Xue Jiang
Disco: Densely-overlapping Cell Instance Segmentation via Adjacency-aware Collaborative Coloring
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Accurate cell instance segmentation is foundational for digital pathology analysis. Existing methods based on contour detection and distance mapping still face significant challenges in processing complex and dense cellular regions. Graph coloring-based methods provide a new paradigm for this task, yet the effectiveness of this paradigm in real-world scenarios with dense overlaps and complex topologies has not been verified. Addressing this issue, we release a large-scale dataset GBC-FS 2025, which contains highly complex and dense sub-cellular nuclear arrangements. We conduct the first systematic analysis of the chromatic properties of cell adjacency graphs across four diverse datasets and reveal an important discovery: most real-world cell graphs are non-bipartite, with a high prevalence of odd-length cycles (predominantly triangles). This makes simple 2-coloring theory insufficient for handling complex tissues, while higher-chromaticity models would cause representational redundancy and optimization difficulties. Building on this observation of complex real-world contexts, we propose Disco (Densely-overlapping Cell Instance Segmentation via Adjacency-aware COllaborative Coloring), an adjacency-aware framework based on the "divide and conquer" principle. It uniquely combines a data-driven topological labeling strategy with a constrained deep learning system to resolve complex adjacency conflicts. First, "Explicit Marking" strategy transforms the topological challenge into a learnable classification task by recursively decomposing the cell graph and isolating a "conflict set." Second, "Implicit Disambiguation" mechanism resolves ambiguities in conflict regions by enforcing feature dissimilarity between different instances, enabling the model to learn separable feature representations.
KOCO-BENCH: Can Large Language Models Leverage Domain Knowledge in Software Development?
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at general programming but struggle with domain-specific software development, necessitating domain specialization methods for LLMs to learn and utilize domain knowledge and data. However, existing domain-specific code benchmarks cannot evaluate the effectiveness of domain specialization methods, which focus on assessing what knowledge LLMs possess rather than how they acquire and apply new knowledge, lacking explicit knowledge corpora for developing domain specialization methods. To this end, we present KOCO-BENCH, a novel benchmark designed for evaluating domain specialization methods in real-world software development. KOCO-BENCH contains 6 emerging domains with 11 software frameworks and 25 projects, featuring curated knowledge corpora alongside multi-granularity evaluation tasks including domain code generation (from function-level to project-level with rigorous test suites) and domain knowledge understanding (via multiple-choice Q&A). Unlike previous benchmarks that only provide test sets for direct evaluation, KOCO-BENCH requires acquiring and applying diverse domain knowledge (APIs, rules, constraints, etc.) from knowledge corpora to solve evaluation tasks. Our evaluations reveal that KOCO-BENCH poses significant challenges to state-of-the-art LLMs. Even with domain specialization methods (e.g., SFT, RAG, kNN-LM) applied, improvements remain marginal. Best-performing coding agent, Claude Code, achieves only 34.2%, highlighting the urgent need for more effective domain specialization methods. We release KOCO-BENCH, evaluation code, and baselines to advance further research at https://github.com/jiangxxxue/KOCO-bench.
AirSpatialBot: A Spatially-Aware Aerial Agent for Fine-Grained Vehicle Attribute Recognization and Retrieval
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Despite notable advancements in remote sensing vision-language models (VLMs), existing models often struggle with spatial understanding, limiting their effectiveness in real-world applications. To push the boundaries of VLMs in remote sensing, we specifically address vehicle imagery captured by drones and introduce a spatially-aware dataset AirSpatial, which comprises over 206K instructions and introduces two novel tasks: Spatial Grounding and Spatial Question Answering. It is also the first remote sensing grounding dataset to provide 3DBB. To effectively leverage existing image understanding of VLMs to spatial domains, we adopt a two-stage training strategy comprising Image Understanding Pre-training and Spatial Understanding Fine-tuning. Utilizing this trained spatially-aware VLM, we develop an aerial agent, AirSpatialBot, which is capable of fine-grained vehicle attribute recognition and retrieval. By dynamically integrating task planning, image understanding, spatial understanding, and task execution capabilities, AirSpatialBot adapts to diverse query requirements. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, revealing the spatial limitations of existing VLMs while providing valuable insights. The model, code, and datasets will be released at https://github.com/VisionXLab/AirSpatialBot
DVGBench: Implicit-to-Explicit Visual Grounding Benchmark in UAV Imagery with Large Vision-Language Models
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Remote sensing (RS) large vision-language models (LVLMs) have shown strong promise across visual grounding (VG) tasks. However, existing RS VG datasets predominantly rely on explicit referring expressions-such as relative position, relative size, and color cues-thereby constraining performance on implicit VG tasks that require scenario-specific domain knowledge. This article introduces DVGBench, a high-quality implicit VG benchmark for drones, covering six major application scenarios: traffic, disaster, security, sport, social activity, and productive activity. Each object provides both explicit and implicit queries. Based on the dataset, we design DroneVG-R1, an LVLM that integrates the novel Implicit-to-Explicit Chain-of-Thought (I2E-CoT) within a reinforcement learning paradigm. This enables the model to take advantage of scene-specific expertise, converting implicit references into explicit ones and thus reducing grounding difficulty. Finally, an evaluation of mainstream models on both explicit and implicit VG tasks reveals substantial limitations in their reasoning capabilities. These findings provide actionable insights for advancing the reasoning capacity of LVLMs for drone-based agents. The code and datasets will be released at https://github.com/zytx121/DVGBench
A Survey on Code Generation with LLM-based Agents
Jul 31, 2025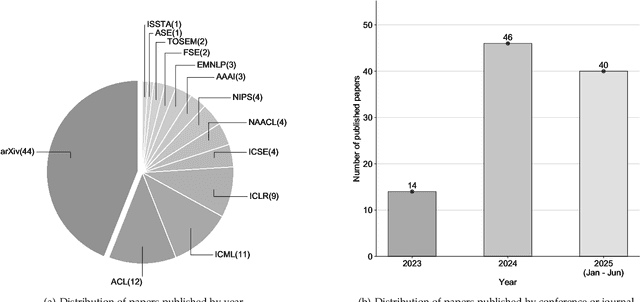
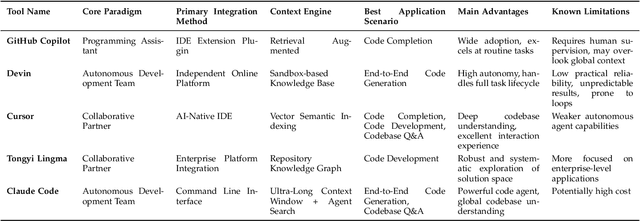
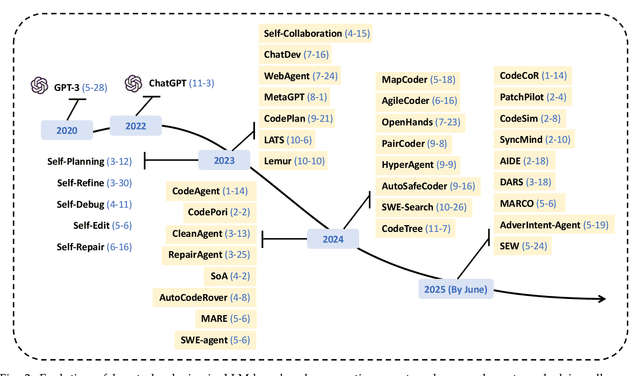
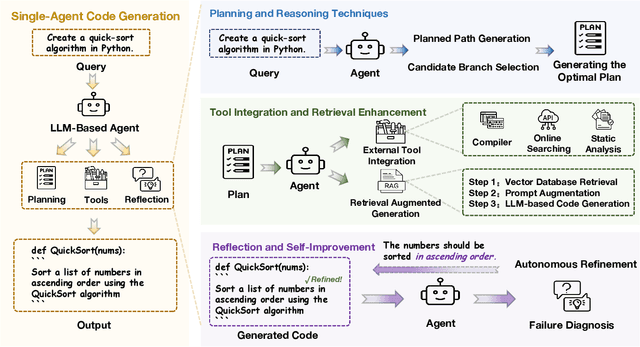
Abstract:Code generation agents powered by large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing the software development paradigm. Distinct from previous code generation techniques, code generation agents are characterized by three core features. 1) Autonomy: the ability to independently manage the entire workflow, from task decomposition to coding and debugging. 2) Expanded task scope: capabilities that extend beyond generating code snippets to encompass the full software development lifecycle (SDLC). 3) Enhancement of engineering practicality: a shift in research emphasis from algorithmic innovation toward practical engineering challenges, such as system reliability, process management, and tool integration. This domain has recently witnessed rapid development and an explosion in research, demonstrating significant application potential. This paper presents a systematic survey of the field of LLM-based code generation agents. We trace the technology's developmental trajectory from its inception and systematically categorize its core techniques, including both single-agent and multi-agent architectures. Furthermore, this survey details the applications of LLM-based agents across the full SDLC, summarizes mainstream evaluation benchmarks and metrics, and catalogs representative tools. Finally, by analyzing the primary challenges, we identify and propose several foundational, long-term research directions for the future work of the field.
RL-PLUS: Countering Capability Boundary Collapse of LLMs in Reinforcement Learning with Hybrid-policy Optimization
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward (RLVR) has significantly advanced the complex reasoning abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, it struggles to break through the inherent capability boundaries of the base LLM, due to its inherently on-policy strategy with LLM's immense action space and sparse reward. Further, RLVR can lead to the capability boundary collapse, narrowing the LLM's problem-solving scope. To address this problem, we propose RL-PLUS, a novel approach that synergizes internal exploitation (i.e., Thinking) with external data (i.e., Learning) to achieve stronger reasoning capabilities and surpass the boundaries of base models. RL-PLUS integrates two core components: Multiple Importance Sampling to address for distributional mismatch from external data, and an Exploration-Based Advantage Function to guide the model towards high-value, unexplored reasoning paths. We provide both theoretical analysis and extensive experiments to demonstrate the superiority and generalizability of our approach. The results show that RL-PLUS achieves state-of-the-art performance compared with existing RLVR methods on six math reasoning benchmarks and exhibits superior performance on six out-of-distribution reasoning tasks. It also achieves consistent and significant gains across diverse model families, with average relative improvements ranging from 21.1\% to 69.2\%. Moreover, Pass@k curves across multiple benchmarks indicate that RL-PLUS effectively resolves the capability boundary collapse problem.
Multi-objective Aligned Bidword Generation Model for E-commerce Search Advertising
Jun 04, 2025

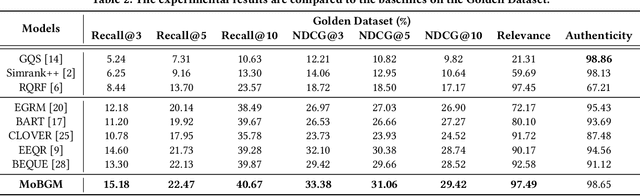

Abstract:Retrieval systems primarily address the challenge of matching user queries with the most relevant advertisements, playing a crucial role in e-commerce search advertising. The diversity of user needs and expressions often produces massive long-tail queries that cannot be matched with merchant bidwords or product titles, which results in some advertisements not being recalled, ultimately harming user experience and search efficiency. Existing query rewriting research focuses on various methods such as query log mining, query-bidword vector matching, or generation-based rewriting. However, these methods often fail to simultaneously optimize the relevance and authenticity of the user's original query and rewrite and maximize the revenue potential of recalled ads. In this paper, we propose a Multi-objective aligned Bidword Generation Model (MoBGM), which is composed of a discriminator, generator, and preference alignment module, to address these challenges. To simultaneously improve the relevance and authenticity of the query and rewrite and maximize the platform revenue, we design a discriminator to optimize these key objectives. Using the feedback signal of the discriminator, we train a multi-objective aligned bidword generator that aims to maximize the combined effect of the three objectives. Extensive offline and online experiments show that our proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the state of the art. After deployment, the algorithm has created huge commercial value for the platform, further verifying its feasibility and robustness.
Text-Queried Audio Source Separation via Hierarchical Modeling
May 27, 2025



Abstract:Target audio source separation with natural language queries presents a promising paradigm for extracting arbitrary audio events through arbitrary text descriptions. Existing methods mainly face two challenges, the difficulty in jointly modeling acoustic-textual alignment and semantic-aware separation within a blindly-learned single-stage architecture, and the reliance on large-scale accurately-labeled training data to compensate for inefficient cross-modal learning and separation. To address these challenges, we propose a hierarchical decomposition framework, HSM-TSS, that decouples the task into global-local semantic-guided feature separation and structure-preserving acoustic reconstruction. Our approach introduces a dual-stage mechanism for semantic separation, operating on distinct global and local semantic feature spaces. We first perform global-semantic separation through a global semantic feature space aligned with text queries. A Q-Audio architecture is employed to align audio and text modalities, serving as pretrained global-semantic encoders. Conditioned on the predicted global feature, we then perform the second-stage local-semantic separation on AudioMAE features that preserve time-frequency structures, followed by acoustic reconstruction. We also propose an instruction processing pipeline to parse arbitrary text queries into structured operations, extraction or removal, coupled with audio descriptions, enabling flexible sound manipulation. Our method achieves state-of-the-art separation performance with data-efficient training while maintaining superior semantic consistency with queries in complex auditory scenes.
Rethinking Repetition Problems of LLMs in Code Generation
May 15, 2025Abstract:With the advent of neural language models, the performance of code generation has been significantly boosted. However, the problem of repetitions during the generation process continues to linger. Previous work has primarily focused on content repetition, which is merely a fraction of the broader repetition problem in code generation. A more prevalent and challenging problem is structural repetition. In structural repetition, the repeated code appears in various patterns but possesses a fixed structure, which can be inherently reflected in grammar. In this paper, we formally define structural repetition and propose an efficient decoding approach called RPG, which stands for Repetition Penalization based on Grammar, to alleviate the repetition problems in code generation for LLMs. Specifically, RPG first leverages grammar rules to identify repetition problems during code generation, and then strategically decays the likelihood of critical tokens that contribute to repetitions, thereby mitigating them in code generation. To facilitate this study, we construct a new dataset CodeRepetEval to comprehensively evaluate approaches for mitigating the repetition problems in code generation. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that RPG substantially outperforms the best-performing baselines on CodeRepetEval dataset as well as HumanEval and MBPP benchmarks, effectively reducing repetitions and enhancing the quality of generated code.
Generative Retrieval and Alignment Model: A New Paradigm for E-commerce Retrieval
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Traditional sparse and dense retrieval methods struggle to leverage general world knowledge and often fail to capture the nuanced features of queries and products. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), industrial search systems have started to employ LLMs to generate identifiers for product retrieval. Commonly used identifiers include (1) static/semantic IDs and (2) product term sets. The first approach requires creating a product ID system from scratch, missing out on the world knowledge embedded within LLMs. While the second approach leverages this general knowledge, the significant difference in word distribution between queries and products means that product-based identifiers often do not align well with user search queries, leading to missed product recalls. Furthermore, when queries contain numerous attributes, these algorithms generate a large number of identifiers, making it difficult to assess their quality, which results in low overall recall efficiency. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel e-commerce retrieval paradigm: the Generative Retrieval and Alignment Model (GRAM). GRAM employs joint training on text information from both queries and products to generate shared text identifier codes, effectively bridging the gap between queries and products. This approach not only enhances the connection between queries and products but also improves inference efficiency. The model uses a co-alignment strategy to generate codes optimized for maximizing retrieval efficiency. Additionally, it introduces a query-product scoring mechanism to compare product values across different codes, further boosting retrieval efficiency. Extensive offline and online A/B testing demonstrates that GRAM significantly outperforms traditional models and the latest generative retrieval models, confirming its effectiveness and practicality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge