Xu Zhu
Low-Complexity Sparse Superimposed Coding for Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Sparse superimposed coding (SSC) has emerged as a promising technique for short-packet transmission in ultra-reliable low-latency communication scenarios. However, conventional SSC schemes often suffer from high encoding and decoding complexity due to the use of dense codebook matrices. In this paper, we propose a low-complexity SSC scheme by designing a sparse codebook structure, where each codeword contains only a small number of non-zero elements. The decoding is performed using the traditional multipath matching pursuit algorithm, and the overall complexity is significantly reduced by exploiting the sparsity of the codebook. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme achieves a favorable trade-off between BLER performance and computational complexity, and exhibits strong robustness across different transmission block lengths.
Dual-Mapping Sparse Vector Transmission for Short Packet URLLC
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Sparse vector coding (SVC) is a promising short-packet transmission method for ultra reliable low latency communication (URLLC) in next generation communication systems. In this paper, a dual-mapping SVC (DM-SVC) based short packet transmission scheme is proposed to further enhance the transmission performance of SVC. The core idea behind the proposed scheme lies in mapping the transmitted information bits onto sparse vectors via block and single-element sparse mappings. The block sparse mapping pattern is able to concentrate the transmit power in a small number of non-zero blocks thus improving the decoding accuracy, while the single-element sparse mapping pattern ensures that the code length does not increase dramatically with the number of transmitted information bits. At the receiver, a two-stage decoding algorithm is proposed to sequentially identify non-zero block indexes and single-element non-zero indexes. Extensive simulation results verify that proposed DM-SVC scheme outperforms the existing SVC schemes in terms of block error rate and spectral efficiency.
Hierarchical Sparse Vector Transmission for Ultra Reliable and Low Latency Communications
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Sparse vector transmission (SVT) is a promising candidate technology for achieving ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC). In this paper, a hierarchical SVT scheme is proposed for multi-user URLLC scenarios. The hierarchical SVT scheme partitions the transmitted bits into common and private parts. The common information is conveyed by the indices of non-zero sections in a sparse vector, while each user's private information is embedded into non-zero blocks with specific block lengths. At the receiver, the common bits are first recovered from the detected non-zero sections, followed by user-specific private bits decoding based on the corresponding non-zero block indices. Simulation results show the proposed scheme outperforms state-of-the-art SVT schemes in terms of block error rate.
OMUDA: Omni-level Masking for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) enables semantic segmentation models to generalize from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. However, existing UDA methods still struggle to bridge the domain gap due to cross-domain contextual ambiguity, inconsistent feature representations, and class-wise pseudo-label noise. To address these challenges, we propose Omni-level Masking for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (OMUDA), a unified framework that introduces hierarchical masking strategies across distinct representation levels. Specifically, OMUDA comprises: 1) a Context-Aware Masking (CAM) strategy that adaptively distinguishes foreground from background to balance global context and local details; 2) a Feature Distillation Masking (FDM) strategy that enhances robust and consistent feature learning through knowledge transfer from pre-trained models; and 3) a Class Decoupling Masking (CDM) strategy that mitigates the impact of noisy pseudo-labels by explicitly modeling class-wise uncertainty. This hierarchical masking paradigm effectively reduces the domain shift at the contextual, representational, and categorical levels, providing a unified solution beyond existing approaches. Extensive experiments on multiple challenging cross-domain semantic segmentation benchmarks validate the effectiveness of OMUDA. Notably, on the SYNTHIA->Cityscapes and GTA5->Cityscapes tasks, OMUDA can be seamlessly integrated into existing UDA methods and consistently achieving state-of-the-art results with an average improvement of 7%.
Basis Expansion Extrapolation based Long-Term Channel Prediction for Massive MIMO OTFS Systems
Jul 02, 2025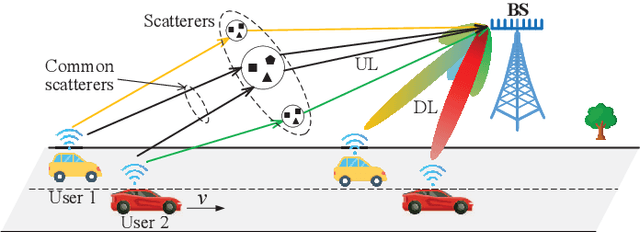
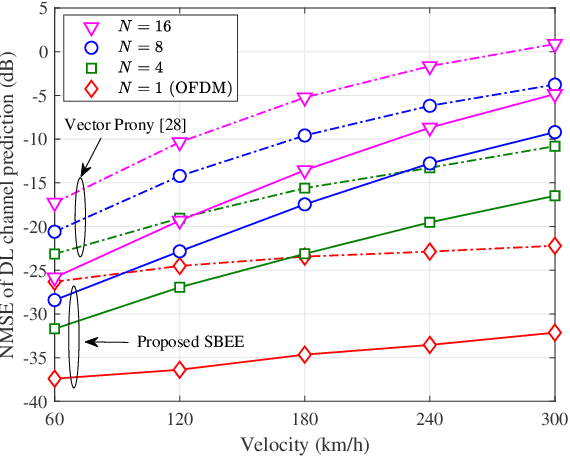
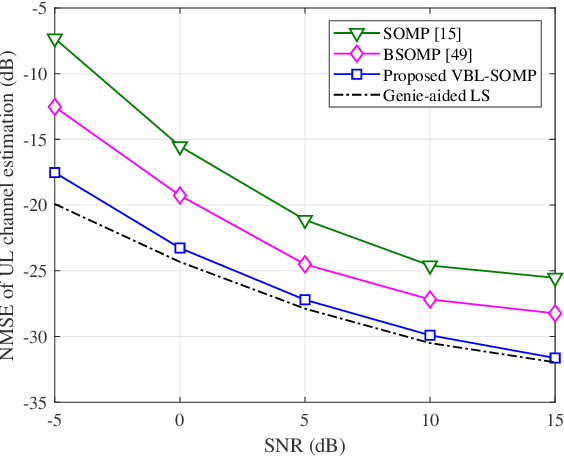
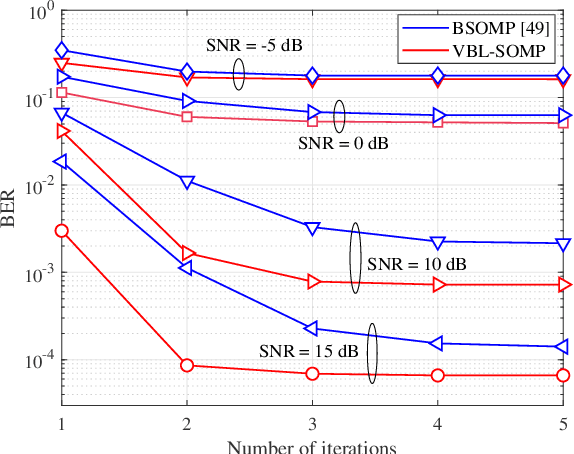
Abstract:Massive multi-input multi-output (MIMO) combined with orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation has emerged as a promising technique for high-mobility scenarios. However, its performance could be severely degraded due to channel aging caused by user mobility and high processing latency. In this paper, an integrated scheme of uplink (UL) channel estimation and downlink (DL) channel prediction is proposed to alleviate channel aging in time division duplex (TDD) massive MIMO-OTFS systems. Specifically, first, an iterative basis expansion model (BEM) based UL channel estimation scheme is proposed to accurately estimate UL channels with the aid of carefully designed OTFS frame pattern. Then a set of Slepian sequences are used to model the estimated UL channels, and the dynamic Slepian coefficients are fitted by a set of orthogonal polynomials. A channel predictor is derived to predict DL channels by iteratively extrapolating the Slepian coefficients. Simulation results verify that the proposed UL channel estimation and DL channel prediction schemes outperform the existing schemes in terms of normalized mean square error of channel estimation/prediction and DL spectral efficiency, with less pilot overhead.
Multi-Reference and Adaptive Nonlinear Transform Source-Channel Coding for Wireless Image Semantic Transmission
May 19, 2025Abstract:We propose a multi-reference and adaptive nonlinear transform source-channel coding (MA-NTSCC) system for wireless image semantic transmission to improve rate-distortion (RD) performance by introducing multi-dimensional contexts into the entropy model of the state-of-the-art (SOTA) NTSCC system. Improvements in RD performance of the proposed MA-NTSCC system are particularly significant in high-resolution image transmission under low bandwidth constraints. The proposed multi-reference entropy model leverages correlations within the latent representation in both spatial and channel dimensions. In the spatial dimension, the latent representation is divided into anchors and non-anchors in a checkerboard pattern, where anchors serve as reference to estimate the mutual information between anchors and non-anchors. In the channel dimension, the latent representation is partitioned into multiple groups, and features in previous groups are analyzed to estimate the mutual information between features in previous and current groups. Taking mutual information into account, the entropy model provides an accurate estimation on the entropy, which enables efficient bandwidth allocation and enhances RD performance. Additionally, the proposed lightweight adaptation modules enable the proposed MA-NTSCC model to achieve transmission quality comparable to separately trained models across various channel conditions and bandwidth requirements. In contrast, traditional NTSCC models provide signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)-distortion performance degrading with channel quality deviating from the fixed training SNR, and consume inflexible bandwidth to transmit an image. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to verify the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) performance and adaptability of the proposed MA-NTSCC model superior to SOTA methods over both additive white Gaussian noise channel and Rayleigh fading channel.
OptMetaOpenFOAM: Large Language Model Driven Chain of Thought for Sensitivity Analysis and Parameter Optimization based on CFD
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Merging natural language interfaces with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) workflows presents transformative opportunities for both industry and research. In this study, we introduce OptMetaOpenFOAM - a novel framework that bridges MetaOpenFOAM with external analysis and optimization tool libraries through a large language model (LLM)-driven chain-of-thought (COT) methodology. By automating complex CFD tasks via natural language inputs, the framework empowers non-expert users to perform sensitivity analyses and parameter optimizations with markedly improved efficiency. The test dataset comprises 11 distinct CFD analysis or optimization tasks, including a baseline simulation task derived from an OpenFOAM tutorial covering fluid dynamics, combustion, and heat transfer. Results confirm that OptMetaOpenFOAM can accurately interpret user requirements expressed in natural language and effectively invoke external tool libraries alongside MetaOpenFOAM to complete the tasks. Furthermore, validation on a non-OpenFOAM tutorial case - namely, a hydrogen combustion chamber - demonstrates that a mere 200-character natural language input can trigger a sequence of simulation, postprocessing, analysis, and optimization tasks spanning over 2,000 lines of code. These findings underscore the transformative potential of LLM-driven COT methodologies in linking external tool for advanced analysis and optimization, positioning OptMetaOpenFOAM as an effective tool that streamlines CFD simulations and enhances their convenience and efficiency for both industrial and research applications. Code is available at https://github.com/Terry-cyx/MetaOpenFOAM.
RSSI Positioning with Fluid Antenna Systems
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:We introduce a novel received signal strength intensity (RSSI)-based positioning method using fluid antenna systems (FAS), leveraging their inherent channel correlation properties to improve location accuracy. By enabling a single antenna to sample multiple spatial positions, FAS exhibits high correlation between its ports. We integrate this high inter-port correlation with a logarithmic path loss model to mitigate the impact of fast fading on RSSI signals, and derive a simplified multipoint positioning model based on the established relationship between channel correlation and RSSI signal correlation. A maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) is then developed, for which we provide a closed-form solution. Results demonstrate that our approach outperforms both traditional least squares (LS) methods and single-antenna systems, achieving accuracy comparable to conventional multi-antenna positioning. Furthermore, we analyze the impact of different antenna structures on positioning performance, offering practical guidance for FAS antenna design.
Goal-Oriented Integration of Sensing, Communication, Computing, and Control for Mission-Critical Internet-of-Things
Jan 02, 2024Abstract:Driven by the development goal of network paradigm and demand for various functions in the sixth-generation (6G) mission-critical Internet-of-Things (MC-IoT), we foresee a goal-oriented integration of sensing, communication, computing, and control (GIS3C) in this paper. We first provide an overview of the tasks, requirements, and challenges of MC-IoT. Then we introduce an end-to-end GIS3C architecture, in which goal-oriented communication is leveraged to bridge and empower sensing, communication, control, and computing functionalities. By revealing the interplay among multiple subsystems in terms of key performance indicators and parameters, this paper introduces unified metrics, i.e., task completion effectiveness and cost, to facilitate S3C co-design in MC-IoT. The preliminary results demonstrate the benefits of GIS3C in improving task completion effectiveness while reducing costs. We also identify and highlight the gaps and challenges in applying GIS3C in the future 6G networks.
Towards Structural Sparse Precoding: Dynamic Time, Frequency, Space, and Power Multistage Resource Programming
Oct 15, 2023Abstract:In last decades, dynamic resource programming in partial resource domains has been extensively investigated for single time slot optimizations. However, with the emerging real-time media applications in fifth-generation communications, their new quality of service requirements are often measured in temporal dimension. This requires multistage optimization for full resource domain dynamic programming. Taking experience rate as a typical temporal multistage metric, we jointly optimize time, frequency, space and power domains resource for multistage optimization. To strike a good tradeoff between system performance and computational complexity, we first transform the formulated mixed integer non-linear constraints into equivalent convex second order cone constraints, by exploiting the coupling effect among the resources. Leveraging the concept of structural sparsity, the objective of max-min experience rate is given as a weighted 1-norm term associated with the precoding matrix. Finally, a low-complexity iterative algorithm is proposed for full resource domain programming, aided by another simple conic optimization for obtaining its feasible initial result. Simulation verifies that our design significantly outperform the benchmarks while maintaining a fast convergence rate, shedding light on full domain dynamic resource programming of multistage optimizations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge