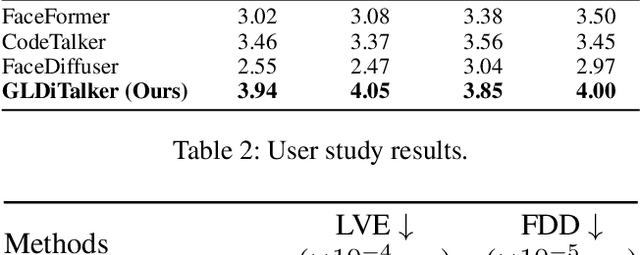
Abstract:3D speech-driven facial animation generation has received much attention in both industrial applications and academic research. Since the non-verbal facial cues that exist across the face in reality are non-deterministic, the generated results should be diverse. However, most recent methods are deterministic models that cannot learn a many-to-many mapping between audio and facial motion to generate diverse facial animations. To address this problem, we propose GLDiTalker, which introduces a motion prior along with some stochasticity to reduce the uncertainty of cross-modal mapping while increasing non-determinacy of the non-verbal facial cues that reside throughout the face. Particularly, GLDiTalker uses VQ-VAE to map facial motion mesh sequences into latent space in the first stage, and then iteratively adds and removes noise to the latent facial motion features in the second stage. In order to integrate different levels of spatial information, the Spatial Pyramidal SpiralConv Encoder is also designed to extract multi-scale features. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge