Bo Peng
AgenticTagger: Structured Item Representation for Recommendation with LLM Agents
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:High-quality representations are a core requirement for effective recommendation. In this work, we study the problem of LLM-based descriptor generation, i.e., keyphrase-like natural language item representation generation frameworks with minimal constraints on downstream applications. We propose AgenticTagger, a framework that queries LLMs for representing items with sequences of text descriptors. However, open-ended generation provides little control over the generation space, leading to high cardinality, low-performance descriptors that renders downstream modeling challenging. To this end, AgenticTagger features two core stages: (1) a vocabulary building stage where a set of hierarchical, low-cardinality, and high-quality descriptors is identified, and (2) a vocabulary assignment stage where LLMs assign in-vocabulary descriptors to items. To effectively and efficiently ground vocabulary in the item corpus of interest, we design a multi-agent reflection mechanism where an architect LLM iteratively refines the vocabulary guided by parallelized feedback from annotator LLMs that validates the vocabulary against item data. Experiments on public and private data show AgenticTagger brings consistent improvements across diverse recommendation scenarios, including generative and term-based retrieval, ranking, and controllability-oriented, critique-based recommendation.
GeoNorm: Unify Pre-Norm and Post-Norm with Geodesic Optimization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The placement of normalization layers, specifically Pre-Norm and Post-Norm, remains an open question in Transformer architecture design. In this work, we rethink these approaches through the lens of manifold optimization, interpreting the outputs of the Feed-Forward Network (FFN) and attention layers as update directions in optimization. Building on this perspective, we introduce GeoNorm, a novel method that replaces standard normalization with geodesic updates on the manifold. Furthermore, analogous to learning rate schedules, we propose a layer-wise update decay for the FFN and attention components. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that GeoNorm consistently outperforms existing normalization methods in Transformer models. Crucially, GeoNorm can be seamlessly integrated into standard Transformer architectures, achieving performance improvements with negligible additional computational cost.
Endogenous Reprompting: Self-Evolving Cognitive Alignment for Unified Multimodal Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Unified Multimodal Models (UMMs) exhibit strong understanding, yet this capability often fails to effectively guide generation. We identify this as a Cognitive Gap: the model lacks the understanding of how to enhance its own generation process. To bridge this gap, we propose Endogenous Reprompting, a mechanism that transforms the model's understanding from a passive encoding process into an explicit generative reasoning step by generating self-aligned descriptors during generation. To achieve this, we introduce SEER (Self-Evolving Evaluator and Reprompter), a training framework that establishes a two-stage endogenous loop using only 300 samples from a compact proxy task, Visual Instruction Elaboration. First, Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) activates the model's latent evaluation ability via curriculum learning, producing a high-fidelity endogenous reward signal. Second, Reinforcement Learning with Model-rewarded Thinking (RLMT) leverages this signal to optimize the generative reasoning policy. Experiments show that SEER consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in evaluation accuracy, reprompting efficiency, and generation quality, without sacrificing general multimodal capabilities.
CauScientist: Teaching LLMs to Respect Data for Causal Discovery
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Causal discovery is fundamental to scientific understanding and reliable decision-making. Existing approaches face critical limitations: purely data-driven methods suffer from statistical indistinguishability and modeling assumptions, while recent LLM-based methods either ignore statistical evidence or incorporate unverified priors that can mislead result. To this end, we propose CauScientist, a collaborative framework that synergizes LLMs as hypothesis-generating "data scientists" with probabilistic statistics as rigorous "verifiers". CauScientist employs hybrid initialization to select superior starting graphs, iteratively refines structures through LLM-proposed modifications validated by statistical criteria, and maintains error memory to guide efficient search space. Experiments demonstrate that CauScientist substantially outperforms purely data-driven baselines, achieving up to 53.8% F1 score improvement and enhancing recall from 35.0% to 100.0%. Notably, while standalone LLM performance degrades with graph complexity, CauScientist reduces structural hamming distance (SHD) by 44.0% compared to Qwen3-32B on 37-node graphs. Our project page is at https://github.com/OpenCausaLab/CauScientist.
PACEvolve: Enabling Long-Horizon Progress-Aware Consistent Evolution
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful operators for evolutionary search, yet the design of efficient search scaffolds remains ad hoc. While promising, current LLM-in-the-loop systems lack a systematic approach to managing the evolutionary process. We identify three distinct failure modes: Context Pollution, where experiment history biases future candidate generation; Mode Collapse, where agents stagnate in local minima due to poor exploration-exploitation balance; and Weak Collaboration, where rigid crossover strategies fail to leverage parallel search trajectories effectively. We introduce Progress-Aware Consistent Evolution (PACEvolve), a framework designed to robustly govern the agent's context and search dynamics, to address these challenges. PACEvolve combines hierarchical context management (HCM) with pruning to address context pollution; momentum-based backtracking (MBB) to escape local minima; and a self-adaptive sampling policy that unifies backtracking and crossover for dynamic search coordination (CE), allowing agents to balance internal refinement with cross-trajectory collaboration. We demonstrate that PACEvolve provides a systematic path to consistent, long-horizon self-improvement, achieving state-of-the-art results on LLM-SR and KernelBench, while discovering solutions surpassing the record on Modded NanoGPT.
Revisiting MLLM Based Image Quality Assessment: Errors and Remedy
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress of multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) has boosted the task of image quality assessment (IQA). However, a key challenge arises from the inherent mismatch between the discrete token outputs of MLLMs and the continuous nature of quality scores required by IQA tasks. This discrepancy significantly hinders the performance of MLLM-based IQA methods. Previous approaches that convert discrete token predictions into continuous scores often suffer from conversion errors. Moreover, the semantic confusion introduced by level tokens (e.g., ``good'') further constrains the performance of MLLMs on IQA tasks and degrades their original capabilities for related tasks. To tackle these problems, we provide a theoretical analysis of the errors inherent in previous approaches and, motivated by this analysis, propose a simple yet effective framework, Q-Scorer. This framework incorporates a lightweight regression module and IQA-specific score tokens into the MLLM pipeline. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Q-Scorer achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple IQA benchmarks, generalizes well to mixed datasets, and further improves when combined with other methods.
GeoPurify: A Data-Efficient Geometric Distillation Framework for Open-Vocabulary 3D Segmentation
Oct 02, 2025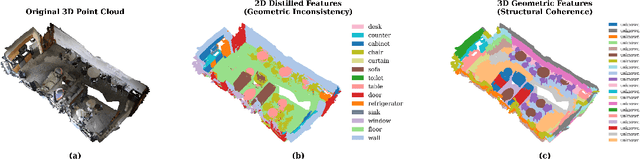
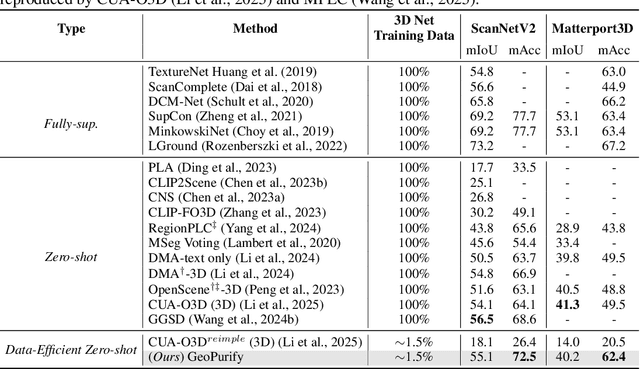
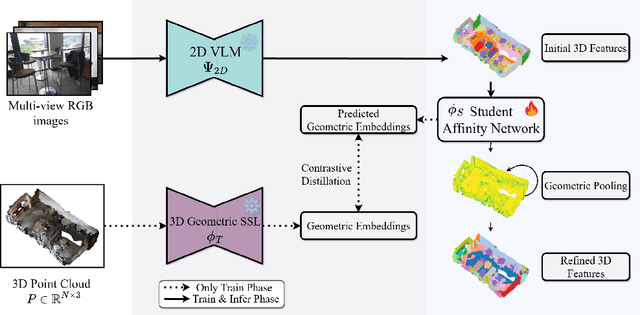
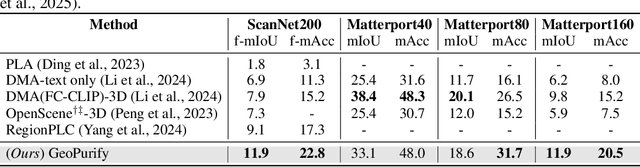
Abstract:Recent attempts to transfer features from 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to 3D semantic segmentation expose a persistent trade-off. Directly projecting 2D features into 3D yields noisy and fragmented predictions, whereas enforcing geometric coherence necessitates costly training pipelines and large-scale annotated 3D data. We argue that this limitation stems from the dominant segmentation-and-matching paradigm, which fails to reconcile 2D semantics with 3D geometric structure. The geometric cues are not eliminated during the 2D-to-3D transfer but remain latent within the noisy and view-aggregated features. To exploit this property, we propose GeoPurify that applies a small Student Affinity Network to purify 2D VLM-generated 3D point features using geometric priors distilled from a 3D self-supervised teacher model. During inference, we devise a Geometry-Guided Pooling module to further denoise the point cloud and ensure the semantic and structural consistency. Benefiting from latent geometric information and the learned affinity network, GeoPurify effectively mitigates the trade-off and achieves superior data efficiency. Extensive experiments on major 3D benchmarks demonstrate that GeoPurify achieves or surpasses state-of-the-art performance while utilizing only about 1.5% of the training data. Our codes and checkpoints are available at [https://github.com/tj12323/GeoPurify](https://github.com/tj12323/GeoPurify).
AnchorDP3: 3D Affordance Guided Sparse Diffusion Policy for Robotic Manipulation
Jun 24, 2025
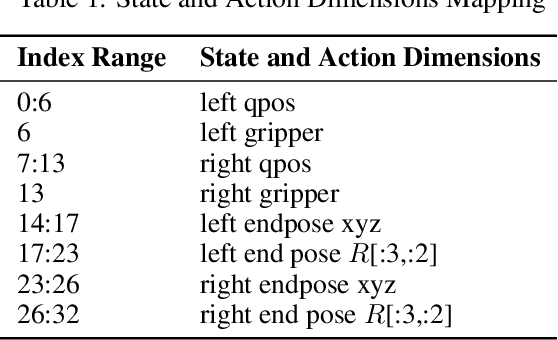
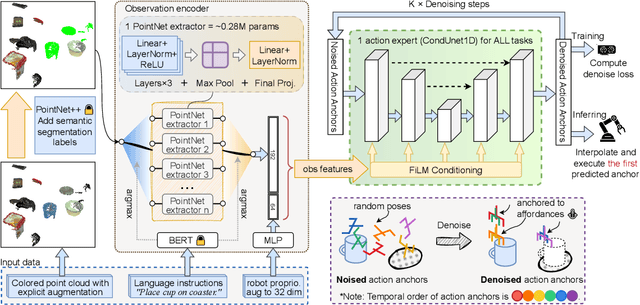
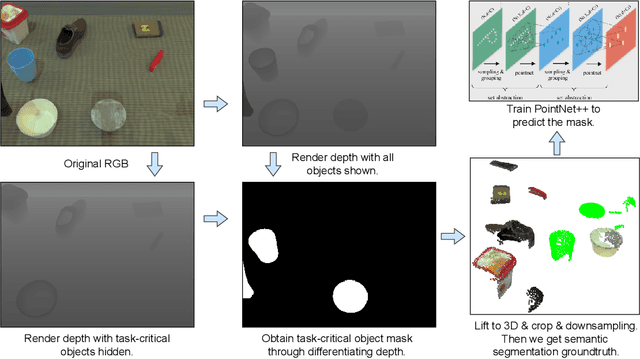
Abstract:We present AnchorDP3, a diffusion policy framework for dual-arm robotic manipulation that achieves state-of-the-art performance in highly randomized environments. AnchorDP3 integrates three key innovations: (1) Simulator-Supervised Semantic Segmentation, using rendered ground truth to explicitly segment task-critical objects within the point cloud, which provides strong affordance priors; (2) Task-Conditioned Feature Encoders, lightweight modules processing augmented point clouds per task, enabling efficient multi-task learning through a shared diffusion-based action expert; (3) Affordance-Anchored Keypose Diffusion with Full State Supervision, replacing dense trajectory prediction with sparse, geometrically meaningful action anchors, i.e., keyposes such as pre-grasp pose, grasp pose directly anchored to affordances, drastically simplifying the prediction space; the action expert is forced to predict both robot joint angles and end-effector poses simultaneously, which exploits geometric consistency to accelerate convergence and boost accuracy. Trained on large-scale, procedurally generated simulation data, AnchorDP3 achieves a 98.7% average success rate in the RoboTwin benchmark across diverse tasks under extreme randomization of objects, clutter, table height, lighting, and backgrounds. This framework, when integrated with the RoboTwin real-to-sim pipeline, has the potential to enable fully autonomous generation of deployable visuomotor policies from only scene and instruction, totally eliminating human demonstrations from learning manipulation skills.
Pro-AD: Learning Comprehensive Prototypes with Prototype-based Constraint for Multi-class Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
Jun 16, 2025



Abstract:Prototype-based reconstruction methods for unsupervised anomaly detection utilize a limited set of learnable prototypes which only aggregates insufficient normal information, resulting in undesirable reconstruction. However, increasing the number of prototypes may lead to anomalies being well reconstructed through the attention mechanism, which we refer to as the "Soft Identity Mapping" problem. In this paper, we propose Pro-AD to address these issues and fully utilize the prototypes to boost the performance of anomaly detection. Specifically, we first introduce an expanded set of learnable prototypes to provide sufficient capacity for semantic information. Then we employ a Dynamic Bidirectional Decoder which integrates the process of the normal information aggregation and the target feature reconstruction via prototypes, with the aim of allowing the prototypes to aggregate more comprehensive normal semantic information from different levels of the image features and the target feature reconstruction to not only utilize its contextual information but also dynamically leverage the learned comprehensive prototypes. Additionally, to prevent the anomalies from being well reconstructed using sufficient semantic information through the attention mechanism, Pro-AD introduces a Prototype-based Constraint that applied within the target feature reconstruction process of the decoder, which further improves the performance of our approach. Extensive experiments on multiple challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our Pro-AD achieve state-of-the-art performance, highlighting its superior robustness and practical effectiveness for Multi-class Unsupervised Anomaly Detection task.
Analyzing Fine-Grained Alignment and Enhancing Vision Understanding in Multimodal Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Achieving better alignment between vision embeddings and Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial for enhancing the abilities of Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), particularly for recent models that rely on powerful pretrained vision encoders and LLMs. A common approach to connect the pretrained vision encoder and LLM is through a projector applied after the vision encoder. However, the projector is often trained to enable the LLM to generate captions, and hence the mechanism by which LLMs understand each vision token remains unclear. In this work, we first investigate the role of the projector in compressing vision embeddings and aligning them with word embeddings. We show that the projector significantly compresses visual information, removing redundant details while preserving essential elements necessary for the LLM to understand visual content. We then examine patch-level alignment -- the alignment between each vision patch and its corresponding semantic words -- and propose a *multi-semantic alignment hypothesis*. Our analysis indicates that the projector trained by caption loss improves patch-level alignment but only to a limited extent, resulting in weak and coarse alignment. To address this issue, we propose *patch-aligned training* to efficiently enhance patch-level alignment. Our experiments show that patch-aligned training (1) achieves stronger compression capability and improved patch-level alignment, enabling the MLLM to generate higher-quality captions, (2) improves the MLLM's performance by 16% on referring expression grounding tasks, 4% on question-answering tasks, and 3% on modern instruction-following benchmarks when using the same supervised fine-tuning (SFT) setting. The proposed method can be easily extended to other multimodal models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge