Qingqing Wu
Low-Altitude Reflection via UAV-Mounted Rotatable IRS
Feb 28, 2026Abstract:Low-altitude network is a key enabler for extending coverage and recovering connectivity in 6G systems, especially when terrestrial infrastructure is unavailable. This paper studies a uncrewed aerial vehicle (UAV)-mounted rotatable intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) as a low-altitude reflector between a blocked base station (BS) and a ground terminal (GT). Unlike the conventional isotropic-element assumption, each IRS element is modeled with a hemispherical directive radiation pattern, whose boresight can be adjusted via element rotations. We formulate a new optimization problem that jointly designs IRS phase shifts, per-element rotation vectors, and UAV placement to maximize the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Leveraging the problem structure, we derive closed-form solutions for phase alignment and element rotations, showing that the optimal boresight points are along the internal angular bisector between the BS-IRS and GT-IRS directions. With these closed forms, the design reduces to a placement optimization problem over a box-constrained airspace; we solve it using an efficient projected gradient algorithm with majorization-minimization update and a global Lipschitz constant. Numerical results demonstrate substantial SNR gains from directive elements and reveal a fundamental trade-off between directional gain and path loss, yielding useful insights into low-altitude deployment of UAV-mounted IRSs.
DRL-Enabled Trajectory Planing for UAV-Assisted VLC: Optimal Altitude and Reward Design
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recently, the integration of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and visible light communication (VLC) technologies has emerged as a promising solution to offer flexible communication and efficient lighting. This letter investigates the three-dimensional trajectory planning in a UAV-assisted VLC system, where a UAV is dispatched to collect data from ground users (GUs). The core objective is to develop a trajectory planning framework that minimizes UAV flight distance, which is equivalent to maximizing the data collection efficiency. This issue is formulated as a challenging mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem. To tackle it, we first derive a closed-form optimal flight altitude under specific VLC channel gain threshold. Subsequently, we optimize the UAV horizontal trajectory by integrating a novel pheromone-driven reward mechanism with the twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm, which enables adaptive UAV motion strategy in complex environments. Simulation results validate that the derived optimal altitude effectively reduces the flight distance by up to 35% compared to baseline methods. Additionally, the proposed reward mechanism significantly shortens the convergence steps by approximately 50%, demonstrating notable efficiency gains in the context of UAV-assisted VLC data collection.
Cell-Free MIMO with Rotatable Antennas: When Macro-Diversity Meets Antenna Directivity
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Cell-free networks leverage distributed access points (APs) to achieve macro-diversity, yet their performance is often constrained by large disparities in channel quality arising from user geometry and blockages. To address this, rotatable antennas (RAs) add a lightweight hardware degree of freedom by steering the antenna boresight toward dominant propagation directions to strengthen unfavorable links, thereby enabling the network to better exploit macro-diversity for higher and more uniform performance. This paper investigates an RA-enabled cell-free downlink network and formulates a max-min rate problem that jointly optimizes transmit beamforming and antenna orientations. To tackle this challenging problem, we develop an alternating-optimization-based algorithm that iteratively updates the beamformers via a second-order cone program (SOCP) and optimizes the antenna orientations using successive convex approximation. To reduce complexity, we further propose an efficient two-stage scheme that first designs orientations by maximizing a proportional-fair log-utility using manifold-aware Frank-Wolfe updates, and then computes the beamformers using an SOCP-based design. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed orientation-aware designs achieve a substantially higher worst-user rate than conventional beamforming-only benchmarks. Furthermore, larger antenna directivity enhances fairness with proper orientation but can degrade the worst-user performance otherwise.
Two-Scale Spatial Deployment for Cost-Effective Wireless Networks via Cooperative IRSs and Movable Antennas
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:This paper proposes a two-scale spatial deployment strategy to ensure reliable coverage for multiple target areas, integrating macroscopic intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) and fine-grained movable antennas (MAs). Specifically, IRSs are selectively deployed from candidate sites to shape the propagation geometry, while MAs are locally repositioned among discretized locations to exploit small-scale channel variations. The objective is to minimize the total deployment cost of MAs and IRSs by jointly optimizing the IRS site selection, MA positions, transmit precoding, and IRS phase shifts, subject to the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) requirements for all target areas. This leads to a challenging mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem that is intractable to solve directly. To address this, we first formulate an auxiliary problem to verify the feasibility. A penalty-based double-loop algorithm integrating alternating optimization and successive convex approximation (SCA) is developed to solve this feasibility issue, which is subsequently adapted to obtain a suboptimal solution for the original cost minimization problem. Finally, based on the obtained solution, we formulate an element refinement problem to further reduce the deployment cost, which is solved by a penalty-based SCA algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed designs consistently outperform benchmarks relying on independent area planning or full IRS deployment in terms of cost-efficiency. Moreover, for cost minimization, MA architectures are preferable in large placement apertures, whereas fully populated FPA architectures excel in compact ones; for worst-case SNR maximization, MA architectures exhibit a lower cost threshold for feasibility, while FPA architectures can attain peak SNR at a lower total cost.
Low-Altitude ISAC with Rotatable Active and Passive Arrays
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates a low-altitude integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system that leverages cooperative rotatable active and passive arrays. We consider a downlink scenario where a base station (BS) with an active rotatable array serves multiple communication users and senses low-altitude targets, assisted by a rotatable reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS). A rotation-aware geometry-based multipath model is developed to capture the impact of three-dimensional (3D) array orientations on both steering vectors and direction-dependent element gains. On this basis, we formulate a new optimization problem that maximizes the downlink sum rate subject to a transmit power budget, RIS unit-modulus constraints, mechanical rotation limits, and a sensing beampattern mean-squared-error (MSE) constraint. To address the resulting highly non-convex problem, we propose a penalty-based alternating-optimization (AO) framework that alternately updates the BS precoder, RIS phase shifts, and BS/RIS array rotation angles. The three blocks are efficiently handled via a convex optimization method based on quadratic-transform (QT) and majorization-minorization (MM), Riemannian conjugate gradient (RCG) on the unit-modulus manifold, and projected gradient descent (PGD) with Barzilai-Borwein step sizes, respectively. Numerical results in low-altitude geometries demonstrate that the proposed jointly rotatable BS-RIS architecture achieves significant sum-rate gains over fixed or partially rotatable baselines while guaranteeing sensing requirements, especially with directional antennas and in interference-limited regimes.
A Covariance-Surrogate Framework for Movable-Antenna Enabled Anti-Jamming with Unknown Jammers
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we investigate a movable antenna (MA) enabled anti-jamming optimization problem, where a legitimate uplink system is exposed to multiple jammers with unknown jamming channels. To enhance the anti-jamming capability of the considered system, an MA array is deployed at the receiver, and the antenna positions and the minimum-variance distortionless-response (MVDR) receive beamformer are jointly optimized to maximize the output signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR). The main challenge arises from the fact that the interference covariance matrix is unknown and nonlinearly dependent on the antenna positions. To overcome these issues, we propose a surrogate objective by replacing the unknown covariance with the sample covariance evaluated at the current antenna position anchor. Under a two-timescale framework, the surrogate objective is updated once per block (contains multiple snapshots) at the current anchor position, while the MVDR beamformer is adapted on a per-snapshot basis. We establish a local bound on the discrepancy between the surrogate and the true objective by leveraging matrix concentration inequalities, and further prove that a natural historical-averaging surrogate suffers from a non-vanishing geometric bias. Building on these insights, we develop a low-complexity projected trust-region (TR) surrogate optimization (PTRSO) algorithm that maintains the locality of each iteration via TR constraints and enforces feasibility through projection, which is guaranteed to converge to a stationary point near the anchor. Numerical results verify the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed PTRSO algorithm, which consistently achieves higher output SINR than existing baselines.
Cooperative Rotatable IRSs for Wireless Communications: Joint Beamforming and Orientation Optimization
Dec 16, 2025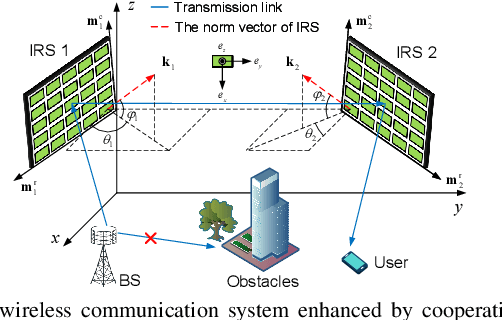
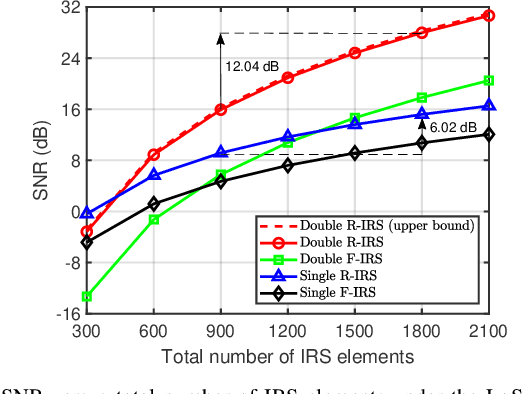
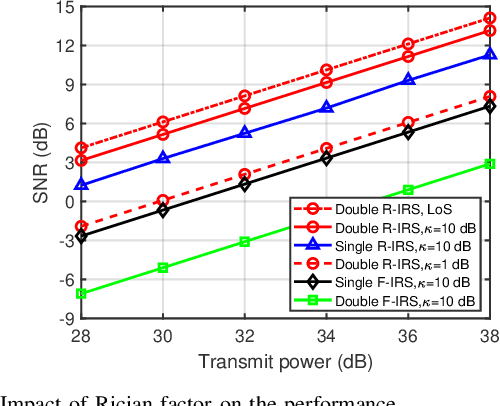
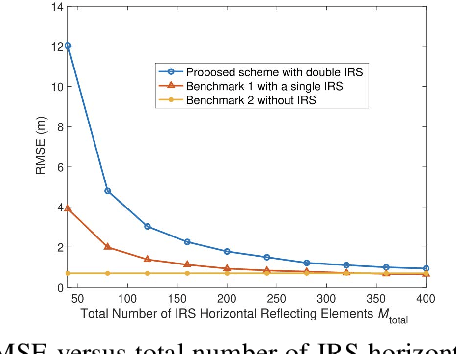
Abstract:Rotatable intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) introduce a new degree of freedom (DoF) for shaping wireless propagation by adaptively adjusting the orientation of IRSs. This paper considers an angle-dependent reflection model in a wireless communication system aided by two rotatable IRSs. Specifically, we study the joint design of the base station transmit beamforming, as well as the cooperative passive beamforming and orientation of the two IRSs, to maximize the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Under the light-of-sight (LoS) channels, we first develop a particle swarm optimization (PSO) based method to determine the IRS rotation and derive an optimal rotation in a closed-form expression for a two-dimensional IRS deployment. Then, we extend the design to the general Rician fading channels by proposing an efficient alternating optimization and PSO (AO-PSO) algorithm. Numerical results validate the substantial gains achieved by the IRS rotation over fixed-IRS schemes and also demonstrate the superior performance of the double rotatable IRSs over a single rotatable IRS given a sufficient total number of IRS elements.
Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces for Integrated Sensing and Communications: A Survey
Nov 14, 2025
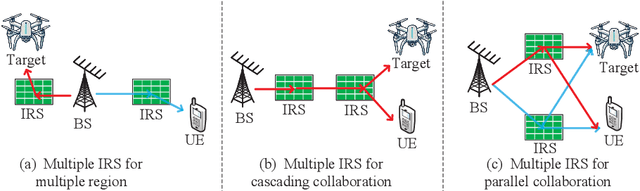
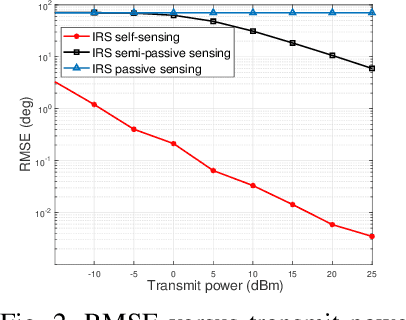
Abstract:The rapid development of sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks requires seamless integration of communication and sensing to support ubiquitous intelligence and real-time, high-reliability applications. Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a key solution for achieving this convergence, offering joint utilization of spectral, hardware, and computing resources. However, realizing high-performance ISAC remains challenging due to environmental line-of-sight (LoS) blockage, limited spatial resolution, and the inherent coverage asymmetry and resource coupling between sensing and communication. Intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs), featuring low-cost, energy-efficient, and programmable electromagnetic reconfiguration, provide a promising solution to overcome these limitations. This article presents a comprehensive overview of IRS-aided wireless sensing and ISAC technologies, including IRS architectures, target detection and estimation techniques, beamforming designs, and performance metrics. It further explores IRS-enabled new opportunities for more efficient performance balancing, coexistence, and networking in ISAC systems, focuses on current design bottlenecks, and outlines future research directions. This article aims to offer a unified design framework that guides the development of practical and scalable IRS-aided ISAC systems for the next-generation wireless network.
Rotatable IRS Aided Wireless Communication
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Rotatable intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) introduces a new spatial degree of freedom (DoF) by dynamically adjusting orientations without the need of changing its elements' positions in real time. To unleash the full potential of rotatable IRSs for wireless communications, this paper investigates the joint optimization of IRS rotation angles to maximize the minimum expected signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) over all locations within a given target area. We first propose an angle-dependent channel model that accurately characterizes the reception and reflection of each IRS element. Different from the conventional cosine-law assumption, the proposed model captures the practical electromagnetic characteristics of the IRS, including the effective reception area and reflection efficiency. For the single target location case, a particle swarm optimization (PSO)-based algorithm is developed to solve the SNR maximization problem, and a closed-form expression for a near-optimal solution is derived to provide useful insights. For the general area coverage enhancement case, the optimal rotation is obtained through a two-loop PSO-based iterative algorithm with null-point detection. In this algorithm, the outer loop updates the global rotation angles to maximize the minimum SNR over the target area, whereas the inner loop evaluates the SNR distribution within the area to identify the location corresponding to the minimum SNR through null-point detection. Numerical results demonstrate significant SNR improvement achieved by the proposed rotatable IRS design over various benchmark schemes under different system setups.
Reconfigurable Airspace: Synergizing Movable Antenna and Intelligent Surface for Low-Altitude ISAC Networks
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks are integral to future 6G integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems. However, their deployment is hindered by challenges stemming from high mobility of UAVs, complex propagation environments, and the inherent trade-offs between coexisting sensing and communication functions. This article proposes a novel framework that leverages movable antennas (MAs) and intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) as dual enablers to overcome these limitations. MAs, through active transceiver reconfiguration, and IRSs, via passive channel reconstruction, can work in synergy to significantly enhance system performance. Our analysis first elaborates on the fundamental gains offered by MAs and IRSs, and provides simulation results that validate the immense potential of the MA-IRS-enabled ISAC architecture. Two core UAV deployment scenarios are then investigated: (i) UAVs as ISAC users, where we focus on achieving high-precision tracking and aerial safety, and (ii) UAVs as aerial network nodes, where we address robust design and complex coupled resource optimization. Finally, key technical challenges and research opportunities are identified and analyzed for each scenario, charting a clear course for the future design of advanced low-altitude ISAC networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge