Jiahui Liang
Beyond Alignment: Expanding Reasoning Capacity via Manifold-Reshaping Policy Optimization
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has demonstrated remarkable success in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, recent studies question whether RL genuinely expands reasoning capacity or merely aligns existing latent capabilities, arguing that exploration remains confined within the pre-trained model's low-rank bias manifold. In this work, we challenge this accessibility boundary hypothesis by demonstrating that the latent reasoning space can be fundamentally expanded through targeted geometric interventions. We propose Manifold-Reshaping Policy Optimization (MRPO), a geometric framework designed to fundamentally restructure the inference space of LLMs. MRPO operates in two stages: first, we employ Spectral Orthogonal Exploration (SOE) to eject the policy initialization into the null space of the bias manifold; second, we integrate an Effective Rank regularization term into the policy optimization objective. This approach incentivizes the discovery and maintenance of high-dimensional reasoning trajectories against the entropy-reducing tendency of standard RL. Empirically, our 4B-parameter method achieves state-of-the-art performance on mathematical tasks, significantly outperforming larger models (e.g., Qwen3-32B) and expanding the capability boundary beyond standard GRPO. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/MRPO-D57B/
Relaying Signal When Monitoring Traffic: Double Use of Aerial Vehicles Towards Intelligent Low-Altitude Networking
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:In intelligent low-altitude networks, integrating monitoring tasks into communication unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can consume resources and increase handoff latency for communication links. To address this challenge, we propose a strategy that enables a "double use" of UAVs, unifying the monitoring and relay handoff functions into a single, efficient process. Our scheme, guided by an integrated sensing and communication framework, coordinates these multi-role UAVs through a proactive handoff network that fuses multi-view sensory data from aerial and ground vehicles. A lightweight vehicle inspection module and a two-stage training procedure are developed to ensure monitoring accuracy and collaborative efficiency. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of this integrated approach: it reduces communication outage probability by nearly 10% at a 200 Mbps requirement without compromising monitoring performance and maintains high resilience (86% achievable rate) even in the absence of multiple UAVs, outperforming traditional ground-based handoff schemes. Our code is available at the https://github.com/Jiahui-L/UAP.
Reducing Cognitive Load in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Mathematical Problem Solving: Decoupling Reasoning and Code Generation
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Current tool-integrated mathematical reasoning systems often adopt a single-agent paradigm, where one large language model handles problem reasoning, code generation, and code execution in an integrated workflow. While this design eases coordination, we hypothesize that it imposes cognitive load interference, as the agent must interleave long-horizon reasoning with precise program synthesis. We validate this hypothesis through a controlled comparison between a reasoning-only agent and a reasoning-plus-code agent, finding that the latter produces significantly fewer correct reasoning paths despite having tool-calling capabilities. To address this, we propose a dual-agent hybrid framework: a Reasoning Agent performs stepwise problem decomposition, and a Code Agent handles code generation and execution. Training combines imitation learning and reinforcement learning: the Code Agent receives strong rewards for matching intermediate ground-truth programs and weaker rewards for valid execution, while the Reasoning Agent is optimized chiefly via final-answer accuracy using advantage estimation to credit intermediate steps. This decoupled role design reduces cognitive interference and promotes stable reasoning-coding coordination.
Aligning Beam with Imbalanced Multi-modality: A Generative Federated Learning Approach
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:As vehicle intelligence advances, multi-modal sensing-aided communication emerges as a key enabler for reliable Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) connectivity through precise environmental characterization. As centralized learning may suffer from data privacy, model heterogeneity and communication overhead issues, federated learning (FL) has been introduced to support V2X. However, the practical deployment of FL faces critical challenges: model performance degradation from label imbalance across vehicles and training instability induced by modality disparities in sensor-equipped agents. To overcome these limitations, we propose a generative FL approach for beam selection (GFL4BS). Our solution features two core innovations: 1) An adaptive zero-shot multi-modal generator coupled with spectral-regularized loss functions to enhance the expressiveness of synthetic data compensating for both label scarcity and missing modalities; 2) A hybrid training paradigm integrating feature fusion with decentralized optimization to ensure training resilience while minimizing communication costs. Experimental evaluations demonstrate significant improvements over baselines achieving 16.2% higher accuracy than the current state-of-the-art under severe label imbalance conditions while maintaining over 70% successful rate even when two agents lack both LiDAR and RGB camera inputs.
OPERA:Operation-Pivoted Discrete Reasoning over Text
May 04, 2022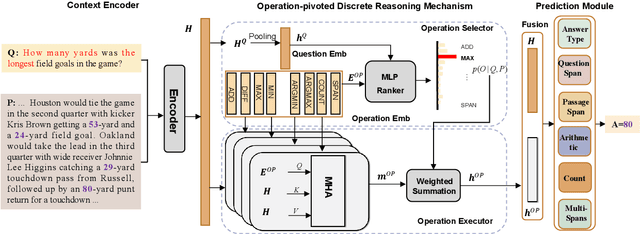
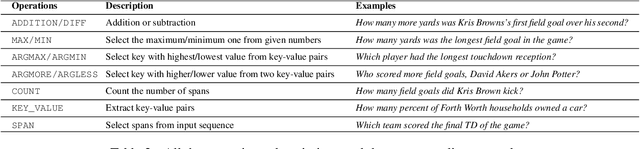
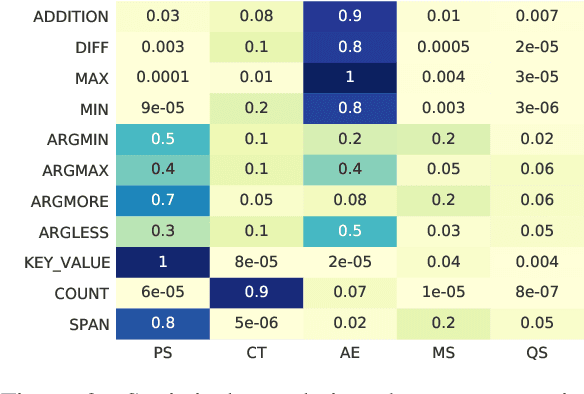

Abstract:Machine reading comprehension (MRC) that requires discrete reasoning involving symbolic operations, e.g., addition, sorting, and counting, is a challenging task. According to this nature, semantic parsing-based methods predict interpretable but complex logical forms. However, logical form generation is nontrivial and even a little perturbation in a logical form will lead to wrong answers. To alleviate this issue, multi-predictor -based methods are proposed to directly predict different types of answers and achieve improvements. However, they ignore the utilization of symbolic operations and encounter a lack of reasoning ability and interpretability. To inherit the advantages of these two types of methods, we propose OPERA, an operation-pivoted discrete reasoning framework, where lightweight symbolic operations (compared with logical forms) as neural modules are utilized to facilitate the reasoning ability and interpretability. Specifically, operations are first selected and then softly executed to simulate the answer reasoning procedure. Extensive experiments on both DROP and RACENum datasets show the reasoning ability of OPERA. Moreover, further analysis verifies its interpretability.
CUSTOM: Aspect-Oriented Product Summarization for E-Commerce
Aug 18, 2021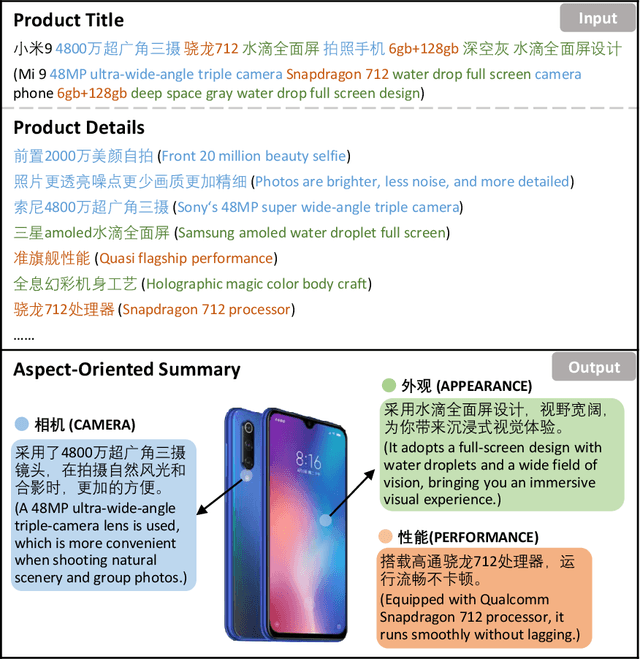
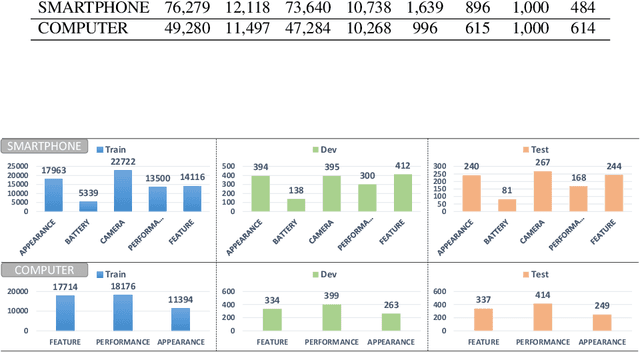
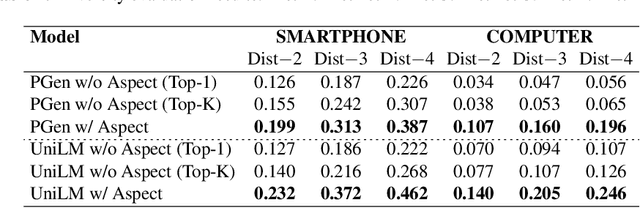
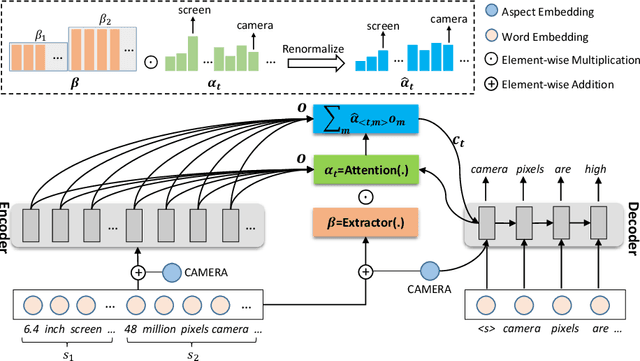
Abstract:Product summarization aims to automatically generate product descriptions, which is of great commercial potential. Considering the customer preferences on different product aspects, it would benefit from generating aspect-oriented customized summaries. However, conventional systems typically focus on providing general product summaries, which may miss the opportunity to match products with customer interests. To address the problem, we propose CUSTOM, aspect-oriented product summarization for e-commerce, which generates diverse and controllable summaries towards different product aspects. To support the study of CUSTOM and further this line of research, we construct two Chinese datasets, i.e., SMARTPHONE and COMPUTER, including 76,279 / 49,280 short summaries for 12,118 / 11,497 real-world commercial products, respectively. Furthermore, we introduce EXT, an extraction-enhanced generation framework for CUSTOM, where two famous sequence-to-sequence models are implemented in this paper. We conduct extensive experiments on the two proposed datasets for CUSTOM and show results of two famous baseline models and EXT, which indicates that EXT can generate diverse, high-quality, and consistent summaries.
EviDR: Evidence-Emphasized Discrete Reasoning for Reasoning Machine Reading Comprehension
Aug 18, 2021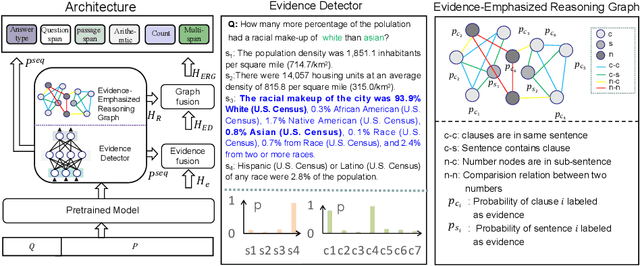
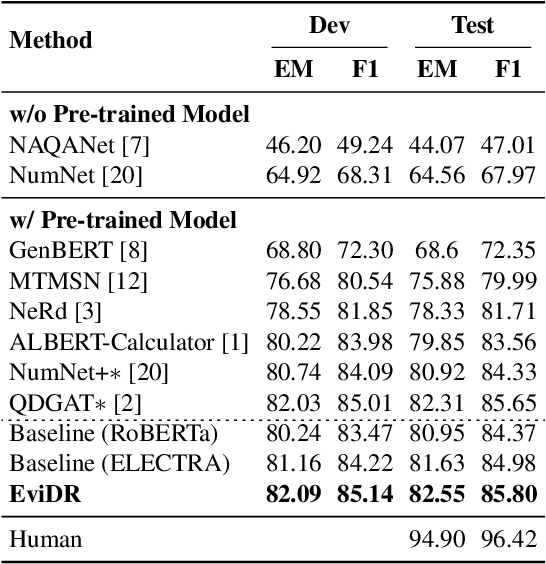
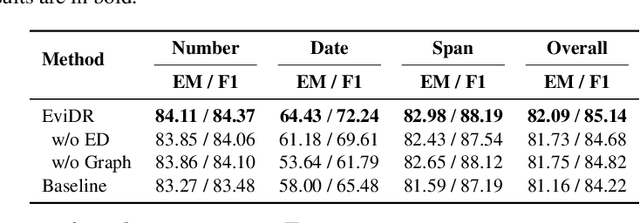
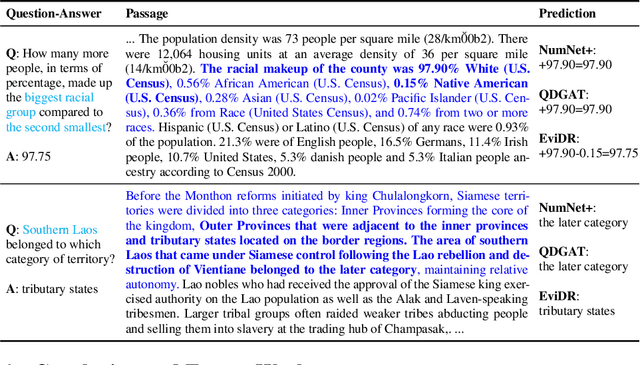
Abstract:Reasoning machine reading comprehension (R-MRC) aims to answer complex questions that require discrete reasoning based on text. To support discrete reasoning, evidence, typically the concise textual fragments that describe question-related facts, including topic entities and attribute values, are crucial clues from question to answer. However, previous end-to-end methods that achieve state-of-the-art performance rarely solve the problem by paying enough emphasis on the modeling of evidence, missing the opportunity to further improve the model's reasoning ability for R-MRC. To alleviate the above issue, in this paper, we propose an evidence-emphasized discrete reasoning approach (EviDR), in which sentence and clause level evidence is first detected based on distant supervision, and then used to drive a reasoning module implemented with a relational heterogeneous graph convolutional network to derive answers. Extensive experiments are conducted on DROP (discrete reasoning over paragraphs) dataset, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach. In addition, qualitative analysis verifies the capability of the proposed evidence-emphasized discrete reasoning for R-MRC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge