Bingzheng Liu
Boosting Multi-View Stereo with Depth Foundation Model in the Absence of Real-World Labels
Apr 16, 2025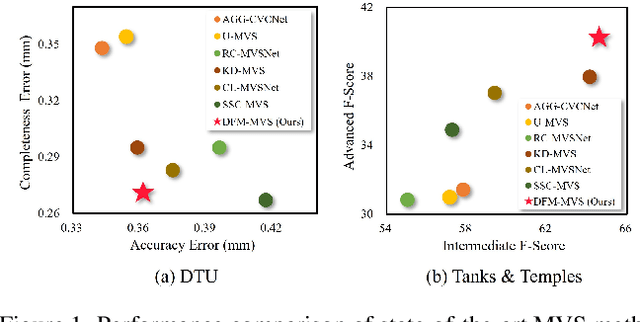



Abstract:Learning-based Multi-View Stereo (MVS) methods have made remarkable progress in recent years. However, how to effectively train the network without using real-world labels remains a challenging problem. In this paper, driven by the recent advancements of vision foundation models, a novel method termed DFM-MVS, is proposed to leverage the depth foundation model to generate the effective depth prior, so as to boost MVS in the absence of real-world labels. Specifically, a depth prior-based pseudo-supervised training mechanism is developed to simulate realistic stereo correspondences using the generated depth prior, thereby constructing effective supervision for the MVS network. Besides, a depth prior-guided error correction strategy is presented to leverage the depth prior as guidance to mitigate the error propagation problem inherent in the widely-used coarse-to-fine network structure. Experimental results on DTU and Tanks & Temples datasets demonstrate that the proposed DFM-MVS significantly outperforms existing MVS methods without using real-world labels.
Novel View Synthesis from a Single Image via Unsupervised learning
Oct 29, 2021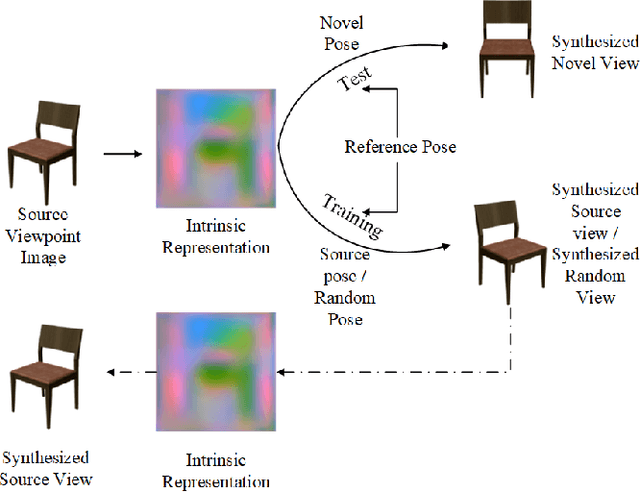
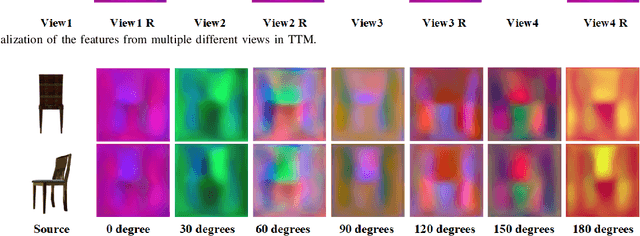
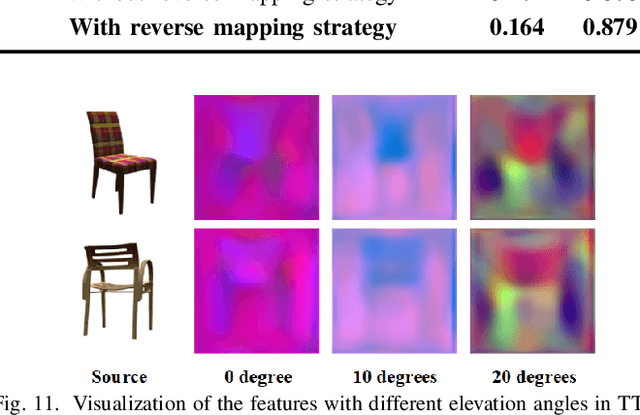
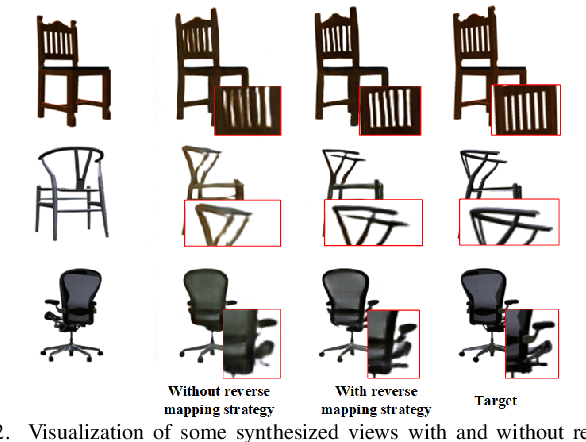
Abstract:View synthesis aims to generate novel views from one or more given source views. Although existing methods have achieved promising performance, they usually require paired views of different poses to learn a pixel transformation. This paper proposes an unsupervised network to learn such a pixel transformation from a single source viewpoint. In particular, the network consists of a token transformation module (TTM) that facilities the transformation of the features extracted from a source viewpoint image into an intrinsic representation with respect to a pre-defined reference pose and a view generation module (VGM) that synthesizes an arbitrary view from the representation. The learned transformation allows us to synthesize a novel view from any single source viewpoint image of unknown pose. Experiments on the widely used view synthesis datasets have demonstrated that the proposed network is able to produce comparable results to the state-of-the-art methods despite the fact that learning is unsupervised and only a single source viewpoint image is required for generating a novel view. The code will be available soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge