Chau Yuen
Nanyang Technological University
Low-Complexity Multi-Agent Continual Learning for Stacked Intelligent Metasurface-Assisted Secure Communications
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Stacked intelligent metasurfaces (SIMs), composed of multiple layers of reconfigurable transmissive metasurfaces, are gaining prominence as a transformative technology for future wireless communication security. This paper investigates the integration of SIM into multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems to enhance physical layer security. A novel system architecture is proposed, wherein each base station (BS) antenna transmits a dedicated single-user stream, while a multi-layer SIM executes wave-based beamforming in the electromagnetic domain, thereby avoiding the need for complex baseband digital precoding and significantly reducing hardware overhead. To maximize the weighted sum secrecy rate (WSSR), we formulate a joint precoding optimization problem over BS power allocation and SIM phase shifts, which is high-dimensional and non-convex due to the complexity of the objective function and the coupling among optimization variables. To address this, we propose a manifold-enhanced heterogeneous multi-agent continual learning (MHACL) framework that incorporates gradient representation and dual-scale policy optimization to achieve robust performance in dynamic environments with high demands for secure communication. Furthermore, we develop SIM-MHACL (SIMHACL), a low-complexity learning template that embeds phase coordination into a product manifold structure, reducing the exponential search space to linear complexity while maintaining physical feasibility. Simulation results validate that the proposed framework achieves millisecond-level per-iteratio ntraining in SIM-assisted systems, significantly outperforming various baseline schemes, with SIMHACL achieving comparable WSSR to MHACL while reducing computation time by 30\%.
Stacked Intelligent Metasurfaces-Based Electromagnetic Wave Domain Interference-Free Precoding
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:This paper introduces an interference-free multi-stream transmission architecture leveraging stacked intelligent metasurfaces (SIMs), from a new perspective of interference exploitation. Unlike traditional interference exploitation precoding (IEP) which relies on computational hardware circuitry, we perform the precoding operations within the analog wave domain provided by SIMs. However, the benefits of SIM-enabled IEP are limited by the nonlinear distortion (NLD) caused by power amplifiers. A hardware-efficient interference-free transmitter architecture is developed to exploit SIM's high and flexible degree of freedom (DoF), where the NLD on modulated symbols can be directly compensated in the wave domain. Moreover, we design a frame-level SIM configuration scheme and formulate a maxmin problem on the safety margin function. With respect to the optimization of SIM phase shifts, we propose a recursive oblique manifold (ROM) algorithm to tackle the complex coupling among phase shifts across multiple layers. A flexible DoF-driven antenna selection (AS) scheme is explored in the SIM-enabled IEP system. Using an ROM-based alternating optimization (ROM-AO) framework, our approach jointly optimizes transmit AS, SIM phase shift design, and power allocation (PA), and develops a greedy safety margin-based AS algorithm. Simulations show that the proposed SIM-enabled frame-level IEP scheme significantly outperforms benchmarks. Specifically, the strategy with AS and PA can achieve a 20 dB performance gain compared to the case without any strategy under the 12 dB signal-to-noise ratio, which confirms the superiority of the NLD-aware IEP scheme and the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Invisible Walls: Privacy-Preserving ISAC Empowered by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The environmental and target-related information inherently carried in wireless signals, such as channel state information (CSI), has brought increasing attention to integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). However, it also raises pressing concerns about privacy leakage through eavesdropping. While existing efforts have attempted to mitigate this issue, they either fail to account for the needs of legitimate communication and sensing users or rely on hardware with high complexity and cost. To overcome these limitations, we propose PrivISAC, a plug-and-play, low-cost solution that leverages RIS to protect user privacy while preserving ISAC performance. At the core of PrivISAC is a novel strategy in which each RIS row is assigned two distinct beamforming vectors, from which we deliberately construct a limited set of RIS configurations. During operation, exactly one configuration is randomly activated at each time slot to introduce additional perturbations, effectively masking sensitive sensing information from unauthorized eavesdroppers. To jointly ensure privacy protection and communication performance, we design the two vectors such that their responses remain nearly identical in the communication direction, thereby preserving stable, high-throughput transmission, while exhibiting pronounced differences in the sensing direction, which introduces sufficient perturbations to thwart eavesdroppers. Additionally, to enable legitimate sensing under such randomized configurations, we introduce a time-domain masking and demasking method that allows the authorized receiver to associate each CSI sample with its underlying configuration and eliminate configuration-induced discrepancies, thereby recovering valid CSI. We implement PrivISAC on commodity wireless devices and experiment results show that PrivISAC provides strong privacy protection while preserving high-quality legitimate ISAC.
Achievable Rate and Coding Principle for MIMO Multicarrier Systems With Cross-Domain MAMP Receiver Over Doubly Selective Channels
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The integration of multicarrier modulation and multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) is critical for reliable transmission of wireless signals in complex environments, which significantly improve spectrum efficiency. Existing studies have shown that popular orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) and affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) offer significant advantages over orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) in uncoded doubly selective channels. However, it remains uncertain whether these benefits extend to coded systems. Meanwhile, the information-theoretic limit analysis of coded MIMO multicarrier systems and the corresponding low-complexity receiver design remain unclear. To overcome these challenges, this paper proposes a multi-slot cross-domain memory approximate message passing (MS-CD-MAMP) receiver as well as develops its information-theoretic (i.e., achievable rate) limit and optimal coding principle for MIMO-multicarrier modulation (e.g., OFDM, OTFS, and AFDM) systems. The proposed MS-CD-MAMP receiver can exploit not only the time domain channel sparsity for low complexity but also the corresponding symbol domain constellation constraints for performance enhancement. Meanwhile, limited by the high-dimensional complex state evolution (SE), a simplified single-input single-output variational SE is proposed to derive the achievable rate of MS-CD-MAMP and the optimal coding principle with the goal of maximizing the achievable rate. Numerical results show that coded MIMO-OFDM/OTFS/AFDM with MS-CD-MAMP achieve the same maximum achievable rate in doubly selective channels, whose finite-length performance with practical optimized low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes is only 0.5 $\sim$ 1.8 dB away from the associated theoretical limit, and has 0.8 $\sim$ 4.4 dB gain over the well-designed point-to-point LDPC codes.
A Lightweight Transfer Learning-Based State-of-Health Monitoring with Application to Lithium-ion Batteries in Autonomous Air Vehicles
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Accurate and rapid state-of-health (SOH) monitoring plays an important role in indicating energy information for lithium-ion battery-powered portable mobile devices. To confront their variable working conditions, transfer learning (TL) emerges as a promising technique for leveraging knowledge from data-rich source working conditions, significantly reducing the training data required for SOH monitoring from target working conditions. However, traditional TL-based SOH monitoring is infeasible when applied in portable mobile devices since substantial computational resources are consumed during the TL stage and unexpectedly reduce the working endurance. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a lightweight TL-based SOH monitoring approach with constructive incremental transfer learning (CITL). First, taking advantage of the unlabeled data in the target domain, a semi-supervised TL mechanism is proposed to minimize the monitoring residual in a constructive way, through iteratively adding network nodes in the CITL. Second, the cross-domain learning ability of node parameters for CITL is comprehensively guaranteed through structural risk minimization, transfer mismatching minimization, and manifold consistency maximization. Moreover, the convergence analysis of the CITL is given, theoretically guaranteeing the efficacy of TL performance and network compactness. Finally, the proposed approach is verified through extensive experiments with a realistic autonomous air vehicles (AAV) battery dataset collected from dozens of flight missions. Specifically, the CITL outperforms SS-TCA, MMD-LSTM-DA, DDAN, BO-CNN-TL, and AS$^3$LSTM, in SOH estimation by 83.73%, 61.15%, 28.24%, 87.70%, and 57.34%, respectively, as evaluated using the index root mean square error.
Enhanced Information Security via Wave-Field Selectivity and Structured Wavefront Manipulation
Dec 11, 2025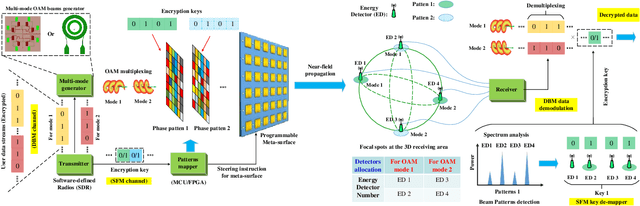
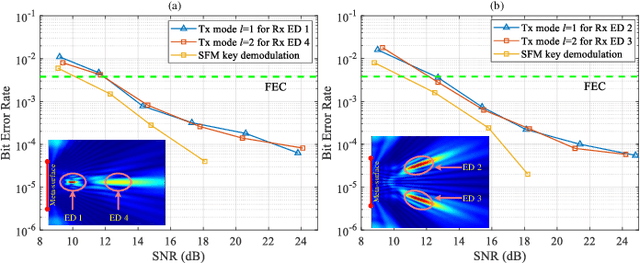
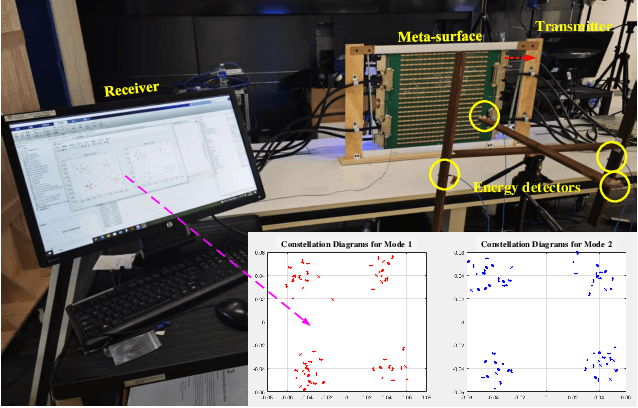
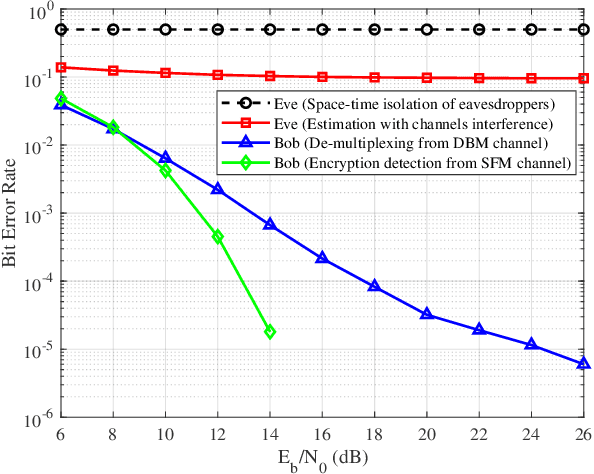
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel secure wireless transmission architecture that enables the co-existence of spatial field modulation (SFM) and digital bandpass modulation (DBM), utilizing multi-mode vortex waves and programmable meta-surfaces (PMS). Distinct from conventional joint modulation schemes, our approach establishes two logically independent transmission channels--SFM and DBM--thereby eliminating the need for joint signal design or time synchronization. Specifically, the orthogonality of vortex wave modes is exploited to construct a high-capacity multi-mode DBM channel, in which each mode carries modulated symbols independently. As the composite waveform passes through the PMS, energy from different vortex modes is spatially focused onto distinct positions, dynamically determined by the PMS configuration. This spatial mapping forms a unique lookup table that encodes additional information in the electro-magnetic (EM) field distribution, effectively enabling a second, concurrent SFM channel. To enhance physical-layer security, the DBM channel transmits encrypted symbols transformed via dynamic symbol-domain mapping, while the corresponding mapping relations--or key information--are carried by the SFM channel. This lightweight dual-channel encryption strategy provides strong confidentiality without requiring complex joint decoding. To validate the feasibility of the proposed architecture, we design and implement a proof-of-concept prototype system, and conduct experimental demonstrations under real-world wireless communication conditions. The experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the co-existent DBM-SFM design in achieving reliable and secure transmission. The proposed architecture offers a scalable, low-complexity, and secure transmission solution for future IoT networks, especially in scenarios demanding both spectral efficiency and physical-layer confidentiality.
Stacked Intelligent Metasurface-Enhanced Wideband Multiuser MIMO OFDM-IM Communications
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Leveraging the multilayer realization of programmable metasurfaces, stacked intelligent metasurfaces (SIM) enable fine-grained wave-domain control. However, their wideband deployment is impeded by two structural factors: (i) a single, quasi-static SIM phase tensor must adapt to all subcarriers, and (ii) multiuser scheduling changes the subcarrier activation pattern frame by frame, requiring rapid reconfiguration. To address both challenges, we develop a SIM-enhanced wideband multiuser transceiver built on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing with index modulation (OFDM-IM). The sparse activation of OFDM-IM confines high-fidelity equalization to the active tones, effectively widening the usable bandwidth. To make the design reliability-aware, we directly target the worst-link bit-error rate (BER) and adopt a max-min per-tone signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) as a principled surrogate, turning the reliability optimization tractable. For frame-rate inference and interpretability, we propose an unfolded projected-gradient-descent network (UPGD-Net) that double-unrolls across the SIM's layers and algorithmic iterations: each cell computes the analytic gradient from the cascaded precoder with a learnable per-iteration step size. Simulations on wideband multiuser downlinks show fast, monotone convergence, an evident layer-depth sweet spot, and consistent gains in worst-link BER and sum rate. By combining structural sparsity with a BER-driven, deep-unfolded optimization backbone, the proposed framework directly addresses the key wideband deficiencies of SIM.
Distributed Multi-Task Learning for Joint Wireless Signal Enhancement and Recognition
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Wireless signal recognition (WSR) is crucial in modern and future wireless communication networks since it aims to identify the properties of the received signal in a no-collaborative manner. However, it is challenging to accurately classify signals in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions and distributed network settings. In this paper, we propose a novel distributed multi-task learning framework for joint wireless signal enhancement and recognition (WSER), addressing the crucial need for non-collaborative signal identification in modern wireless networks. Our approach integrates a wireless signal enhancement and recognition network (WSERNet) with FedProx+, an enhanced federated learning algorithm designed for heterogeneous data distributions. Specifically, WSERNet leverages an asymmetric convolution block (ACBlock) to capture long-range dependencies in the input signal and improve the performance of the deep learning model. FedProx+ introduces a proximal term to the loss function to encourage the model updates to be closer to the previous model, enhancing the convergence speed and robustness of federated learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework for joint WSER, achieving superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods under both centralized and distributed settings including independent and identically distributed (IID) and non-IID data distributions.
* accepted by Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking
Fundamental Trade-off in Wideband Stacked Intelligent Metasurface Assisted OFDMA Systems
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Conventional digital beamforming for wideband multiuser orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) demands numerous power-hungry components, increasing hardware costs and complexity. By contrast, the stacked intelligent metasurfaces (SIM) can perform wave-based precoding at near-light speed, drastically reducing baseband overhead. However, realizing SIM-enhanced fully-analog beamforming for wideband multiuser transmissions remains challenging, as the SIM configuration has to handle interference across all subcarriers. To address this, this paper proposes a flexible subcarrier allocation strategy to fully reap the SIM-assisted fully-analog beamforming capability in an orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) system, where each subcarrier selectively serves one or more users to balance interference mitigation and resource utilization of SIM. We propose an iterative algorithm to jointly optimize the subcarrier assignment matrix and SIM transmission coefficients, approximating an interference-free channel for those selected subcarriers. Results show that the proposed system has low fitting errors yet allows each user to exploit more subcarriers. Further comparisons highlight a fundamental trade-off: our system achieves near-zero interference and robust data reliability without incurring the hardware burdens of digital precoding.
Stacked Intelligent Metasurface Assisted Multiuser Communications: From a Rate Fairness Perspective
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Stacked intelligent metasurface (SIM) extends the concept of single-layer reconfigurable holographic surfaces (RHS) by incorporating a multi-layered structure, thereby providing enhanced control over electromagnetic wave propagation and improved signal processing capabilities. This study investigates the potential of SIM in enhancing the rate fairness in multiuser downlink systems by addressing two key optimization problems: maximizing the minimum rate (MR) and maximizing the geometric mean of rates (GMR). {The former strives to enhance the minimum user rate, thereby ensuring fairness among users, while the latter relaxes fairness requirements to strike a better trade-off between user fairness and system sum-rate (SR).} For the MR maximization, we adopt a consensus alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM)-based approach, which decomposes the approximated problem into sub-problems with closed-form solutions. {For GMR maximization, we develop an alternating optimization (AO)-based algorithm that also yields closed-form solutions and can be seamlessly adapted for SR maximization. Numerical results validate the effectiveness and convergence of the proposed algorithms.} Comparative evaluations show that MR maximization ensures near-perfect fairness, while GMR maximization balances fairness and system SR. Furthermore, the two proposed algorithms respectively outperform existing related works in terms of MR and SR performance. Lastly, SIM with lower power consumption achieves performance comparable to that of multi-antenna digital beamforming.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge