Pengcheng Xu
A Very Big Video Reasoning Suite
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Rapid progress in video models has largely focused on visual quality, leaving their reasoning capabilities underexplored. Video reasoning grounds intelligence in spatiotemporally consistent visual environments that go beyond what text can naturally capture, enabling intuitive reasoning over spatiotemporal structure such as continuity, interaction, and causality. However, systematically studying video reasoning and its scaling behavior is hindered by the lack of large-scale training data. To address this gap, we introduce the Very Big Video Reasoning (VBVR) Dataset, an unprecedentedly large-scale resource spanning 200 curated reasoning tasks following a principled taxonomy and over one million video clips, approximately three orders of magnitude larger than existing datasets. We further present VBVR-Bench, a verifiable evaluation framework that moves beyond model-based judging by incorporating rule-based, human-aligned scorers, enabling reproducible and interpretable diagnosis of video reasoning capabilities. Leveraging the VBVR suite, we conduct one of the first large-scale scaling studies of video reasoning and observe early signs of emergent generalization to unseen reasoning tasks. Together, VBVR lays a foundation for the next stage of research in generalizable video reasoning. The data, benchmark toolkit, and models are publicly available at https://video-reason.com/ .
The devil is in the details: Enhancing Video Virtual Try-On via Keyframe-Driven Details Injection
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Although diffusion transformer (DiT)-based video virtual try-on (VVT) has made significant progress in synthesizing realistic videos, existing methods still struggle to capture fine-grained garment dynamics and preserve background integrity across video frames. They also incur high computational costs due to additional interaction modules introduced into DiTs, while the limited scale and quality of existing public datasets also restrict model generalization and effective training. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework, KeyTailor, along with a large-scale, high-definition dataset, ViT-HD. The core idea of KeyTailor is a keyframe-driven details injection strategy, motivated by the fact that keyframes inherently contain both foreground dynamics and background consistency. Specifically, KeyTailor adopts an instruction-guided keyframe sampling strategy to filter informative frames from the input video. Subsequently,two tailored keyframe-driven modules, the garment details enhancement module and the collaborative background optimization module, are employed to distill garment dynamics into garment-related latents and to optimize the integrity of background latents, both guided by keyframes.These enriched details are then injected into standard DiT blocks together with pose, mask, and noise latents, enabling efficient and realistic try-on video synthesis. This design ensures consistency without explicitly modifying the DiT architecture, while simultaneously avoiding additional complexity. In addition, our dataset ViT-HD comprises 15, 070 high-quality video samples at a resolution of 810*1080, covering diverse garments. Extensive experiments demonstrate that KeyTailor outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of garment fidelity and background integrity across both dynamic and static scenarios.
Semantic-guided Representation Learning for Multi-Label Recognition
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Multi-label Recognition (MLR) involves assigning multiple labels to each data instance in an image, offering advantages over single-label classification in complex scenarios. However, it faces the challenge of annotating all relevant categories, often leading to uncertain annotations, such as unseen or incomplete labels. Recent Vision and Language Pre-training (VLP) based methods have made significant progress in tackling zero-shot MLR tasks by leveraging rich vision-language correlations. However, the correlation between multi-label semantics has not been fully explored, and the learned visual features often lack essential semantic information. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a Semantic-guided Representation Learning approach (SigRL) that enables the model to learn effective visual and textual representations, thereby improving the downstream alignment of visual images and categories. Specifically, we first introduce a graph-based multi-label correlation module (GMC) to facilitate information exchange between labels, enriching the semantic representation across the multi-label texts. Next, we propose a Semantic Visual Feature Reconstruction module (SVFR) to enhance the semantic information in the visual representation by integrating the learned textual representation during reconstruction. Finally, we optimize the image-text matching capability of the VLP model using both local and global features to achieve zero-shot MLR. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on several MLR benchmarks, encompassing both zero-shot MLR (with unseen labels) and single positive multi-label learning (with limited labels), demonstrating the superior performance of our approach compared to state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/MVL-Lab/SigRL.
PixelPonder: Dynamic Patch Adaptation for Enhanced Multi-Conditional Text-to-Image Generation
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion-based text-to-image generation have demonstrated promising results through visual condition control. However, existing ControlNet-like methods struggle with compositional visual conditioning - simultaneously preserving semantic fidelity across multiple heterogeneous control signals while maintaining high visual quality, where they employ separate control branches that often introduce conflicting guidance during the denoising process, leading to structural distortions and artifacts in generated images. To address this issue, we present PixelPonder, a novel unified control framework, which allows for effective control of multiple visual conditions under a single control structure. Specifically, we design a patch-level adaptive condition selection mechanism that dynamically prioritizes spatially relevant control signals at the sub-region level, enabling precise local guidance without global interference. Additionally, a time-aware control injection scheme is deployed to modulate condition influence according to denoising timesteps, progressively transitioning from structural preservation to texture refinement and fully utilizing the control information from different categories to promote more harmonious image generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PixelPonder surpasses previous methods across different benchmark datasets, showing superior improvement in spatial alignment accuracy while maintaining high textual semantic consistency.
Textualize Visual Prompt for Image Editing via Diffusion Bridge
Jan 07, 2025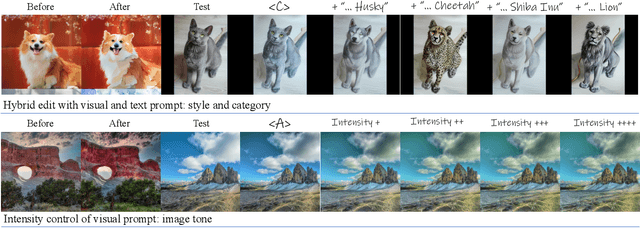


Abstract:Visual prompt, a pair of before-and-after edited images, can convey indescribable imagery transformations and prosper in image editing. However, current visual prompt methods rely on a pretrained text-guided image-to-image generative model that requires a triplet of text, before, and after images for retraining over a text-to-image model. Such crafting triplets and retraining processes limit the scalability and generalization of editing. In this paper, we present a framework based on any single text-to-image model without reliance on the explicit image-to-image model thus enhancing the generalizability and scalability. Specifically, by leveraging the probability-flow ordinary equation, we construct a diffusion bridge to transfer the distribution between before-and-after images under the text guidance. By optimizing the text via the bridge, the framework adaptively textualizes the editing transformation conveyed by visual prompts into text embeddings without other models. Meanwhile, we introduce differential attention control during text optimization, which disentangles the text embedding from the invariance of the before-and-after images and makes it solely capture the delicate transformation and generalize to edit various images. Experiments on real images validate competitive results on the generalization, contextual coherence, and high fidelity for delicate editing with just one image pair as the visual prompt.
Plug-and-Play Tri-Branch Invertible Block for Image Rescaling
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:High-resolution (HR) images are commonly downscaled to low-resolution (LR) to reduce bandwidth, followed by upscaling to restore their original details. Recent advancements in image rescaling algorithms have employed invertible neural networks (INNs) to create a unified framework for downscaling and upscaling, ensuring a one-to-one mapping between LR and HR images. Traditional methods, utilizing dual-branch based vanilla invertible blocks, process high-frequency and low-frequency information separately, often relying on specific distributions to model high-frequency components. However, processing the low-frequency component directly in the RGB domain introduces channel redundancy, limiting the efficiency of image reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose a plug-and-play tri-branch invertible block (T-InvBlocks) that decomposes the low-frequency branch into luminance (Y) and chrominance (CbCr) components, reducing redundancy and enhancing feature processing. Additionally, we adopt an all-zero mapping strategy for high-frequency components during upscaling, focusing essential rescaling information within the LR image. Our T-InvBlocks can be seamlessly integrated into existing rescaling models, improving performance in both general rescaling tasks and scenarios involving lossy compression. Extensive experiments confirm that our method advances the state of the art in HR image reconstruction.
DynamicControl: Adaptive Condition Selection for Improved Text-to-Image Generation
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:To enhance the controllability of text-to-image diffusion models, current ControlNet-like models have explored various control signals to dictate image attributes. However, existing methods either handle conditions inefficiently or use a fixed number of conditions, which does not fully address the complexity of multiple conditions and their potential conflicts. This underscores the need for innovative approaches to manage multiple conditions effectively for more reliable and detailed image synthesis. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework, DynamicControl, which supports dynamic combinations of diverse control signals, allowing adaptive selection of different numbers and types of conditions. Our approach begins with a double-cycle controller that generates an initial real score sorting for all input conditions by leveraging pre-trained conditional generation models and discriminative models. This controller evaluates the similarity between extracted conditions and input conditions, as well as the pixel-level similarity with the source image. Then, we integrate a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to build an efficient condition evaluator. This evaluator optimizes the ordering of conditions based on the double-cycle controller's score ranking. Our method jointly optimizes MLLMs and diffusion models, utilizing MLLMs' reasoning capabilities to facilitate multi-condition text-to-image (T2I) tasks. The final sorted conditions are fed into a parallel multi-control adapter, which learns feature maps from dynamic visual conditions and integrates them to modulate ControlNet, thereby enhancing control over generated images. Through both quantitative and qualitative comparisons, DynamicControl demonstrates its superiority over existing methods in terms of controllability, generation quality and composability under various conditional controls.
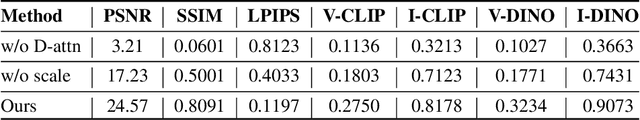
Unveil Inversion and Invariance in Flow Transformer for Versatile Image Editing
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Leveraging the large generative prior of the flow transformer for tuning-free image editing requires authentic inversion to project the image into the model's domain and a flexible invariance control mechanism to preserve non-target contents. However, the prevailing diffusion inversion performs deficiently in flow-based models, and the invariance control cannot reconcile diverse rigid and non-rigid editing tasks. To address these, we systematically analyze the \textbf{inversion and invariance} control based on the flow transformer. Specifically, we unveil that the Euler inversion shares a similar structure to DDIM yet is more susceptible to the approximation error. Thus, we propose a two-stage inversion to first refine the velocity estimation and then compensate for the leftover error, which pivots closely to the model prior and benefits editing. Meanwhile, we propose the invariance control that manipulates the text features within the adaptive layer normalization, connecting the changes in the text prompt to image semantics. This mechanism can simultaneously preserve the non-target contents while allowing rigid and non-rigid manipulation, enabling a wide range of editing types such as visual text, quantity, facial expression, etc. Experiments on versatile scenarios validate that our framework achieves flexible and accurate editing, unlocking the potential of the flow transformer for versatile image editing.
Exploring applications of topological data analysis in stock index movement prediction
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Topological Data Analysis (TDA) has recently gained significant attention in the field of financial prediction. However, the choice of point cloud construction methods, topological feature representations, and classification models has a substantial impact on prediction results. This paper addresses the classification problem of stock index movement. First, we construct point clouds for stock indices using three different methods. Next, we apply TDA to extract topological structures from the point clouds. Four distinct topological features are computed to represent the patterns in the data, and 15 combinations of these features are enumerated and input into six different machine learning models. We evaluate the predictive performance of various TDA configurations by conducting index movement classification tasks on datasets such as CSI, DAX, HSI and FTSE providing insights into the efficiency of different TDA setups.
From Challenges and Pitfalls to Recommendations and Opportunities: Implementing Federated Learning in Healthcare
Sep 15, 2024
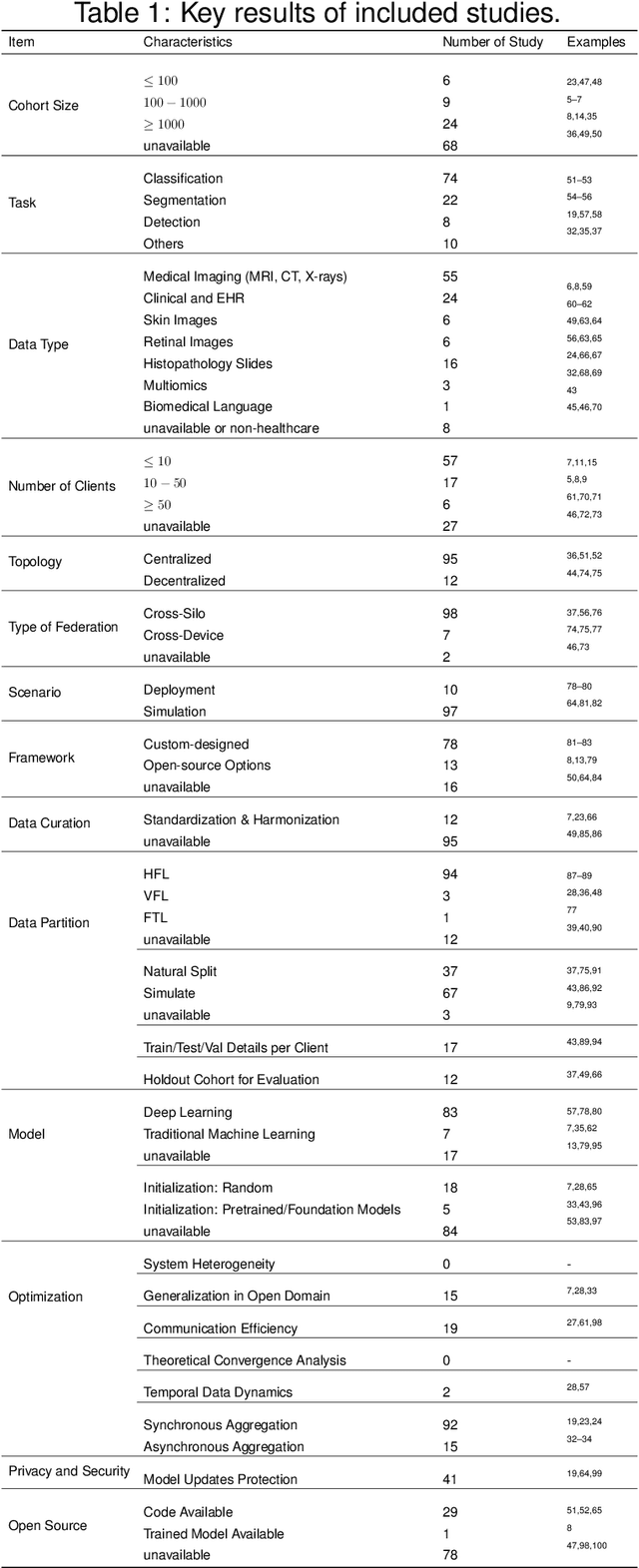
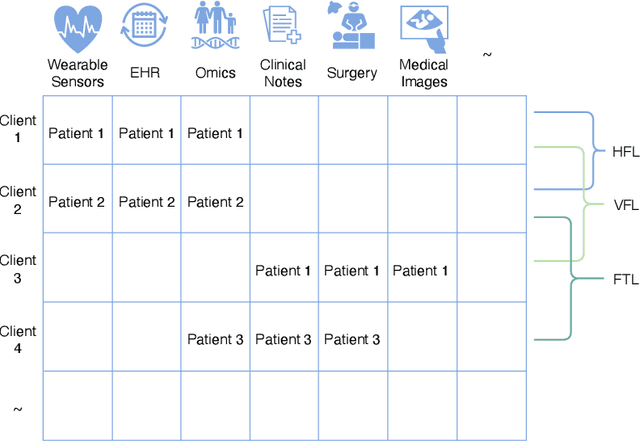

Abstract:Federated learning holds great potential for enabling large-scale healthcare research and collaboration across multiple centres while ensuring data privacy and security are not compromised. Although numerous recent studies suggest or utilize federated learning based methods in healthcare, it remains unclear which ones have potential clinical utility. This review paper considers and analyzes the most recent studies up to May 2024 that describe federated learning based methods in healthcare. After a thorough review, we find that the vast majority are not appropriate for clinical use due to their methodological flaws and/or underlying biases which include but are not limited to privacy concerns, generalization issues, and communication costs. As a result, the effectiveness of federated learning in healthcare is significantly compromised. To overcome these challenges, we provide recommendations and promising opportunities that might be implemented to resolve these problems and improve the quality of model development in federated learning with healthcare.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge