Miaowen Wen
South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
A Comprehensive Survey of Channel Estimation Techniques for OTFS in 6G and Beyond Wireless Networks
Dec 15, 2025
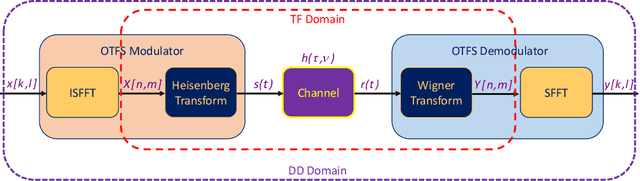
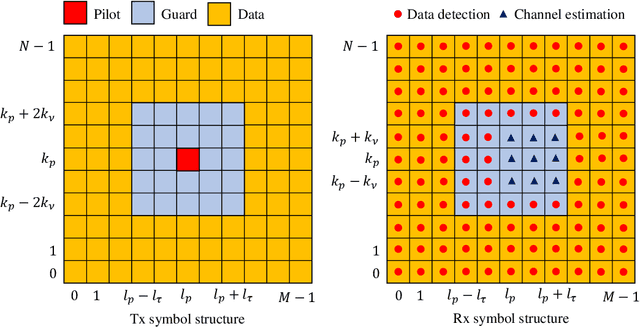
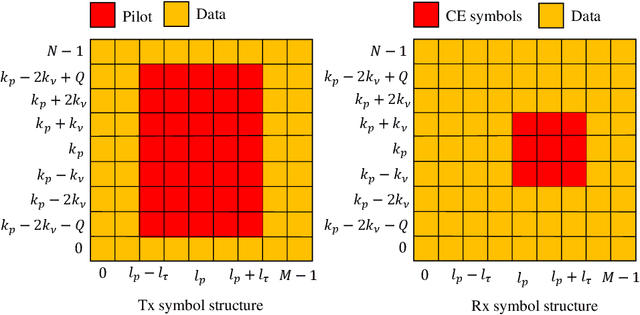
Abstract:Orthogonal time-frequency space (OTFS) modulation has emerged as a powerful wireless communication technology that is specifically designed to address the challenges of high-mobility scenarios and significant Doppler effects. Unlike conventional modulation schemes that operate in the time-frequency (TF) domain, OTFS projects signals to the delay-Doppler (DD) domain, where wireless channels exhibit sparse and quasi-static characteristics. This fundamental transformation enables superior channel estimation (CE) performance in challenging propagation environments characterized by high-mobility, severe multipath effects, and rapidly time-varying channel conditions. This article provides a systematic examination of CE techniques for OTFS systems, covering the extensive research landscape from foundational methods to cutting-edge approaches. We present a detailed analysis of DD and TF domain CE techniques presented in the literature, including separate pilot, embedded pilot, and superimposed pilot approaches. The article encompasses various algorithmic frameworks including Bayesian learning, matching pursuit-based techniques, message passing algorithms, deep learning (DL)-based methods, and recent CE approaches. Additionally, we explore joint CE and signal detection (SD) strategies, the integration of OTFS with next-generation wireless systems including massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO), millimeter wave (mmWave) communications, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), and integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems. Critical implementation challenges are presented, including leakage suppression, inter-Doppler interference mitigation, impulsive noise handling, signaling overhead reduction, guard space requirements, peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) management, beam squint effects, and hardware impairments.
Planning Oriented Integrated Sensing and Communication
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) enables simultaneous localization, environment perception, and data exchange for connected autonomous vehicles. However, most existing ISAC designs prioritize sensing accuracy and communication throughput, treating all targets uniformly and overlooking the impact of critical obstacles on motion efficiency. To overcome this limitation, we propose a planning-oriented ISAC (PISAC) framework that reduces the sensing uncertainty of planning-bottleneck obstacles and expands the safe navigable path for the ego-vehicle, thereby bridging the gap between physical-layer optimization and motion-level planning. The core of PISAC lies in deriving a closed-form safety bound that explicitly links ISAC transmit power to sensing uncertainty, based on the Cram\'er-Rao Bound and occupancy inflation principles. Using this model, we formulate a bilevel power allocation and motion planning (PAMP) problem, where the inner layer optimizes the ISAC beam power distribution and the outer layer computes a collision-free trajectory under uncertainty-aware safety constraints. Comprehensive simulations in high-fidelity urban driving environments demonstrate that PISAC achieves up to 40% higher success rates and over 5% shorter traversal times than existing ISAC-based and communication-oriented benchmarks, validating its effectiveness in enhancing both safety and efficiency.
Edge-Enabled VIO with Long-Tracked Features for High-Accuracy Low-Altitude IoT Navigation
May 10, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a visual-inertial odometry (VIO) method using long-tracked features. Long-tracked features can constrain more visual frames, reducing localization drift. However, they may also lead to accumulated matching errors and drift in feature tracking. Current VIO methods adjust observation weights based on re-projection errors, yet this approach has flaws. Re-projection errors depend on estimated camera poses and map points, so increased errors might come from estimation inaccuracies, not actual feature tracking errors. This can mislead the optimization process and make long-tracked features ineffective for suppressing localization drift. Furthermore, long-tracked features constrain a larger number of frames, which poses a significant challenge to real-time performance of the system. To tackle these issues, we propose an active decoupling mechanism for accumulated errors in long-tracked feature utilization. We introduce a visual reference frame reset strategy to eliminate accumulated tracking errors and a depth prediction strategy to leverage the long-term constraint. To ensure real time preformane, we implement three strategies for efficient system state estimation: a parallel elimination strategy based on predefined elimination order, an inverse-depth elimination simplification strategy, and an elimination skipping strategy. Experiments on various datasets show that our method offers higher positioning accuracy with relatively short consumption time, making it more suitable for edge-enabled low-altitude IoT navigation, where high-accuracy positioning and real-time operation on edge device are required. The code will be published at github.
Aligning Beam with Imbalanced Multi-modality: A Generative Federated Learning Approach
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:As vehicle intelligence advances, multi-modal sensing-aided communication emerges as a key enabler for reliable Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) connectivity through precise environmental characterization. As centralized learning may suffer from data privacy, model heterogeneity and communication overhead issues, federated learning (FL) has been introduced to support V2X. However, the practical deployment of FL faces critical challenges: model performance degradation from label imbalance across vehicles and training instability induced by modality disparities in sensor-equipped agents. To overcome these limitations, we propose a generative FL approach for beam selection (GFL4BS). Our solution features two core innovations: 1) An adaptive zero-shot multi-modal generator coupled with spectral-regularized loss functions to enhance the expressiveness of synthetic data compensating for both label scarcity and missing modalities; 2) A hybrid training paradigm integrating feature fusion with decentralized optimization to ensure training resilience while minimizing communication costs. Experimental evaluations demonstrate significant improvements over baselines achieving 16.2% higher accuracy than the current state-of-the-art under severe label imbalance conditions while maintaining over 70% successful rate even when two agents lack both LiDAR and RGB camera inputs.
Orthogonal Time-Frequency Space (OTFS) Aided Media-Based Modulation System For 6G and Beyond Wireless Communications Networks
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a new orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS)-based index modulation system called OTFS-aided media-based modulation (MBM) scheme (OTFS-MBM), which is a promising technique for high-mobility wireless communication systems. The OTFS technique transforms information into the delay-Doppler domain, providing robustness against channel variations, while the MBM system utilizes controllable radio frequency (RF) mirrors to enhance spectral efficiency. The combination of these two techniques offers improved bit error rate (BER) performance compared to conventional OTFS and OTFS-based spatial modulation (OTFS-SM) systems. The proposed system is evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations over high-mobility Rayleigh channels for various system parameters. Comparative throughput, spectral efficiency, and energy efficiency analyses are presented, and it is shown that OTFS-MBM outperforms traditional OTFS and OTFS-SM techniques. The proposed OTFS-MBM scheme stands out as a viable solution for sixth generation (6G) and next-generation wireless networks, enabling reliable communication in dynamic wireless environments.
A New OTFS-Based Index Modulation System for 6G and Beyond: OTFS-Based Code Index Modulation
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes the orthogonal time frequency space-based code index modulation (OTFS-CIM) scheme, a novel wireless communication system that combines OTFS modulation, which enhances error performance in high-mobility Rayleigh channels, with CIM technique, which improves spectral and energy efficiency, within a single-input multiple-output (SIMO) architecture. The proposed system is evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations for various system parameters. Results show that increasing the modulation order degrades performance, while more receive antennas enhance it. Comparative analyses of error performance, throughput, spectral efficiency, and energy saving demonstrate that OTFS-CIM outperforms traditional OTFS and OTFS-based spatial modulation (OTFS-SM) systems. Also, the proposed OTFS-CIM system outperforms benchmark systems in many performance metrics under high-mobility scenarios, making it a strong candidate for sixth generation (6G) and beyond.
Towards a Molecular Computer: Enabling Arithmetic Operations in Molecular Communication
Feb 27, 2025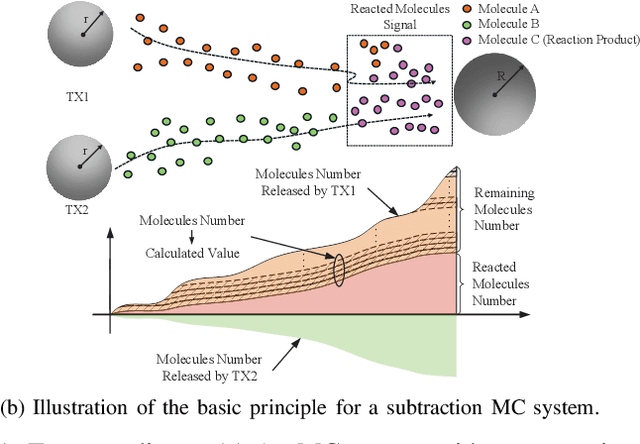
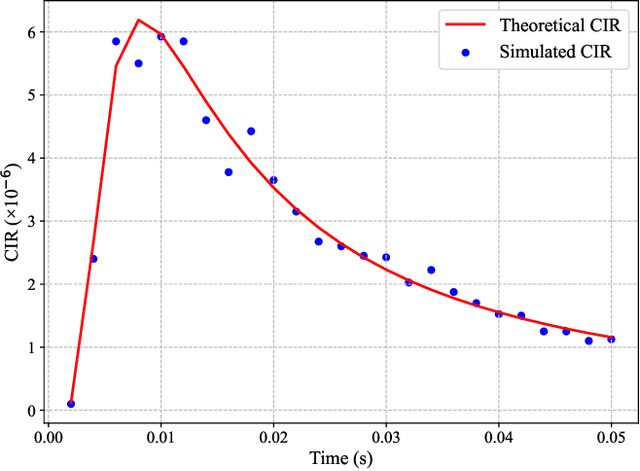
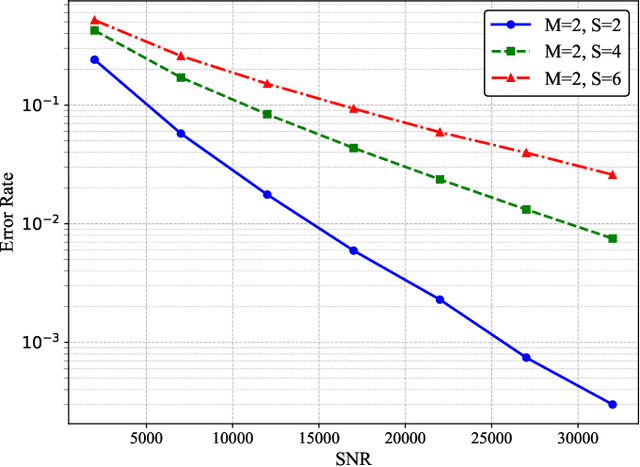
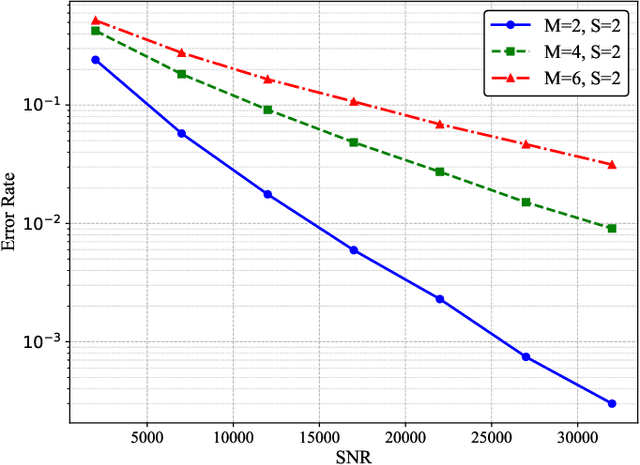
Abstract:In current molecular communication (MC) systems, performing computational operations at the nanoscale remains challenging, restricting their applicability in complex scenarios such as adaptive biochemical control and advanced nanoscale sensing. To overcome this challenge, this paper proposes a novel framework that seamlessly integrates computation into the molecular communication process. The system enables arithmetic operations, namely addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, by encoding numerical values into two types of molecules emitted by each transmitter to represent positive and negative values, respectively. Specifically, addition is achieved by transmitting non-reactive molecules, while subtraction employs reactive molecules that interact during propagation. The receiver demodulates molecular counts to directly compute the desired results. Theoretical analysis for an upper bound on the bit error rate (BER), and computational simulations confirm the system's robustness in performing complex arithmetic tasks. Compared to conventional MC methods, the proposed approach not only enables fundamental computational operations at the nanoscale but also lays the groundwork for intelligent, autonomous molecular networks.
AFDM-Enabled Integrated Sensing and Communication: Theoretical Framework and Pilot Design
Feb 20, 2025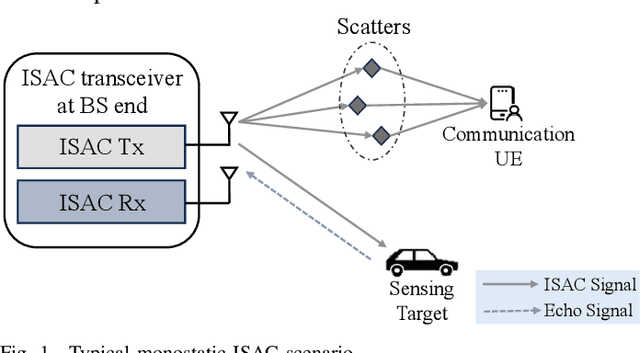
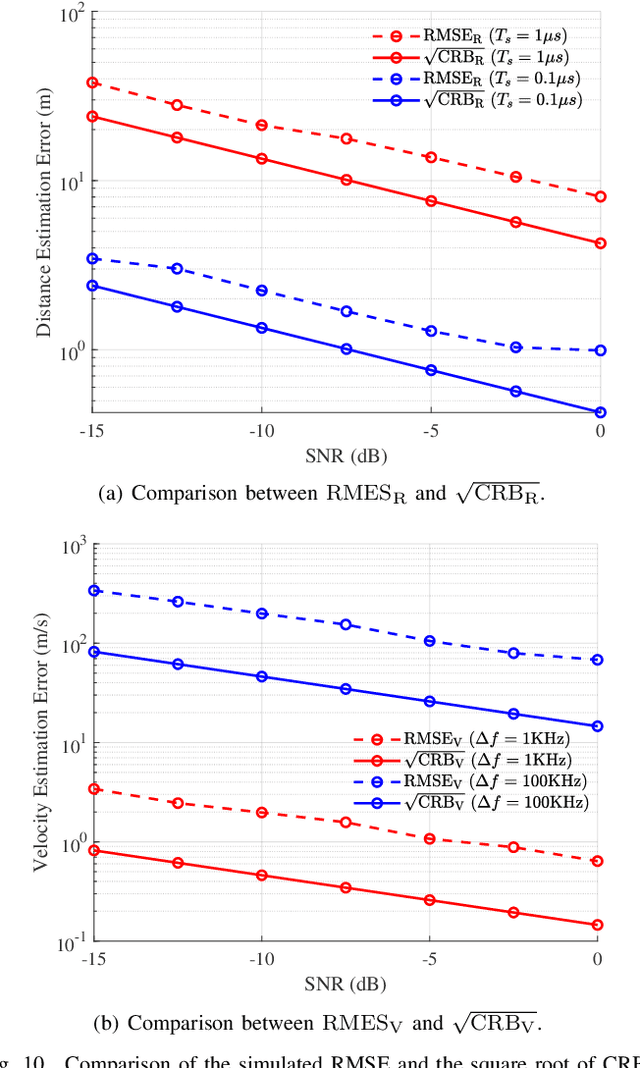
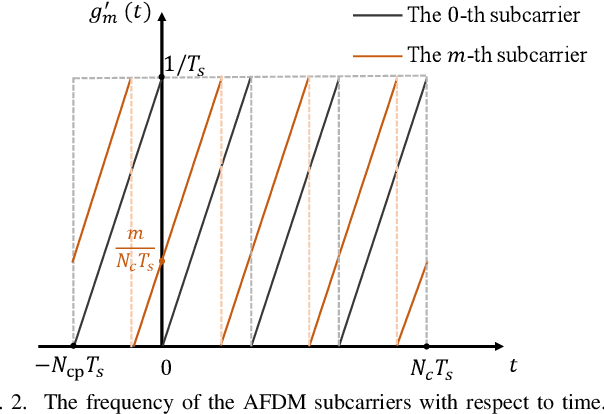
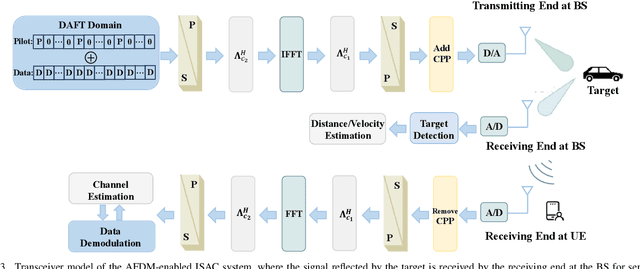
Abstract:The integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has been envisioned as one representative usage scenario of sixth-generation (6G) network. However, the unprecedented characteristics of 6G, especially the doubly dispersive channel, make classical ISAC waveforms rather challenging to guarantee a desirable performance level. The recently proposed affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) can attain full diversity even under doubly dispersive effects, thus becoming a competitive candidate for next-generation ISAC waveforms. Relevant investigations are still at an early stage, which involve only straightforward design lacking explicit theoretical analysis. This paper provides an in-depth investigation on AFDM waveform design for ISAC applications. Specifically, the closed-form Cr\'{a}mer-Rao bounds of target detection for AFDM are derived, followed by a demonstration on its merits over existing counterparts. Furthermore, we formulate the ambiguity function of the pilot-assisted AFDM waveform for the first time, revealing conditions for stable sensing performance. To further enhance both the communication and sensing performance of the AFDM waveform, we propose a novel pilot design by exploiting the characteristics of AFDM signals. The proposed design is analytically validated to be capable of optimizing the ambiguity function property and channel estimation accuracy simultaneously as well as overcoming the sensing and channel estimation range limitation originated from the pilot spacing. Numerical results have verified the superiority of the proposed pilot design in terms of dual-functional performance.
Predictive Target-to-User Association in Complex Scenarios via Hybrid-Field ISAC Signaling
Jan 18, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a novel and robust target-to-user (T2U) association framework to support reliable vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) networks that potentially operate within the hybrid field (near-field and far-field). To address the challenges posed by complex vehicle maneuvers and user association ambiguity, an interacting multiple-model filtering scheme is developed, which combines coordinated turn and constant velocity models for predictive beamforming. Building upon this foundation, a lightweight association scheme leverages user-specific integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) signaling while employing probabilistic data association to manage clutter measurements in dense traffic. Numerical results validate that the proposed framework significantly outperforms conventional methods in terms of both tracking accuracy and association reliability.
Linear Precoding Design for OTFS Systems in Time/Frequency Selective Fading Channels
Dec 31, 2024

Abstract:Even orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) has been shown as a promising modulation scheme for high mobility doubly-selective fading channels, its attainability of full diversity order in either time or frequency selective fading channels has not been clarified. By performing pairwise error probability (PEP) analysis, we observe that the original OTFS system can not always guarantee full exploitation of the embedded diversity in either time or frequency selective fading channels. To address this issue and further improve system performance, this work proposes linear precoding solutions based on algebraic number theory for OTFS systems over time and frequency selective fading channels, respectively. The proposed linear precoded OTFS systems can guarantee the maximal diversity and potential coding gains in time/frequency selective fading channels without any transmission rate loss and do not require the channel state information (CSI) at the transmitter. Simulation results are finally provided to illustrate the superiority of our proposed precoded OTFS over both the original unprecoded and the existing phase rotation OTFS systems in time/frequency selective fading channels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge