Rongjun Ge
DINO-BOLDNet: A DINOv3-Guided Multi-Slice Attention Network for T1-to-BOLD Generation
Dec 09, 2025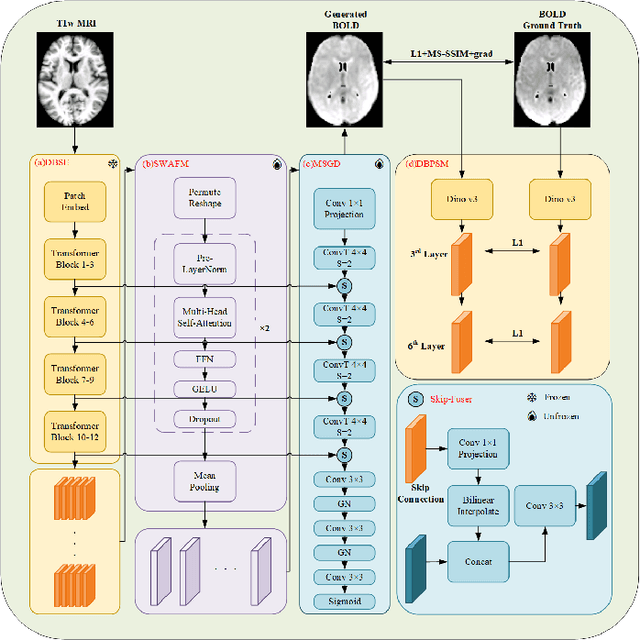
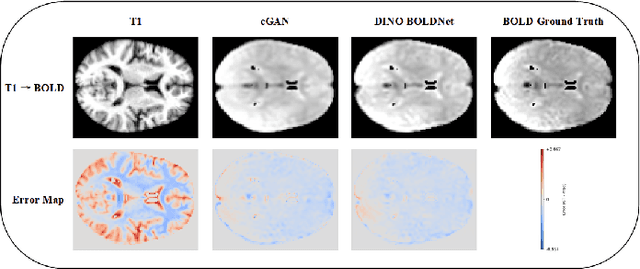
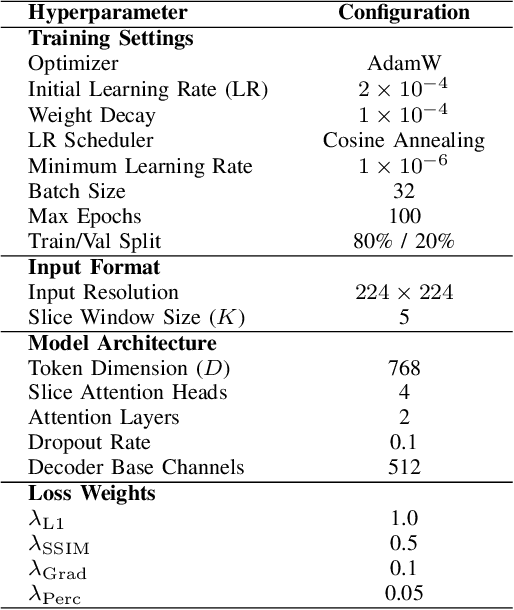
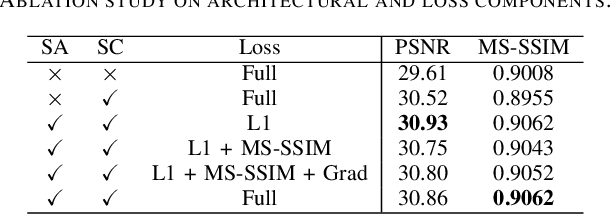
Abstract:Generating BOLD images from T1w images offers a promising solution for recovering missing BOLD information and enabling downstream tasks when BOLD images are corrupted or unavailable. Motivated by this, we propose DINO-BOLDNet, a DINOv3-guided multi-slice attention framework that integrates a frozen self-supervised DINOv3 encoder with a lightweight trainable decoder. The model uses DINOv3 to extract within-slice structural representations, and a separate slice-attention module to fuse contextual information across neighboring slices. A multi-scale generation decoder then restores fine-grained functional contrast, while a DINO-based perceptual loss encourages structural and textural consistency between predictions and ground-truth BOLD in the transformer feature space. Experiments on a clinical dataset of 248 subjects show that DINO-BOLDNet surpasses a conditional GAN baseline in both PSNR and MS-SSIM. To our knowledge, this is the first framework capable of generating mean BOLD images directly from T1w images, highlighting the potential of self-supervised transformer guidance for structural-to-functional mapping.
Think as Cardiac Sonographers: Marrying SAM with Left Ventricular Indicators Measurements According to Clinical Guidelines
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Left ventricular (LV) indicator measurements following clinical echocardiog-raphy guidelines are important for diagnosing cardiovascular disease. Alt-hough existing algorithms have explored automated LV quantification, they can struggle to capture generic visual representations due to the normally small training datasets. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce vision founda-tional models (VFM) with abundant knowledge. However, VFMs represented by the segment anything model (SAM) are usually suitable for segmentation but incapable of identifying key anatomical points, which are critical in LV indicator measurements. In this paper, we propose a novel framework named AutoSAME, combining the powerful visual understanding of SAM with seg-mentation and landmark localization tasks simultaneously. Consequently, the framework mimics the operation of cardiac sonographers, achieving LV indi-cator measurements consistent with clinical guidelines. We further present fil-tered cross-branch attention (FCBA) in AutoSAME, which leverages relatively comprehensive features in the segmentation to enhance the heatmap regression (HR) of key points from the frequency domain perspective, optimizing the vis-ual representation learned by the latter. Moreover, we propose spatial-guided prompt alignment (SGPA) to automatically generate prompt embeddings guid-ed by spatial properties of LV, thereby improving the accuracy of dense pre-dictions by prior spatial knowledge. The extensive experiments on an echocar-diography dataset demonstrate the efficiency of each design and the superiori-ty of our AutoSAME in LV segmentation, landmark localization, and indicator measurements. The code will be available at https://github.com/QC-LIU-1997/AutoSAME.
Homeomorphism Prior for False Positive and Negative Problem in Medical Image Dense Contrastive Representation Learning
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Dense contrastive representation learning (DCRL) has greatly improved the learning efficiency for image-dense prediction tasks, showing its great potential to reduce the large costs of medical image collection and dense annotation. However, the properties of medical images make unreliable correspondence discovery, bringing an open problem of large-scale false positive and negative (FP&N) pairs in DCRL. In this paper, we propose GEoMetric vIsual deNse sImilarity (GEMINI) learning which embeds the homeomorphism prior to DCRL and enables a reliable correspondence discovery for effective dense contrast. We propose a deformable homeomorphism learning (DHL) which models the homeomorphism of medical images and learns to estimate a deformable mapping to predict the pixels' correspondence under topological preservation. It effectively reduces the searching space of pairing and drives an implicit and soft learning of negative pairs via a gradient. We also propose a geometric semantic similarity (GSS) which extracts semantic information in features to measure the alignment degree for the correspondence learning. It will promote the learning efficiency and performance of deformation, constructing positive pairs reliably. We implement two practical variants on two typical representation learning tasks in our experiments. Our promising results on seven datasets which outperform the existing methods show our great superiority. We will release our code on a companion link: https://github.com/YutingHe-list/GEMINI.
Gaze-Assisted Human-Centric Domain Adaptation for Cardiac Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Feb 06, 2025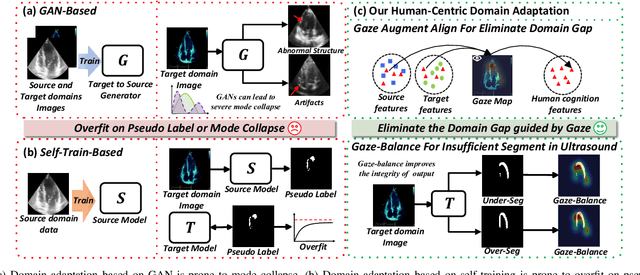
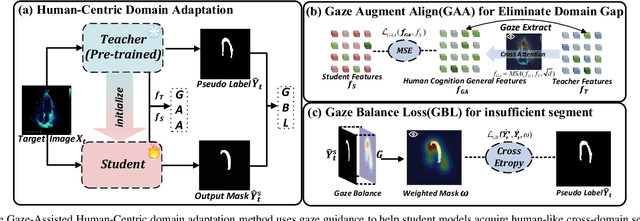
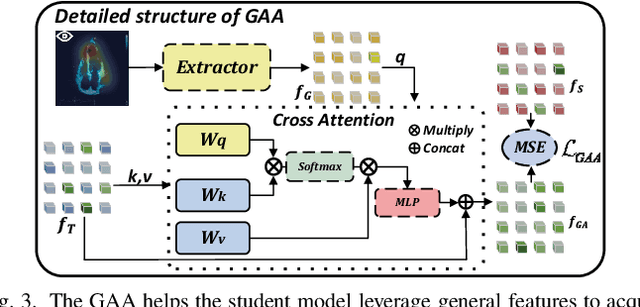
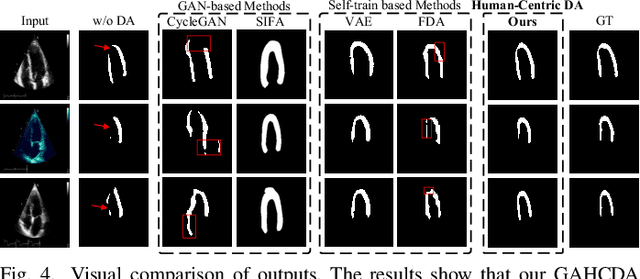
Abstract:Domain adaptation (DA) for cardiac ultrasound image segmentation is clinically significant and valuable. However, previous domain adaptation methods are prone to be affected by the incomplete pseudo-label and low-quality target to source images. Human-centric domain adaptation has great advantages of human cognitive guidance to help model adapt to target domain and reduce reliance on labels. Doctor gaze trajectories contains a large amount of cross-domain human guidance. To leverage gaze information and human cognition for guiding domain adaptation, we propose gaze-assisted human-centric domain adaptation (GAHCDA), which reliably guides the domain adaptation of cardiac ultrasound images. GAHCDA includes following modules: (1) Gaze Augment Alignment (GAA): GAA enables the model to obtain human cognition general features to recognize segmentation target in different domain of cardiac ultrasound images like humans. (2) Gaze Balance Loss (GBL): GBL fused gaze heatmap with outputs which makes the segmentation result structurally closer to the target domain. The experimental results illustrate that our proposed framework is able to segment cardiac ultrasound images more effectively in the target domain than GAN-based methods and other self-train based methods, showing great potential in clinical application.
Poisson Flow Joint Model for Multiphase contrast-enhanced CT
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:In clinical practice, multiphase contrast-enhanced CT (MCCT) is important for physiological and pathological imaging with contrast injection, which undergoes non-contrast, venous, and delayed phases. Inevitably, the accumulated radiation dose to a patient is higher for multiphase scans than for a plain CT scan. Low-dose CECT is thus highly desirable, but it often leads to suboptimal image quality due to reduced radiation dose. Recently, a generalized Poisson flow generative model (PFGM++) was proposed to unify the diffusion model and the Poisson flow generative models (PFGM), and outperform either of them with an optimized dimensionality of the augmentation data space, holding a significant promise for generic or conditional image generation. In this paper, we propose a Poisson flow joint model (PFJM) for low-dose MCCT to suppress image noise and preserve clinical features. Our model is built on the PFGM++ architecture to transform the multiphase imaging problem into learning the joint distribution of routine-dose MCCT images by optimizing a task-specific generation path with respect to the dimensionality D of the augmented data space. Then, our PFJM model takes the joint low-dose MCCT images as the condition and robustly drives the generative trajectory towards the solution in the routine-dose MCCT domain. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model is favorably compared with competing models, with MAE of 8.99 HU, SSIM of 98.75% and PSNR of 48.24db, as averaged over all the phases.
Imaging foundation model for universal enhancement of non-ideal measurement CT
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Non-ideal measurement computed tomography (NICT), which sacrifices optimal imaging standards for new advantages in CT imaging, is expanding the clinical application scope of CT images. However, with the reduction of imaging standards, the image quality has also been reduced, extremely limiting the clinical acceptability. Although numerous studies have demonstrated the feasibility of deep learning for the NICT enhancement in specific scenarios, their high data cost and limited generalizability have become large obstacles. The recent research on the foundation model has brought new opportunities for building a universal NICT enhancement model - bridging the image quality degradation with minimal data cost. However, owing to the challenges in the collection of large pre-training datasets and the compatibility of data variation, no success has been reported. In this paper, we propose a multi-scale integrated Transformer AMPlifier (TAMP), the first imaging foundation model for universal NICT enhancement. It has been pre-trained on a large-scale physical-driven simulation dataset with 3.6 million NICT-ICT image pairs, and is able to directly generalize to the NICT enhancement tasks with various non-ideal settings and body regions. Via the adaptation with few data, it can further achieve professional performance in real-world specific scenarios. Our extensive experiments have demonstrated that the proposed TAMP has significant potential for promoting the exploration and application of NICT and serving a wider range of medical scenarios.
Knowledge Boosting: Rethinking Medical Contrastive Vision-Language Pre-Training
Jul 17, 2023



Abstract:The foundation models based on pre-training technology have significantly advanced artificial intelligence from theoretical to practical applications. These models have facilitated the feasibility of computer-aided diagnosis for widespread use. Medical contrastive vision-language pre-training, which does not require human annotations, is an effective approach for guiding representation learning using description information in diagnostic reports. However, the effectiveness of pre-training is limited by the large-scale semantic overlap and shifting problems in medical field. To address these issues, we propose the Knowledge-Boosting Contrastive Vision-Language Pre-training framework (KoBo), which integrates clinical knowledge into the learning of vision-language semantic consistency. The framework uses an unbiased, open-set sample-wise knowledge representation to measure negative sample noise and supplement the correspondence between vision-language mutual information and clinical knowledge. Extensive experiments validate the effect of our framework on eight tasks including classification, segmentation, retrieval, and semantic relatedness, achieving comparable or better performance with the zero-shot or few-shot settings. Our code is open on https://github.com/ChenXiaoFei-CS/KoBo.
JCCS-PFGM: A Novel Circle-Supervision based Poisson Flow Generative Model for Multiphase CECT Progressive Low-Dose Reconstruction with Joint Condition
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Multiphase contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scan is clinically significant to demonstrate the anatomy at different phases. In practice, such a multiphase CECT scan inherently takes longer time and deposits much more radiation dose into a patient body than a regular CT scan, and reduction of the radiation dose typically compromise the CECT image quality and its diagnostic value. With Joint Condition and Circle-Supervision, here we propose a novel Poisson Flow Generative Model (JCCS-PFGM) to promote the progressive low-dose reconstruction for multiphase CECT. JCCS-PFGM is characterized by the following three aspects: a progressive low-dose reconstruction scheme, a circle-supervision strategy, and a joint condition mechanism. Our extensive experiments are performed on a clinical dataset consisting of 11436 images. The results show that our JCCS-PFGM achieves promising PSNR up to 46.3dB, SSIM up to 98.5%, and MAE down to 9.67 HU averagely on phases I, II and III, in quantitative evaluations, as well as gains high-quality readable visualizations in qualitative assessments. All of these findings reveal our method a great potential to be adapted for clinical CECT scans at a much-reduced radiation dose.
Geometric Visual Similarity Learning in 3D Medical Image Self-supervised Pre-training
Mar 02, 2023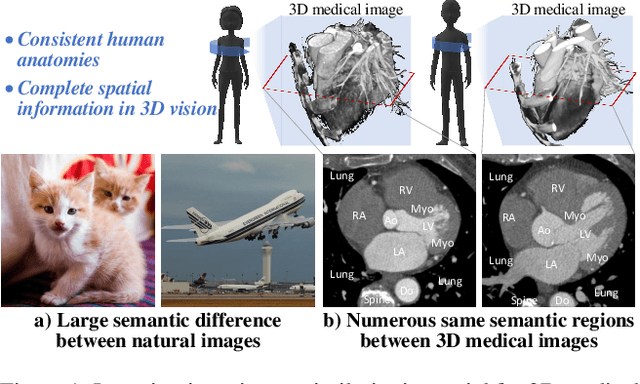
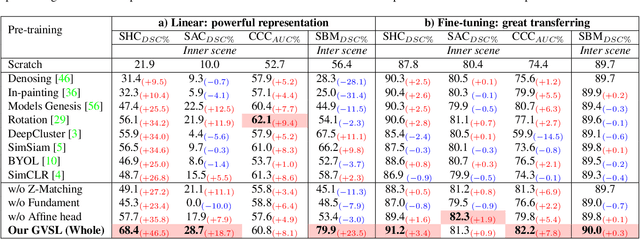
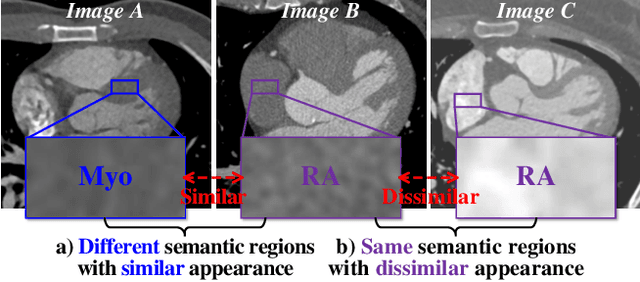

Abstract:Learning inter-image similarity is crucial for 3D medical images self-supervised pre-training, due to their sharing of numerous same semantic regions. However, the lack of the semantic prior in metrics and the semantic-independent variation in 3D medical images make it challenging to get a reliable measurement for the inter-image similarity, hindering the learning of consistent representation for same semantics. We investigate the challenging problem of this task, i.e., learning a consistent representation between images for a clustering effect of same semantic features. We propose a novel visual similarity learning paradigm, Geometric Visual Similarity Learning, which embeds the prior of topological invariance into the measurement of the inter-image similarity for consistent representation of semantic regions. To drive this paradigm, we further construct a novel geometric matching head, the Z-matching head, to collaboratively learn the global and local similarity of semantic regions, guiding the efficient representation learning for different scale-level inter-image semantic features. Our experiments demonstrate that the pre-training with our learning of inter-image similarity yields more powerful inner-scene, inter-scene, and global-local transferring ability on four challenging 3D medical image tasks. Our codes and pre-trained models will be publicly available on https://github.com/YutingHe-list/GVSL.
* Accepted by CVPR 2023
Low-Dose CT Denoising via Sinogram Inner-Structure Transformer
Apr 18, 2022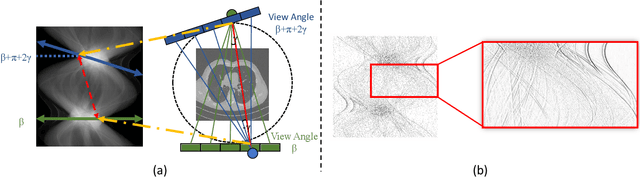
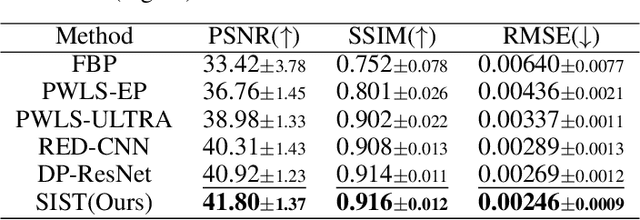
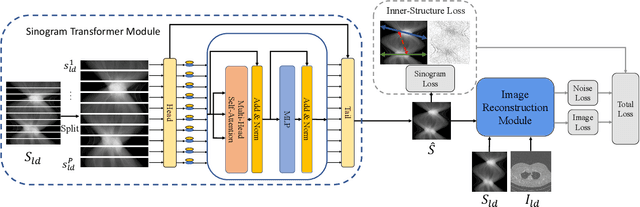
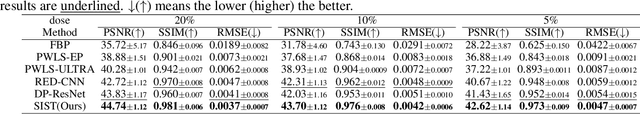
Abstract:Low-Dose Computed Tomography (LDCT) technique, which reduces the radiation harm to human bodies, is now attracting increasing interest in the medical imaging field. As the image quality is degraded by low dose radiation, LDCT exams require specialized reconstruction methods or denoising algorithms. However, most of the recent effective methods overlook the inner-structure of the original projection data (sinogram) which limits their denoising ability. The inner-structure of the sinogram represents special characteristics of the data in the sinogram domain. By maintaining this structure while denoising, the noise can be obviously restrained. Therefore, we propose an LDCT denoising network namely Sinogram Inner-Structure Transformer (SIST) to reduce the noise by utilizing the inner-structure in the sinogram domain. Specifically, we study the CT imaging mechanism and statistical characteristics of sinogram to design the sinogram inner-structure loss including the global and local inner-structure for restoring high-quality CT images. Besides, we propose a sinogram transformer module to better extract sinogram features. The transformer architecture using a self-attention mechanism can exploit interrelations between projections of different view angles, which achieves an outstanding performance in sinogram denoising. Furthermore, in order to improve the performance in the image domain, we propose the image reconstruction module to complementarily denoise both in the sinogram and image domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge