Jianjun Lei
Boosting Multi-View Stereo with Depth Foundation Model in the Absence of Real-World Labels
Apr 16, 2025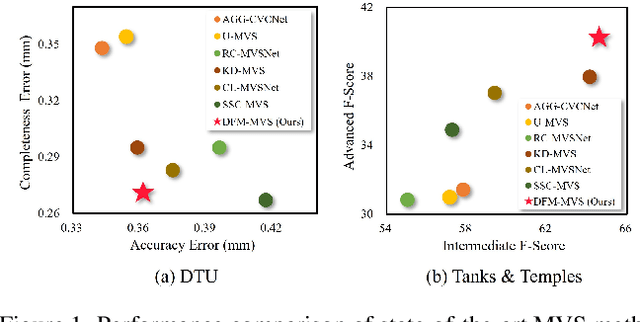



Abstract:Learning-based Multi-View Stereo (MVS) methods have made remarkable progress in recent years. However, how to effectively train the network without using real-world labels remains a challenging problem. In this paper, driven by the recent advancements of vision foundation models, a novel method termed DFM-MVS, is proposed to leverage the depth foundation model to generate the effective depth prior, so as to boost MVS in the absence of real-world labels. Specifically, a depth prior-based pseudo-supervised training mechanism is developed to simulate realistic stereo correspondences using the generated depth prior, thereby constructing effective supervision for the MVS network. Besides, a depth prior-guided error correction strategy is presented to leverage the depth prior as guidance to mitigate the error propagation problem inherent in the widely-used coarse-to-fine network structure. Experimental results on DTU and Tanks & Temples datasets demonstrate that the proposed DFM-MVS significantly outperforms existing MVS methods without using real-world labels.
Stereo Image Coding for Machines with Joint Visual Feature Compression
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:2D image coding for machines (ICM) has achieved great success in coding efficiency, while less effort has been devoted to stereo image fields. To promote the efficiency of stereo image compression (SIC) and intelligent analysis, the stereo image coding for machines (SICM) is formulated and explored in this paper. More specifically, a machine vision-oriented stereo feature compression network (MVSFC-Net) is proposed for SICM, where the stereo visual features are effectively extracted, compressed, and transmitted for 3D visual task. To efficiently compress stereo visual features in MVSFC-Net, a stereo multi-scale feature compression (SMFC) module is designed to gradually transform sparse stereo multi-scale features into compact joint visual representations by removing spatial, inter-view, and cross-scale redundancies simultaneously. Experimental results show that the proposed MVSFC-Net obtains superior compression efficiency as well as 3D visual task performance, when compared with the existing ICM anchors recommended by MPEG and the state-of-the-art SIC method.
Multi-Projection Fusion and Refinement Network for Salient Object Detection in 360° Omnidirectional Image
Dec 23, 2022
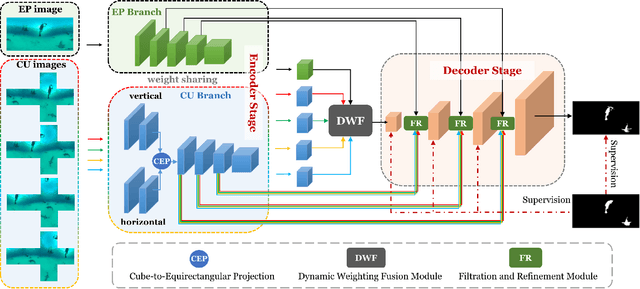
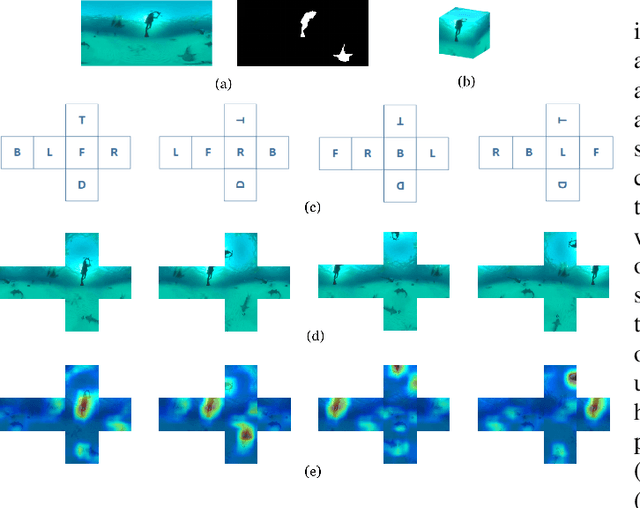
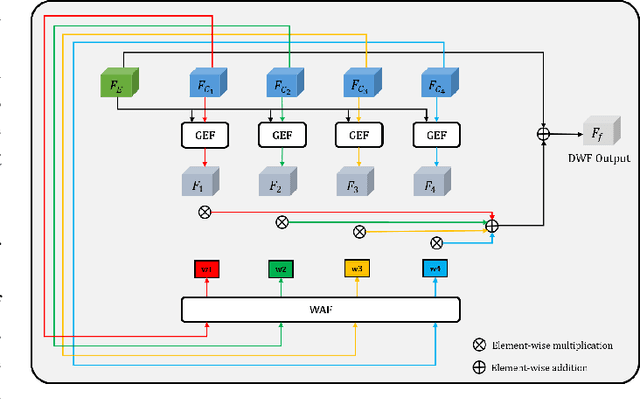
Abstract:Salient object detection (SOD) aims to determine the most visually attractive objects in an image. With the development of virtual reality technology, 360{\deg} omnidirectional image has been widely used, but the SOD task in 360{\deg} omnidirectional image is seldom studied due to its severe distortions and complex scenes. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Projection Fusion and Refinement Network (MPFR-Net) to detect the salient objects in 360{\deg} omnidirectional image. Different from the existing methods, the equirectangular projection image and four corresponding cube-unfolding images are embedded into the network simultaneously as inputs, where the cube-unfolding images not only provide supplementary information for equirectangular projection image, but also ensure the object integrity of the cube-map projection. In order to make full use of these two projection modes, a Dynamic Weighting Fusion (DWF) module is designed to adaptively integrate the features of different projections in a complementary and dynamic manner from the perspective of inter and intra features. Furthermore, in order to fully explore the way of interaction between encoder and decoder features, a Filtration and Refinement (FR) module is designed to suppress the redundant information between the feature itself and the feature. Experimental results on two omnidirectional datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
PSNet: Parallel Symmetric Network for Video Salient Object Detection
Oct 12, 2022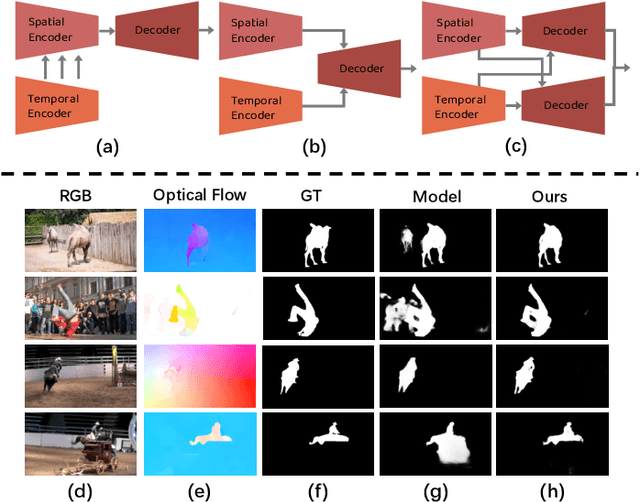
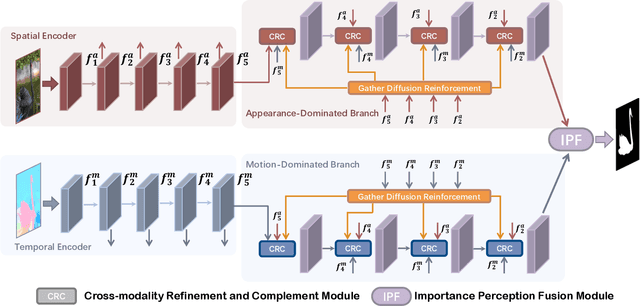
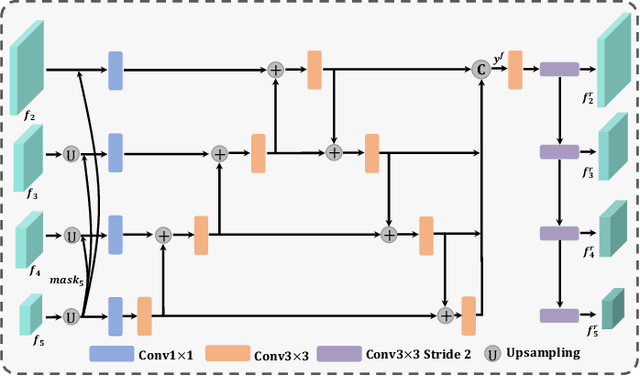
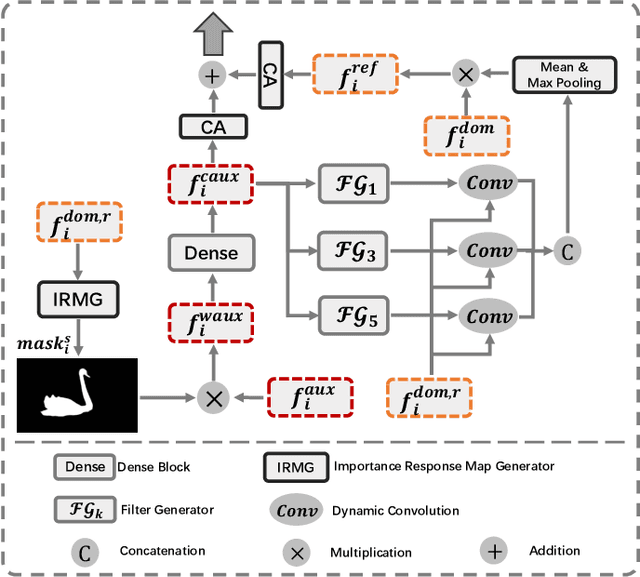
Abstract:For the video salient object detection (VSOD) task, how to excavate the information from the appearance modality and the motion modality has always been a topic of great concern. The two-stream structure, including an RGB appearance stream and an optical flow motion stream, has been widely used as a typical pipeline for VSOD tasks, but the existing methods usually only use motion features to unidirectionally guide appearance features or adaptively but blindly fuse two modality features. However, these methods underperform in diverse scenarios due to the uncomprehensive and unspecific learning schemes. In this paper, following a more secure modeling philosophy, we deeply investigate the importance of appearance modality and motion modality in a more comprehensive way and propose a VSOD network with up and down parallel symmetry, named PSNet. Two parallel branches with different dominant modalities are set to achieve complete video saliency decoding with the cooperation of the Gather Diffusion Reinforcement (GDR) module and Cross-modality Refinement and Complement (CRC) module. Finally, we use the Importance Perception Fusion (IPF) module to fuse the features from two parallel branches according to their different importance in different scenarios. Experiments on four dataset benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves desirable and competitive performance.
Multi-View Stereo with Transformer
Dec 01, 2021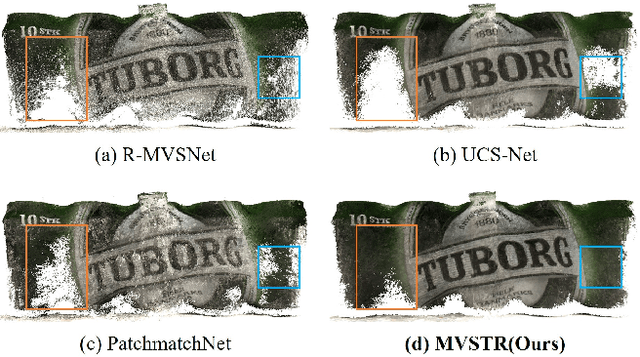
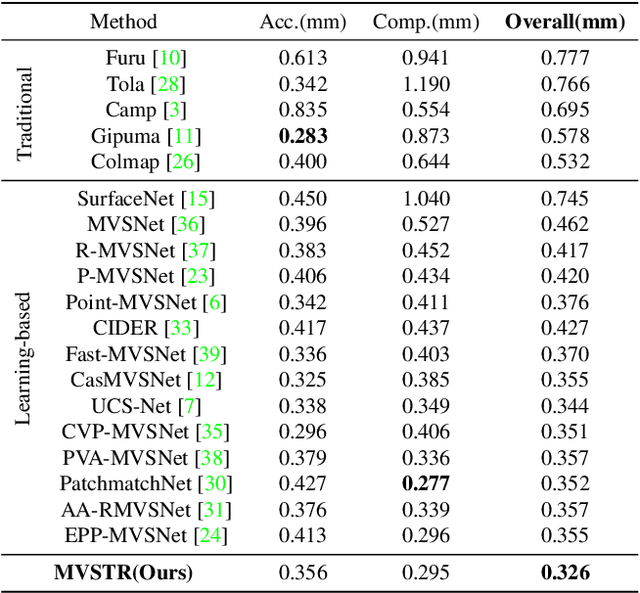
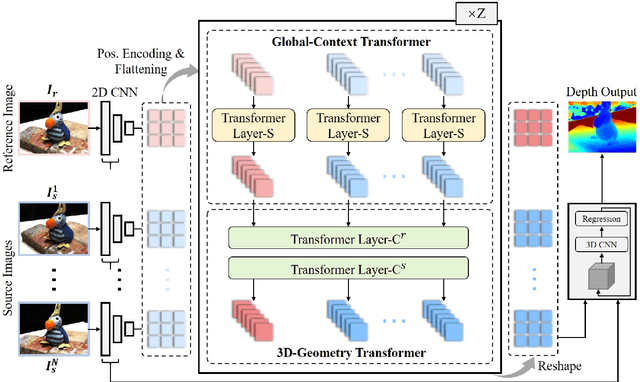
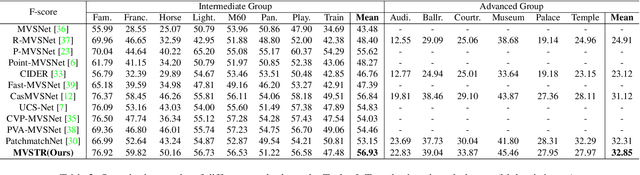
Abstract:This paper proposes a network, referred to as MVSTR, for Multi-View Stereo (MVS). It is built upon Transformer and is capable of extracting dense features with global context and 3D consistency, which are crucial to achieving reliable matching for MVS. Specifically, to tackle the problem of the limited receptive field of existing CNN-based MVS methods, a global-context Transformer module is first proposed to explore intra-view global context. In addition, to further enable dense features to be 3D-consistent, a 3D-geometry Transformer module is built with a well-designed cross-view attention mechanism to facilitate inter-view information interaction. Experimental results show that the proposed MVSTR achieves the best overall performance on the DTU dataset and strong generalization on the Tanks & Temples benchmark dataset.
Novel View Synthesis from a Single Image via Unsupervised learning
Oct 29, 2021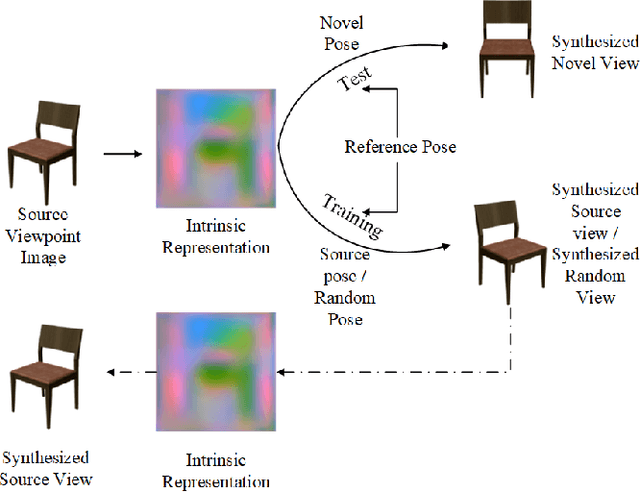
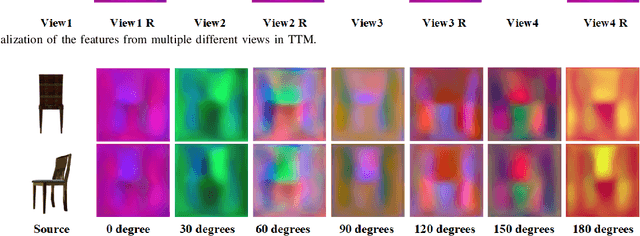
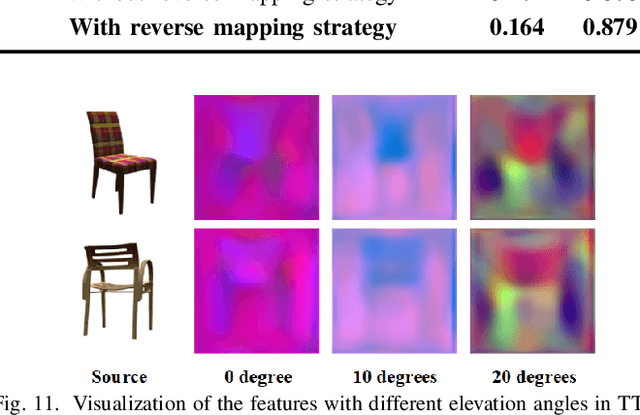
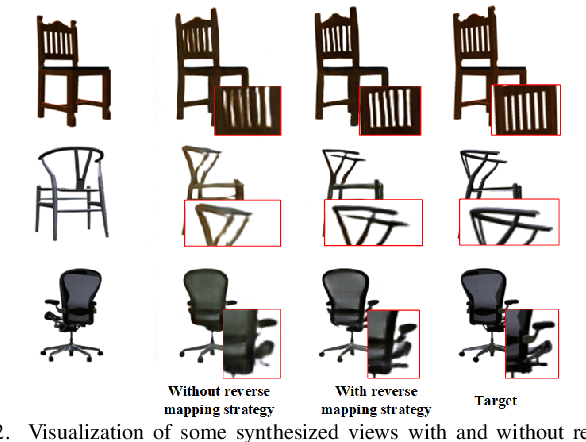
Abstract:View synthesis aims to generate novel views from one or more given source views. Although existing methods have achieved promising performance, they usually require paired views of different poses to learn a pixel transformation. This paper proposes an unsupervised network to learn such a pixel transformation from a single source viewpoint. In particular, the network consists of a token transformation module (TTM) that facilities the transformation of the features extracted from a source viewpoint image into an intrinsic representation with respect to a pre-defined reference pose and a view generation module (VGM) that synthesizes an arbitrary view from the representation. The learned transformation allows us to synthesize a novel view from any single source viewpoint image of unknown pose. Experiments on the widely used view synthesis datasets have demonstrated that the proposed network is able to produce comparable results to the state-of-the-art methods despite the fact that learning is unsupervised and only a single source viewpoint image is required for generating a novel view. The code will be available soon.
Semi-Heterogeneous Three-Way Joint Embedding Network for Sketch-Based Image Retrieval
Nov 10, 2019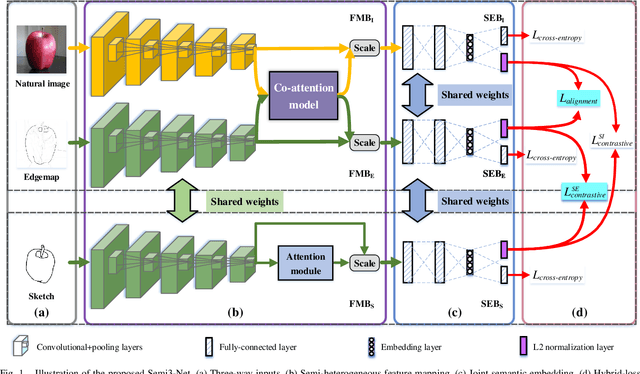
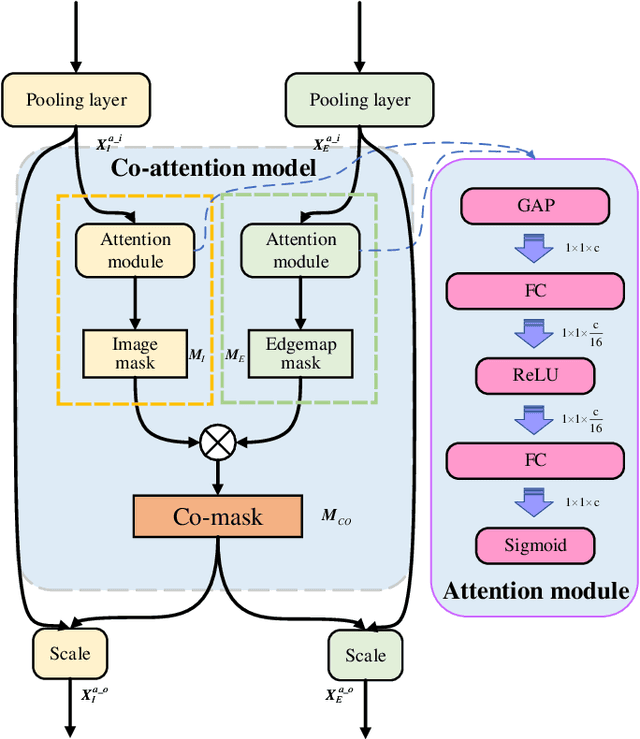
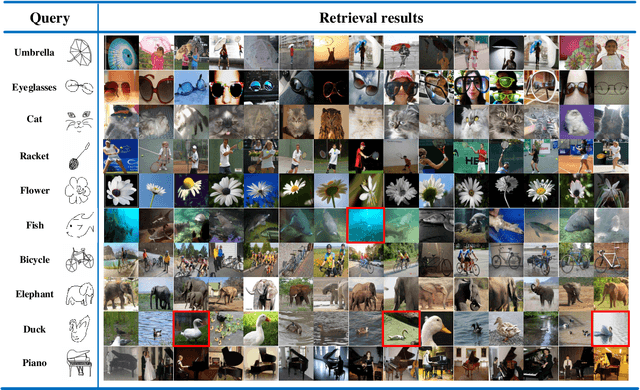
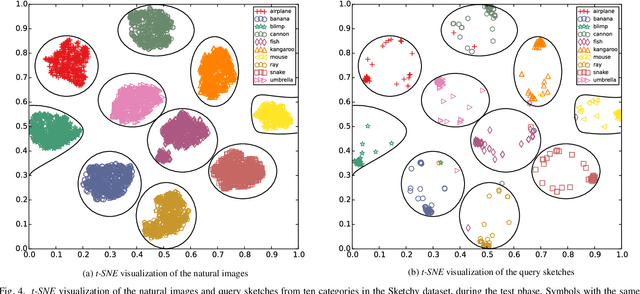
Abstract:Sketch-based image retrieval (SBIR) is a challenging task due to the large cross-domain gap between sketches and natural images. How to align abstract sketches and natural images into a common high-level semantic space remains a key problem in SBIR. In this paper, we propose a novel semi-heterogeneous three-way joint embedding network (Semi3-Net), which integrates three branches (a sketch branch, a natural image branch, and an edgemap branch) to learn more discriminative cross-domain feature representations for the SBIR task. The key insight lies with how we cultivate the mutual and subtle relationships amongst the sketches, natural images, and edgemaps. A semi-heterogeneous feature mapping is designed to extract bottom features from each domain, where the sketch and edgemap branches are shared while the natural image branch is heterogeneous to the other branches. In addition, a joint semantic embedding is introduced to embed the features from different domains into a common high-level semantic space, where all of the three branches are shared. To further capture informative features common to both natural images and the corresponding edgemaps, a co-attention model is introduced to conduct common channel-wise feature recalibration between different domains. A hybrid-loss mechanism is designed to align the three branches, where an alignment loss and a sketch-edgemap contrastive loss are presented to encourage the network to learn invariant cross-domain representations. Experimental results on two widely used category-level datasets (Sketchy and TU-Berlin Extension) demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
HSCS: Hierarchical Sparsity Based Co-saliency Detection for RGBD Images
Nov 16, 2018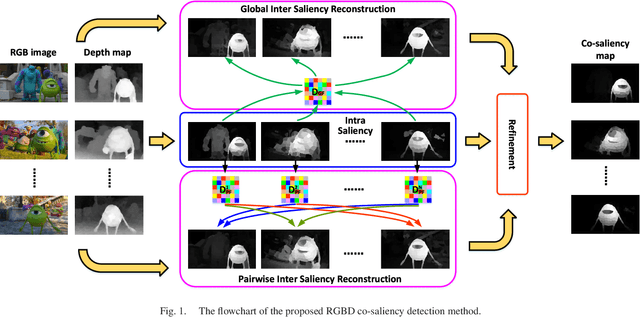

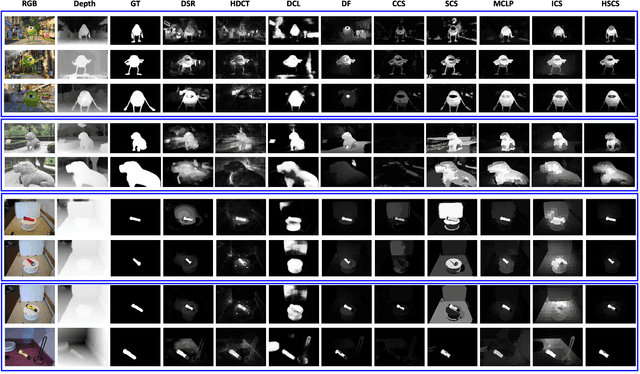
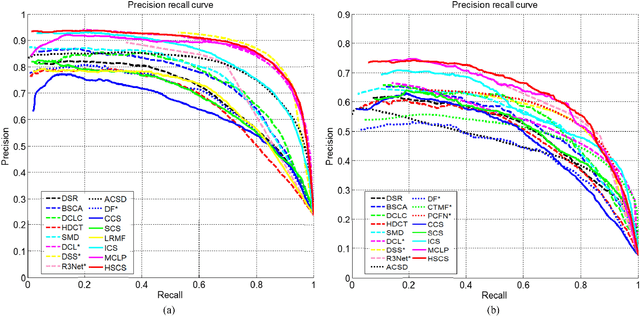
Abstract:Co-saliency detection aims to discover common and salient objects in an image group containing more than two relevant images. Moreover, depth information has been demonstrated to be effective for many computer vision tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel co-saliency detection method for RGBD images based on hierarchical sparsity reconstruction and energy function refinement. With the assistance of the intra saliency map, the inter-image correspondence is formulated as a hierarchical sparsity reconstruction framework. The global sparsity reconstruction model with a ranking scheme focuses on capturing the global characteristics among the whole image group through a common foreground dictionary. The pairwise sparsity reconstruction model aims to explore the corresponding relationship between pairwise images through a set of pairwise dictionaries. In order to improve the intra-image smoothness and inter-image consistency, an energy function refinement model is proposed, which includes the unary data term, spatial smooth term, and holistic consistency term. Experiments on two RGBD co-saliency detection benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art algorithms both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Review of Visual Saliency Detection with Comprehensive Information
Sep 14, 2018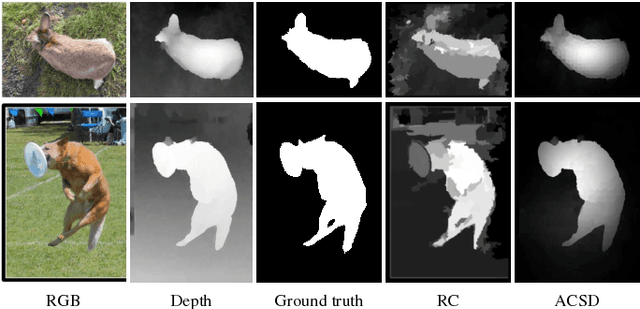

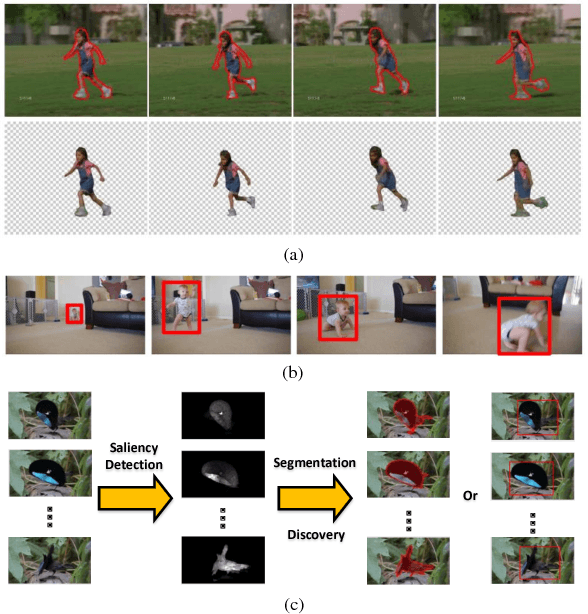

Abstract:Visual saliency detection model simulates the human visual system to perceive the scene, and has been widely used in many vision tasks. With the acquisition technology development, more comprehensive information, such as depth cue, inter-image correspondence, or temporal relationship, is available to extend image saliency detection to RGBD saliency detection, co-saliency detection, or video saliency detection. RGBD saliency detection model focuses on extracting the salient regions from RGBD images by combining the depth information. Co-saliency detection model introduces the inter-image correspondence constraint to discover the common salient object in an image group. The goal of video saliency detection model is to locate the motion-related salient object in video sequences, which considers the motion cue and spatiotemporal constraint jointly. In this paper, we review different types of saliency detection algorithms, summarize the important issues of the existing methods, and discuss the existent problems and future works. Moreover, the evaluation datasets and quantitative measurements are briefly introduced, and the experimental analysis and discission are conducted to provide a holistic overview of different saliency detection methods.
Person Re-Identification by Semantic Region Representation and Topology Constraint
Aug 20, 2018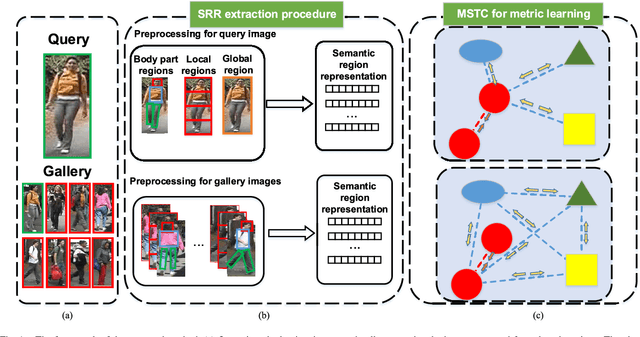


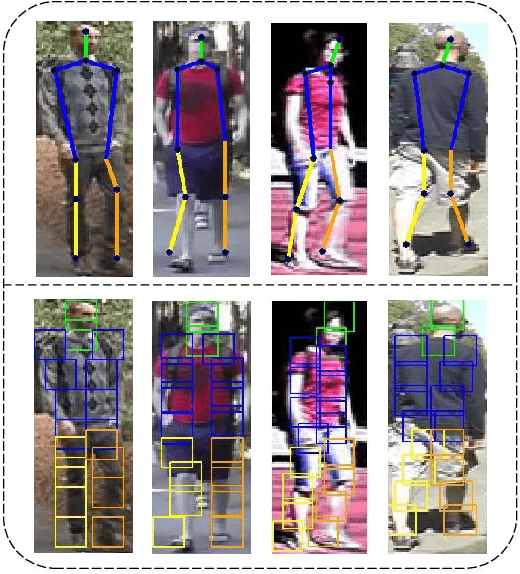
Abstract:Person re-identification is a popular research topic which aims at matching the specific person in a multi-camera network automatically. Feature representation and metric learning are two important issues for person re-identification. In this paper, we propose a novel person re-identification method, which consists of a reliable representation called Semantic Region Representation (SRR), and an effective metric learning with Mapping Space Topology Constraint (MSTC). The SRR integrates semantic representations to achieve effective similarity comparison between the corresponding regions via parsing the body into multiple parts, which focuses on the foreground context against the background interference. To learn a discriminant metric, the MSTC is proposed to take into account the topological relationship among all samples in the feature space. It considers two-fold constraints: the distribution of positive pairs should be more compact than the average distribution of negative pairs with regard to the same probe, while the average distance between different classes should be larger than that between same classes. These two aspects cooperate to maintain the compactness of the intra-class as well as the sparsity of the inter-class. Extensive experiments conducted on five challenging person re-identification datasets, VIPeR, SYSU-sReID, QUML GRID, CUHK03, and Market-1501, show that the proposed method achieves competitive performance with the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge