Yongsheng Yu
High-Fidelity Image Inpainting with Multimodal Guided GAN Inversion
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) inversion have demonstrated excellent performance in image inpainting that aims to restore lost or damaged image texture using its unmasked content. Previous GAN inversion-based methods usually utilize well-trained GAN models as effective priors to generate the realistic regions for missing holes. Despite excellence, they ignore a hard constraint that the unmasked regions in the input and the output should be the same, resulting in a gap between GAN inversion and image inpainting and thus degrading the performance. Besides, existing GAN inversion approaches often consider a single modality of the input image, neglecting other auxiliary cues in images for improvements. Addressing these problems, we propose a novel GAN inversion approach, dubbed MMInvertFill, for image inpainting. MMInvertFill contains primarily a multimodal guided encoder with a pre-modulation and a GAN generator with F&W+ latent space. Specifically, the multimodal encoder aims to enhance the multi-scale structures with additional semantic segmentation edge texture modalities through a gated mask-aware attention module. Afterwards, a pre-modulation is presented to encode these structures into style vectors. To mitigate issues of conspicuous color discrepancy and semantic inconsistency, we introduce the F&W+ latent space to bridge the gap between GAN inversion and image inpainting. Furthermore, in order to reconstruct faithful and photorealistic images, we devise a simple yet effective Soft-update Mean Latent module to capture more diversified in-domain patterns for generating high-fidelity textures for massive corruptions. In our extensive experiments on six challenging datasets, we show that our MMInvertFill qualitatively and quantitatively outperforms other state-of-the-arts and it supports the completion of out-of-domain images effectively.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Single-Image Efficient Super-Resolution (ESR). The challenge aimed to advance the development of deep models that optimize key computational metrics, i.e., runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while achieving a PSNR of at least 26.90 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_valid}$ dataset and 26.99 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_test}$ dataset. A robust participation saw \textbf{244} registered entrants, with \textbf{43} teams submitting valid entries. This report meticulously analyzes these methods and results, emphasizing groundbreaking advancements in state-of-the-art single-image ESR techniques. The analysis highlights innovative approaches and establishes benchmarks for future research in the field.
ZipIR: Latent Pyramid Diffusion Transformer for High-Resolution Image Restoration
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in generative models has significantly improved image restoration capabilities, particularly through powerful diffusion models that offer remarkable recovery of semantic details and local fidelity. However, deploying these models at ultra-high resolutions faces a critical trade-off between quality and efficiency due to the computational demands of long-range attention mechanisms. To address this, we introduce ZipIR, a novel framework that enhances efficiency, scalability, and long-range modeling for high-res image restoration. ZipIR employs a highly compressed latent representation that compresses image 32x, effectively reducing the number of spatial tokens, and enabling the use of high-capacity models like the Diffusion Transformer (DiT). Toward this goal, we propose a Latent Pyramid VAE (LP-VAE) design that structures the latent space into sub-bands to ease diffusion training. Trained on full images up to 2K resolution, ZipIR surpasses existing diffusion-based methods, offering unmatched speed and quality in restoring high-resolution images from severely degraded inputs.
OmniPaint: Mastering Object-Oriented Editing via Disentangled Insertion-Removal Inpainting
Mar 12, 2025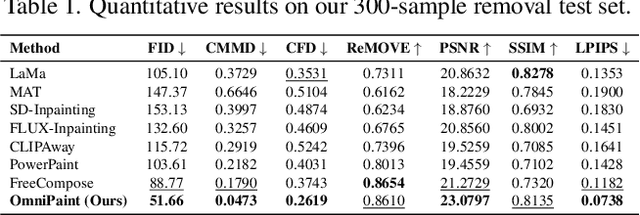

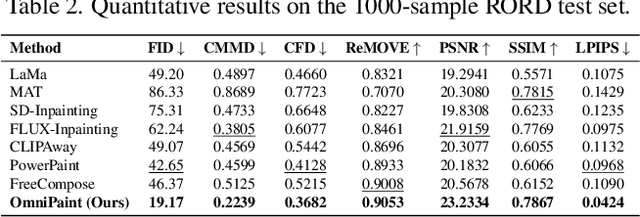

Abstract:Diffusion-based generative models have revolutionized object-oriented image editing, yet their deployment in realistic object removal and insertion remains hampered by challenges such as the intricate interplay of physical effects and insufficient paired training data. In this work, we introduce OmniPaint, a unified framework that re-conceptualizes object removal and insertion as interdependent processes rather than isolated tasks. Leveraging a pre-trained diffusion prior along with a progressive training pipeline comprising initial paired sample optimization and subsequent large-scale unpaired refinement via CycleFlow, OmniPaint achieves precise foreground elimination and seamless object insertion while faithfully preserving scene geometry and intrinsic properties. Furthermore, our novel CFD metric offers a robust, reference-free evaluation of context consistency and object hallucination, establishing a new benchmark for high-fidelity image editing. Project page: https://yeates.github.io/OmniPaint-Page/
PromptFix: You Prompt and We Fix the Photo
May 27, 2024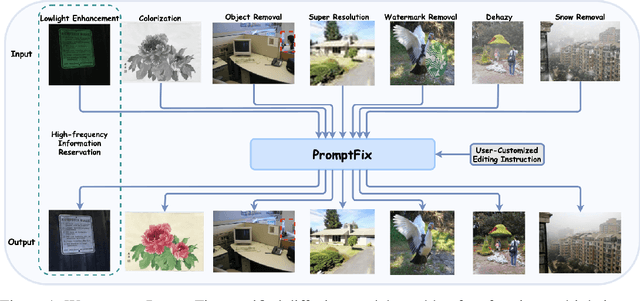
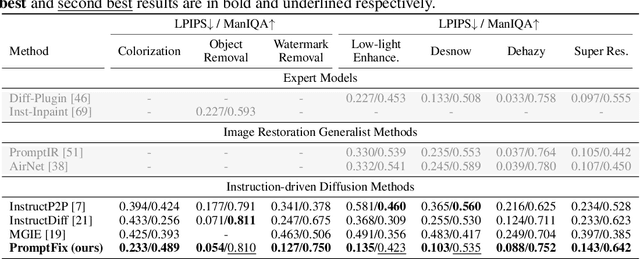
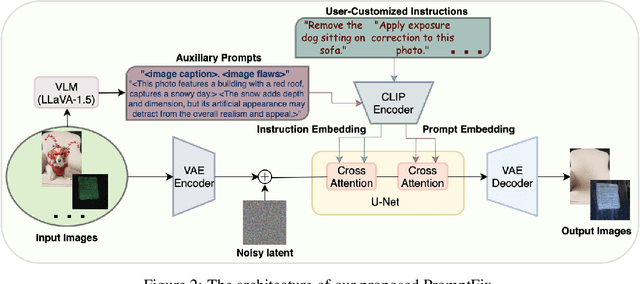
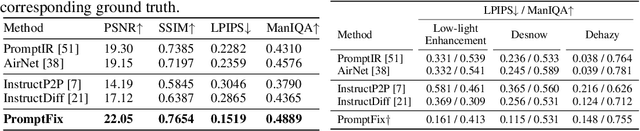
Abstract:Diffusion models equipped with language models demonstrate excellent controllability in image generation tasks, allowing image processing to adhere to human instructions. However, the lack of diverse instruction-following data hampers the development of models that effectively recognize and execute user-customized instructions, particularly in low-level tasks. Moreover, the stochastic nature of the diffusion process leads to deficiencies in image generation or editing tasks that require the detailed preservation of the generated images. To address these limitations, we propose PromptFix, a comprehensive framework that enables diffusion models to follow human instructions to perform a wide variety of image-processing tasks. First, we construct a large-scale instruction-following dataset that covers comprehensive image-processing tasks, including low-level tasks, image editing, and object creation. Next, we propose a high-frequency guidance sampling method to explicitly control the denoising process and preserve high-frequency details in unprocessed areas. Finally, we design an auxiliary prompting adapter, utilizing Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enhance text prompts and improve the model's task generalization. Experimental results show that PromptFix outperforms previous methods in various image-processing tasks. Our proposed model also achieves comparable inference efficiency with these baseline models and exhibits superior zero-shot capabilities in blind restoration and combination tasks. The dataset and code will be aviliable at https://github.com/yeates/PromptFix.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting for Demographic Inference with Large Multimodal Models
May 24, 2024

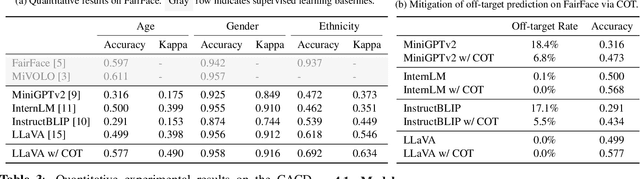

Abstract:Conventional demographic inference methods have predominantly operated under the supervision of accurately labeled data, yet struggle to adapt to shifting social landscapes and diverse cultural contexts, leading to narrow specialization and limited accuracy in applications. Recently, the emergence of large multimodal models (LMMs) has shown transformative potential across various research tasks, such as visual comprehension and description. In this study, we explore the application of LMMs to demographic inference and introduce a benchmark for both quantitative and qualitative evaluation. Our findings indicate that LMMs possess advantages in zero-shot learning, interpretability, and handling uncurated 'in-the-wild' inputs, albeit with a propensity for off-target predictions. To enhance LMM performance and achieve comparability with supervised learning baselines, we propose a Chain-of-Thought augmented prompting approach, which effectively mitigates the off-target prediction issue.
MIPI 2024 Challenge on Demosaic for HybridEVS Camera: Methods and Results
May 08, 2024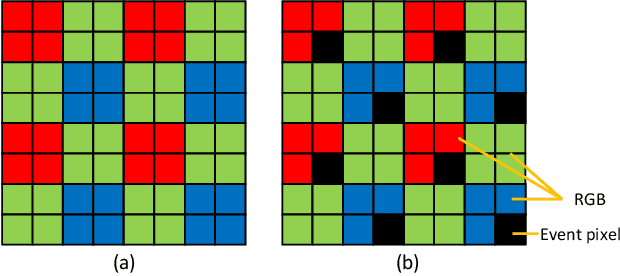
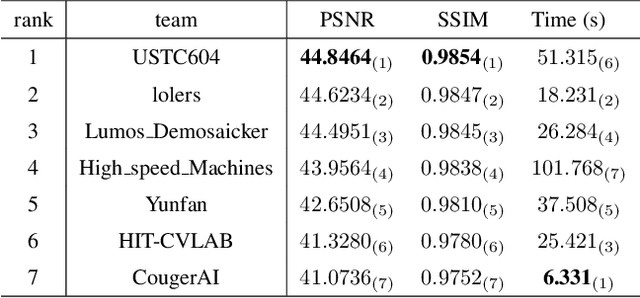
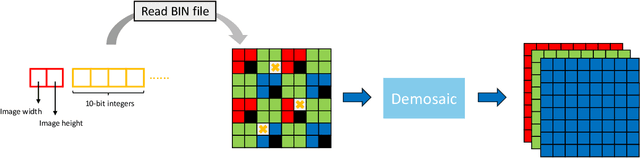

Abstract:The increasing demand for computational photography and imaging on mobile platforms has led to the widespread development and integration of advanced image sensors with novel algorithms in camera systems. However, the scarcity of high-quality data for research and the rare opportunity for in-depth exchange of views from industry and academia constrain the development of mobile intelligent photography and imaging (MIPI). Building on the achievements of the previous MIPI Workshops held at ECCV 2022 and CVPR 2023, we introduce our third MIPI challenge including three tracks focusing on novel image sensors and imaging algorithms. In this paper, we summarize and review the Nighttime Flare Removal track on MIPI 2024. In total, 170 participants were successfully registered, and 14 teams submitted results in the final testing phase. The developed solutions in this challenge achieved state-of-the-art performance on Nighttime Flare Removal. More details of this challenge and the link to the dataset can be found at https://mipi-challenge.org/MIPI2024/.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Image Super-Resolution ($\times$4): Methods and Results
Apr 15, 2024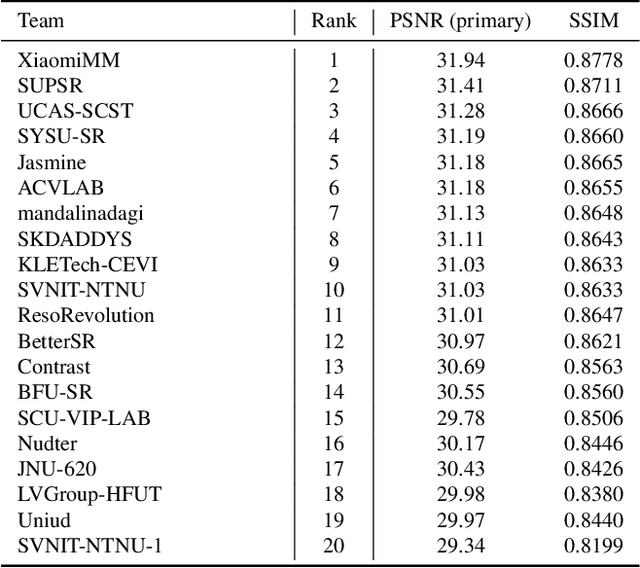
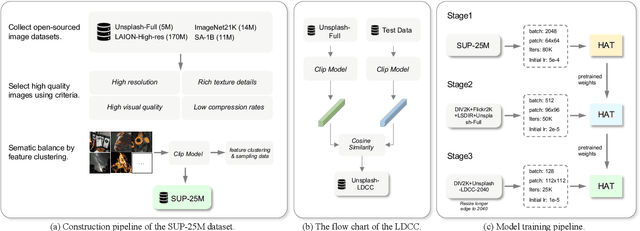
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 challenge on image super-resolution ($\times$4), highlighting the solutions proposed and the outcomes obtained. The challenge involves generating corresponding high-resolution (HR) images, magnified by a factor of four, from low-resolution (LR) inputs using prior information. The LR images originate from bicubic downsampling degradation. The aim of the challenge is to obtain designs/solutions with the most advanced SR performance, with no constraints on computational resources (e.g., model size and FLOPs) or training data. The track of this challenge assesses performance with the PSNR metric on the DIV2K testing dataset. The competition attracted 199 registrants, with 20 teams submitting valid entries. This collective endeavour not only pushes the boundaries of performance in single-image SR but also offers a comprehensive overview of current trends in this field.
Flow-Guided Diffusion for Video Inpainting
Nov 26, 2023



Abstract:Video inpainting has been challenged by complex scenarios like large movements and low-light conditions. Current methods, including emerging diffusion models, face limitations in quality and efficiency. This paper introduces the Flow-Guided Diffusion model for Video Inpainting (FGDVI), a novel approach that significantly enhances temporal consistency and inpainting quality via reusing an off-the-shelf image generation diffusion model. We employ optical flow for precise one-step latent propagation and introduces a model-agnostic flow-guided latent interpolation technique. This technique expedites denoising, seamlessly integrating with any Video Diffusion Model (VDM) without additional training. Our FGDVI demonstrates a remarkable 10% improvement in flow warping error E_warp over existing state-of-the-art methods. Our comprehensive experiments validate superior performance of FGDVI, offering a promising direction for advanced video inpainting. The code and detailed results will be publicly available in https://github.com/NevSNev/FGDVI.
GPT-4V as A Social Media Analysis Engine
Nov 13, 2023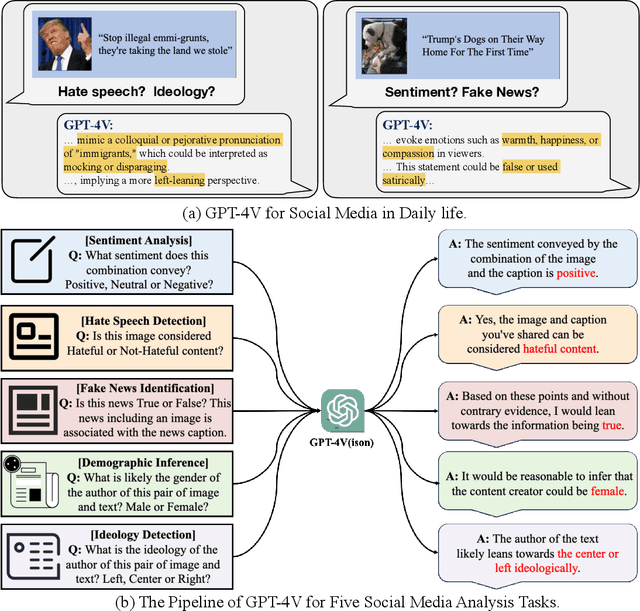
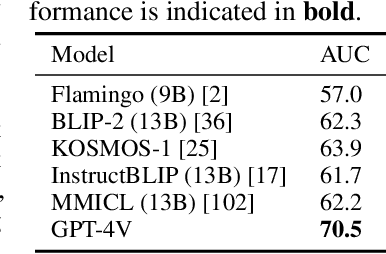
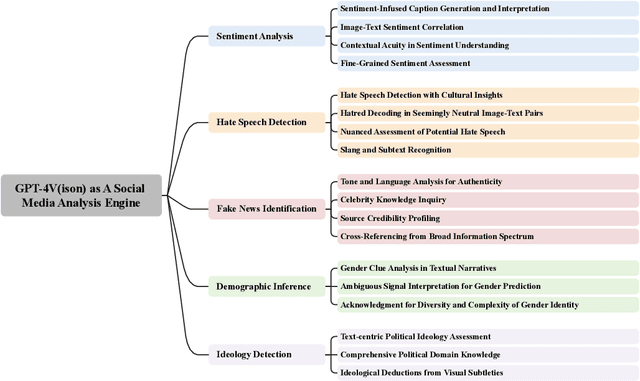
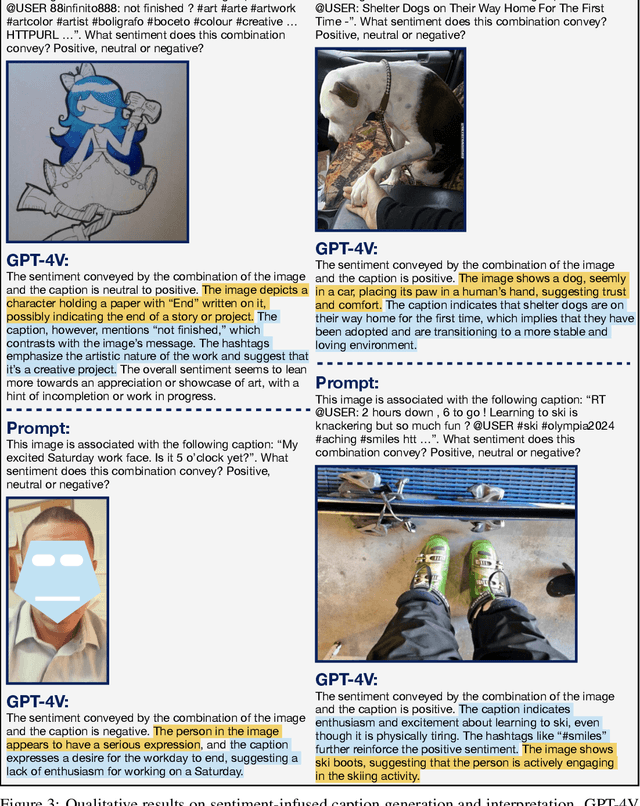
Abstract:Recent research has offered insights into the extraordinary capabilities of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) in various general vision and language tasks. There is growing interest in how LMMs perform in more specialized domains. Social media content, inherently multimodal, blends text, images, videos, and sometimes audio. Understanding social multimedia content remains a challenging problem for contemporary machine learning frameworks. In this paper, we explore GPT-4V(ision)'s capabilities for social multimedia analysis. We select five representative tasks, including sentiment analysis, hate speech detection, fake news identification, demographic inference, and political ideology detection, to evaluate GPT-4V. Our investigation begins with a preliminary quantitative analysis for each task using existing benchmark datasets, followed by a careful review of the results and a selection of qualitative samples that illustrate GPT-4V's potential in understanding multimodal social media content. GPT-4V demonstrates remarkable efficacy in these tasks, showcasing strengths such as joint understanding of image-text pairs, contextual and cultural awareness, and extensive commonsense knowledge. Despite the overall impressive capacity of GPT-4V in the social media domain, there remain notable challenges. GPT-4V struggles with tasks involving multilingual social multimedia comprehension and has difficulties in generalizing to the latest trends in social media. Additionally, it exhibits a tendency to generate erroneous information in the context of evolving celebrity and politician knowledge, reflecting the known hallucination problem. The insights gleaned from our findings underscore a promising future for LMMs in enhancing our comprehension of social media content and its users through the analysis of multimodal information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge