Yao Ge
Singapore
Achievable Rate and Coding Principle for MIMO Multicarrier Systems With Cross-Domain MAMP Receiver Over Doubly Selective Channels
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The integration of multicarrier modulation and multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) is critical for reliable transmission of wireless signals in complex environments, which significantly improve spectrum efficiency. Existing studies have shown that popular orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) and affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) offer significant advantages over orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) in uncoded doubly selective channels. However, it remains uncertain whether these benefits extend to coded systems. Meanwhile, the information-theoretic limit analysis of coded MIMO multicarrier systems and the corresponding low-complexity receiver design remain unclear. To overcome these challenges, this paper proposes a multi-slot cross-domain memory approximate message passing (MS-CD-MAMP) receiver as well as develops its information-theoretic (i.e., achievable rate) limit and optimal coding principle for MIMO-multicarrier modulation (e.g., OFDM, OTFS, and AFDM) systems. The proposed MS-CD-MAMP receiver can exploit not only the time domain channel sparsity for low complexity but also the corresponding symbol domain constellation constraints for performance enhancement. Meanwhile, limited by the high-dimensional complex state evolution (SE), a simplified single-input single-output variational SE is proposed to derive the achievable rate of MS-CD-MAMP and the optimal coding principle with the goal of maximizing the achievable rate. Numerical results show that coded MIMO-OFDM/OTFS/AFDM with MS-CD-MAMP achieve the same maximum achievable rate in doubly selective channels, whose finite-length performance with practical optimized low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes is only 0.5 $\sim$ 1.8 dB away from the associated theoretical limit, and has 0.8 $\sim$ 4.4 dB gain over the well-designed point-to-point LDPC codes.
A Novel Angle-Delay-Doppler Estimation Scheme for AFDM-ISAC System in Mixed Near-field and Far-field Scenarios
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:The recently proposed multi-chirp waveform, affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM), is considered as a potential candidate for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). However, acquiring accurate target sensing parameter information becomes challenging due to fractional delay and Doppler shift occurrence, as well as effects introduced by the coexistence of near-field (NF) and far-field (FF) targets associated with large-scale antenna systems. In this paper, we propose a novel angle-delay-Doppler estimation scheme for AFDM-ISAC system in mixed NF and FF scenarios. Specifically, we model the received ISAC signals as a third-order tensor that admits a low-rank CANDECOMP/PARAFAC (CP) format. By employing the Vandermonde nature of the factor matrix and the spatial smoothing technique, we develop a structured CP decomposition method that guarantees the condition for uniqueness. We further propose a low-complexity estimation scheme to acquire target sensing parameters with fractional values, including angle of arrival/departure (AoA/AoD), delay and Doppler shift accurately. We also derive the Cram\'er-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) as a benchmark and analyze the complexity of our proposed scheme. Finally, simulation results are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed scheme.
Target Sensing With Off-grid Sparse Bayesian Learning for AFDM-ISAC System
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:The recently proposed multi-chirp waveform, affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM), is regarded as a prospective candidate for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) due to its robust performance in high-mobility scenarios and full diversity achievement in doubly dispersive channels. However, the insufficient Doppler resolution caused by limited transmission duration can reduce the accuracy of parameter estimation. In this paper, we propose a new off-grid target parameter estimation scheme to jointly estimate the range and velocity of the targets for AFDM-ISAC system, where the off-grid Doppler components are incorporated to enhance estimation accuracy. Specifically, we form the sensing model as an off-grid sparse signal recovery problem relying on the virtual delay and Doppler grids defined in the discrete affine Fourier (DAF) domain, where the off-grid components are regarded as hyper-parameters for estimation. We also employ the expectation-maximization (EM) technique via a sparse Bayesian learning (SBL) framework to update hyper-parameters iteratively. Simulation results indicate that our proposed off-grid algorithm outperforms existing algorithms in sensing performance and is highly robust to the AFDM-ISAC high-mobility scenario.
HILGEN: Hierarchically-Informed Data Generation for Biomedical NER Using Knowledgebases and Large Language Models
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:We present HILGEN, a Hierarchically-Informed Data Generation approach that combines domain knowledge from the Unified Medical Language System (UMLS) with synthetic data generated by large language models (LLMs), specifically GPT-3.5. Our approach leverages UMLS's hierarchical structure to expand training data with related concepts, while incorporating contextual information from LLMs through targeted prompts aimed at automatically generating synthetic examples for sparsely occurring named entities. The performance of the HILGEN approach was evaluated across four biomedical NER datasets (MIMIC III, BC5CDR, NCBI-Disease, and Med-Mentions) using BERT-Large and DANN (Data Augmentation with Nearest Neighbor Classifier) models, applying various data generation strategies, including UMLS, GPT-3.5, and their best ensemble. For the BERT-Large model, incorporating UMLS led to an average F1 score improvement of 40.36%, while using GPT-3.5 resulted in a comparable average increase of 40.52%. The Best-Ensemble approach using BERT-Large achieved the highest improvement, with an average increase of 42.29%. DANN model's F1 score improved by 22.74% on average using the UMLS-only approach. The GPT-3.5-based method resulted in a 21.53% increase, and the Best-Ensemble DANN model showed a more notable improvement, with an average increase of 25.03%. Our proposed HILGEN approach improves NER performance in few-shot settings without requiring additional manually annotated data. Our experiments demonstrate that an effective strategy for optimizing biomedical NER is to combine biomedical knowledge curated in the past, such as the UMLS, and generative LLMs to create synthetic training instances. Our future research will focus on exploring additional innovative synthetic data generation strategies for further improving NER performance.
A Unifying View of OTFS and Its Many Variants
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:High mobility environment leads to severe Doppler effects and poses serious challenges to the conventional physical layer based on the widely popular orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). The recent emergence of orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation, along with its many related variants, presents a promising solution to overcome such channel Doppler effects. This paper aims to clearly establish the relationships among the various manifestations of OTFS. Among these related modulations, we identify their connections, common features, and distinctions. Building on existing works, this work provides a general overview of various OTFS-related detection schemes and performance comparisons. We first provide an overview of OFDM and filter bank multi-carrier (FBMC) by demonstrating OTFS as a precoded FBMC through the introduction of inverse symplectic finite Fourier transform (ISFFT). We explore the relationship between OTFS and related modulation schemes with similar characteristics. We provide an effective channel model for high-mobility channels and offer a unified detection representation. We provide numerical comparisons of power spectrum density (PSD) and bit error rate (BER) to underscore the benefit of these modulation schemes in high-mobility scenarios. We also evaluate various detection schemes, revealing insights into their efficacies. We discuss opportunities and challenges for OTFS in high mobility, setting the stage for future research and development in this field.
STAR-RIS Aided Dynamic Scatterers Tracking for Integrated Sensing and Communications
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has become an attractive technology for future wireless networks. In this paper, we propose a simultaneous transmission and reflection reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) aided dynamic scatterers tracking scheme for ISAC in high mobility millimeter wave communication systems, where the STAR-RIS is employed to provide communication service for indoor user with the base station (BS) and simultaneously sense and track the interested outdoor dynamic scatterers. Specifically, we resort to an active STAR-RIS to respectively receive and further deal with the impinging signal from its double sides at the same time. Then, we develop a transmission strategy with the activation scheme of the STAR-RIS elements, and construct the signal models within the system. After acquiring the channel parameters related to the BS-RIS channel, the dynamic paths can be identified from all the scattering paths, and the dynamic targets can be classified with respect to their radar cross sections. We further track the outdoor scatterers at STAR-RIS by resorting to the Gaussian mixture-probability hypothesis density filter. With the tracked locations of the outdoor scatterers, a beam prediction strategy for both the precoder of BS and the refraction phase shift vector of STAR-RIS is developed to enhance the communication performance of the indoor user. Besides, a target mismatch detection and path collision prediction mechanism is proposed to reduce the training overhead and improve the transmission performance. Finally, the feasibility and effectiveness of our proposed STAR-RIS aided dynamic scatterers tracking scheme for ISAC are demonstrated and verified via simulation results.
Linear Precoding Design for OTFS Systems in Time/Frequency Selective Fading Channels
Dec 31, 2024

Abstract:Even orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) has been shown as a promising modulation scheme for high mobility doubly-selective fading channels, its attainability of full diversity order in either time or frequency selective fading channels has not been clarified. By performing pairwise error probability (PEP) analysis, we observe that the original OTFS system can not always guarantee full exploitation of the embedded diversity in either time or frequency selective fading channels. To address this issue and further improve system performance, this work proposes linear precoding solutions based on algebraic number theory for OTFS systems over time and frequency selective fading channels, respectively. The proposed linear precoded OTFS systems can guarantee the maximal diversity and potential coding gains in time/frequency selective fading channels without any transmission rate loss and do not require the channel state information (CSI) at the transmitter. Simulation results are finally provided to illustrate the superiority of our proposed precoded OTFS over both the original unprecoded and the existing phase rotation OTFS systems in time/frequency selective fading channels.
Low Complexity Joint Channel Estimation and Data Detection for AFDM Receivers With Oversampling
Oct 07, 2024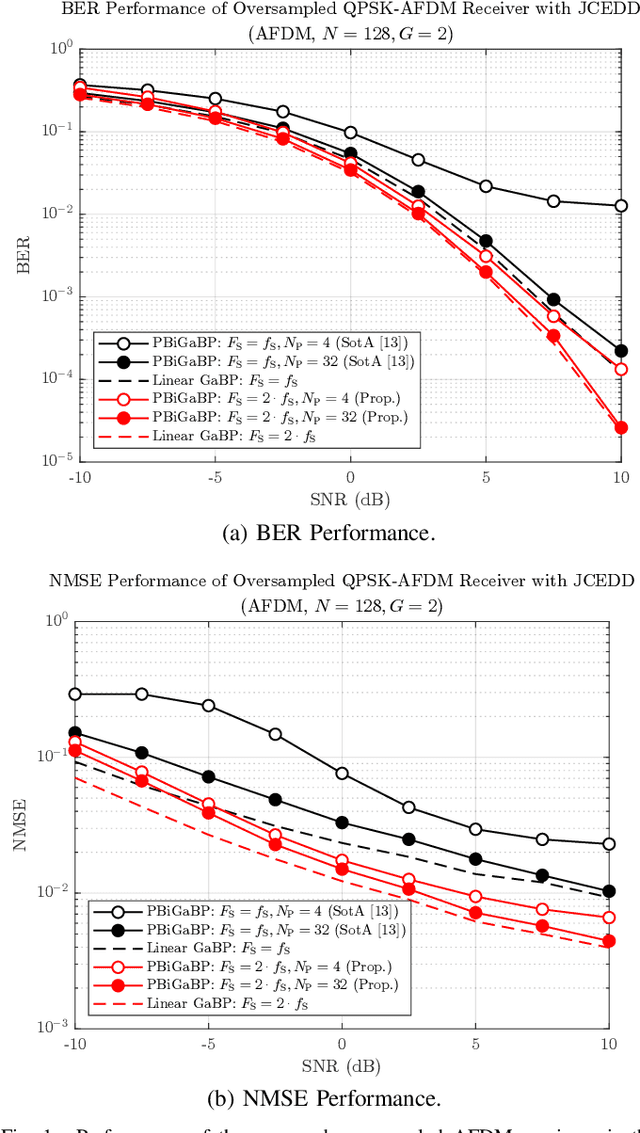
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel low complexity time domain (TD) oversampling receiver framework under affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) waveforms for joint channel estimation and data detection (JCEDD). Leveraging a generalized doubly-dispersive channel model, we first derive the input-output (I/O) relationship for arbitrary waveforms when oversampled in the TD and present the I/O relationship for AFDM as an example. Subsequently, utilizing the multiple sample streams created via the oversampling procedure, we use the parametric bilinear Gaussian belief propagation (PBiGaBP) technique to conduct JCEDD for decoding the transmitted data and estimating the complex channel coefficients. Simulation results verify significant performance improvements both in terms of data decoding and complex channel coefficient estimation with improved robustness against a varying number of pilots over a conventional Nyquist sampling rate receiver.
Two-layer retrieval augmented generation framework for low-resource medical question-answering: proof of concept using Reddit data
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) provides the capability to constrain generative model outputs, and mitigate the possibility of hallucination, by providing relevant in-context text. The number of tokens a generative large language model (LLM) can incorporate as context is finite, thus limiting the volume of knowledge from which to generate an answer. We propose a two-layer RAG framework for query-focused answer generation and evaluate a proof-of-concept for this framework in the context of query-focused summary generation from social media forums, focusing on emerging drug-related information. The evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of the two-layer framework in resource constrained settings to enable researchers in obtaining near real-time data from users.
Reddit-Impacts: A Named Entity Recognition Dataset for Analyzing Clinical and Social Effects of Substance Use Derived from Social Media
May 09, 2024



Abstract:Substance use disorders (SUDs) are a growing concern globally, necessitating enhanced understanding of the problem and its trends through data-driven research. Social media are unique and important sources of information about SUDs, particularly since the data in such sources are often generated by people with lived experiences. In this paper, we introduce Reddit-Impacts, a challenging Named Entity Recognition (NER) dataset curated from subreddits dedicated to discussions on prescription and illicit opioids, as well as medications for opioid use disorder. The dataset specifically concentrates on the lesser-studied, yet critically important, aspects of substance use--its clinical and social impacts. We collected data from chosen subreddits using the publicly available Application Programming Interface for Reddit. We manually annotated text spans representing clinical and social impacts reported by people who also reported personal nonmedical use of substances including but not limited to opioids, stimulants and benzodiazepines. Our objective is to create a resource that can enable the development of systems that can automatically detect clinical and social impacts of substance use from text-based social media data. The successful development of such systems may enable us to better understand how nonmedical use of substances affects individual health and societal dynamics, aiding the development of effective public health strategies. In addition to creating the annotated data set, we applied several machine learning models to establish baseline performances. Specifically, we experimented with transformer models like BERT, and RoBERTa, one few-shot learning model DANN by leveraging the full training dataset, and GPT-3.5 by using one-shot learning, for automatic NER of clinical and social impacts. The dataset has been made available through the 2024 SMM4H shared tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge