Rudra Dutta
Collection: Datasets from AFAR Challenge
May 11, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive real-world and Digital Twin (DT) dataset collected as part of the Find A Rover (AFAR) Challenge, organized by the NSF Aerial Experimentation and Research Platform for Advanced Wireless (AERPAW) testbed and hosted at the Lake Wheeler Field in Raleigh, North Carolina. The AFAR Challenge was a competition involving five finalist university teams, focused on promoting innovation in UAV-assisted radio frequency (RF) source localization. Participating teams were tasked with designing UAV flight trajectories and localization algorithms to detect the position of a hidden unmanned ground vehicle (UGV), also referred to as a rover, emitting wireless probe signals generated by GNU Radio. The competition was structured to evaluate solutions in a DT environment first, followed by deployment and testing in AERPAW's outdoor wireless testbed. For each team, the UGV was placed at three different positions, resulting in a total of 30 datasets, 15 collected in a DT simulation environment and 15 in a physical outdoor testbed. Each dataset contains time-synchronized measurements of received signal strength (RSS), received signal quality (RSQ), GPS coordinates, UAV velocity, and UAV orientation (roll, pitch, and yaw). Data is organized into structured folders by team, environment (DT and real-world), and UGV location. The dataset supports research in UAV-assisted RF source localization, air-to-ground (A2G) wireless propagation modeling, trajectory optimization, signal prediction, autonomous navigation, and DT validation. With approximately 300k time-synchronized samples collected from real-world experiments, the dataset provides a substantial foundation for training and evaluating deep learning (DL) models. Overall, the AFAR dataset serves as a valuable resource for advancing robust, real-world solutions in UAV-enabled wireless communications and sensing systems.
Digital Twins for Supporting AI Research with Autonomous Vehicle Networks
Apr 01, 2024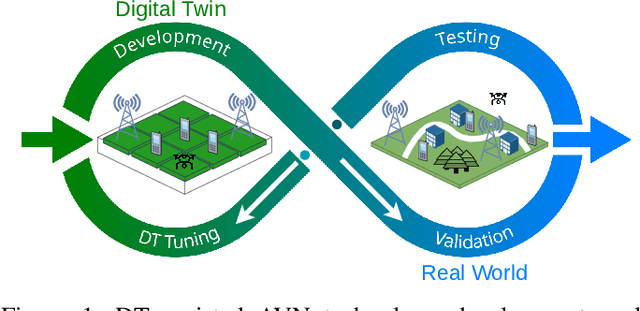
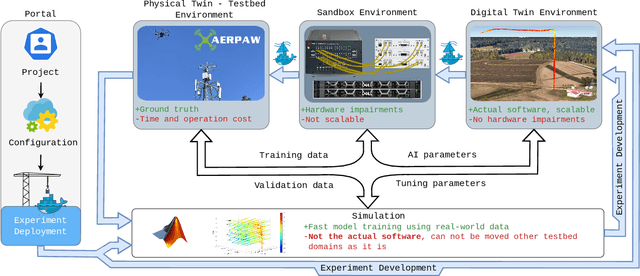
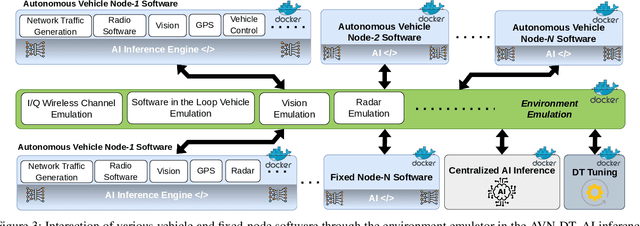
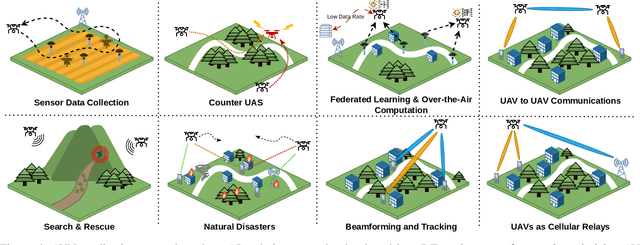
Abstract:Digital twins (DTs), which are virtual environments that simulate, predict, and optimize the performance of their physical counterparts, are envisioned to be essential technologies for advancing next-generation wireless networks. While DTs have been studied extensively for wireless networks, their use in conjunction with autonomous vehicles with programmable mobility remains relatively under-explored. In this paper, we study DTs used as a development environment to design, deploy, and test artificial intelligence (AI) techniques that use real-time observations, e.g. radio key performance indicators, for vehicle trajectory and network optimization decisions in an autonomous vehicle networks (AVN). We first compare and contrast the use of simulation, digital twin (software in the loop (SITL)), sandbox (hardware-in-the-loop (HITL)), and physical testbed environments for their suitability in developing and testing AI algorithms for AVNs. We then review various representative use cases of DTs for AVN scenarios. Finally, we provide an example from the NSF AERPAW platform where a DT is used to develop and test AI-aided solutions for autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles for localizing a signal source based solely on link quality measurements. Our results in the physical testbed show that SITL DTs, when supplemented with data from real-world (RW) measurements and simulations, can serve as an ideal environment for developing and testing innovative AI solutions for AVNs.
SDR-Based 5G NR C-Band I/Q Monitoring and Surveillance in Urban Area Using a Helikite
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we report experimental results in collectting and processing 5G NR I/Q samples in the 3.7~GHz C-band by using software-defined radio (SDR)-mounted helikite. We use MATLAB's 5G toolbox to post-process the collected data, to obtain the synchronization signal block (SSB) from the I/Q samples and then go through the cell search, synchronization procedures, and reference signal received power (RSRP) and reference signal received quality (RSRQ) calculation. We plot these performance metrics for various physical cell identities as a function of the helikite's altitude. Furthermore, building on our experience with the collected and post-processed data, we discuss potential vulnerabilities of 5G NR systems to surveillance, jamming attacks, and post quantum era attacks.
LTE I/Q Data Set for UAV Propagation Modeling, Communication, and Navigation Research
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:Recently, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have been receiving significant attention due to their wide range of potential application areas. To support UAV use cases with beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) and autonomous flights, cellular networks can serve as ground connectivity points, and they can provide remote control and payload communication for UAV links. However, there are limited data sets to study the coverage of cellular technologies for UAV flights at different altitudes and develop machine learning (ML) techniques for improving UAV communication and navigation. In this article, we present raw LTE I/Q sample data sets from physical field experiments in the Lake Wheeler farm area of the NSF AERPAW experimentation platform. We fly a UAV that carries a software-defined radio (SDR) at altitudes ranging from 30~m to 110~m and collect raw I/Q samples from an SDR-based LTE base station on the ground operating at 3.51 GHz. We adopt a standard metadata format for reproducing the results from the collected data sets. The post-processing of raw I/Q samples using MATLAB's 4G LTE toolbox is described and various representative results are provided. In the end, we discuss the possible ways that our provided data set, post-processing sample code, and sample experiment code for collecting I/Q measurements and vehicle control can be used by other ML researchers in the future.
AERIQ: SDR-Based LTE I/Q Measurement and Analysis Framework for Air-to-Ground Propagation Modeling
Oct 14, 2022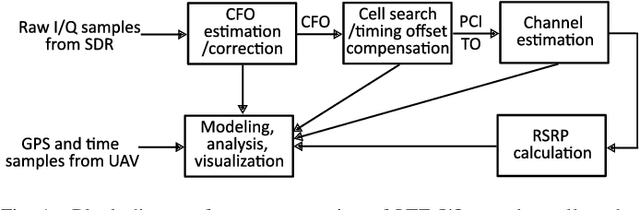
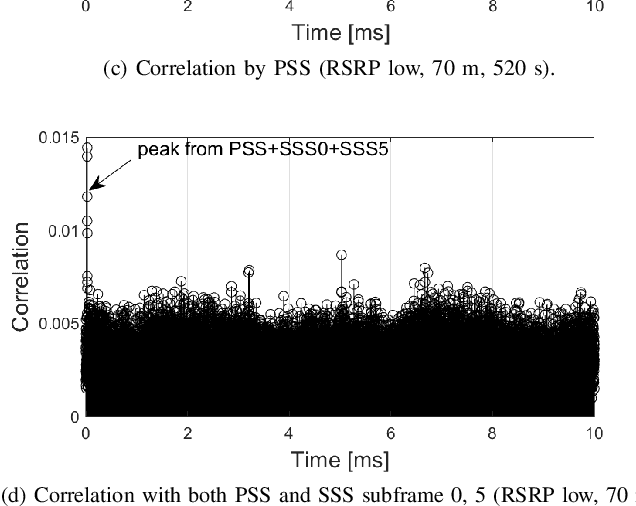
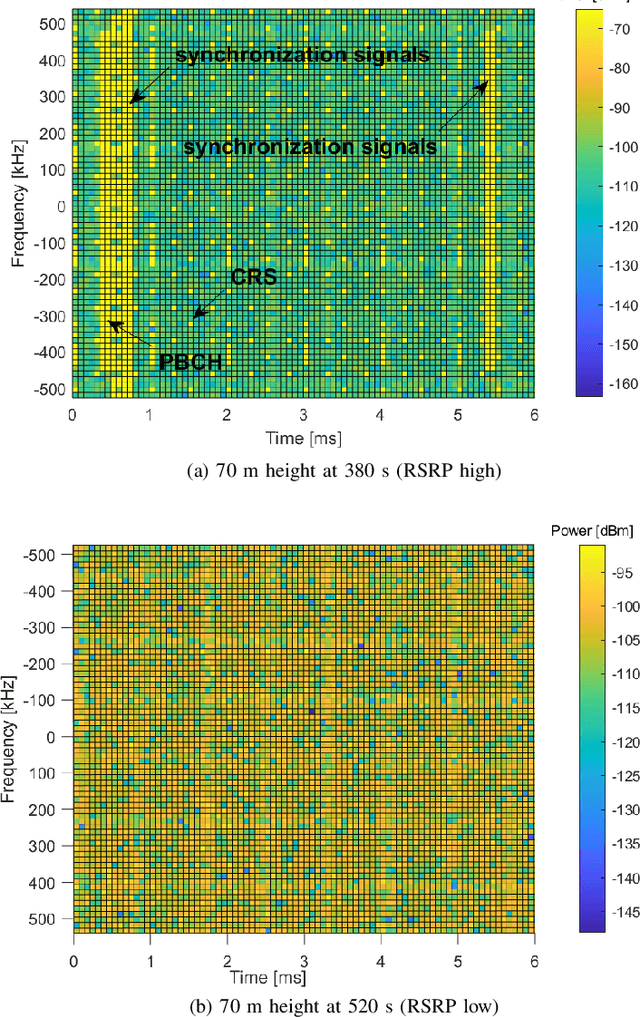
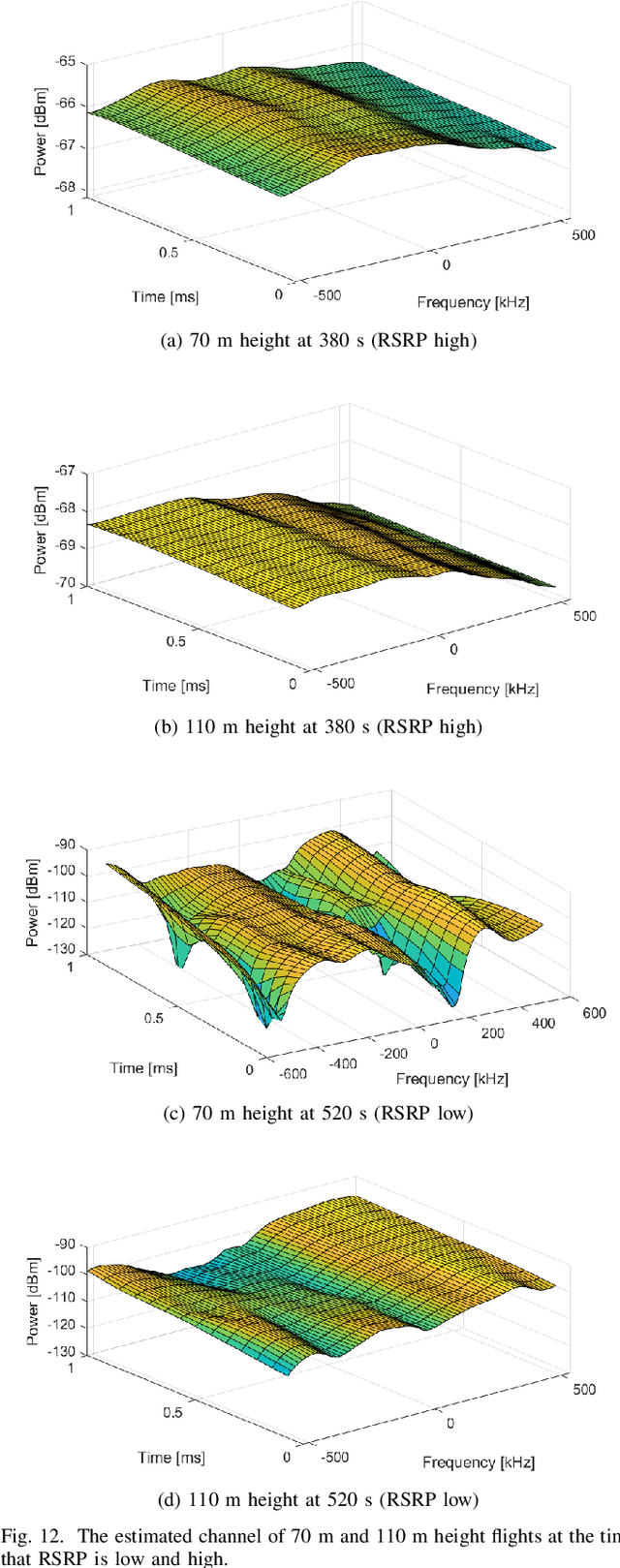
Abstract:Radio dynamic zones (RDZs) are areas or volumes with automatic spectrum management mechanisms that control electromagnetic energy entering, escaping, or occupying the zone. In order to have real-time volumetric spectrum awareness in an RDZ, it is critical to understand the propagation characteristics throughout that RDZ, such as time, frequency, and spatial correlation for various communications scenarios and configurations. This requires wireless measurement campaigns that can be carried out flexibly and are repeatable for different experiment configurations, parameters, and transmitter/receiver locations. Such measurements should also provide raw data from which various key parameters of interest (KPIs) can be conveniently extracted for further analysis. In this paper, we propose AERIQ: a software-defined radio (SDR) based I/Q measurement and analysis framework that is flexible, repeatable, and provides raw I/Q samples for post-processing the data to extract various KPIs. Using SDRs, we collect I/Q data with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) flying at various different altitudes in an RDZ-like outdoor environment, from a 4G LTE eNB that we configure to operate at 3.51 GHz. Using the raw I/Q samples, and using Matlab's LTE Toolbox, we provide a step-by-step description for the following post-processing stages of an aerial receiver: frequency offset estimation/correction, synchronization, cell search, channel estimation, and reference signal received power (RSRP). We provide various representative results for each step, such as RSRP measurements and corresponding analytical approximation at different UAV altitudes, and coherence bandwidth of the channel at different UAV altitudes and link distances. The collected raw data as well as the software developed for obtaining and post-processing such data are provided publicly for potential use by other researchers.
National Radio Dynamic Zone Concept with Autonomous Aerial and Ground Spectrum Sensors
Mar 17, 2022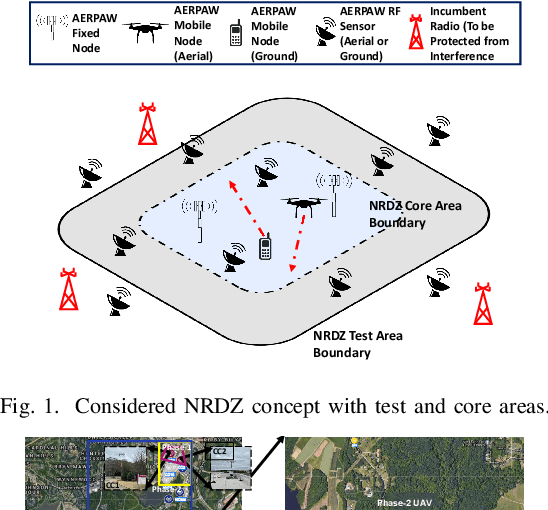
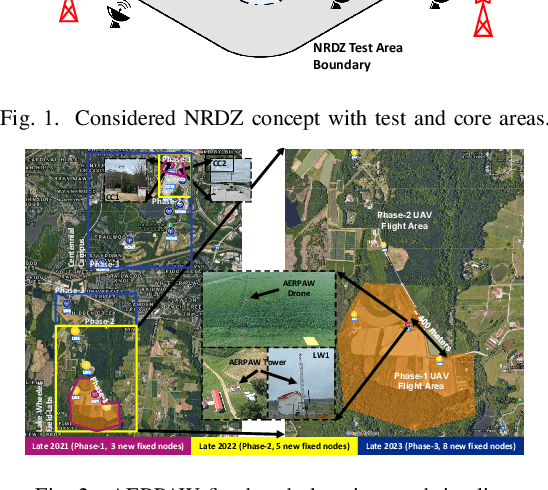
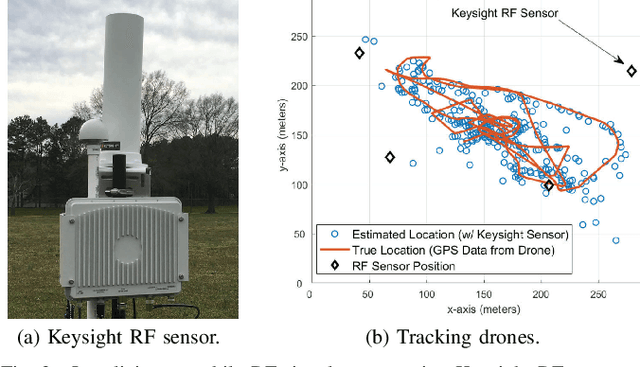

Abstract:National radio dynamic zone (NRDZs) are intended to be geographically bounded areas within which controlled experiments can be carried out while protecting the nearby licensed users of the spectrum. An NRDZ will facilitate research and development of new spectrum technologies, waveforms, and protocols, in typical outdoor operational environments of such technologies. In this paper, we introduce and describe an NRDZ concept that relies on a combination of autonomous aerial and ground sensor nodes for spectrum sensing and radio environment monitoring (REM). We elaborate on key characteristics and features of an NRDZ to enable advanced wireless experimentation while also coexisting with licensed users. Some preliminary results based on simulation and experimental evaluations are also provided on out-of-zone leakage monitoring and real-time REMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge