Xiaodong He
Department of R and D, UnionString Technology Co. Ltd
JoyAvatar: Unlocking Highly Expressive Avatars via Harmonized Text-Audio Conditioning
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Existing video avatar models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in scenarios such as talking, public speaking, and singing. However, the majority of these methods exhibit limited alignment with respect to text instructions, particularly when the prompts involve complex elements including large full-body movement, dynamic camera trajectory, background transitions, or human-object interactions. To break out this limitation, we present JoyAvatar, a framework capable of generating long duration avatar videos, featuring two key technical innovations. Firstly, we introduce a twin-teacher enhanced training algorithm that enables the model to transfer inherent text-controllability from the foundation model while simultaneously learning audio-visual synchronization. Secondly, during training, we dynamically modulate the strength of multi-modal conditions (e.g., audio and text) based on the distinct denoising timestep, aiming to mitigate conflicts between the heterogeneous conditioning signals. These two key designs serve to substantially expand the avatar model's capacity to generate natural, temporally coherent full-body motions and dynamic camera movements as well as preserve the basic avatar capabilities, such as accurate lip-sync and identity consistency. GSB evaluation results demonstrate that our JoyAvatar model outperforms the state-of-the-art models such as Omnihuman-1.5 and KlingAvatar 2.0. Moreover, our approach enables complex applications including multi-person dialogues and non-human subjects role-playing. Some video samples are provided on https://joyavatar.github.io/.
AdaMorph: Unified Motion Retargeting via Embodiment-Aware Adaptive Transformers
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Retargeting human motion to heterogeneous robots is a fundamental challenge in robotics, primarily due to the severe kinematic and dynamic discrepancies between varying embodiments. Existing solutions typically resort to training embodiment-specific models, which scales poorly and fails to exploit shared motion semantics. To address this, we present AdaMorph, a unified neural retargeting framework that enables a single model to adapt human motion to diverse robot morphologies. Our approach treats retargeting as a conditional generation task. We map human motion into a morphology-agnostic latent intent space and utilize a dual-purpose prompting mechanism to condition the generation. Instead of simple input concatenation, we leverage Adaptive Layer Normalization (AdaLN) to dynamically modulate the decoder's feature space based on embodiment constraints. Furthermore, we enforce physical plausibility through a curriculum-based training objective that ensures orientation and trajectory consistency via integration. Experimental results on 12 distinct humanoid robots demonstrate that AdaMorph effectively unifies control across heterogeneous topologies, exhibiting strong zero-shot generalization to unseen complex motions while preserving the dynamic essence of the source behaviors.
JoyVoice: Long-Context Conditioning for Anthropomorphic Multi-Speaker Conversational Synthesis
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Large speech generation models are evolving from single-speaker, short sentence synthesis to multi-speaker, long conversation geneartion. Current long-form speech generation models are predominately constrained to dyadic, turn-based interactions. To address this, we introduce JoyVoice, a novel anthropomorphic foundation model designed for flexible, boundary-free synthesis of up to eight speakers. Unlike conventional cascaded systems, JoyVoice employs a unified E2E-Transformer-DiT architecture that utilizes autoregressive hidden representations directly for diffusion inputs, enabling holistic end-to-end optimization. We further propose a MM-Tokenizer operating at a low bitrate of 12.5 Hz, which integrates multitask semantic and MMSE losses to effectively model both semantic and acoustic information. Additionally, the model incorporates robust text front-end processing via large-scale data perturbation. Experiments show that JoyVoice achieves state-of-the-art results in multilingual generation (Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean) and zero-shot voice cloning. JoyVoice achieves top-tier results on both the Seed-TTS-Eval Benchmark and multi-speaker long-form conversational voice cloning tasks, demonstrating superior audio quality and generalization. It achieves significant improvements in prosodic continuity for long-form speech, rhythm richness in multi-speaker conversations, paralinguistic naturalness, besides superior intelligibility. We encourage readers to listen to the demo at https://jea-speech.github.io/JoyVoice
JoyAvatar: Real-time and Infinite Audio-Driven Avatar Generation with Autoregressive Diffusion
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Existing DiT-based audio-driven avatar generation methods have achieved considerable progress, yet their broader application is constrained by limitations such as high computational overhead and the inability to synthesize long-duration videos. Autoregressive methods address this problem by applying block-wise autoregressive diffusion methods. However, these methods suffer from the problem of error accumulation and quality degradation. To address this, we propose JoyAvatar, an audio-driven autoregressive model capable of real-time inference and infinite-length video generation with the following contributions: (1) Progressive Step Bootstrapping (PSB), which allocates more denoising steps to initial frames to stabilize generation and reduce error accumulation; (2) Motion Condition Injection (MCI), enhancing temporal coherence by injecting noise-corrupted previous frames as motion condition; and (3) Unbounded RoPE via Cache-Resetting (URCR), enabling infinite-length generation through dynamic positional encoding. Our 1.3B-parameter causal model achieves 16 FPS on a single GPU and achieves competitive results in visual quality, temporal consistency, and lip synchronization.
Efficient Reasoning via Thought-Training and Thought-Free Inference
Nov 05, 2025
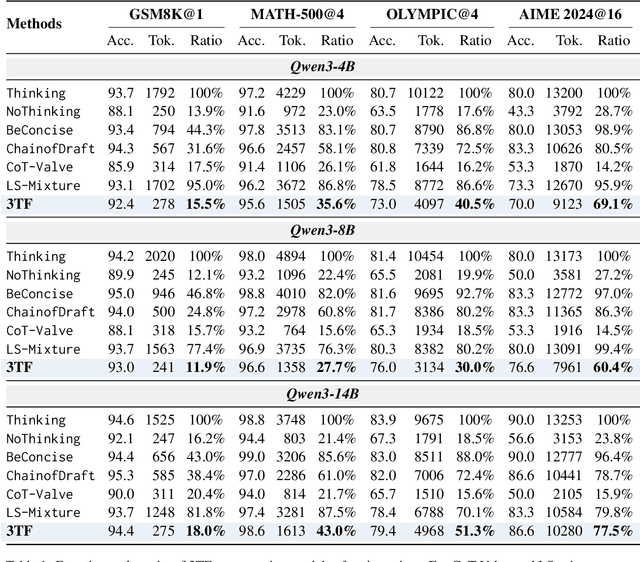
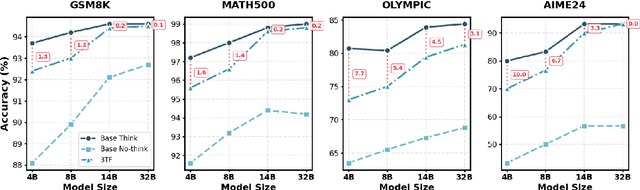
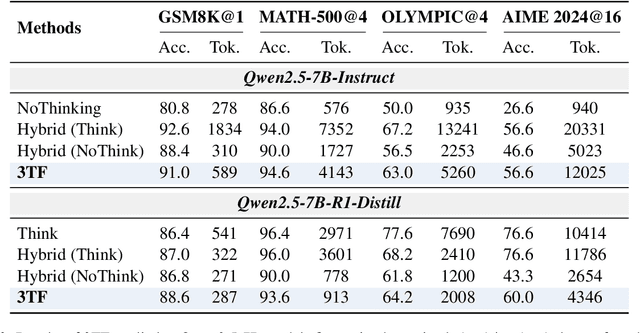
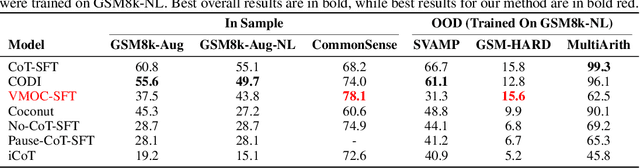
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have leveraged explicit Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting to improve reasoning accuracy. However, most existing methods primarily compress verbose reasoning outputs. These Long-to-Short transformations aim to improve efficiency, but still rely on explicit reasoning during inference. In this work, we introduce \textbf{3TF} (\textbf{T}hought-\textbf{T}raining and \textbf{T}hought-\textbf{F}ree inference), a framework for efficient reasoning that takes a Short-to-Long perspective. We first train a hybrid model that can operate in both reasoning and non-reasoning modes, and then further train it on CoT-annotated data to internalize structured reasoning, while enforcing concise, thought-free outputs at inference time using the no-reasoning mode. Unlike compression-based approaches, 3TF improves the reasoning quality of non-reasoning outputs, enabling models to perform rich internal reasoning implicitly while keeping external outputs short. Empirically, 3TF-trained models obtain large improvements on reasoning benchmarks under thought-free inference, demonstrating that high quality reasoning can be learned and executed implicitly without explicit step-by-step generation.
PAC: Pronunciation-Aware Contextualized Large Language Model-based Automatic Speech Recognition
Sep 16, 2025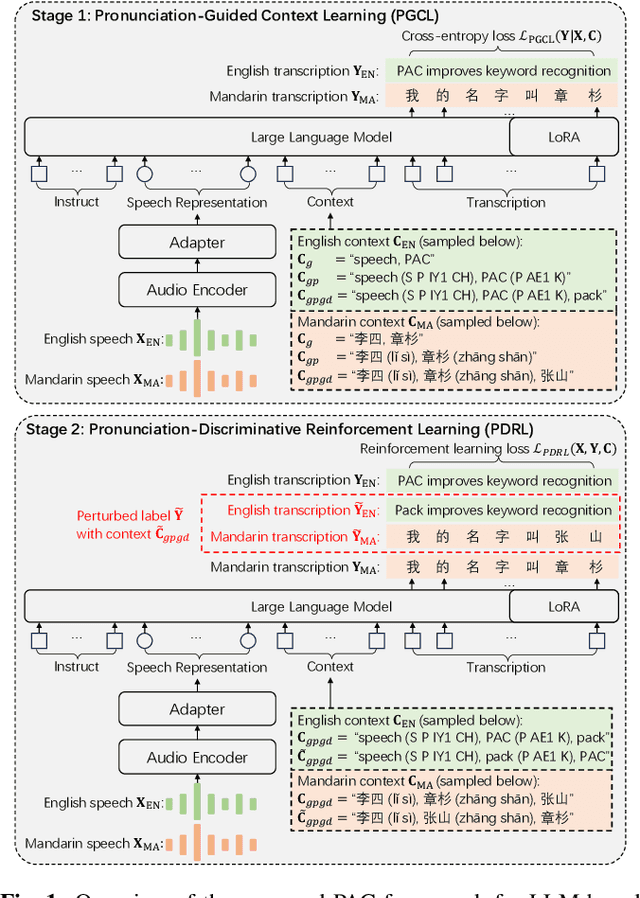
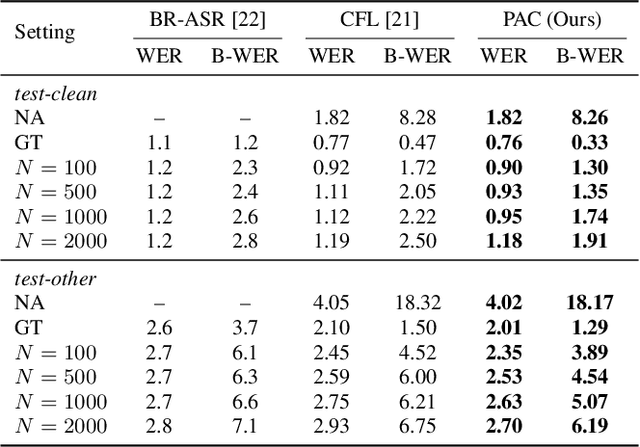
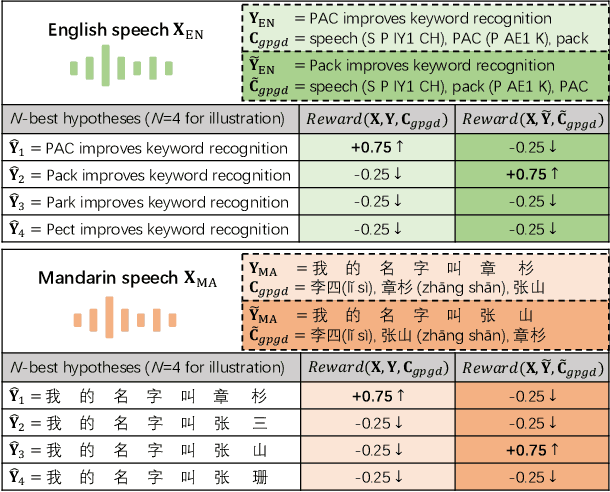
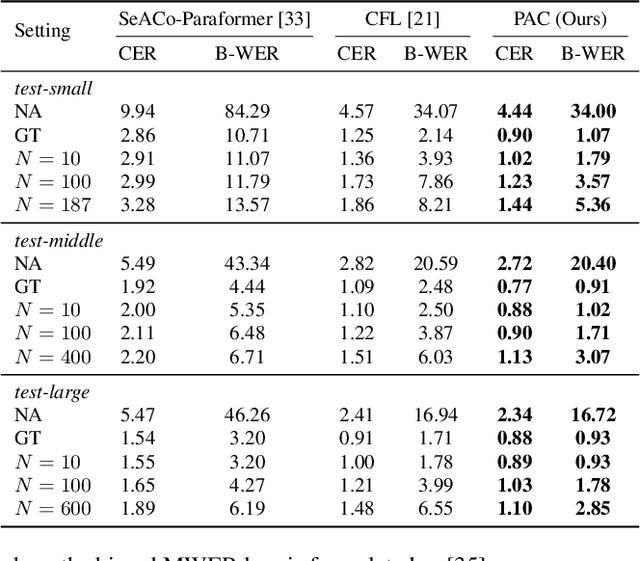
Abstract:This paper presents a Pronunciation-Aware Contextualized (PAC) framework to address two key challenges in Large Language Model (LLM)-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems: effective pronunciation modeling and robust homophone discrimination. Both are essential for raw or long-tail word recognition. The proposed approach adopts a two-stage learning paradigm. First, we introduce a pronunciation-guided context learning method. It employs an interleaved grapheme-phoneme context modeling strategy that incorporates grapheme-only distractors, encouraging the model to leverage phonemic cues for accurate recognition. Then, we propose a pronunciation-discriminative reinforcement learning method with perturbed label sampling to further enhance the model\'s ability to distinguish contextualized homophones. Experimental results on the public English Librispeech and Mandarin AISHELL-1 datasets indicate that PAC: (1) reduces relative Word Error Rate (WER) by 30.2% and 53.8% compared to pre-trained LLM-based ASR models, and (2) achieves 31.8% and 60.5% relative reductions in biased WER for long-tail words compared to strong baselines, respectively.
ChartMaster: Advancing Chart-to-Code Generation with Real-World Charts and Chart Similarity Reinforcement Learning
Aug 25, 2025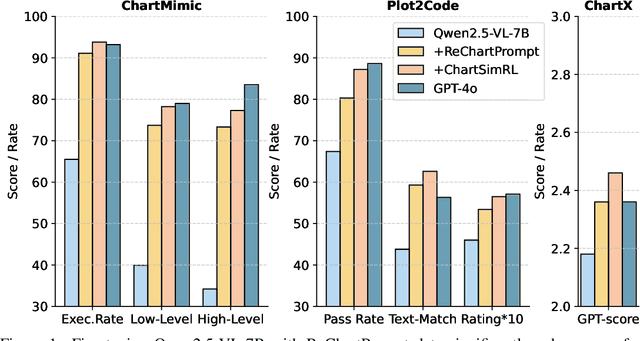

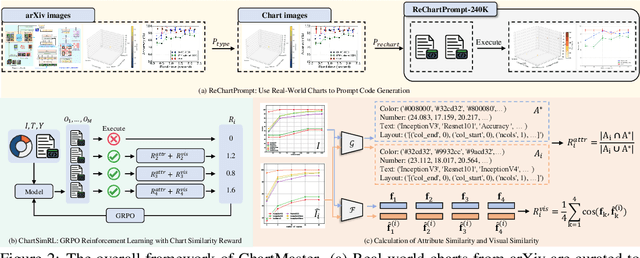

Abstract:The chart-to-code generation task requires MLLMs to convert chart images into executable code. This task faces two major challenges: limited data diversity and insufficient maintenance of visual consistency between generated and original charts during training. Existing datasets mainly rely on seed data to prompt GPT models for code generation, resulting in homogeneous samples. To address this, we propose ReChartPrompt, which leverages real-world, human-designed charts from arXiv papers as prompts instead of synthetic seeds. Using the diverse styles and rich content of arXiv charts, we construct ReChartPrompt-240K, a large-scale and highly diverse dataset. Another challenge is that although SFT effectively improve code understanding, it often fails to ensure that generated charts are visually consistent with the originals. To address this, we propose ChartSimRL, a GRPO-based reinforcement learning algorithm guided by a novel chart similarity reward. This reward consists of attribute similarity, which measures the overlap of chart attributes such as layout and color between the generated and original charts, and visual similarity, which assesses similarity in texture and other overall visual features using convolutional neural networks. Unlike traditional text-based rewards such as accuracy or format rewards, our reward considers the multimodal nature of the chart-to-code task and effectively enhances the model's ability to accurately reproduce charts. By integrating ReChartPrompt and ChartSimRL, we develop the ChartMaster model, which achieves state-of-the-art results among 7B-parameter models and even rivals GPT-4o on various chart-to-code generation benchmarks. All resources are available at https://github.com/WentaoTan/ChartMaster.
Learning Temporal Abstractions via Variational Homomorphisms in Option-Induced Abstract MDPs
Jul 24, 2025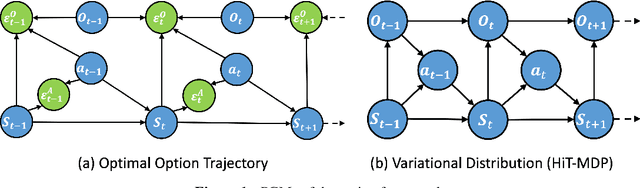
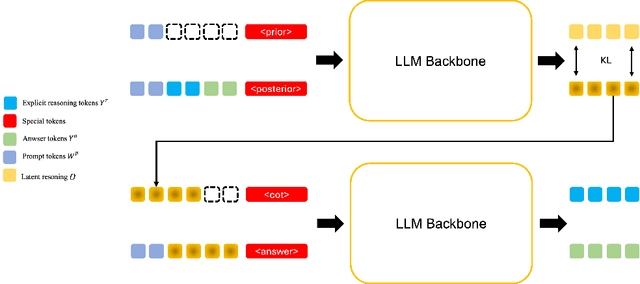
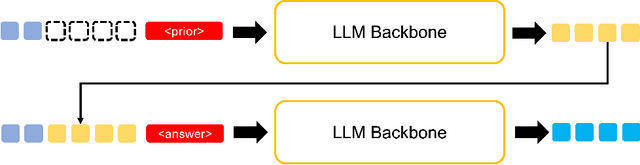
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable reasoning ability through explicit Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting, but generating these step-by-step textual explanations is computationally expensive and slow. To overcome this, we aim to develop a framework for efficient, implicit reasoning, where the model "thinks" in a latent space without generating explicit text for every step. We propose that these latent thoughts can be modeled as temporally-extended abstract actions, or options, within a hierarchical reinforcement learning framework. To effectively learn a diverse library of options as latent embeddings, we first introduce the Variational Markovian Option Critic (VMOC), an off-policy algorithm that uses variational inference within the HiT-MDP framework. To provide a rigorous foundation for using these options as an abstract reasoning space, we extend the theory of continuous MDP homomorphisms. This proves that learning a policy in the simplified, abstract latent space, for which VMOC is suited, preserves the optimality of the solution to the original, complex problem. Finally, we propose a cold-start procedure that leverages supervised fine-tuning (SFT) data to distill human reasoning demonstrations into this latent option space, providing a rich initialization for the model's reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves strong performance on complex logical reasoning benchmarks and challenging locomotion tasks, validating our framework as a principled method for learning abstract skills for both language and control.
Object-Focus Actor for Data-efficient Robot Generalization Dexterous Manipulation
May 21, 2025Abstract:Robot manipulation learning from human demonstrations offers a rapid means to acquire skills but often lacks generalization across diverse scenes and object placements. This limitation hinders real-world applications, particularly in complex tasks requiring dexterous manipulation. Vision-Language-Action (VLA) paradigm leverages large-scale data to enhance generalization. However, due to data scarcity, VLA's performance remains limited. In this work, we introduce Object-Focus Actor (OFA), a novel, data-efficient approach for generalized dexterous manipulation. OFA exploits the consistent end trajectories observed in dexterous manipulation tasks, allowing for efficient policy training. Our method employs a hierarchical pipeline: object perception and pose estimation, pre-manipulation pose arrival and OFA policy execution. This process ensures that the manipulation is focused and efficient, even in varied backgrounds and positional layout. Comprehensive real-world experiments across seven tasks demonstrate that OFA significantly outperforms baseline methods in both positional and background generalization tests. Notably, OFA achieves robust performance with only 10 demonstrations, highlighting its data efficiency.
HOIGen-1M: A Large-scale Dataset for Human-Object Interaction Video Generation
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Text-to-video (T2V) generation has made tremendous progress in generating complicated scenes based on texts. However, human-object interaction (HOI) often cannot be precisely generated by current T2V models due to the lack of large-scale videos with accurate captions for HOI. To address this issue, we introduce HOIGen-1M, the first largescale dataset for HOI Generation, consisting of over one million high-quality videos collected from diverse sources. In particular, to guarantee the high quality of videos, we first design an efficient framework to automatically curate HOI videos using the powerful multimodal large language models (MLLMs), and then the videos are further cleaned by human annotators. Moreover, to obtain accurate textual captions for HOI videos, we design a novel video description method based on a Mixture-of-Multimodal-Experts (MoME) strategy that not only generates expressive captions but also eliminates the hallucination by individual MLLM. Furthermore, due to the lack of an evaluation framework for generated HOI videos, we propose two new metrics to assess the quality of generated videos in a coarse-to-fine manner. Extensive experiments reveal that current T2V models struggle to generate high-quality HOI videos and confirm that our HOIGen-1M dataset is instrumental for improving HOI video generation. Project webpage is available at https://liuqi-creat.github.io/HOIGen.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge