Guangji Chen
Cooperative Rotatable IRSs for Wireless Communications: Joint Beamforming and Orientation Optimization
Dec 16, 2025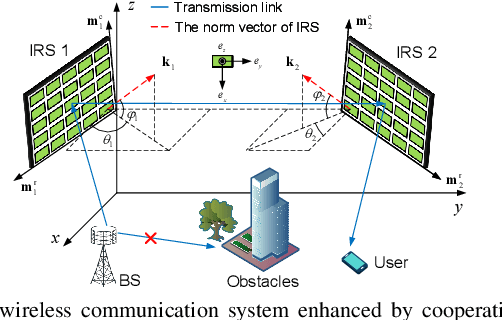
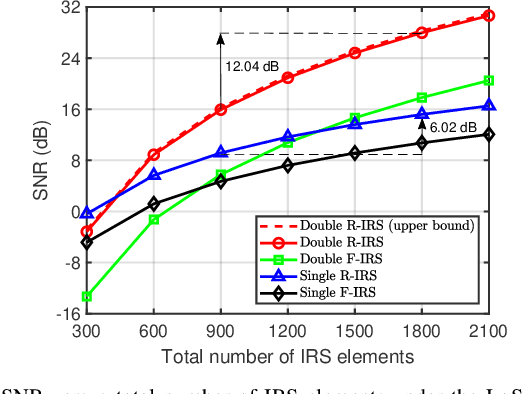
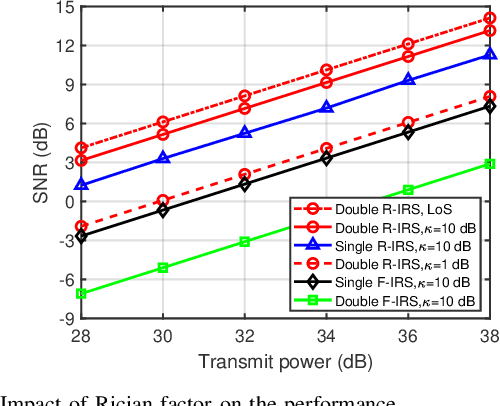
Abstract:Rotatable intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) introduce a new degree of freedom (DoF) for shaping wireless propagation by adaptively adjusting the orientation of IRSs. This paper considers an angle-dependent reflection model in a wireless communication system aided by two rotatable IRSs. Specifically, we study the joint design of the base station transmit beamforming, as well as the cooperative passive beamforming and orientation of the two IRSs, to maximize the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Under the light-of-sight (LoS) channels, we first develop a particle swarm optimization (PSO) based method to determine the IRS rotation and derive an optimal rotation in a closed-form expression for a two-dimensional IRS deployment. Then, we extend the design to the general Rician fading channels by proposing an efficient alternating optimization and PSO (AO-PSO) algorithm. Numerical results validate the substantial gains achieved by the IRS rotation over fixed-IRS schemes and also demonstrate the superior performance of the double rotatable IRSs over a single rotatable IRS given a sufficient total number of IRS elements.
Rotatable IRS Aided Wireless Communication
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Rotatable intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) introduces a new spatial degree of freedom (DoF) by dynamically adjusting orientations without the need of changing its elements' positions in real time. To unleash the full potential of rotatable IRSs for wireless communications, this paper investigates the joint optimization of IRS rotation angles to maximize the minimum expected signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) over all locations within a given target area. We first propose an angle-dependent channel model that accurately characterizes the reception and reflection of each IRS element. Different from the conventional cosine-law assumption, the proposed model captures the practical electromagnetic characteristics of the IRS, including the effective reception area and reflection efficiency. For the single target location case, a particle swarm optimization (PSO)-based algorithm is developed to solve the SNR maximization problem, and a closed-form expression for a near-optimal solution is derived to provide useful insights. For the general area coverage enhancement case, the optimal rotation is obtained through a two-loop PSO-based iterative algorithm with null-point detection. In this algorithm, the outer loop updates the global rotation angles to maximize the minimum SNR over the target area, whereas the inner loop evaluates the SNR distribution within the area to identify the location corresponding to the minimum SNR through null-point detection. Numerical results demonstrate significant SNR improvement achieved by the proposed rotatable IRS design over various benchmark schemes under different system setups.
Conditional Diffusion Model-Driven Generative Channels for Double RIS-Aided Wireless Systems
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:With the development of the upcoming sixth-generation networks (6G), reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have gained significant attention due to its ability of reconfiguring wireless channels via smart reflections. However, traditional channel state information (CSI) acquisition techniques for double-RIS systems face challenges (e.g., high pilot overhead or multipath interference). This paper proposes a new channel generation method in double-RIS communication systems based on the tool of conditional diffusion model (CDM). The CDM is trained on synthetic channel data to capture channel characteristics. It addresses the limitations of traditional CSI generation methods, such as insufficient model understanding capability and poor environmental adaptability. We provide a detailed analysis of the diffusion process for channel generation, and it is validated through simulations. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed CDM based method outperforms traditional channel acquisition methods in terms of normalized mean squared error (NMSE). This method offers a new paradigm for channel acquisition in double-RIS systems, which is expected to improve the quality of channel acquisition with low pilot overhead.
Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces Aided Wireless Network: Deployment Architectures and Solutions
Jan 15, 2025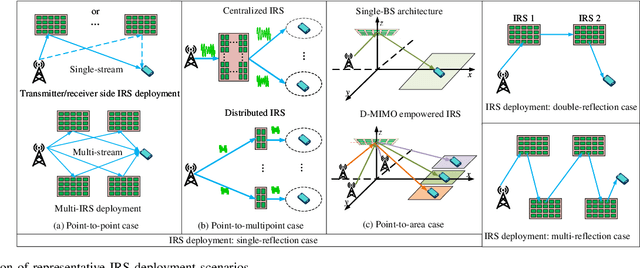
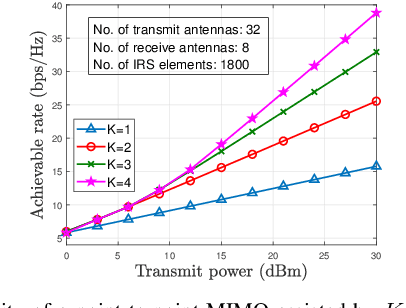
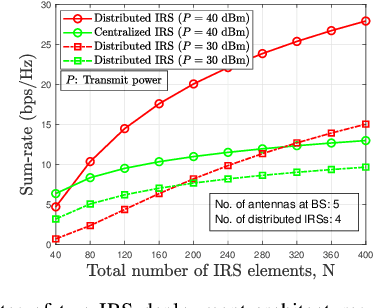
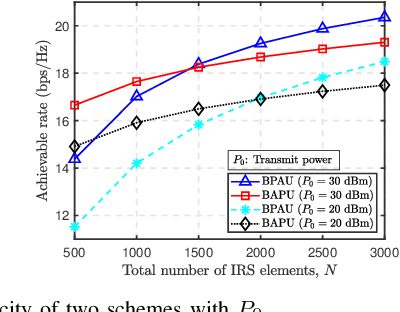
Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) have emerged as a transformative technology for wireless networks by improving coverage, capacity, and energy efficiency through intelligent manipulation of wireless propagation environments. This paper provides a comprehensive study on the deployment and coordination of IRSs for wireless networks. By addressing both single- and multi-reflection IRS architectures, we examine their deployment strategies across diverse scenarios, including point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and point-to-area setups. For the single-reflection case, we highlight the trade-offs between passive and active IRS architectures in terms of beamforming gain, coverage extension, and spatial multiplexing. For the multi-reflection case, we discuss practical strategies to optimize IRS deployment and element allocation, balancing cooperative beamforming gains and path loss. The paper further discusses practical challenges in IRS implementation, including environmental conditions, system compatibility, and hardware limitations. Numerical results and field tests validate the effectiveness of IRS-aided wireless networks and demonstrate their capacity and coverage improvements. Lastly, promising research directions, including movable IRSs, near-field deployments, and network-level optimization, are outlined to guide future investigations.
Decision Transformers for RIS-Assisted Systems with Diffusion Model-Based Channel Acquisition
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have been recognized as a revolutionary technology for future wireless networks. However, RIS-assisted communications have to continuously tune phase-shifts relying on accurate channel state information (CSI) that is generally difficult to obtain due to the large number of RIS channels. The joint design of CSI acquisition and subsection RIS phase-shifts remains a significant challenge in dynamic environments. In this paper, we propose a diffusion-enhanced decision Transformer (DEDT) framework consisting of a diffusion model (DM) designed for efficient CSI acquisition and a decision Transformer (DT) utilized for phase-shift optimizations. Specifically, we first propose a novel DM mechanism, i.e., conditional imputation based on denoising diffusion probabilistic model, for rapidly acquiring real-time full CSI by exploiting the spatial correlations inherent in wireless channels. Then, we optimize beamforming schemes based on the DT architecture, which pre-trains on historical environments to establish a robust policy model. Next, we incorporate a fine-tuning mechanism to ensure rapid beamforming adaptation to new environments, eliminating the retraining process that is imperative in conventional reinforcement learning (RL) methods. Simulation results demonstrate that DEDT can enhance efficiency and adaptability of RIS-aided communications with fluctuating channel conditions compared to state-of-the-art RL methods.
IRS Aided Federated Learning: Multiple Access and Fundamental Tradeoff
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:This paper investigates an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) aided wireless federated learning (FL) system, where an access point (AP) coordinates multiple edge devices to train a machine leaning model without sharing their own raw data. During the training process, we exploit the joint channel reconfiguration via IRS and resource allocation design to reduce the latency of a FL task. Particularly, we propose three transmission protocols for assisting the local model uploading from multiple devices to an AP, namely IRS aided time division multiple access (I-TDMA), IRS aided frequency division multiple access (I-FDMA), and IRS aided non-orthogonal multiple access (INOMA), to investigate the impact of IRS on the multiple access for FL. Under the three protocols, we minimize the per-round latency subject to a given training loss by jointly optimizing the device scheduling, IRS phase-shifts, and communicationcomputation resource allocation. For the associated problem under I-TDMA, an efficient algorithm is proposed to solve it optimally by exploiting its intrinsic structure, whereas the highquality solutions of the problems under I-FDMA and I-NOMA are obtained by invoking a successive convex approximation (SCA) based approach. Then, we further develop a theoretical framework for the performance comparison of the proposed three transmission protocols. Sufficient conditions for ensuring that I-TDMA outperforms I-NOMA and those of its opposite are unveiled, which is fundamentally different from that NOMA always outperforms TDMA in the system without IRS. Simulation results validate our theoretical findings and also demonstrate the usefulness of IRS for enhancing the fundamental tradeoff between the learning latency and learning accuracy.
Spatial Multiplexing Oriented Channel Reconfiguration in Multi-IRS Aided MIMO Systems
Oct 06, 2024



Abstract:Spatial multiplexing plays a significant role in improving the capacity of multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication systems. To improve the spectral efficiency (SE) of a point-to-point MIMO system, we exploit the channel reconfiguration capabilities provided by multiple intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) to enhance the spatial multiplexing. Unlike most existing works, we address both the issues of the IRSs placement and elements allocation. To this end, we first introduce an orthogonal placement strategy to mitigate channel correlation, thereby enabling interference-free multi-stream transmission. Subsequently, we propose a successive convex approximation (SCA)-based approach to jointly optimize the IRS elements and power allocation. Our theoretical analysis unveils that equal IRS elements/power allocation scheme becomes asymptotically optimal as the number of IRS elements and transmit power tend to be infinite. Numerical results demonstrate that when the total number of IRS elements or the power exceeds a certain threshold, a multi-IRS assisted system outperforms a single IRS configuration.
Deploying Graph Neural Networks in Wireless Networks: A Link Stability Viewpoint
May 09, 2024Abstract:As an emerging artificial intelligence technology, graph neural networks (GNNs) have exhibited promising performance across a wide range of graph-related applications. However, information exchanges among neighbor nodes in GNN pose new challenges in the resource-constrained scenario, especially in wireless systems. In practical wireless systems, the communication links among nodes are usually unreliable due to wireless fading and receiver noise, consequently resulting in performance degradation of GNNs. To improve the learning performance of GNNs, we aim to maximize the number of long-term average (LTA) communication links by the optimized power control under energy consumption constraints. Using the Lyapunov optimization method, we first transform the intractable long-term problem into a deterministic problem in each time slot by converting the long-term energy constraints into the objective function. In spite of this non-convex combinatorial optimization problem, we address this problem via equivalently solving a sequence of convex feasibility problems together with a greedy based solver. Simulation results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed scheme over the baselines.
Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided AirComp: Multi-Timescale Design and Performance Analysis
May 09, 2024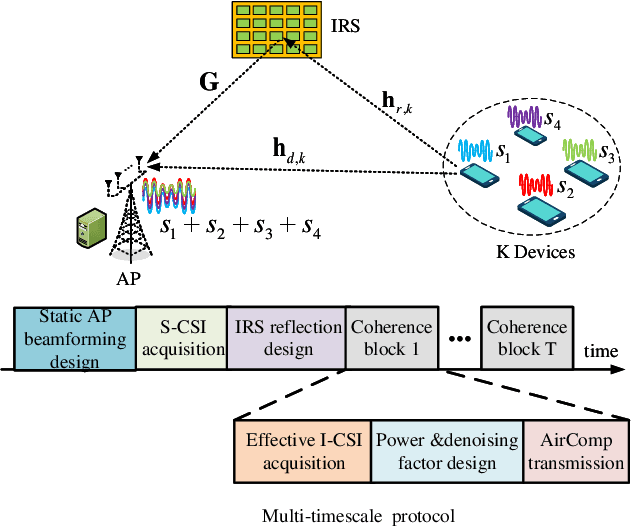
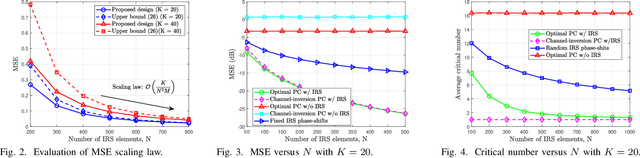
Abstract:The integration of intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) into over-the-air computation (AirComp) is an effective solution for reducing the computational mean squared error (MSE) via its high passive beamforming gain. Prior works on IRS aided AirComp generally rely on the full instantaneous channel state information (I-CSI), which is not applicable to large-scale systems due to its heavy signalling overhead. To address this issue, we propose a novel multi-timescale transmission protocol. In particular, the receive beamforming at the access point (AP) is pre-determined based on the static angle information and the IRS phase-shifts are optimized relying on the long-term statistical CSI. With the obtained AP receive beamforming and IRS phase-shifts, the effective low-dimensional I-CSI is exploited to determine devices' transmit power in each coherence block, thus substantially reducing the signalling overhead. Theoretical analysis unveils that the achievable MSE scales on the order of ${\cal O}\left( {K/\left( {{N^2}M} \right)} \right)$, where $M$, $N$, and $K$ are the number of AP antennas, IRS elements, and devices, respectively. We also prove that the channel-inversion power control is asymptotically optimal for large $N$, which reveals that the full power transmission policy is not needed for lowering the power consumption of energy-limited devices.
Network-Level Integrated Sensing and Communication: Interference Management and BS Coordination Using Stochastic Geometry
Nov 15, 2023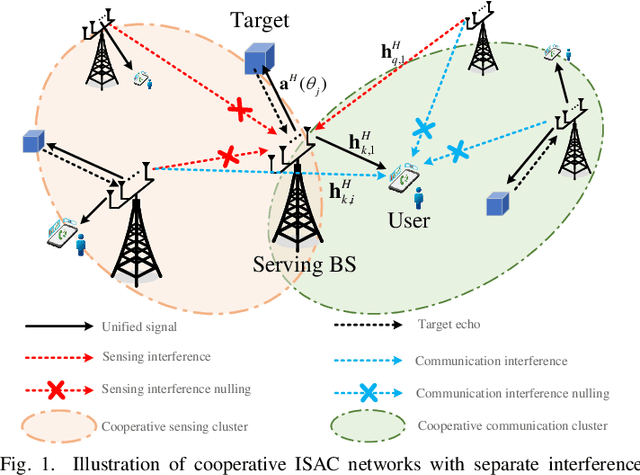
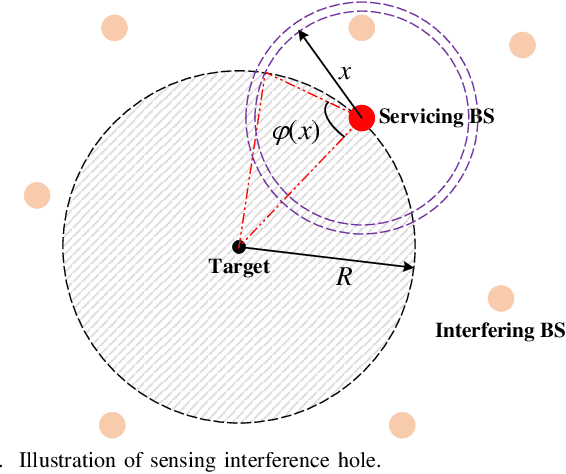
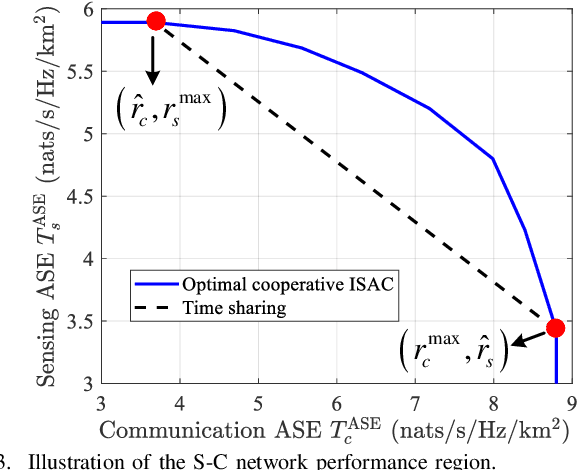
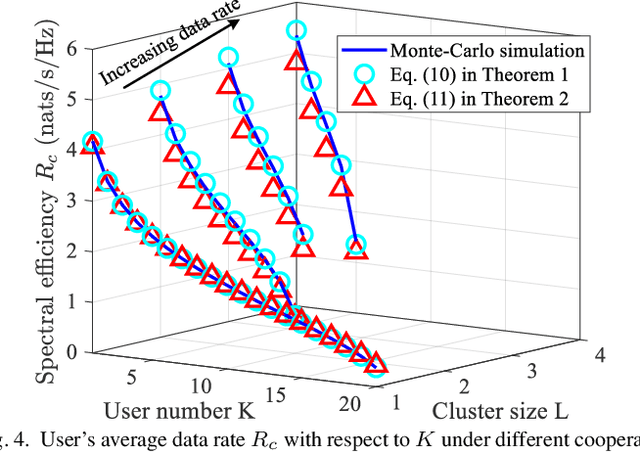
Abstract:In this work, we study integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks with the aim of effectively balancing sensing and communication (S&C) performance at the network level. Focusing on monostatic sensing, the tool of stochastic geometry is exploited to capture the S&C performance, which facilitates us to illuminate key cooperative dependencies in the ISAC network and optimize key network-level parameters. Based on the derived tractable expression of area spectral efficiency (ASE), we formulate the optimization problem to maximize the network performance from the view point of two joint S&C metrics. Towards this end, we further jointly optimize the cooperative BS cluster sizes for S&C and the serving/probing numbers of users/targets to achieve a flexible tradeoff between S&C at the network level. It is verified that interference nulling can effectively improve the average data rate and radar information rate. Surprisingly, the optimal communication tradeoff for the case of the ASE maximization tends to employ all spacial resources towards multiplexing and diversity gain, without interference nulling. By contrast, for the sensing objectives, resource allocation tends to eliminate certain interference especially when the antenna resources are sufficient, because the inter-cell interference becomes a more dominant factor affecting sensing performance. Furthermore, we prove that the ratio of the optimal number of users and the number of transmit antennas is a constant value when the communication performance is optimal. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed cooperative ISAC scheme achieves a substantial gain in S&C performance at the network level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge