Libo Zhang
National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China
VisRefiner: Learning from Visual Differences for Screenshot-to-Code Generation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Screenshot-to-code generation aims to translate user interface screenshots into executable frontend code that faithfully reproduces the target layout and style. Existing multimodal large language models perform this mapping directly from screenshots but are trained without observing the visual outcomes of their generated code. In contrast, human developers iteratively render their implementation, compare it with the design, and learn how visual differences relate to code changes. Inspired by this process, we propose VisRefiner, a training framework that enables models to learn from visual differences between rendered predictions and reference designs. We construct difference-aligned supervision that associates visual discrepancies with corresponding code edits, allowing the model to understand how appearance variations arise from implementation changes. Building on this, we introduce a reinforcement learning stage for self-refinement, where the model improves its generated code by observing both the rendered output and the target design, identifying their visual differences, and updating the code accordingly. Experiments show that VisRefiner substantially improves single-step generation quality and layout fidelity, while also endowing models with strong self-refinement ability. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of learning from visual differences for advancing screenshot-to-code generation.
EgoReAct: Egocentric Video-Driven 3D Human Reaction Generation
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Humans exhibit adaptive, context-sensitive responses to egocentric visual input. However, faithfully modeling such reactions from egocentric video remains challenging due to the dual requirements of strictly causal generation and precise 3D spatial alignment. To tackle this problem, we first construct the Human Reaction Dataset (HRD) to address data scarcity and misalignment by building a spatially aligned egocentric video-reaction dataset, as existing datasets (e.g., ViMo) suffer from significant spatial inconsistency between the egocentric video and reaction motion, e.g., dynamically moving motions are always paired with fixed-camera videos. Leveraging HRD, we present EgoReAct, the first autoregressive framework that generates 3D-aligned human reaction motions from egocentric video streams in real-time. We first compress the reaction motion into a compact yet expressive latent space via a Vector Quantised-Variational AutoEncoder and then train a Generative Pre-trained Transformer for reaction generation from the visual input. EgoReAct incorporates 3D dynamic features, i.e., metric depth, and head dynamics during the generation, which effectively enhance spatial grounding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EgoReAct achieves remarkably higher realism, spatial consistency, and generation efficiency compared with prior methods, while maintaining strict causality during generation. We will release code, models, and data upon acceptance.
Nightjar: Dynamic Adaptive Speculative Decoding for Large Language Models Serving
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding (SD) accelerates LLM inference by verifying draft tokens in parallel. However, this method presents a critical trade-off: it improves throughput in low-load, memory-bound systems but degrades performance in high-load, compute-bound environments due to verification overhead. Current SD implementations use a fixed speculative length, failing to adapt to dynamic request rates and creating a significant performance bottleneck in real-world serving scenarios. To overcome this, we propose Nightjar, a novel learning-based algorithm for adaptive speculative inference that adjusts to request load by dynamically selecting the optimal speculative length for different batch sizes and even disabling speculative decoding when it provides no benefit. Experiments show that Nightjar achieves up to 14.8% higher throughput and 20.2% lower latency compared to standard speculative decoding, demonstrating robust efficiency for real-time serving.
G3CN: Gaussian Topology Refinement Gated Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Sep 09, 2025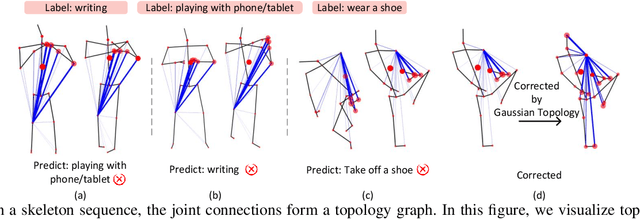
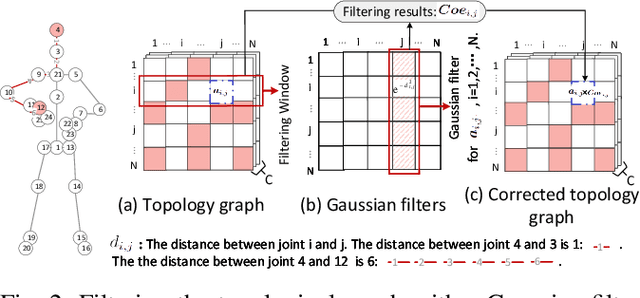
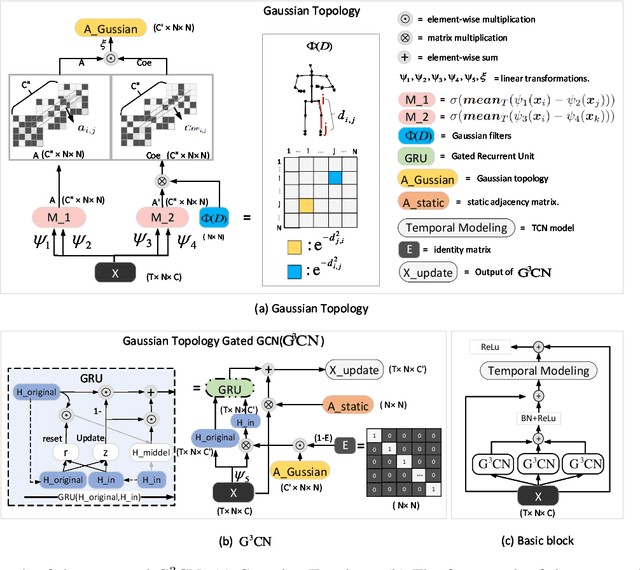
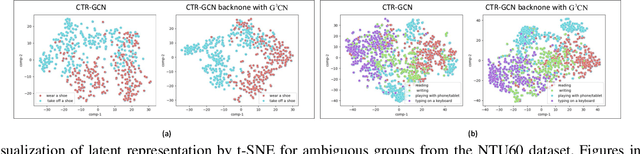
Abstract:Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) have proven to be highly effective for skeleton-based action recognition, primarily due to their ability to leverage graph topology for feature aggregation, a key factor in extracting meaningful representations. However, despite their success, GCNs often struggle to effectively distinguish between ambiguous actions, revealing limitations in the representation of learned topological and spatial features. To address this challenge, we propose a novel approach, Gaussian Topology Refinement Gated Graph Convolution (G$^{3}$CN), to address the challenge of distinguishing ambiguous actions in skeleton-based action recognition. G$^{3}$CN incorporates a Gaussian filter to refine the skeleton topology graph, improving the representation of ambiguous actions. Additionally, Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) are integrated into the GCN framework to enhance information propagation between skeleton points. Our method shows strong generalization across various GCN backbones. Extensive experiments on NTU RGB+D, NTU RGB+D 120, and NW-UCLA benchmarks demonstrate that G$^{3}$CN effectively improves action recognition, particularly for ambiguous samples.
Meta-Inverse Reinforcement Learning for Mean Field Games via Probabilistic Context Variables
Sep 04, 2025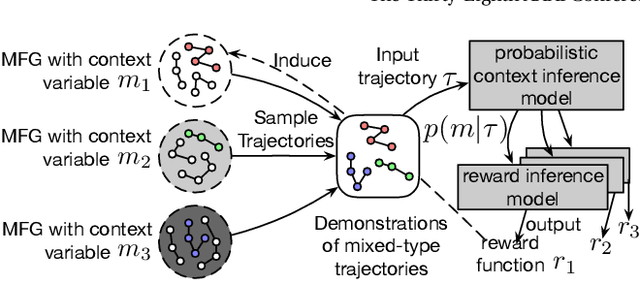


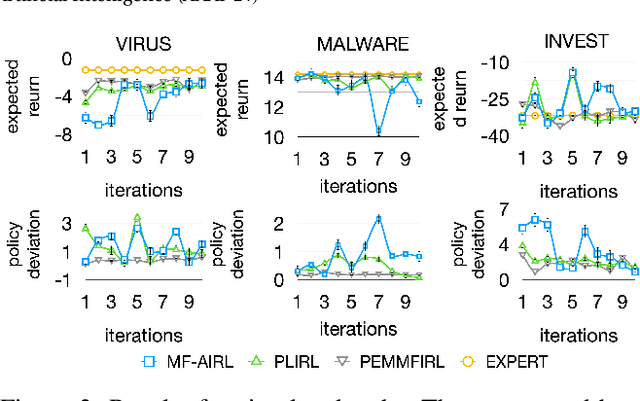
Abstract:Designing suitable reward functions for numerous interacting intelligent agents is challenging in real-world applications. Inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) in mean field games (MFGs) offers a practical framework to infer reward functions from expert demonstrations. While promising, the assumption of agent homogeneity limits the capability of existing methods to handle demonstrations with heterogeneous and unknown objectives, which are common in practice. To this end, we propose a deep latent variable MFG model and an associated IRL method. Critically, our method can infer rewards from different yet structurally similar tasks without prior knowledge about underlying contexts or modifying the MFG model itself. Our experiments, conducted on simulated scenarios and a real-world spatial taxi-ride pricing problem, demonstrate the superiority of our approach over state-of-the-art IRL methods in MFGs.
OS-R1: Agentic Operating System Kernel Tuning with Reinforcement Learning
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:Linux kernel tuning is essential for optimizing operating system (OS) performance. However, existing methods often face challenges in terms of efficiency, scalability, and generalization. This paper introduces OS-R1, an agentic Linux kernel tuning framework powered by rule-based reinforcement learning (RL). By abstracting the kernel configuration space as an RL environment, OS-R1 facilitates efficient exploration by large language models (LLMs) and ensures accurate configuration modifications. Additionally, custom reward functions are designed to enhance reasoning standardization, configuration modification accuracy, and system performance awareness of the LLMs. Furthermore, we propose a two-phase training process that accelerates convergence and minimizes retraining across diverse tuning scenarios. Experimental results show that OS-R1 significantly outperforms existing baseline methods, achieving up to 5.6% performance improvement over heuristic tuning and maintaining high data efficiency. Notably, OS-R1 is adaptable across various real-world applications, demonstrating its potential for practical deployment in diverse environments. Our dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/LHY-24/OS-R1.
Situational-Constrained Sequential Resources Allocation via Reinforcement Learning
Jun 17, 2025



Abstract:Sequential Resource Allocation with situational constraints presents a significant challenge in real-world applications, where resource demands and priorities are context-dependent. This paper introduces a novel framework, SCRL, to address this problem. We formalize situational constraints as logic implications and develop a new algorithm that dynamically penalizes constraint violations. To handle situational constraints effectively, we propose a probabilistic selection mechanism to overcome limitations of traditional constraint reinforcement learning (CRL) approaches. We evaluate SCRL across two scenarios: medical resource allocation during a pandemic and pesticide distribution in agriculture. Experiments demonstrate that SCRL outperforms existing baselines in satisfying constraints while maintaining high resource efficiency, showcasing its potential for real-world, context-sensitive decision-making tasks.
CGTrack: Cascade Gating Network with Hierarchical Feature Aggregation for UAV Tracking
May 09, 2025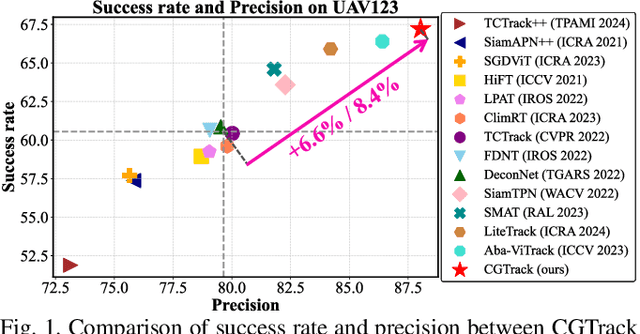

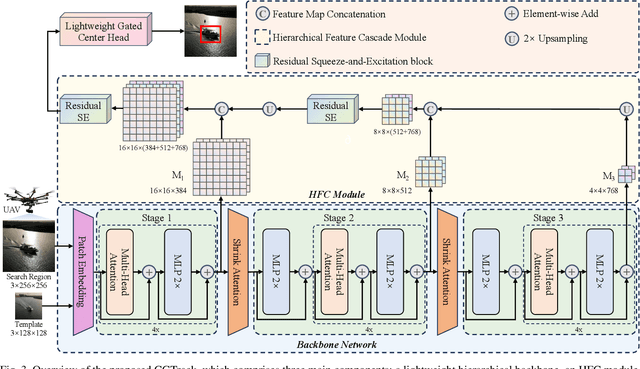
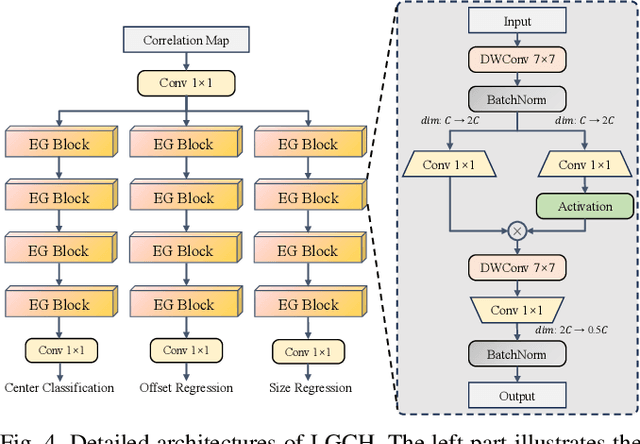
Abstract:Recent advancements in visual object tracking have markedly improved the capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking, which is a critical component in real-world robotics applications. While the integration of hierarchical lightweight networks has become a prevalent strategy for enhancing efficiency in UAV tracking, it often results in a significant drop in network capacity, which further exacerbates challenges in UAV scenarios, such as frequent occlusions and extreme changes in viewing angles. To address these issues, we introduce a novel family of UAV trackers, termed CGTrack, which combines explicit and implicit techniques to expand network capacity within a coarse-to-fine framework. Specifically, we first introduce a Hierarchical Feature Cascade (HFC) module that leverages the spirit of feature reuse to increase network capacity by integrating the deep semantic cues with the rich spatial information, incurring minimal computational costs while enhancing feature representation. Based on this, we design a novel Lightweight Gated Center Head (LGCH) that utilizes gating mechanisms to decouple target-oriented coordinates from previously expanded features, which contain dense local discriminative information. Extensive experiments on three challenging UAV tracking benchmarks demonstrate that CGTrack achieves state-of-the-art performance while running fast. Code will be available at https://github.com/Nightwatch-Fox11/CGTrack.
High-Fidelity Image Inpainting with Multimodal Guided GAN Inversion
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) inversion have demonstrated excellent performance in image inpainting that aims to restore lost or damaged image texture using its unmasked content. Previous GAN inversion-based methods usually utilize well-trained GAN models as effective priors to generate the realistic regions for missing holes. Despite excellence, they ignore a hard constraint that the unmasked regions in the input and the output should be the same, resulting in a gap between GAN inversion and image inpainting and thus degrading the performance. Besides, existing GAN inversion approaches often consider a single modality of the input image, neglecting other auxiliary cues in images for improvements. Addressing these problems, we propose a novel GAN inversion approach, dubbed MMInvertFill, for image inpainting. MMInvertFill contains primarily a multimodal guided encoder with a pre-modulation and a GAN generator with F&W+ latent space. Specifically, the multimodal encoder aims to enhance the multi-scale structures with additional semantic segmentation edge texture modalities through a gated mask-aware attention module. Afterwards, a pre-modulation is presented to encode these structures into style vectors. To mitigate issues of conspicuous color discrepancy and semantic inconsistency, we introduce the F&W+ latent space to bridge the gap between GAN inversion and image inpainting. Furthermore, in order to reconstruct faithful and photorealistic images, we devise a simple yet effective Soft-update Mean Latent module to capture more diversified in-domain patterns for generating high-fidelity textures for massive corruptions. In our extensive experiments on six challenging datasets, we show that our MMInvertFill qualitatively and quantitatively outperforms other state-of-the-arts and it supports the completion of out-of-domain images effectively.
OmniSTVG: Toward Spatio-Temporal Omni-Object Video Grounding
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose spatio-temporal omni-object video grounding, dubbed OmniSTVG, a new STVG task that aims at localizing spatially and temporally all targets mentioned in the textual query from videos. Compared to classic STVG locating only a single target, OmniSTVG enables localization of not only an arbitrary number of text-referred targets but also their interacting counterparts in the query from the video, making it more flexible and practical in real scenarios for comprehensive understanding. In order to facilitate exploration of OmniSTVG, we introduce BOSTVG, a large-scale benchmark dedicated to OmniSTVG. Specifically, our BOSTVG consists of 10,018 videos with 10.2M frames and covers a wide selection of 287 classes from diverse scenarios. Each sequence in BOSTVG, paired with a free-form textual query, encompasses a varying number of targets ranging from 1 to 10. To ensure high quality, each video is manually annotated with meticulous inspection and refinement. To our best knowledge, BOSTVG is to date the first and the largest benchmark for OmniSTVG. To encourage future research, we introduce a simple yet effective approach, named OmniTube, which, drawing inspiration from Transformer-based STVG methods, is specially designed for OmniSTVG and demonstrates promising results. By releasing BOSTVG, we hope to go beyond classic STVG by locating every object appearing in the query for more comprehensive understanding, opening up a new direction for STVG. Our benchmark, model, and results will be released at https://github.com/JellyYao3000/OmniSTVG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge