Yong Liang Guan
ComAgent: Multi-LLM based Agentic AI Empowered Intelligent Wireless Networks
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Emerging 6G networks rely on complex cross-layer optimization, yet manually translating high-level intents into mathematical formulations remains a bottleneck. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promise, monolithic approaches often lack sufficient domain grounding, constraint awareness, and verification capabilities. To address this, we present ComAgent, a multi-LLM agentic AI framework. ComAgent employs a closed-loop Perception-Planning-Action-Reflection cycle, coordinating specialized agents for literature search, coding, and scoring to autonomously generate solver-ready formulations and reproducible simulations. By iteratively decomposing problems and self-correcting errors, the framework effectively bridges the gap between user intent and execution. Evaluations demonstrate that ComAgent achieves expert-comparable performance in complex beamforming optimization and outperforms monolithic LLMs across diverse wireless tasks, highlighting its potential for automating design in emerging wireless networks.
Dual-Mapping Sparse Vector Transmission for Short Packet URLLC
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Sparse vector coding (SVC) is a promising short-packet transmission method for ultra reliable low latency communication (URLLC) in next generation communication systems. In this paper, a dual-mapping SVC (DM-SVC) based short packet transmission scheme is proposed to further enhance the transmission performance of SVC. The core idea behind the proposed scheme lies in mapping the transmitted information bits onto sparse vectors via block and single-element sparse mappings. The block sparse mapping pattern is able to concentrate the transmit power in a small number of non-zero blocks thus improving the decoding accuracy, while the single-element sparse mapping pattern ensures that the code length does not increase dramatically with the number of transmitted information bits. At the receiver, a two-stage decoding algorithm is proposed to sequentially identify non-zero block indexes and single-element non-zero indexes. Extensive simulation results verify that proposed DM-SVC scheme outperforms the existing SVC schemes in terms of block error rate and spectral efficiency.
MIMO-AFDM Outperforms MIMO-OFDM in the Face of Hardware Impairments
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:The impact of both multiplicative and additive hardware impairments (HWIs) on multiple-input multiple-output affine frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-AFDM) systems is investigated. For small-scale MIMO-AFDM systems, a tight bit error rate (BER) upper bound associated with the maximum likelihood (ML) detector is derived. By contrast, for large-scale systems, a closed-form BER approximation associated with the linear minimum mean squared error (LMMSE) detector is presented, including realistic imperfect channel estimation scenarios. Our first key observation is that the full diversity order of a hardware-impaired AFDM system remains unaffected, which is a unique advantage. Furthermore, our analysis shows that 1) the BER results derived accurately predict the simulated ML performance in moderate-to-high signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs), while the theoretical BER curve of the LMMSE detector closely matches that of the Monte-Carlo based one. 2) MIMO-AFDM is more resilient to multiplicative distortions, such as phase noise and carrier frequency offset, compared to its orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) counterparts. This is attributed to its inherent chirp signal characteristics; 3) MIMO-AFDM consistently achieves superior BER performance compared to conventional MIMO-OFDM systems under the same additive HWI conditions, as well as different velocity values. The latter is because MIMO-AFDM is also resilient to the additional inter-carrier interference (ICI) imposed by the nonlinear distortions of additive HWIs. In a nutshell, compared to OFDM, AFDM demonstrates stronger ICI resilience and achieves the maximum full diversity attainable gain even under HWIs, thanks to its intrinsic chirp signalling structure as well as to the beneficial spreading effect of the discrete affine Fourier transform.
Enhanced Information Security via Wave-Field Selectivity and Structured Wavefront Manipulation
Dec 11, 2025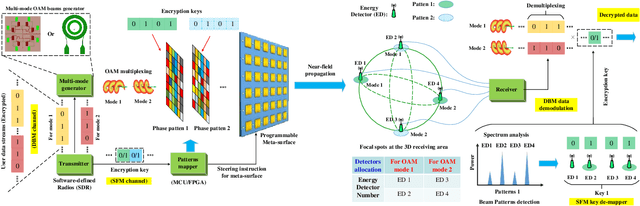
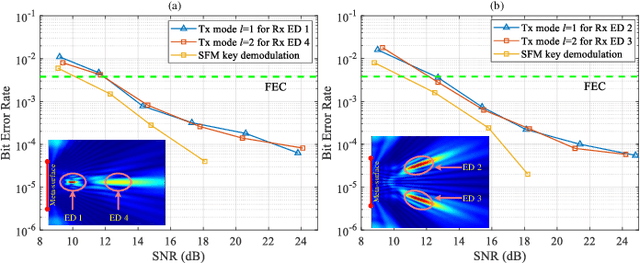
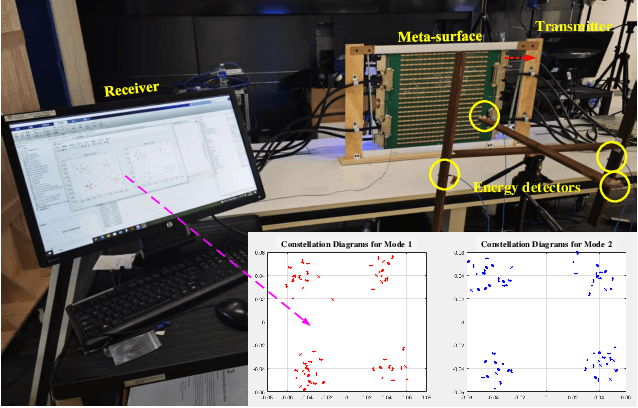
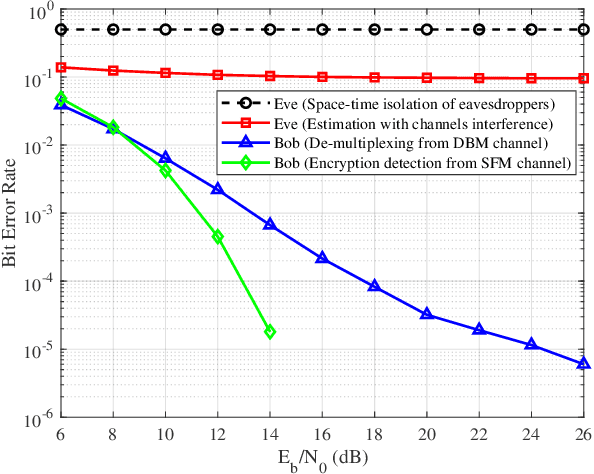
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel secure wireless transmission architecture that enables the co-existence of spatial field modulation (SFM) and digital bandpass modulation (DBM), utilizing multi-mode vortex waves and programmable meta-surfaces (PMS). Distinct from conventional joint modulation schemes, our approach establishes two logically independent transmission channels--SFM and DBM--thereby eliminating the need for joint signal design or time synchronization. Specifically, the orthogonality of vortex wave modes is exploited to construct a high-capacity multi-mode DBM channel, in which each mode carries modulated symbols independently. As the composite waveform passes through the PMS, energy from different vortex modes is spatially focused onto distinct positions, dynamically determined by the PMS configuration. This spatial mapping forms a unique lookup table that encodes additional information in the electro-magnetic (EM) field distribution, effectively enabling a second, concurrent SFM channel. To enhance physical-layer security, the DBM channel transmits encrypted symbols transformed via dynamic symbol-domain mapping, while the corresponding mapping relations--or key information--are carried by the SFM channel. This lightweight dual-channel encryption strategy provides strong confidentiality without requiring complex joint decoding. To validate the feasibility of the proposed architecture, we design and implement a proof-of-concept prototype system, and conduct experimental demonstrations under real-world wireless communication conditions. The experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the co-existent DBM-SFM design in achieving reliable and secure transmission. The proposed architecture offers a scalable, low-complexity, and secure transmission solution for future IoT networks, especially in scenarios demanding both spectral efficiency and physical-layer confidentiality.
DFT-s-OFDM with Chirp Modulation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:In this paper, a new waveform called discrete Fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency division multiplexing with chirp modulation (DFT-s-OFDM-CM) is proposed for the next generation of wireless communications. The information bits are conveyed by not only Q-ary constellation symbols but also the starting frequency of chirp signal. It could maintain the benefits provided by the chirped discrete Fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (DFT-s-OFDM), e.g., low peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR), full frequency diversity exploitation, etc. Simulation results confirm that the proposed DFT-s-OFDM-CM could achieve higher spectral efficiency while keeping the similar bit error rate (BER) to that of chirped DFT-s-OFDM. In addition, when maintaining the same spectral efficiency, the proposed DFT-s-OFDM-CM with the splitting of information bits into two streams enables the use of lower-order constellation modulation and offers greater resilience to noise, resulting in a lower BER than the chirped DFT-s-OFDM.
Pinching-Antenna-Assisted Index Modulation: Channel Modeling, Transceiver Design, and Performance Analysis
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:In this paper, a novel pinching-antenna assisted index modulation (PA-IM) scheme is proposed for improving the spectral efficiency without increasing the hardware complexity, where the information bits are conveyed not only by the conventional M-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) symbols but also by the indices of pinching antenna (PA) position patterns. To realize the full potential of this scheme, this paper focuses on the comprehensive transceiver design, addressing key challenges in signal detection at the receiver and performance optimization at thetransmitter. First, a comprehensive channel model is formulated for this architecture, which sophisticatedly integrates the deterministic in-waveguide propagation effects with the stochastic nature of wireless channels, including both largescale path loss and small-scale fading. Next, to overcome the prohibitive complexity of optimal maximum likelihood (ML) detection, a low-complexity box-optimized sphere decoding (BOSD) algorithm is designed, which adaptively prunes the search space whilst preserving optimal ML performance. Furthermore, an analytical upper bound on the bit error rate (BER) is derived and validated by the simulations. Moreover, a new transmit precoding method is designed using manifold optimization, which minimizes the BER by jointly optimizing the complex-valued precoding coefficients across the waveguides for the sake of maximizing the minimum Euclidean distance of all received signal points. Finally, the simulation results demonstrate that the proposed PA-IM scheme attains a significant performance gain over its conventional counterparts and that the overall BER of the pinching-antenna system is substantially improved by the proposed precoding design.
Basis Expansion Extrapolation based Long-Term Channel Prediction for Massive MIMO OTFS Systems
Jul 02, 2025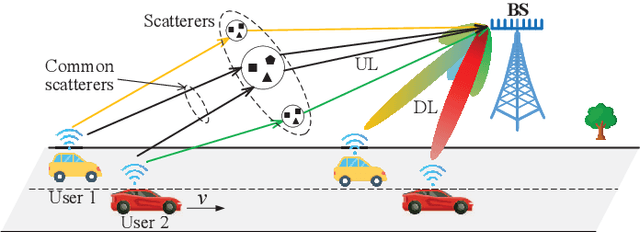
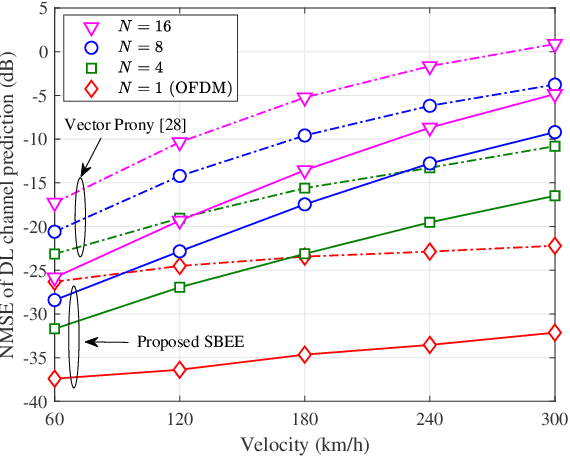
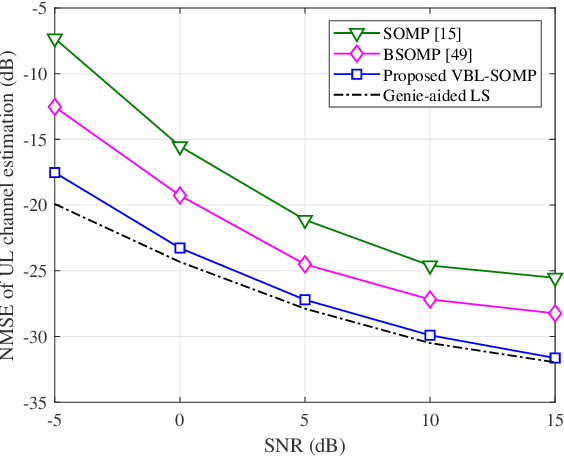
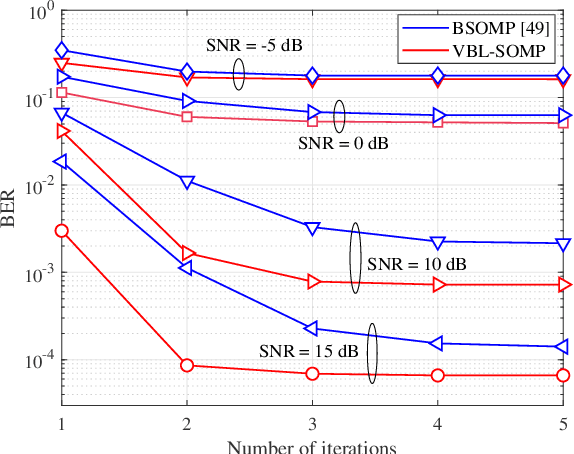
Abstract:Massive multi-input multi-output (MIMO) combined with orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation has emerged as a promising technique for high-mobility scenarios. However, its performance could be severely degraded due to channel aging caused by user mobility and high processing latency. In this paper, an integrated scheme of uplink (UL) channel estimation and downlink (DL) channel prediction is proposed to alleviate channel aging in time division duplex (TDD) massive MIMO-OTFS systems. Specifically, first, an iterative basis expansion model (BEM) based UL channel estimation scheme is proposed to accurately estimate UL channels with the aid of carefully designed OTFS frame pattern. Then a set of Slepian sequences are used to model the estimated UL channels, and the dynamic Slepian coefficients are fitted by a set of orthogonal polynomials. A channel predictor is derived to predict DL channels by iteratively extrapolating the Slepian coefficients. Simulation results verify that the proposed UL channel estimation and DL channel prediction schemes outperform the existing schemes in terms of normalized mean square error of channel estimation/prediction and DL spectral efficiency, with less pilot overhead.
Joint User Association and Beamforming Design for ISAC Networks with Large Language Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has been envisioned to play a more important role in future wireless networks. However, the design of ISAC networks is challenging, especially when there are multiple communication and sensing (C\&S) nodes and multiple sensing targets. We investigate a multi-base station (BS) ISAC network in which multiple BSs equipped with multiple antennas simultaneously provide C\&S services for multiple ground communication users (CUs) and targets. To enhance the overall performance of C\&S, we formulate a joint user association (UA) and multi-BS transmit beamforming optimization problem with the objective of maximizing the total sum rate of all CUs while ensuring both the minimum target detection and parameter estimation requirements. To efficiently solve the highly non-convex mixed integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) optimization problem, we propose an alternating optimization (AO)-based algorithm that decomposes the problem into two sub-problems, i.e., UA optimization and multi-BS transmit beamforming optimization. Inspired by large language models (LLMs) for prediction and inference, we propose a unified framework integrating LLMs with convex-based optimization methods. First, we propose a comprehensive design of prompt engineering, including few-shot, chain of thought, and self-reflection techniques to guide LLMs in solving the binary integer programming UA optimization problem. Second, we utilize convex-based optimization methods to handle the non-convex beamforming optimization problem based on fractional programming (FP), majorization minimization (MM), and the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) with an optimized UA from LLMs. Numerical results demonstrate that our proposed LLM-enabled AO-based algorithm achieves fast convergence and near upper-bound performance with the GPT-o1 model, outperforming various benchmark schemes.
Compact Varactor-Integrated RIS for Wideband and Continuously Tunable Beamforming
May 08, 2025Abstract:This letter presents a novel Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) that features a low-profile structure, wide operating bandwidth, and continuous phase control. By incorporating a middle patch layer without introducing an additional air gap, the proposed design maintains a thin form factor, while achieving a smooth 310{\deg} phase shift over 10\% bandwidth at 6.1 GHz with excellent reflection. A fabricated 10*10 RIS array exhibits stable performance, enabling precise beam control across a 600 MHz bandwidth. These results highlight the potential of the proposed low-profile, wideband RIS with continuous phase tuning for next-generation wireless communication systems.
A Novel Angle-Delay-Doppler Estimation Scheme for AFDM-ISAC System in Mixed Near-field and Far-field Scenarios
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:The recently proposed multi-chirp waveform, affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM), is considered as a potential candidate for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). However, acquiring accurate target sensing parameter information becomes challenging due to fractional delay and Doppler shift occurrence, as well as effects introduced by the coexistence of near-field (NF) and far-field (FF) targets associated with large-scale antenna systems. In this paper, we propose a novel angle-delay-Doppler estimation scheme for AFDM-ISAC system in mixed NF and FF scenarios. Specifically, we model the received ISAC signals as a third-order tensor that admits a low-rank CANDECOMP/PARAFAC (CP) format. By employing the Vandermonde nature of the factor matrix and the spatial smoothing technique, we develop a structured CP decomposition method that guarantees the condition for uniqueness. We further propose a low-complexity estimation scheme to acquire target sensing parameters with fractional values, including angle of arrival/departure (AoA/AoD), delay and Doppler shift accurately. We also derive the Cram\'er-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) as a benchmark and analyze the complexity of our proposed scheme. Finally, simulation results are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge