Wen Li
From Single Scan to Sequential Consistency: A New Paradigm for LIDAR Relocalization
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:LiDAR relocalization aims to estimate the global 6-DoF pose of a sensor in the environment. However, existing regression-based approaches are prone to dynamic or ambiguous scenarios, as they either solely rely on single-frame inference or neglect the spatio-temporal consistency across scans. In this paper, we propose TempLoc, a new LiDAR relocalization framework that enhances the robustness of localization by effectively modeling sequential consistency. Specifically, a Global Coordinate Estimation module is first introduced to predict point-wise global coordinates and associated uncertainties for each LiDAR scan. A Prior Coordinate Generation module is then presented to estimate inter-frame point correspondences by the attention mechanism. Lastly, an Uncertainty-Guided Coordinate Fusion module is deployed to integrate both predictions of point correspondence in an end-to-end fashion, yielding a more temporally consistent and accurate global 6-DoF pose. Experimental results on the NCLT and Oxford Robot-Car benchmarks show that our TempLoc outperforms stateof-the-art methods by a large margin, demonstrating the effectiveness of temporal-aware correspondence modeling in LiDAR relocalization. Our code will be released soon.
Let Samples Speak: Mitigating Spurious Correlation by Exploiting the Clusterness of Samples
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models are known to often learn features that spuriously correlate with the class label during training but are irrelevant to the prediction task. Existing methods typically address this issue by annotating potential spurious attributes, or filtering spurious features based on some empirical assumptions (e.g., simplicity of bias). However, these methods may yield unsatisfactory performance due to the intricate and elusive nature of spurious correlations in real-world data. In this paper, we propose a data-oriented approach to mitigate the spurious correlation in deep learning models. We observe that samples that are influenced by spurious features tend to exhibit a dispersed distribution in the learned feature space. This allows us to identify the presence of spurious features. Subsequently, we obtain a bias-invariant representation by neutralizing the spurious features based on a simple grouping strategy. Then, we learn a feature transformation to eliminate the spurious features by aligning with this bias-invariant representation. Finally, we update the classifier by incorporating the learned feature transformation and obtain an unbiased model. By integrating the aforementioned identifying, neutralizing, eliminating and updating procedures, we build an effective pipeline for mitigating spurious correlation. Experiments on image and NLP debiasing benchmarks show an improvement in worst group accuracy of more than 20% compared to standard empirical risk minimization (ERM). Codes and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/davelee-uestc/nsf_debiasing .
The Devil is in Attention Sharing: Improving Complex Non-rigid Image Editing Faithfulness via Attention Synergy
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Training-free image editing with large diffusion models has become practical, yet faithfully performing complex non-rigid edits (e.g., pose or shape changes) remains highly challenging. We identify a key underlying cause: attention collapse in existing attention sharing mechanisms, where either positional embeddings or semantic features dominate visual content retrieval, leading to over-editing or under-editing. To address this issue, we introduce SynPS, a method that Synergistically leverages Positional embeddings and Semantic information for faithful non-rigid image editing. We first propose an editing measurement that quantifies the required editing magnitude at each denoising step. Based on this measurement, we design an attention synergy pipeline that dynamically modulates the influence of positional embeddings, enabling SynPS to balance semantic modifications and fidelity preservation. By adaptively integrating positional and semantic cues, SynPS effectively avoids both over- and under-editing. Extensive experiments on public and newly curated benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance and faithfulness of our approach.
V2VLoc: Robust GNSS-Free Collaborative Perception via LiDAR Localization
Nov 18, 2025


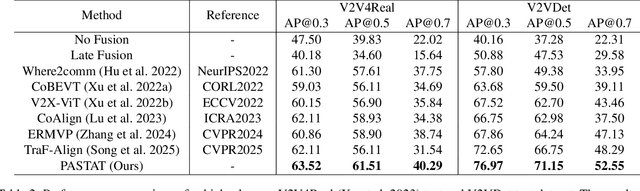
Abstract:Multi-agents rely on accurate poses to share and align observations, enabling a collaborative perception of the environment. However, traditional GNSS-based localization often fails in GNSS-denied environments, making consistent feature alignment difficult in collaboration. To tackle this challenge, we propose a robust GNSS-free collaborative perception framework based on LiDAR localization. Specifically, we propose a lightweight Pose Generator with Confidence (PGC) to estimate compact pose and confidence representations. To alleviate the effects of localization errors, we further develop the Pose-Aware Spatio-Temporal Alignment Transformer (PASTAT), which performs confidence-aware spatial alignment while capturing essential temporal context. Additionally, we present a new simulation dataset, V2VLoc, which can be adapted for both LiDAR localization and collaborative detection tasks. V2VLoc comprises three subsets: Town1Loc, Town4Loc, and V2VDet. Town1Loc and Town4Loc offer multi-traversal sequences for training in localization tasks, whereas V2VDet is specifically intended for the collaborative detection task. Extensive experiments conducted on the V2VLoc dataset demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance under GNSS-denied conditions. We further conduct extended experiments on the real-world V2V4Real dataset to validate the effectiveness and generalizability of PASTAT.
Unsupervised Robust Domain Adaptation: Paradigm, Theory and Algorithm
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) aims to transfer knowledge from a label-rich source domain to an unlabeled target domain by addressing domain shifts. Most UDA approaches emphasize transfer ability, but often overlook robustness against adversarial attacks. Although vanilla adversarial training (VAT) improves the robustness of deep neural networks, it has little effect on UDA. This paper focuses on answering three key questions: 1) Why does VAT, known for its defensive effectiveness, fail in the UDA paradigm? 2) What is the generalization bound theory under attacks and how does it evolve from classical UDA theory? 3) How can we implement a robustification training procedure without complex modifications? Specifically, we explore and reveal the inherent entanglement challenge in general UDA+VAT paradigm, and propose an unsupervised robust domain adaptation (URDA) paradigm. We further derive the generalization bound theory of the URDA paradigm so that it can resist adversarial noise and domain shift. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time to establish the URDA paradigm and theory. We further introduce a simple, novel yet effective URDA algorithm called Disentangled Adversarial Robustness Training (DART), a two-step training procedure that ensures both transferability and robustness. DART first pre-trains an arbitrary UDA model, and then applies an instantaneous robustification post-training step via disentangled distillation.Experiments on four benchmark datasets with/without attacks show that DART effectively enhances robustness while maintaining domain adaptability, and validate the URDA paradigm and theory.
FreDN: Spectral Disentanglement for Time Series Forecasting via Learnable Frequency Decomposition
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting is essential in a wide range of real world applications. Recently, frequency-domain methods have attracted increasing interest for their ability to capture global dependencies. However, when applied to non-stationary time series, these methods encounter the $\textit{spectral entanglement}$ and the computational burden of complex-valued learning. The $\textit{spectral entanglement}$ refers to the overlap of trends, periodicities, and noise across the spectrum due to $\textit{spectral leakage}$ and the presence of non-stationarity. However, existing decompositions are not suited to resolving spectral entanglement. To address this, we propose the Frequency Decomposition Network (FreDN), which introduces a learnable Frequency Disentangler module to separate trend and periodic components directly in the frequency domain. Furthermore, we propose a theoretically supported ReIm Block to reduce the complexity of complex-valued operations while maintaining performance. We also re-examine the frequency-domain loss function and provide new theoretical insights into its effectiveness. Extensive experiments on seven long-term forecasting benchmarks demonstrate that FreDN outperforms state-of-the-art methods by up to 10\%. Furthermore, compared with standard complex-valued architectures, our real-imaginary shared-parameter design reduces the parameter count and computational cost by at least 50\%.
ToolExpander: Extending the Frontiers of Tool-Using Reinforcement Learning to Weak LLMs
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Training Large Language Models (LLMs) with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) encounters a significant challenge: models often fail to produce accurate responses, particularly in small-scale architectures. This limitation not only diminishes performance improvements and undermines the potential of GRPO but also frequently leads to mid-training collapse, adversely affecting stability and final efficacy. To address these issues, we propose ToolExpander, a novel framework that advances tool-oriented reinforcement learning for resource-constrained LLMs through two key innovations:(1) Dynamic Multi-Round Hard Sampling, which dynamically substitutes challenging samples(those without correct outputs over 10 rollouts) with high-quality few-shot demonstrations during training, coupled with an exponential learning rate decay strategy to mitigate oscillations;(2) Self-Exemplifying Thinking, an enhanced GRPO framework that eliminates KL divergence and incorporates adjusted clipping coefficients, encouraging models to autonomously generate and analyze few-shot examples via a minimal additional reward (0.01).Experimental results demonstrate that ToolExpander significantly enhances tool-using capabilities in LLMs, especially in weaker small-scale models, improving both training stability and overall performance.
FastAvatar: Towards Unified Fast High-Fidelity 3D Avatar Reconstruction with Large Gaussian Reconstruction Transformers
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Despite significant progress in 3D avatar reconstruction, it still faces challenges such as high time complexity, sensitivity to data quality, and low data utilization. We propose FastAvatar, a feedforward 3D avatar framework capable of flexibly leveraging diverse daily recordings (e.g., a single image, multi-view observations, or monocular video) to reconstruct a high-quality 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) model within seconds, using only a single unified model. FastAvatar's core is a Large Gaussian Reconstruction Transformer featuring three key designs: First, a variant VGGT-style transformer architecture aggregating multi-frame cues while injecting initial 3D prompt to predict an aggregatable canonical 3DGS representation; Second, multi-granular guidance encoding (camera pose, FLAME expression, head pose) mitigating animation-induced misalignment for variable-length inputs; Third, incremental Gaussian aggregation via landmark tracking and sliced fusion losses. Integrating these features, FastAvatar enables incremental reconstruction, i.e., improving quality with more observations, unlike prior work wasting input data. This yields a quality-speed-tunable paradigm for highly usable avatar modeling. Extensive experiments show that FastAvatar has higher quality and highly competitive speed compared to existing methods.
Balanced Sharpness-Aware Minimization for Imbalanced Regression
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Regression is fundamental in computer vision and is widely used in various tasks including age estimation, depth estimation, target localization, \etc However, real-world data often exhibits imbalanced distribution, making regression models perform poorly especially for target values with rare observations~(known as the imbalanced regression problem). In this paper, we reframe imbalanced regression as an imbalanced generalization problem. To tackle that, we look into the loss sharpness property for measuring the generalization ability of regression models in the observation space. Namely, given a certain perturbation on the model parameters, we check how model performance changes according to the loss values of different target observations. We propose a simple yet effective approach called Balanced Sharpness-Aware Minimization~(BSAM) to enforce the uniform generalization ability of regression models for the entire observation space. In particular, we start from the traditional sharpness-aware minimization and then introduce a novel targeted reweighting strategy to homogenize the generalization ability across the observation space, which guarantees a theoretical generalization bound. Extensive experiments on multiple vision regression tasks, including age and depth estimation, demonstrate that our BSAM method consistently outperforms existing approaches. The code is available \href{https://github.com/manmanjun/BSAM_for_Imbalanced_Regression}{here}.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025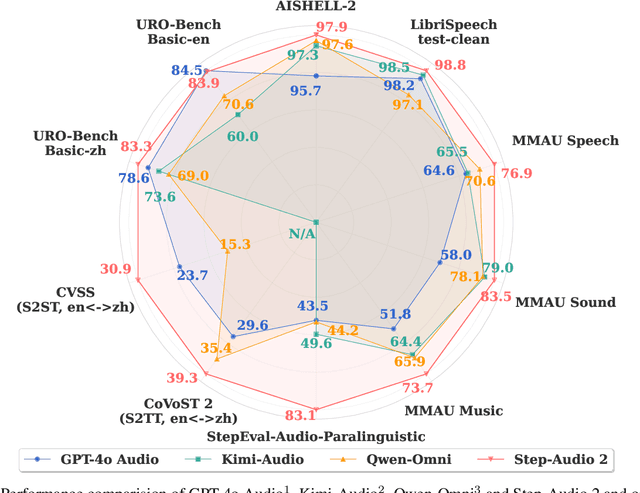

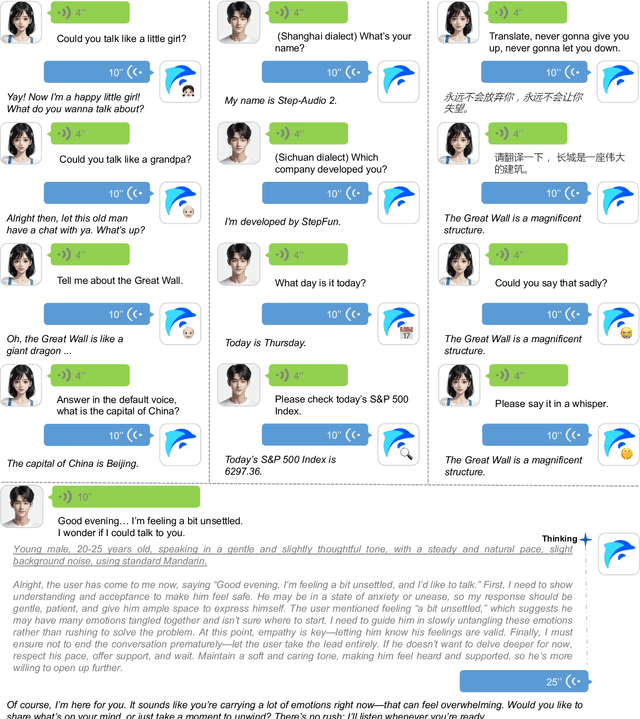

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge