Haipeng Sun
MoNET: Tackle State Momentum via Noise-Enhanced Training for Dialogue State Tracking
Nov 11, 2022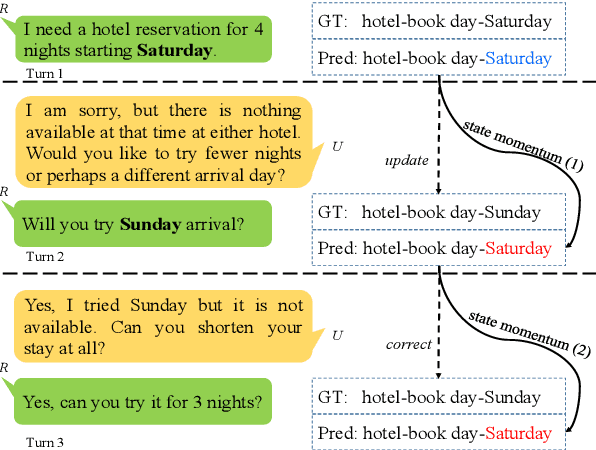
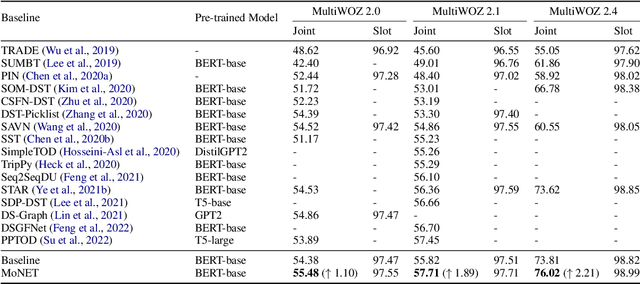
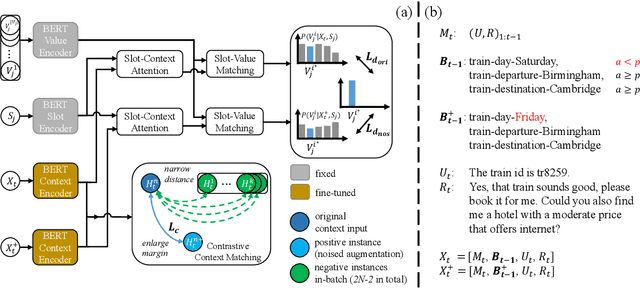
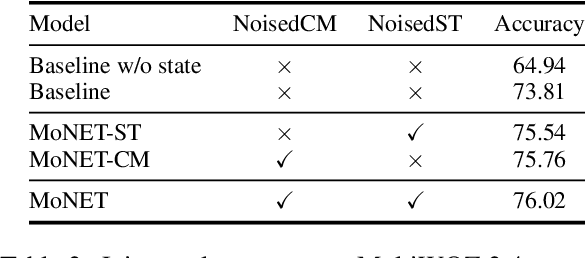
Abstract:Dialogue state tracking (DST) aims to convert the dialogue history into dialogue states which consist of slot-value pairs. As condensed structural information memorizing all history information, the dialogue state in the last turn is typically adopted as the input for predicting the current state by DST models. However, these models tend to keep the predicted slot values unchanged, which is defined as state momentum in this paper. Specifically, the models struggle to update slot values that need to be changed and correct wrongly predicted slot values in the last turn. To this end, we propose MoNET to tackle state momentum via noise-enhanced training. First, the previous state of each turn in the training data is noised via replacing some of its slot values. Then, the noised previous state is used as the input to learn to predict the current state, improving the model's ability to update and correct slot values. Furthermore, a contrastive context matching framework is designed to narrow the representation distance between a state and its corresponding noised variant, which reduces the impact of noised state and makes the model better understand the dialogue history. Experimental results on MultiWOZ datasets show that MoNET outperforms previous DST methods. Ablations and analysis verify the effectiveness of MoNET in alleviating state momentum and improving anti-noise ability.
Mars: Semantic-aware Contrastive Learning for End-to-End Task-Oriented Dialog
Oct 17, 2022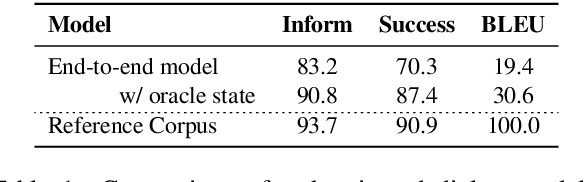
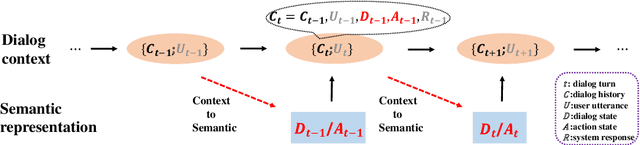
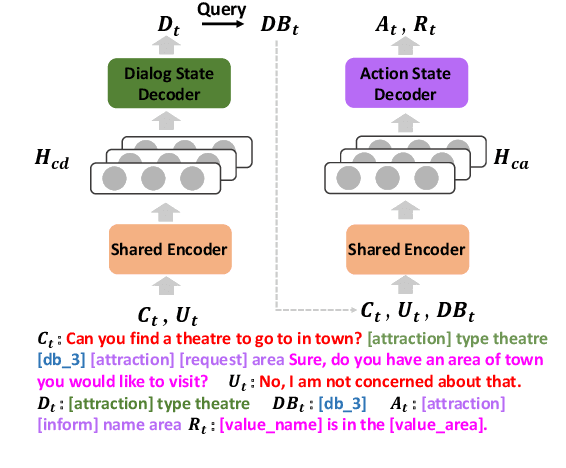
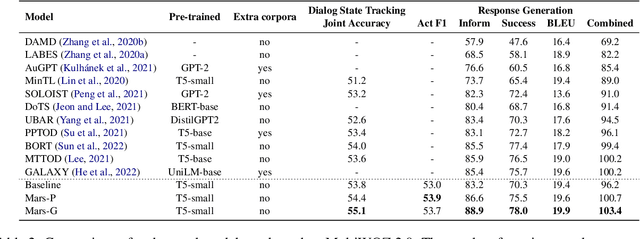
Abstract:Traditional end-to-end task-oriented dialog systems first convert dialog context into dialog state and action state, before generating the system response. In this paper, we first empirically investigate the relationship between dialog/action state and generated system response. The empirical exploration shows that the system response performance is significantly affected by the quality of dialog state and action state. Based on these findings, we argue that enhancing the relationship modeling between dialog context and dialog/action state is beneficial to improving the quality of the dialog state and action state, which further improves the generated response quality. Therefore, we propose Mars, an end-to-end task-oriented dialog system with semantic-aware contrastive learning strategies to model the relationship between dialog context and dialog/action state. Empirical results show our proposed Mars achieves state-of-the-art performance on the MultiWOZ 2.0, CamRest676, and CrossWOZ.
CSS: Combining Self-training and Self-supervised Learning for Few-shot Dialogue State Tracking
Oct 11, 2022
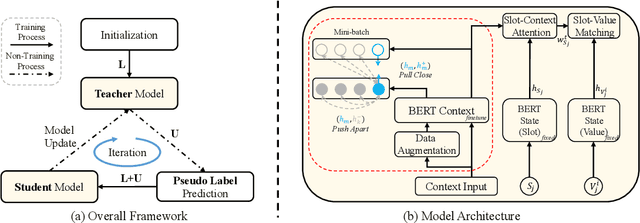
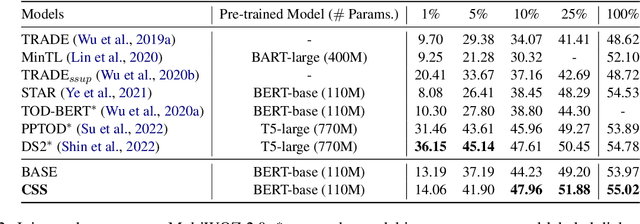
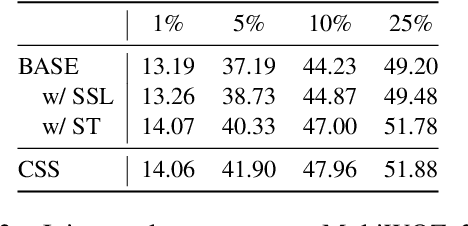
Abstract:Few-shot dialogue state tracking (DST) is a realistic problem that trains the DST model with limited labeled data. Existing few-shot methods mainly transfer knowledge learned from external labeled dialogue data (e.g., from question answering, dialogue summarization, machine reading comprehension tasks, etc.) into DST, whereas collecting a large amount of external labeled data is laborious, and the external data may not effectively contribute to the DST-specific task. In this paper, we propose a few-shot DST framework called CSS, which Combines Self-training and Self-supervised learning methods. The unlabeled data of the DST task is incorporated into the self-training iterations, where the pseudo labels are predicted by a DST model trained on limited labeled data in advance. Besides, a contrastive self-supervised method is used to learn better representations, where the data is augmented by the dropout operation to train the model. Experimental results on the MultiWOZ dataset show that our proposed CSS achieves competitive performance in several few-shot scenarios.
BORT: Back and Denoising Reconstruction for End-to-End Task-Oriented Dialog
May 05, 2022

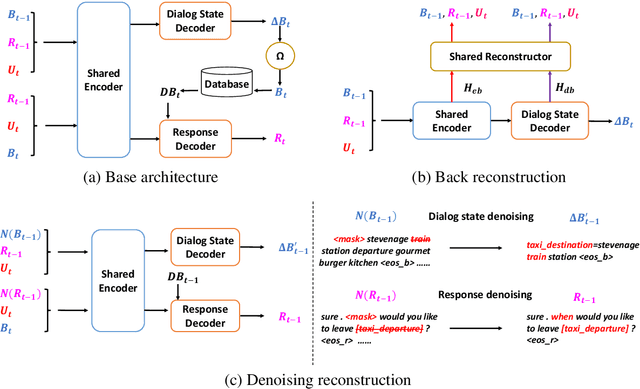

Abstract:A typical end-to-end task-oriented dialog system transfers context into dialog state, and upon which generates a response, which usually faces the problem of error propagation from both previously generated inaccurate dialog states and responses, especially in low-resource scenarios. To alleviate these issues, we propose BORT, a back and denoising reconstruction approach for end-to-end task-oriented dialog system. Squarely, to improve the accuracy of dialog states, back reconstruction is used to reconstruct the original input context from the generated dialog states since inaccurate dialog states cannot recover the corresponding input context. To enhance the denoising capability of the model to reduce the impact of error propagation, denoising reconstruction is used to reconstruct the corrupted dialog state and response. Extensive experiments conducted on MultiWOZ 2.0 and CamRest676 show the effectiveness of BORT. Furthermore, BORT demonstrates its advanced capabilities in the zero-shot domain and low-resource scenarios.
OPERA:Operation-Pivoted Discrete Reasoning over Text
May 04, 2022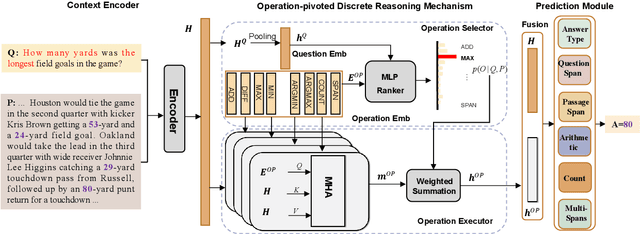
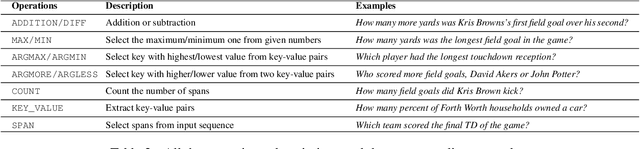
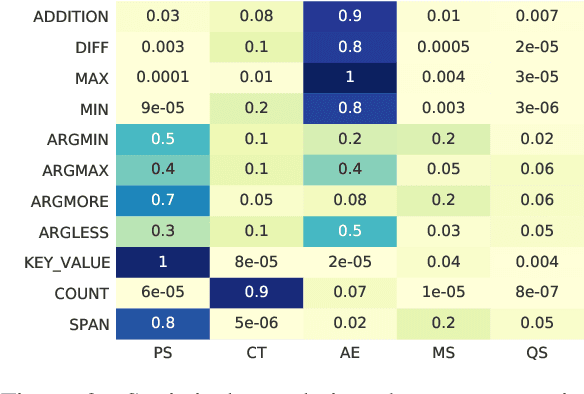

Abstract:Machine reading comprehension (MRC) that requires discrete reasoning involving symbolic operations, e.g., addition, sorting, and counting, is a challenging task. According to this nature, semantic parsing-based methods predict interpretable but complex logical forms. However, logical form generation is nontrivial and even a little perturbation in a logical form will lead to wrong answers. To alleviate this issue, multi-predictor -based methods are proposed to directly predict different types of answers and achieve improvements. However, they ignore the utilization of symbolic operations and encounter a lack of reasoning ability and interpretability. To inherit the advantages of these two types of methods, we propose OPERA, an operation-pivoted discrete reasoning framework, where lightweight symbolic operations (compared with logical forms) as neural modules are utilized to facilitate the reasoning ability and interpretability. Specifically, operations are first selected and then softly executed to simulate the answer reasoning procedure. Extensive experiments on both DROP and RACENum datasets show the reasoning ability of OPERA. Moreover, further analysis verifies its interpretability.
EviDR: Evidence-Emphasized Discrete Reasoning for Reasoning Machine Reading Comprehension
Aug 18, 2021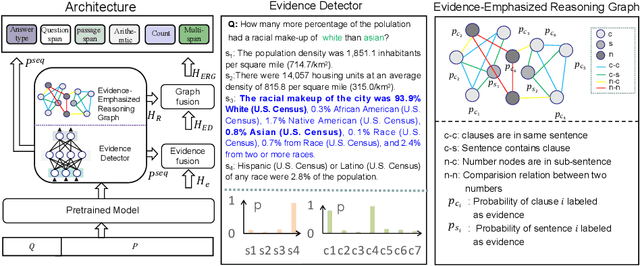
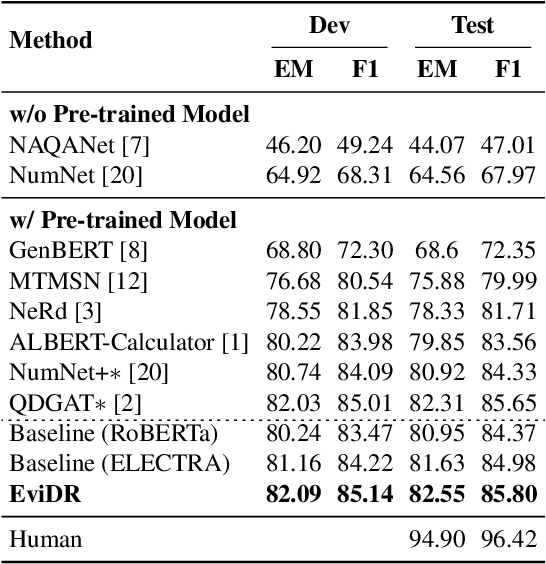
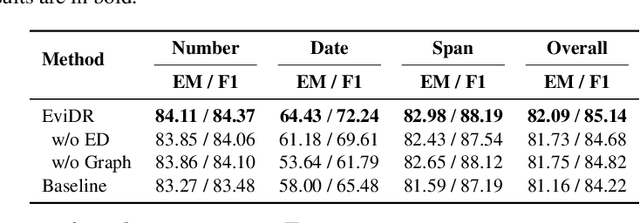
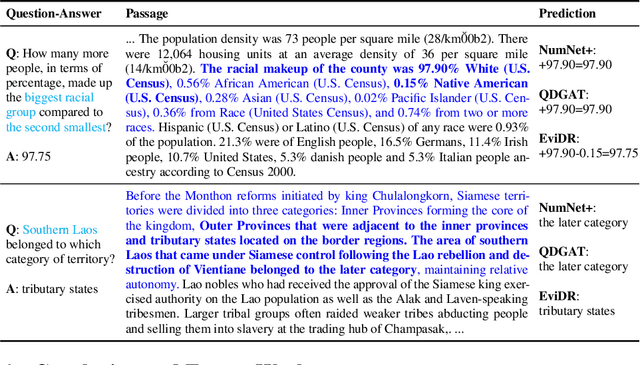
Abstract:Reasoning machine reading comprehension (R-MRC) aims to answer complex questions that require discrete reasoning based on text. To support discrete reasoning, evidence, typically the concise textual fragments that describe question-related facts, including topic entities and attribute values, are crucial clues from question to answer. However, previous end-to-end methods that achieve state-of-the-art performance rarely solve the problem by paying enough emphasis on the modeling of evidence, missing the opportunity to further improve the model's reasoning ability for R-MRC. To alleviate the above issue, in this paper, we propose an evidence-emphasized discrete reasoning approach (EviDR), in which sentence and clause level evidence is first detected based on distant supervision, and then used to drive a reasoning module implemented with a relational heterogeneous graph convolutional network to derive answers. Extensive experiments are conducted on DROP (discrete reasoning over paragraphs) dataset, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach. In addition, qualitative analysis verifies the capability of the proposed evidence-emphasized discrete reasoning for R-MRC.
Knowledge Distillation for Multilingual Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation
Apr 21, 2020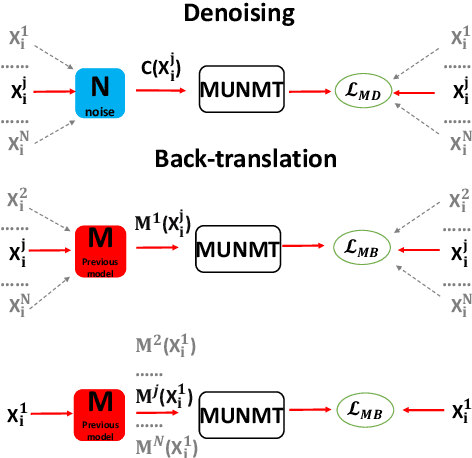


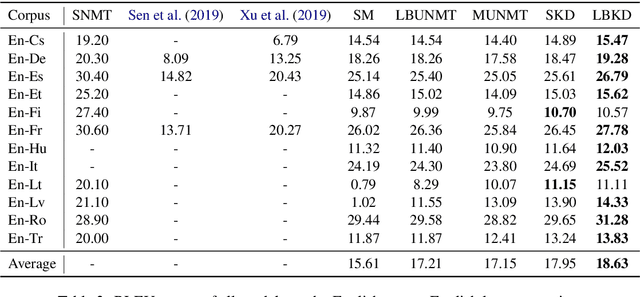
Abstract:Unsupervised neural machine translation (UNMT) has recently achieved remarkable results for several language pairs. However, it can only translate between a single language pair and cannot produce translation results for multiple language pairs at the same time. That is, research on multilingual UNMT has been limited. In this paper, we empirically introduce a simple method to translate between thirteen languages using a single encoder and a single decoder, making use of multilingual data to improve UNMT for all language pairs. On the basis of the empirical findings, we propose two knowledge distillation methods to further enhance multilingual UNMT performance. Our experiments on a dataset with English translated to and from twelve other languages (including three language families and six language branches) show remarkable results, surpassing strong unsupervised individual baselines while achieving promising performance between non-English language pairs in zero-shot translation scenarios and alleviating poor performance in low-resource language pairs.
Self-Training for Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation in Unbalanced Training Data Scenarios
Apr 09, 2020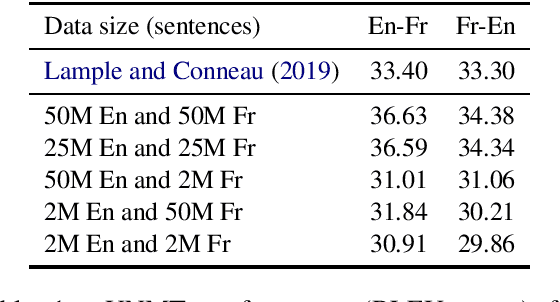

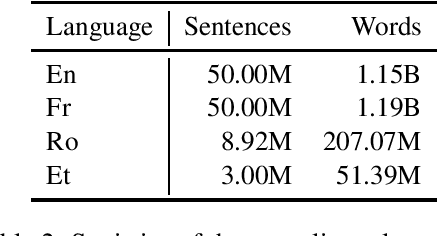
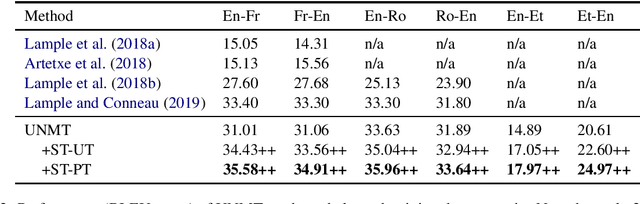
Abstract:Unsupervised neural machine translation (UNMT) that relies solely on massive monolingual corpora has achieved remarkable results in several translation tasks. However, in real-world scenarios, massive monolingual corpora do not exist for some extremely low-resource languages such as Estonian, and UNMT systems usually perform poorly when there is not an adequate training corpus for one language. In this paper, we first define and analyze the unbalanced training data scenario for UNMT. Based on this scenario, we propose UNMT self-training mechanisms to train a robust UNMT system and improve its performance in this case. Experimental results on several language pairs show that the proposed methods substantially outperform conventional UNMT systems.
Robust Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation with Adversarial Training
Feb 28, 2020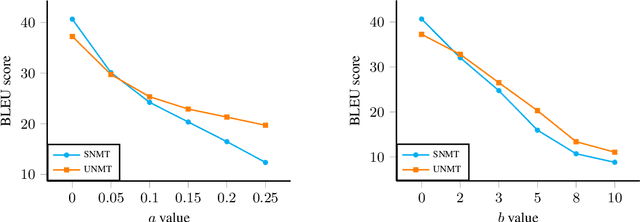
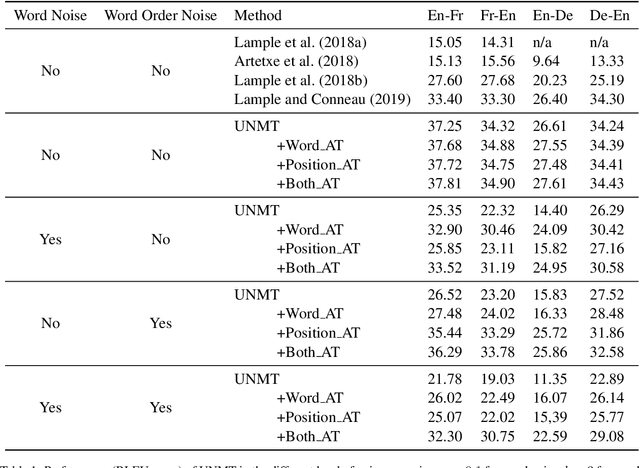

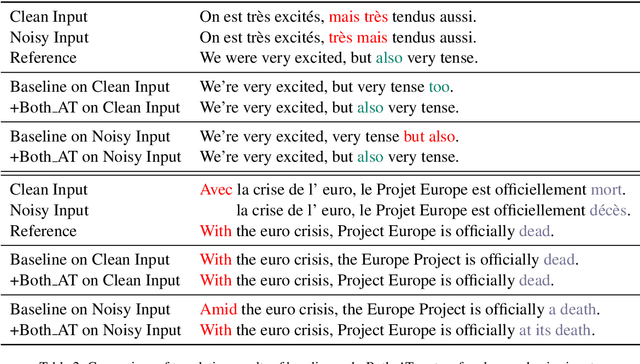
Abstract:Unsupervised neural machine translation (UNMT) has recently attracted great interest in the machine translation community, achieving only slightly worse results than supervised neural machine translation. However, in real-world scenarios, there usually exists minor noise in the input sentence and the neural translation system is sensitive to the small perturbations in the input, leading to poor performance. In this paper, we first define two types of noises and empirically show the effect of these noisy data on UNMT performance. Moreover, we propose adversarial training methods to improve the robustness of UNMT in the noisy scenario. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first work to explore the robustness of UNMT. Experimental results on several language pairs show that our proposed methods substantially outperform conventional UNMT systems in the noisy scenario.
An Empirical Study of Domain Adaptation for Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation
Aug 26, 2019
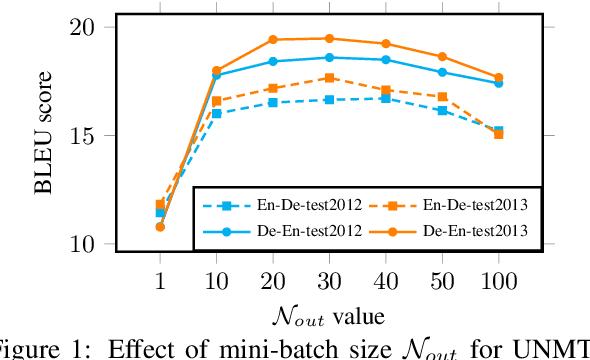


Abstract:Domain adaptation methods have been well-studied in supervised neural machine translation (NMT). However, domain adaptation methods for unsupervised neural machine translation (UNMT) have not been well-studied although UNMT has recently achieved remarkable results in some specific domains for several language pairs. Besides the inconsistent domains between training data and test data for supervised NMT, there sometimes exists an inconsistent domain between two monolingual training data for UNMT. In this work, we empirically show different scenarios for unsupervised domain-specific neural machine translation. Based on these scenarios, we propose several potential solutions to improve the performances of domain-specific UNMT systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge