Guoxin Li
Achieving Hiding and Smart Anti-Jamming Communication: A Parallel DRL Approach against Moving Reactive Jammer
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of anti-jamming in moving reactive jamming scenarios. The moving reactive jammer initiates high-power tracking jamming upon detecting any transmission activity, and when unable to detect a signal, resorts to indiscriminate jamming. This presents dual imperatives: maintaining hiding to avoid the jammer's detection and simultaneously evading indiscriminate jamming. Spread spectrum techniques effectively reduce transmitting power to elude detection but fall short in countering indiscriminate jamming. Conversely, changing communication frequencies can help evade indiscriminate jamming but makes the transmission vulnerable to tracking jamming without spread spectrum techniques to remain hidden. Current methodologies struggle with the complexity of simultaneously optimizing these two requirements due to the expansive joint action spaces and the dynamics of moving reactive jammers. To address these challenges, we propose a parallelized deep reinforcement learning (DRL) strategy. The approach includes a parallelized network architecture designed to decompose the action space. A parallel exploration-exploitation selection mechanism replaces the $\varepsilon $-greedy mechanism, accelerating convergence. Simulations demonstrate a nearly 90\% increase in normalized throughput.
Technique Report of CVPR 2024 PBDL Challenges
Jun 15, 2024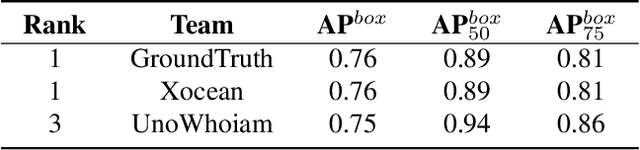

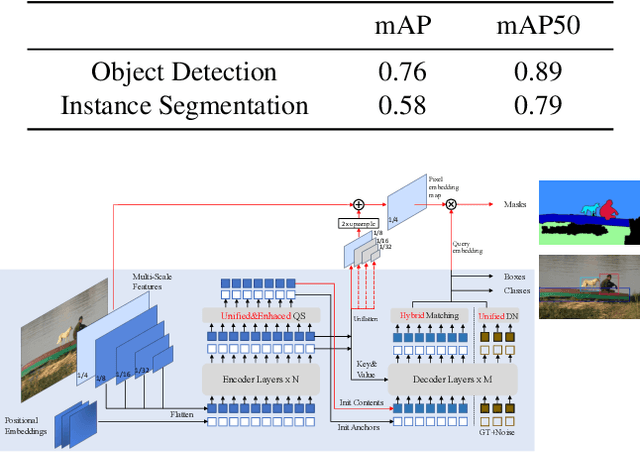
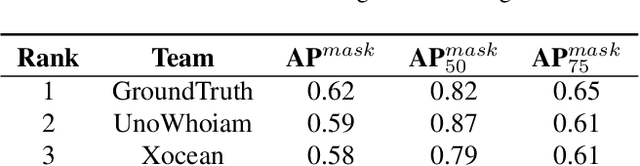
Abstract:The intersection of physics-based vision and deep learning presents an exciting frontier for advancing computer vision technologies. By leveraging the principles of physics to inform and enhance deep learning models, we can develop more robust and accurate vision systems. Physics-based vision aims to invert the processes to recover scene properties such as shape, reflectance, light distribution, and medium properties from images. In recent years, deep learning has shown promising improvements for various vision tasks, and when combined with physics-based vision, these approaches can enhance the robustness and accuracy of vision systems. This technical report summarizes the outcomes of the Physics-Based Vision Meets Deep Learning (PBDL) 2024 challenge, held in CVPR 2024 workshop. The challenge consisted of eight tracks, focusing on Low-Light Enhancement and Detection as well as High Dynamic Range (HDR) Imaging. This report details the objectives, methodologies, and results of each track, highlighting the top-performing solutions and their innovative approaches.
Trajectory and Transmit Power Optimization for IRS-Assisted UAV Communication under Malicious Jamming
Jan 14, 2022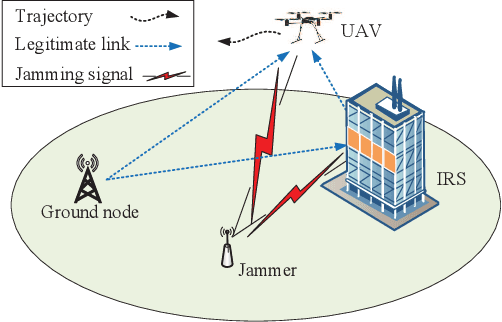
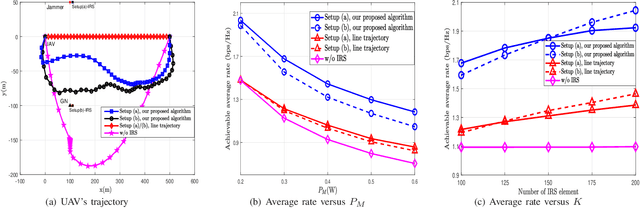
Abstract:In this letter, we investigate an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) communication system, where an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is deployed to assist in the transmission from a ground node (GN) to the UAV in the presence of a jammer. We aim to maximize the average rate of the UAV communication by jointly optimizing the GN's transmit power, the IRS's passive beamforming and the UAV's trajectory. However, the formulated problem is difficult to solve due to the non-convex objective function and the coupled optimization variables. Thus, to tackle it, we propose an alternating optimization (AO) based algorithm by exploiting the successive convex approximation (SCA) and semidefinite relaxation (SDR) techniques. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can significantly improve the average rate compared with the benchmark algorithms. Moreover, it also shows that when the jamming power is large and the number of IRS elements is relatively small, deploying the IRS near the jammer outperforms deploying it near the GN, and vice versa.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge