Özgür Özdemir
Impact of Altitude, Bandwidth, and NLOS Bias on TDOA-Based 3D UAV Localization: Experimental Results and CRLB Analysis
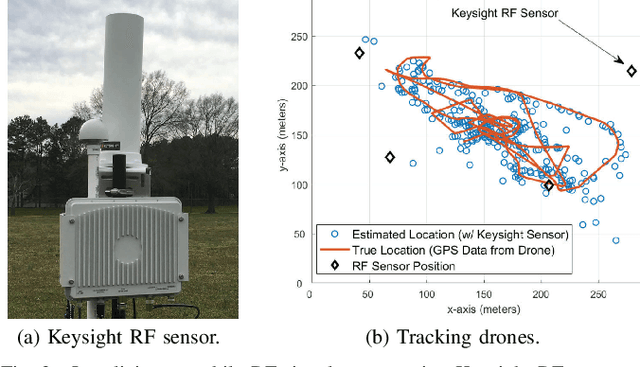
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) localization using time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurements under mixed line-of-sight (LOS) and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) conditions. A 3D TDOA Cram\'er-Rao lower bound (CRLB) model is developed accounting for varying altitudes and signal bandwidths. The model is compared to five real-world UAV flight experiments conducted at different altitudes (40 m, 70 m, 100 m) and bandwidths (1.25 MHz, 2.5 MHz, 5 MHz) using Keysight N6841A radio frequency (RF) sensors of the NSF AERPAW platform. Results show that altitude, bandwidth, and NLOS obstructions significantly impact localization accuracy. Higher bandwidths enhance signal time resolution, while increased altitudes mitigate multipath and NLOS biases, both contributing to improved performance. However, hovering close to RF sensors degrades accuracy due to antenna pattern misalignment and geometric dilution of precision. These findings emphasize the inadequacy of traditional LOS-based models in NLOS environments and highlight the importance of adaptive approaches for accurate localization in challenging scenarios.
Digital Twins for Supporting AI Research with Autonomous Vehicle Networks
Apr 01, 2024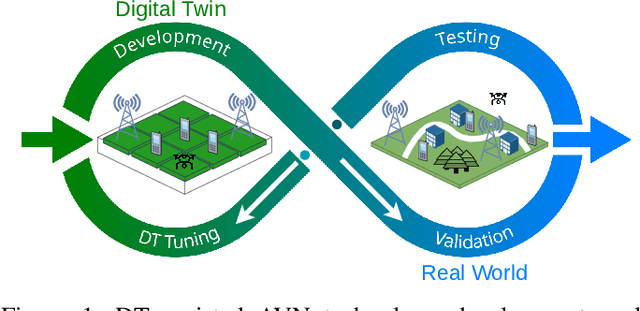
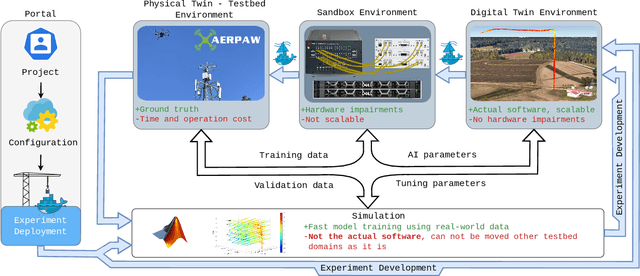
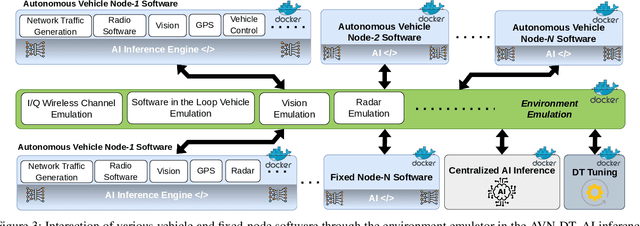
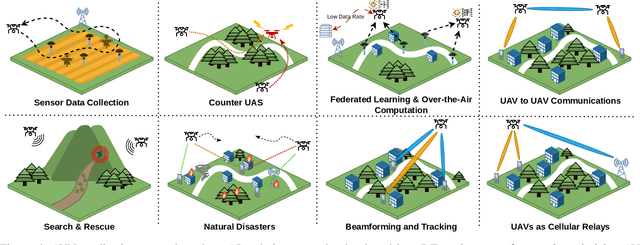
Abstract:Digital twins (DTs), which are virtual environments that simulate, predict, and optimize the performance of their physical counterparts, are envisioned to be essential technologies for advancing next-generation wireless networks. While DTs have been studied extensively for wireless networks, their use in conjunction with autonomous vehicles with programmable mobility remains relatively under-explored. In this paper, we study DTs used as a development environment to design, deploy, and test artificial intelligence (AI) techniques that use real-time observations, e.g. radio key performance indicators, for vehicle trajectory and network optimization decisions in an autonomous vehicle networks (AVN). We first compare and contrast the use of simulation, digital twin (software in the loop (SITL)), sandbox (hardware-in-the-loop (HITL)), and physical testbed environments for their suitability in developing and testing AI algorithms for AVNs. We then review various representative use cases of DTs for AVN scenarios. Finally, we provide an example from the NSF AERPAW platform where a DT is used to develop and test AI-aided solutions for autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles for localizing a signal source based solely on link quality measurements. Our results in the physical testbed show that SITL DTs, when supplemented with data from real-world (RW) measurements and simulations, can serve as an ideal environment for developing and testing innovative AI solutions for AVNs.
National Radio Dynamic Zone Concept with Autonomous Aerial and Ground Spectrum Sensors
Mar 17, 2022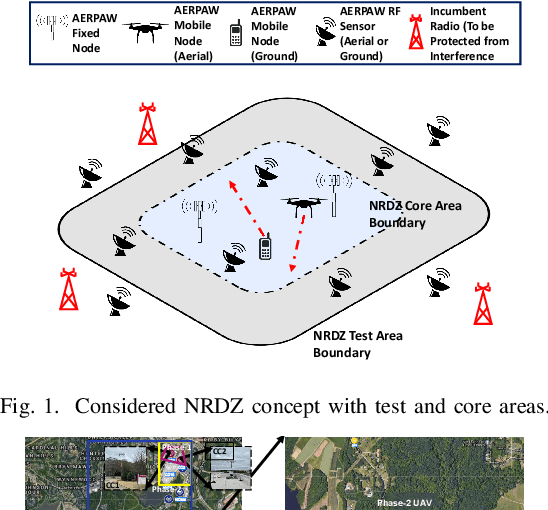
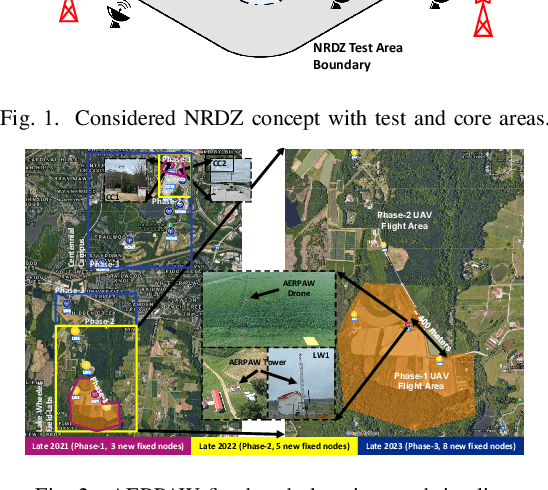

Abstract:National radio dynamic zone (NRDZs) are intended to be geographically bounded areas within which controlled experiments can be carried out while protecting the nearby licensed users of the spectrum. An NRDZ will facilitate research and development of new spectrum technologies, waveforms, and protocols, in typical outdoor operational environments of such technologies. In this paper, we introduce and describe an NRDZ concept that relies on a combination of autonomous aerial and ground sensor nodes for spectrum sensing and radio environment monitoring (REM). We elaborate on key characteristics and features of an NRDZ to enable advanced wireless experimentation while also coexisting with licensed users. Some preliminary results based on simulation and experimental evaluations are also provided on out-of-zone leakage monitoring and real-time REMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge