Cheng Wan
Celine
Anatomically Guided Latent Diffusion for Brain MRI Progression Modeling
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Accurately modeling longitudinal brain MRI progression is crucial for understanding neurodegenerative diseases and predicting individualized structural changes. Existing state-of-the-art approaches, such as Brain Latent Progression (BrLP), often use multi-stage training pipelines with auxiliary conditioning modules but suffer from architectural complexity, suboptimal use of conditional clinical covariates, and limited guarantees of anatomical consistency. We propose Anatomically Guided Latent Diffusion Model (AG-LDM), a segmentation-guided framework that enforces anatomically consistent progression while substantially simplifying the training pipeline. AG-LDM conditions latent diffusion by directly fusing baseline anatomy, noisy follow-up states, and clinical covariates at the input level, a strategy that avoids auxiliary control networks by learning a unified, end-to-end model that represents both anatomy and progression. A lightweight 3D tissue segmentation model (WarpSeg) provides explicit anatomical supervision during both autoencoder fine-tuning and diffusion model training, ensuring consistent brain tissue boundaries and morphometric fidelity. Experiments on 31,713 ADNI longitudinal pairs and zero-shot evaluation on OASIS-3 demonstrate that AG-LDM matches or surpasses more complex diffusion models, achieving state-of-the-art image quality and 15-20\% reduction in volumetric errors in generated images. AG-LDM also exhibits markedly stronger utilization of temporal and clinical covariates (up to 31.5x higher sensitivity than BrLP) and generates biologically plausible counterfactual trajectories, accurately capturing hallmarks of Alzheimer's progression such as limbic atrophy and ventricular expansion. These results highlight AG-LDM as an efficient, anatomically grounded framework for reliable brain MRI progression modeling.
Synthetic Vasculature and Pathology Enhance Vision-Language Model Reasoning
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) offer a promising path toward interpretable medical diagnosis by allowing users to ask about clinical explanations alongside predictions and across different modalities. However, training VLMs for detailed reasoning requires large-scale image-text datasets. In many specialized domains, for example in reading Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) images, such precise text with grounded description of pathologies is scarce or even non-existent. To overcome this bottleneck, we introduce Synthetic Vasculature Reasoning (SVR), a framework that controllably synthesizes images and corresponding text, specifically: realistic retinal vasculature with Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) features: capillary dropout, microaneurysms, neovascularization, and tortuosity, while automatically generating granular reasoning texts. Based on this we curate OCTA-100K-SVR, an OCTA image-reasoning dataset with 100,000 pairs. Our experiments show that a general-purpose VLM (Qwen3-VL-8b) trained on the dataset achieves a zero-shot balanced classification accuracy of 89.67% on real OCTA images, outperforming supervised baselines. Through human expert evaluation we also demonstrate that it significantly enhances explanation quality and pathology localization on clinical data.
Anatomical Similarity as a New Metric to Evaluate Brain Generative Models
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Generative models enhance neuroimaging through data augmentation, quality improvement, and rare condition studies. Despite advances in realistic synthetic MRIs, evaluations focus on texture and perception, lacking sensitivity to crucial anatomical fidelity. This study proposes a new metric, called WASABI (Wasserstein-Based Anatomical Brain Index), to assess the anatomical realism of synthetic brain MRIs. WASABI leverages \textit{SynthSeg}, a deep learning-based brain parcellation tool, to derive volumetric measures of brain regions in each MRI and uses the multivariate Wasserstein distance to compare distributions between real and synthetic anatomies. Based on controlled experiments on two real datasets and synthetic MRIs from five generative models, WASABI demonstrates higher sensitivity in quantifying anatomical discrepancies compared to traditional image-level metrics, even when synthetic images achieve near-perfect visual quality. Our findings advocate for shifting the evaluation paradigm beyond visual inspection and conventional metrics, emphasizing anatomical fidelity as a crucial benchmark for clinically meaningful brain MRI synthesis. Our code is available at https://github.com/BahramJafrasteh/wasabi-mri.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Single-Image Efficient Super-Resolution (ESR). The challenge aimed to advance the development of deep models that optimize key computational metrics, i.e., runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while achieving a PSNR of at least 26.90 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_valid}$ dataset and 26.99 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_test}$ dataset. A robust participation saw \textbf{244} registered entrants, with \textbf{43} teams submitting valid entries. This report meticulously analyzes these methods and results, emphasizing groundbreaking advancements in state-of-the-art single-image ESR techniques. The analysis highlights innovative approaches and establishes benchmarks for future research in the field.
Scaling Laws of Graph Neural Networks for Atomistic Materials Modeling
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Atomistic materials modeling is a critical task with wide-ranging applications, from drug discovery to materials science, where accurate predictions of the target material property can lead to significant advancements in scientific discovery. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) represent the state-of-the-art approach for modeling atomistic material data thanks to their capacity to capture complex relational structures. While machine learning performance has historically improved with larger models and datasets, GNNs for atomistic materials modeling remain relatively small compared to large language models (LLMs), which leverage billions of parameters and terabyte-scale datasets to achieve remarkable performance in their respective domains. To address this gap, we explore the scaling limits of GNNs for atomistic materials modeling by developing a foundational model with billions of parameters, trained on extensive datasets in terabyte-scale. Our approach incorporates techniques from LLM libraries to efficiently manage large-scale data and models, enabling both effective training and deployment of these large-scale GNN models. This work addresses three fundamental questions in scaling GNNs: the potential for scaling GNN model architectures, the effect of dataset size on model accuracy, and the applicability of LLM-inspired techniques to GNN architectures. Specifically, the outcomes of this study include (1) insights into the scaling laws for GNNs, highlighting the relationship between model size, dataset volume, and accuracy, (2) a foundational GNN model optimized for atomistic materials modeling, and (3) a GNN codebase enhanced with advanced LLM-based training techniques. Our findings lay the groundwork for large-scale GNNs with billions of parameters and terabyte-scale datasets, establishing a scalable pathway for future advancements in atomistic materials modeling.
Improved learning rates in multi-unit uniform price auctions
Jan 17, 2025

Abstract:Motivated by the strategic participation of electricity producers in electricity day-ahead market, we study the problem of online learning in repeated multi-unit uniform price auctions focusing on the adversarial opposing bid setting. The main contribution of this paper is the introduction of a new modeling of the bid space. Indeed, we prove that a learning algorithm leveraging the structure of this problem achieves a regret of $\tilde{O}(K^{4/3}T^{2/3})$ under bandit feedback, improving over the bound of $\tilde{O}(K^{7/4}T^{3/4})$ previously obtained in the literature. This improved regret rate is tight up to logarithmic terms. Inspired by electricity reserve markets, we further introduce a different feedback model under which all winning bids are revealed. This feedback interpolates between the full-information and bandit scenarios depending on the auctions' results. We prove that, under this feedback, the algorithm that we propose achieves regret $\tilde{O}(K^{5/2}\sqrt{T})$.
MixGCN: Scalable GCN Training by Mixture of Parallelism and Mixture of Accelerators
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Graph convolutional networks (GCNs) have demonstrated superiority in graph-based learning tasks. However, training GCNs on full graphs is particularly challenging, due to the following two challenges: (1) the associated feature tensors can easily explode the memory and block the communication bandwidth of modern accelerators, and (2) the computation workflow in training GCNs alternates between sparse and dense matrix operations, complicating the efficient utilization of computational resources. Existing solutions for scalable distributed full-graph GCN training mostly adopt partition parallelism, which is unsatisfactory as they only partially address the first challenge while incurring scaled-out communication volume. To this end, we propose MixGCN aiming to simultaneously address both the aforementioned challenges towards GCN training. To tackle the first challenge, MixGCN integrates mixture of parallelism. Both theoretical and empirical analysis verify its constant communication volumes and enhanced balanced workload; For handling the second challenge, we consider mixture of accelerators (i.e., sparse and dense accelerators) with a dedicated accelerator for GCN training and a fine-grain pipeline. Extensive experiments show that MixGCN achieves boosted training efficiency and scalability.
A Multi-scenario Attention-based Generative Model for Personalized Blood Pressure Time Series Forecasting
Sep 07, 2024Abstract:Continuous blood pressure (BP) monitoring is essential for timely diagnosis and intervention in critical care settings. However, BP varies significantly across individuals, this inter-patient variability motivates the development of personalized models tailored to each patient's physiology. In this work, we propose a personalized BP forecasting model mainly using electrocardiogram (ECG) and photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals. This time-series model incorporates 2D representation learning to capture complex physiological relationships. Experiments are conducted on datasets collected from three diverse scenarios with BP measurements from 60 subjects total. Results demonstrate that the model achieves accurate and robust BP forecasts across scenarios within the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) standard criteria. This reliable early detection of abnormal fluctuations in BP is crucial for at-risk patients undergoing surgery or intensive care. The proposed model provides a valuable addition for continuous BP tracking to reduce mortality and improve prognosis.
MG-Verilog: Multi-grained Dataset Towards Enhanced LLM-assisted Verilog Generation
Jul 02, 2024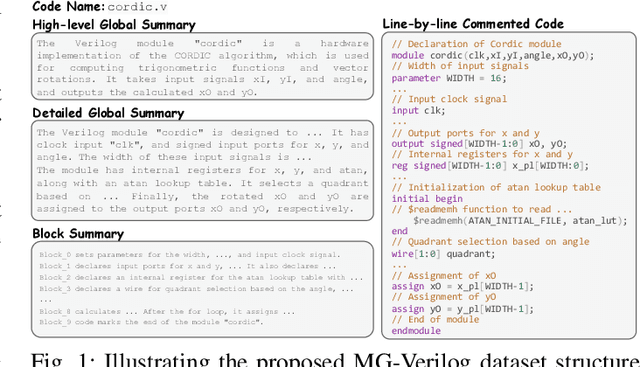
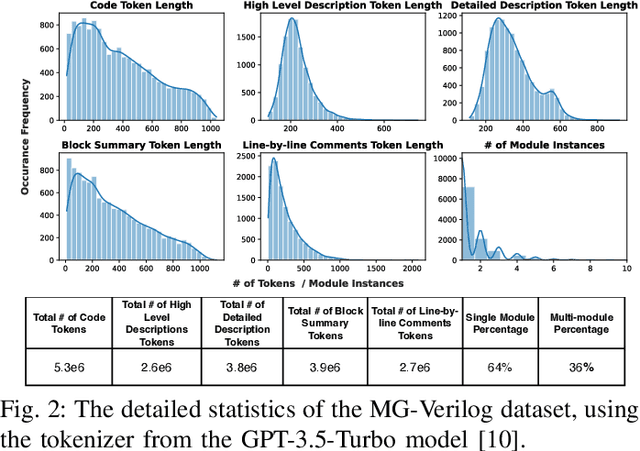
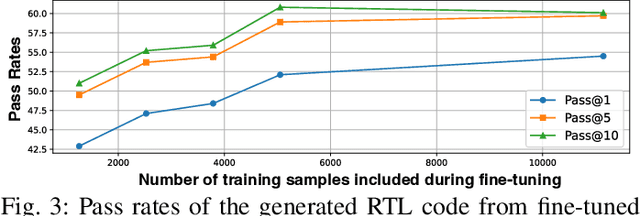
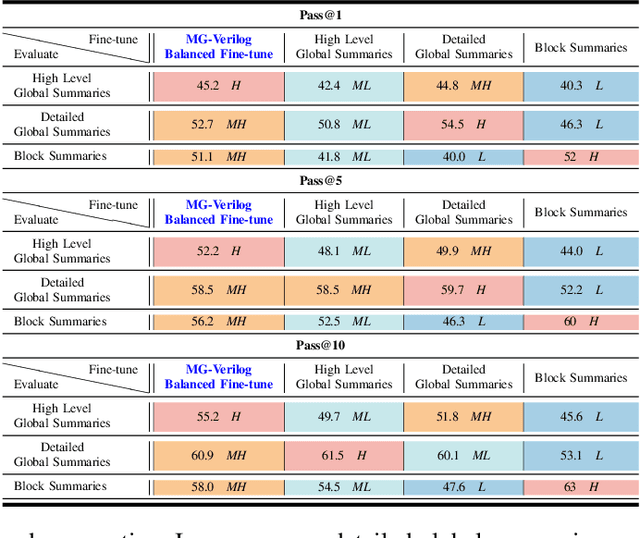
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently shown promise in streamlining hardware design processes by encapsulating vast amounts of domain-specific data. In addition, they allow users to interact with the design processes through natural language instructions, thus making hardware design more accessible to developers. However, effectively leveraging LLMs in hardware design necessitates providing domain-specific data during inference (e.g., through in-context learning), fine-tuning, or pre-training. Unfortunately, existing publicly available hardware datasets are often limited in size, complexity, or detail, which hinders the effectiveness of LLMs in hardware design tasks. To address this issue, we first propose a set of criteria for creating high-quality hardware datasets that can effectively enhance LLM-assisted hardware design. Based on these criteria, we propose a Multi-Grained-Verilog (MG-Verilog) dataset, which encompasses descriptions at various levels of detail and corresponding code samples. To benefit the broader hardware design community, we have developed an open-source infrastructure that facilitates easy access, integration, and extension of the dataset to meet specific project needs. Furthermore, to fully exploit the potential of the MG-Verilog dataset, which varies in complexity and detail, we introduce a balanced fine-tuning scheme. This scheme serves as a unique use case to leverage the diverse levels of detail provided by the dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed dataset and fine-tuning scheme consistently improve the performance of LLMs in hardware design tasks.
RITA: A Real-time Interactive Talking Avatars Framework
Jun 18, 2024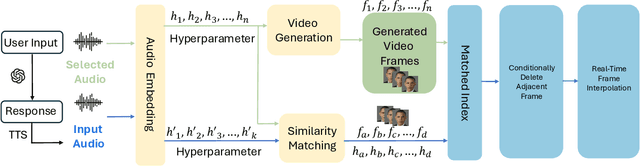
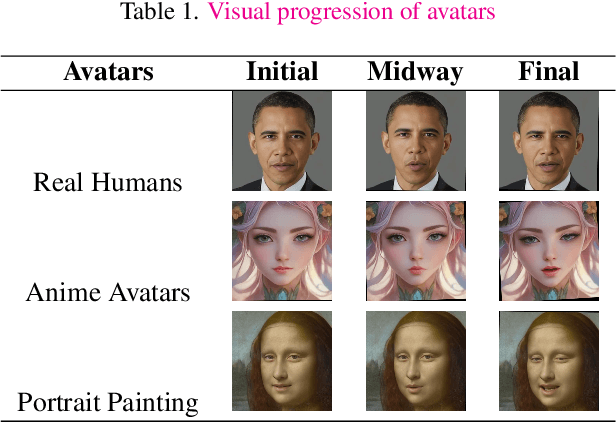

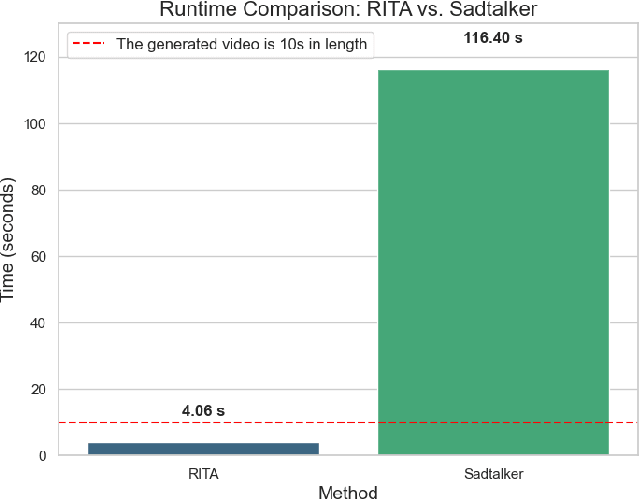
Abstract:RITA presents a high-quality real-time interactive framework built upon generative models, designed with practical applications in mind. Our framework enables the transformation of user-uploaded photos into digital avatars that can engage in real-time dialogue interactions. By leveraging the latest advancements in generative modeling, we have developed a versatile platform that not only enhances the user experience through dynamic conversational avatars but also opens new avenues for applications in virtual reality, online education, and interactive gaming. This work showcases the potential of integrating computer vision and natural language processing technologies to create immersive and interactive digital personas, pushing the boundaries of how we interact with digital content.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge