Yuchen Liu
SSL: Sweet Spot Learning for Differentiated Guidance in Agentic Optimization
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards has emerged as a powerful paradigm for training intelligent agents. However, existing methods typically employ binary rewards that fail to capture quality differences among trajectories achieving identical outcomes, thereby overlooking potential diversity within the solution space. Inspired by the ``sweet spot'' concept in tennis-the racket's core region that produces optimal hitting effects, we introduce \textbf{S}weet \textbf{S}pot \textbf{L}earning (\textbf{SSL}), a novel framework that provides differentiated guidance for agent optimization. SSL follows a simple yet effective principle: progressively amplified, tiered rewards guide policies toward the sweet-spot region of the solution space. This principle naturally adapts across diverse tasks: visual perception tasks leverage distance-tiered modeling to reward proximity, while complex reasoning tasks reward incremental progress toward promising solutions. We theoretically demonstrate that SSL preserves optimal solution ordering and enhances the gradient signal-to-noise ratio, thereby fostering more directed optimization. Extensive experiments across GUI perception, short/long-term planning, and complex reasoning tasks show consistent improvements over strong baselines on 12 benchmarks, achieving up to 2.5X sample efficiency gains and effective cross-task transferability. Our work establishes SSL as a general principle for training capable and robust agents.
GenProve: Learning to Generate Text with Fine-Grained Provenance
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLM) often hallucinate, and while adding citations is a common solution, it is frequently insufficient for accountability as users struggle to verify how a cited source supports a generated claim. Existing methods are typically coarse-grained and fail to distinguish between direct quotes and complex reasoning. In this paper, we introduce Generation-time Fine-grained Provenance, a task where models must generate fluent answers while simultaneously producing structured, sentence-level provenance triples. To enable this, we present ReFInE (Relation-aware Fine-grained Interpretability & Evidence), a dataset featuring expert verified annotations that distinguish between Quotation, Compression, and Inference. Building on ReFInE, we propose GenProve, a framework that combines Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). By optimizing a composite reward for answer fidelity and provenance correctness, GenProve significantly outperforms 14 strong LLMs in joint evaluation. Crucially, our analysis uncovers a reasoning gap where models excel at surface-level quotation but struggle significantly with inference-based provenance, suggesting that verifiable reasoning remains a frontier challenge distinct from surface-level citation.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
CCAD: Compressed Global Feature Conditioned Anomaly Detection
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Anomaly detection holds considerable industrial significance, especially in scenarios with limited anomalous data. Currently, reconstruction-based and unsupervised representation-based approaches are the primary focus. However, unsupervised representation-based methods struggle to extract robust features under domain shift, whereas reconstruction-based methods often suffer from low training efficiency and performance degradation due to insufficient constraints. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method named Compressed Global Feature Conditioned Anomaly Detection (CCAD). CCAD synergizes the strengths of both paradigms by adapting global features as a new modality condition for the reconstruction model. Furthermore, we design an adaptive compression mechanism to enhance both generalization and training efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CCAD consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of AUC while achieving faster convergence. In addition, we contribute a reorganized and re-annotated version of the DAGM 2007 dataset with new annotations to further validate our method's effectiveness. The code for reproducing main results is available at https://github.com/chloeqxq/CCAD.
SemCovert: Secure and Covert Video Transmission via Deep Semantic-Level Hiding
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Video semantic communication, praised for its transmission efficiency, still faces critical challenges related to privacy leakage. Traditional security techniques like steganography and encryption are challenging to apply since they are not inherently robust against semantic-level transformations and abstractions. Moreover, the temporal continuity of video enables framewise statistical modeling over extended periods, which increases the risk of exposing distributional anomalies and reconstructing hidden content. To address these challenges, we propose SemCovert, a deep semantic-level hiding framework for secure and covert video transmission. SemCovert introduces a pair of co-designed models, namely the semantic hiding model and the secret semantic extractor, which are seamlessly integrated into the semantic communication pipeline. This design enables authorized receivers to reliably recover hidden information, while keeping it imperceptible to regular users. To further improve resistance to analysis, we introduce a randomized semantic hiding strategy, which breaks the determinism of embedding and introduces unpredictable distribution patterns. The experimental results demonstrate that SemCovert effectively mitigates potential eavesdropping and detection risks while reliably concealing secret videos during transmission. Meanwhile, video quality suffers only minor degradation, preserving transmission fidelity. These results confirm SemCovert's effectiveness in enabling secure and covert transmission without compromising semantic communication performance.
Seeing is Believing (and Predicting): Context-Aware Multi-Human Behavior Prediction with Vision Language Models
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Accurately predicting human behaviors is crucial for mobile robots operating in human-populated environments. While prior research primarily focuses on predicting actions in single-human scenarios from an egocentric view, several robotic applications require understanding multiple human behaviors from a third-person perspective. To this end, we present CAMP-VLM (Context-Aware Multi-human behavior Prediction): a Vision Language Model (VLM)-based framework that incorporates contextual features from visual input and spatial awareness from scene graphs to enhance prediction of humans-scene interactions. Due to the lack of suitable datasets for multi-human behavior prediction from an observer view, we perform fine-tuning of CAMP-VLM with synthetic human behavior data generated by a photorealistic simulator, and evaluate the resulting models on both synthetic and real-world sequences to assess their generalization capabilities. Leveraging Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), CAMP-VLM outperforms the best-performing baseline by up to 66.9% in prediction accuracy.
HyperVL: An Efficient and Dynamic Multimodal Large Language Model for Edge Devices
Dec 16, 2025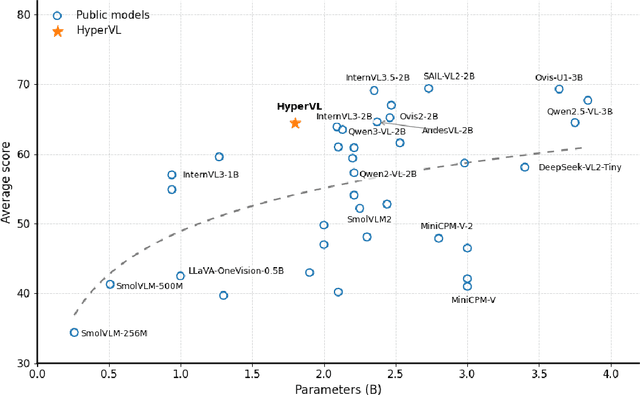

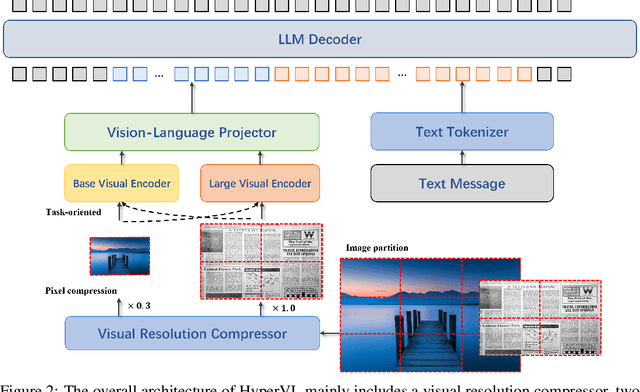
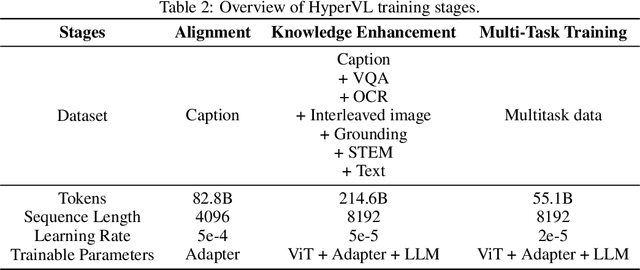
Abstract:Current multimodal large lanauge models possess strong perceptual and reasoning capabilities, however high computational and memory requirements make them difficult to deploy directly on on-device environments. While small-parameter models are progressively endowed with strong general capabilities, standard Vision Transformer (ViT) encoders remain a critical bottleneck, suffering from excessive latency and memory consumption when processing high-resolution inputs.To address these challenges, we introduce HyperVL, an efficient multimodal large language model tailored for on-device inference. HyperVL adopts an image-tiling strategy to cap peak memory usage and incorporates two novel techniques: (1) a Visual Resolution Compressor (VRC) that adaptively predicts optimal encoding resolutions to eliminate redundant computation, and (2) Dual Consistency Learning (DCL), which aligns multi-scale ViT encoders within a unified framework, enabling dynamic switching between visual branches under a shared LLM. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HyperVL achieves state-of-the-art performance among models of comparable size across multiple benchmarks. Furthermore, it significantly significantly reduces latency and power consumption on real mobile devices, demonstrating its practicality for on-device multimodal inference.
MMSense: Adapting Vision-based Foundation Model for Multi-task Multi-modal Wireless Sensing
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Large AI models have been widely adopted in wireless communications for channel modeling, beamforming, and resource optimization. However, most existing efforts remain limited to single-modality inputs and channel-specific objec- tives, overlooking the broader potential of large foundation models for unified wireless sensing. To bridge this gap, we propose MMSense, a multi-modal, multi-task foundation model that jointly addresses channel-centric, environment-aware, and human-centered sensing. Our framework integrates image, radar, LiDAR, and textual data by transforming them into vision- compatible representations, enabling effective cross-modal align- ment within a unified feature space. A modality gating mecha- nism adaptively fuses these representations, while a vision-based large language model backbone enables unified feature align- ment and instruction-driven task adaptation. Furthermore, task- specific sequential attention and uncertainty-based loss weighting mechanisms enhance cross-task generalization. Experiments on real wireless scenario datasets show that our approach outper- forms both task-specific and large-model baselines, confirming its strong generalization across heterogeneous sensing tasks.
Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Graph Neural Network Integration for Text Classification with Large Language Models
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:This study investigates a hybrid method for text classification that integrates deep feature extraction from large language models, multi-scale fusion through feature pyramids, and structured modeling with graph neural networks to enhance performance in complex semantic contexts. First, the large language model captures contextual dependencies and deep semantic representations of the input text, providing a rich feature foundation for subsequent modeling. Then, based on multi-level feature representations, the feature pyramid mechanism effectively integrates semantic features of different scales, balancing global information and local details to construct hierarchical semantic expressions. Furthermore, the fused features are transformed into graph representations, and graph neural networks are employed to capture latent semantic relations and logical dependencies in the text, enabling comprehensive modeling of complex interactions among semantic units. On this basis, the readout and classification modules generate the final category predictions. The proposed method demonstrates significant advantages in robustness alignment experiments, outperforming existing models on ACC, F1-Score, AUC, and Precision, which verifies the effectiveness and stability of the framework. This study not only constructs an integrated framework that balances global and local information as well as semantics and structure, but also provides a new perspective for multi-scale feature fusion and structured semantic modeling in text classification tasks.
Zero-Shot CFC: Fast Real-World Image Denoising based on Cross-Frequency Consistency
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot denoisers address the dataset dependency of deep-learning-based denoisers, enabling the denoising of unseen single images. Nonetheless, existing zero-shot methods suffer from long training times and rely on the assumption of noise independence and a zero-mean property, limiting their effectiveness in real-world denoising scenarios where noise characteristics are more complicated. This paper proposes an efficient and effective method for real-world denoising, the Zero-Shot denoiser based on Cross-Frequency Consistency (ZSCFC), which enables training and denoising with a single noisy image and does not rely on assumptions about noise distribution. Specifically, image textures exhibit position similarity and content consistency across different frequency bands, while noise does not. Based on this property, we developed cross-frequency consistency loss and an ultralight network to realize image denoising. Experiments on various real-world image datasets demonstrate that our ZSCFC outperforms other state-of-the-art zero-shot methods in terms of computational efficiency and denoising performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge