Boyu Wang
Graph Domain Adaptation via Homophily-Agnostic Reconstructing Structure
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Graph Domain Adaptation (GDA) transfers knowledge from labeled source graphs to unlabeled target graphs, addressing the challenge of label scarcity. However, existing GDA methods typically assume that both source and target graphs exhibit homophily, leading existing methods to perform poorly when heterophily is present. Furthermore, the lack of labels in the target graph makes it impossible to assess its homophily level beforehand. To address this challenge, we propose a novel homophily-agnostic approach that effectively transfers knowledge between graphs with varying degrees of homophily. Specifically, we adopt a divide-and-conquer strategy that first separately reconstructs highly homophilic and heterophilic variants of both the source and target graphs, and then performs knowledge alignment separately between corresponding graph variants. Extensive experiments conducted on five benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our approach, particularly highlighting its substantial advantages on heterophilic graphs.
A Study of Adaptive Modeling Towards Robust Generalization
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) increasingly support reasoning over biomolecular structures, but most existing approaches remain modality-specific and rely on either sequence-style encodings or fixed-length connector tokens for structural inputs. These designs can under-expose explicit geometric cues and impose rigid fusion bottlenecks, leading to over-compression and poor token allocation as structural complexity grows. We present a unified all-atom framework that grounds language reasoning in geometric information while adaptively scaling structural tokens. The method first constructs variable-size structural patches on molecular graphs using an instruction-conditioned gating policy, enabling complexity-aware allocation of query tokens. It then refines the resulting patch tokens via cross-attention with modality embeddings and injects geometry-informed tokens into the language model to improve structure grounding and reduce structural hallucinations. Across diverse all-atom benchmarks, the proposed approach yields consistent gains in heterogeneous structure-grounded reasoning. An anonymized implementation is provided in the supplementary material.
Entropy-Guided Dynamic Tokens for Graph-LLM Alignment in Molecular Understanding
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Molecular understanding is central to advancing areas such as scientific discovery, yet Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to understand molecular graphs effectively. Existing graph-LLM bridges often adapt the Q-Former-style connector with fixed-length static tokens, which is originally designed for vision tasks. These designs overlook stereochemistry and substructural context and typically require costly LLM-backbone fine-tuning, limiting efficiency and generalization. We introduce EDT-Former, an Entropy-guided Dynamic Token Transformer that generates tokens aligned with informative molecular patches, thereby preserving both local and global structural features for molecular graph understanding. Beyond prior approaches, EDT-Former enables alignment between frozen graph encoders and LLMs without tuning the LLM backbone (excluding the embedding layer), resulting in computationally efficient finetuning, and achieves stateof-the-art results on MoleculeQA, Molecule-oriented Mol-Instructions, and property prediction benchmarks (TDC, MoleculeNet), underscoring its effectiveness for scalable and generalizable multimodal molecular understanding
Scaling-Aware Adapter for Structure-Grounded LLM Reasoning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are enabling reasoning over biomolecular structures, yet existing methods remain modality-specific and typically compress structural inputs through sequence-based tokenization or fixed-length query connectors. Such architectures either omit the geometric groundings requisite for mitigating structural hallucinations or impose inflexible modality fusion bottlenecks that concurrently over-compress and suboptimally allocate structural tokens, thereby impeding the realization of generalized all-atom reasoning. We introduce Cuttlefish, a unified all-atom LLM that grounds language reasoning in geometric cues while scaling modality tokens with structural complexity. First, Scaling-Aware Patching leverages an instruction-conditioned gating mechanism to generate variable-size patches over structural graphs, adaptively scaling the query token budget with structural complexity to mitigate fixed-length connector bottlenecks. Second, Geometry Grounding Adapter refines these adaptive tokens via cross-attention to modality embeddings and injects the resulting modality tokens into the LLM, exposing explicit geometric cues to reduce structural hallucination. Experiments across diverse all-atom benchmarks demonstrate that Cuttlefish achieves superior performance in heterogeneous structure-grounded reasoning. Code is available at the project repository.
Breaking the Resolution Barrier: Arbitrary-resolution Deep Image Steganography Framework
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Deep image steganography (DIS) has achieved significant results in capacity and invisibility. However, current paradigms enforce the secret image to maintain the same resolution as the cover image during hiding and revealing. This leads to two challenges: secret images with inconsistent resolutions must undergo resampling beforehand which results in detail loss during recovery, and the secret image cannot be recovered to its original resolution when the resolution value is unknown. To address these, we propose ARDIS, the first Arbitrary Resolution DIS framework, which shifts the paradigm from discrete mapping to reference-guided continuous signal reconstruction. Specifically, to minimize the detail loss caused by resolution mismatch, we first design a Frequency Decoupling Architecture in hiding stage. It disentangles the secret into a resolution-aligned global basis and a resolution-agnostic high-frequency latent to hide in a fixed-resolution cover. Second, for recovery, we propose a Latent-Guided Implicit Reconstructor to perform deterministic restoration. The recovered detail latent code modulates a continuous implicit function to accurately query and render high-frequency residuals onto the recovered global basis, ensuring faithful restoration of original details. Furthermore, to achieve blind recovery, we introduce an Implicit Resolution Coding strategy. By transforming discrete resolution values into dense feature maps and hiding them in the redundant space of the feature domain, the reconstructor can correctly decode the secret's resolution directly from the steganographic representation. Experimental results demonstrate that ARDIS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both invisibility and cross-resolution recovery fidelity.
From Spurious to Causal: Low-rank Orthogonal Subspace Intervention for Generalizable Face Forgery Detection
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:The generalization problem remains a critical challenge in face forgery detection. Some researches have discovered that ``a backdoor path" in the representations from forgery-irrelevant information to labels induces biased learning, thereby hindering the generalization. In this paper, these forgery-irrelevant information are collectively termed spurious correlations factors. Previous methods predominantly focused on identifying concrete, specific spurious correlation and designing corresponding solutions to address them. However, spurious correlations arise from unobservable confounding factors, making it impractical to identify and address each one individually. To address this, we propose an intervention paradigm for representation space. Instead of tracking and blocking various instance-level spurious correlation one by one, we uniformly model them as a low-rank subspace and intervene in them. Specifically, we decompose spurious correlation features into a low-rank subspace via orthogonal low-rank projection, subsequently removing this subspace from the original representation and training its orthogonal complement to capture forgery-related features. This low-rank projection removal effectively eliminates spurious correlation factors, ensuring that classification decision is based on authentic forgery cues. With only 0.43M trainable parameters, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across several benchmarks, demonstrating excellent robustness and generalization.
DGS-Net: Distillation-Guided Gradient Surgery for CLIP Fine-Tuning in AI-Generated Image Detection
Nov 17, 2025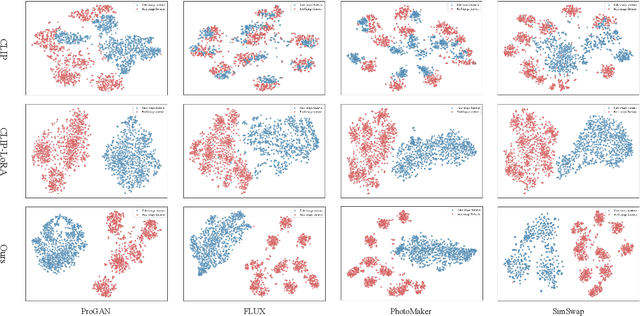
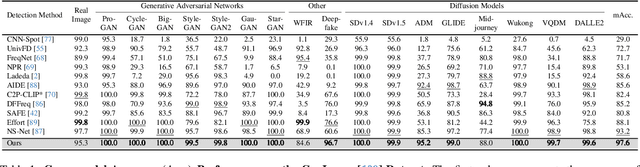
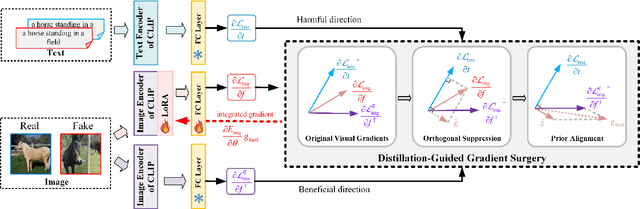
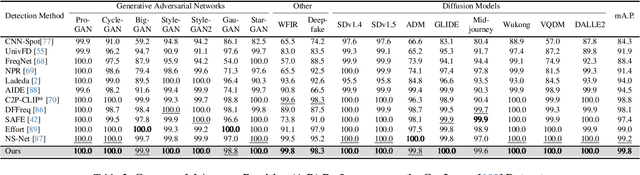
Abstract:The rapid progress of generative models such as GANs and diffusion models has led to the widespread proliferation of AI-generated images, raising concerns about misinformation, privacy violations, and trust erosion in digital media. Although large-scale multimodal models like CLIP offer strong transferable representations for detecting synthetic content, fine-tuning them often induces catastrophic forgetting, which degrades pre-trained priors and limits cross-domain generalization. To address this issue, we propose the Distillation-guided Gradient Surgery Network (DGS-Net), a novel framework that preserves transferable pre-trained priors while suppressing task-irrelevant components. Specifically, we introduce a gradient-space decomposition that separates harmful and beneficial descent directions during optimization. By projecting task gradients onto the orthogonal complement of harmful directions and aligning with beneficial ones distilled from a frozen CLIP encoder, DGS-Net achieves unified optimization of prior preservation and irrelevant suppression. Extensive experiments on 50 generative models demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches by an average margin of 6.6, achieving superior detection performance and generalization across diverse generation techniques.
FedOne: Query-Efficient Federated Learning for Black-box Discrete Prompt Learning
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Black-Box Discrete Prompt Learning is a prompt-tuning method that optimizes discrete prompts without accessing model parameters or gradients, making the prompt tuning on a cloud-based Large Language Model (LLM) feasible. Adapting federated learning to BDPL could further enhance prompt tuning performance by leveraging data from diverse sources. However, all previous research on federated black-box prompt tuning had neglected the substantial query cost associated with the cloud-based LLM service. To address this gap, we conducted a theoretical analysis of query efficiency within the context of federated black-box prompt tuning. Our findings revealed that degrading FedAvg to activate only one client per round, a strategy we called \textit{FedOne}, enabled optimal query efficiency in federated black-box prompt learning. Building on this insight, we proposed the FedOne framework, a federated black-box discrete prompt learning method designed to maximize query efficiency when interacting with cloud-based LLMs. We conducted numerical experiments on various aspects of our framework, demonstrating a significant improvement in query efficiency, which aligns with our theoretical results.
* Published in Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning
Event-Driven Online Vertical Federated Learning
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Online learning is more adaptable to real-world scenarios in Vertical Federated Learning (VFL) compared to offline learning. However, integrating online learning into VFL presents challenges due to the unique nature of VFL, where clients possess non-intersecting feature sets for the same sample. In real-world scenarios, the clients may not receive data streaming for the disjoint features for the same entity synchronously. Instead, the data are typically generated by an \emph{event} relevant to only a subset of clients. We are the first to identify these challenges in online VFL, which have been overlooked by previous research. To address these challenges, we proposed an event-driven online VFL framework. In this framework, only a subset of clients were activated during each event, while the remaining clients passively collaborated in the learning process. Furthermore, we incorporated \emph{dynamic local regret (DLR)} into VFL to address the challenges posed by online learning problems with non-convex models within a non-stationary environment. We conducted a comprehensive regret analysis of our proposed framework, specifically examining the DLR under non-convex conditions with event-driven online VFL. Extensive experiments demonstrated that our proposed framework was more stable than the existing online VFL framework under non-stationary data conditions while also significantly reducing communication and computation costs.
* Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Homophily Enhanced Graph Domain Adaptation
May 26, 2025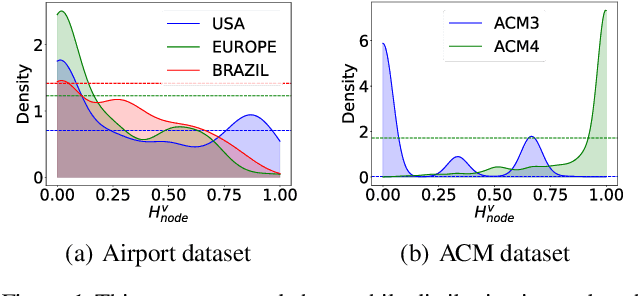



Abstract:Graph Domain Adaptation (GDA) transfers knowledge from labeled source graphs to unlabeled target graphs, addressing the challenge of label scarcity. In this paper, we highlight the significance of graph homophily, a pivotal factor for graph domain alignment, which, however, has long been overlooked in existing approaches. Specifically, our analysis first reveals that homophily discrepancies exist in benchmarks. Moreover, we also show that homophily discrepancies degrade GDA performance from both empirical and theoretical aspects, which further underscores the importance of homophily alignment in GDA. Inspired by this finding, we propose a novel homophily alignment algorithm that employs mixed filters to smooth graph signals, thereby effectively capturing and mitigating homophily discrepancies between graphs. Experimental results on a variety of benchmarks verify the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge