Youyong Kong
STAGE: A Benchmark for Knowledge Graph Construction, Question Answering, and In-Script Role-Playing over Movie Screenplays
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Movie screenplays are rich long-form narratives that interleave complex character relationships, temporally ordered events, and dialogue-driven interactions. While prior benchmarks target individual subtasks such as question answering or dialogue generation, they rarely evaluate whether models can construct a coherent story world and use it consistently across multiple forms of reasoning and generation. We introduce STAGE (Screenplay Text, Agents, Graphs and Evaluation), a unified benchmark for narrative understanding over full-length movie screenplays. STAGE defines four tasks: knowledge graph construction, scene-level event summarization, long-context screenplay question answering, and in-script character role-playing, all grounded in a shared narrative world representation. The benchmark provides cleaned scripts, curated knowledge graphs, and event- and character-centric annotations for 150 films across English and Chinese, enabling holistic evaluation of models' abilities to build world representations, abstract and verify narrative events, reason over long narratives, and generate character-consistent responses.
Intraoperative 2D/3D Registration via Spherical Similarity Learning and Inference-Time Differentiable Levenberg-Marquardt Optimization
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Intraoperative 2D/3D registration aligns preoperative 3D volumes with real-time 2D radiographs, enabling accurate localization of instruments and implants. A recent fully differentiable similarity learning framework approximates geodesic distances on SE(3), expanding the capture range of registration and mitigating the effects of substantial disturbances, but existing Euclidean approximations distort manifold structure and slow convergence. To address these limitations, we explore similarity learning in non-Euclidean spherical feature spaces to better capture and fit complex manifold structure. We extract feature embeddings using a CNN-Transformer encoder, project them into spherical space, and approximate their geodesic distances with Riemannian distances in the bi-invariant SO(4) space. This enables a more expressive and geometrically consistent deep similarity metric, enhancing the ability to distinguish subtle pose differences. During inference, we replace gradient descent with fully differentiable Levenberg-Marquardt optimization to accelerate convergence. Experiments on real and synthetic datasets show superior accuracy in both patient-specific and patient-agnostic scenarios.
Instance-Prototype Affinity Learning for Non-Exemplar Continual Graph Learning
May 15, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNN) endure catastrophic forgetting, undermining their capacity to preserve previously acquired knowledge amid the assimilation of novel information. Rehearsal-based techniques revisit historical examples, adopted as a principal strategy to alleviate this phenomenon. However, memory explosion and privacy infringements impose significant constraints on their utility. Non-Exemplar methods circumvent the prior issues through Prototype Replay (PR), yet feature drift presents new challenges. In this paper, our empirical findings reveal that Prototype Contrastive Learning (PCL) exhibits less pronounced drift than conventional PR. Drawing upon PCL, we propose Instance-Prototype Affinity Learning (IPAL), a novel paradigm for Non-Exemplar Continual Graph Learning (NECGL). Exploiting graph structural information, we formulate Topology-Integrated Gaussian Prototypes (TIGP), guiding feature distributions towards high-impact nodes to augment the model's capacity for assimilating new knowledge. Instance-Prototype Affinity Distillation (IPAD) safeguards task memory by regularizing discontinuities in class relationships. Moreover, we embed a Decision Boundary Perception (DBP) mechanism within PCL, fostering greater inter-class discriminability. Evaluations on four node classification benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving a better trade-off between plasticity and stability.
Topology-Aware Dynamic Reweighting for Distribution Shifts on Graph
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are widely used for node classification tasks but often fail to generalize when training and test nodes come from different distributions, limiting their practicality. To overcome this, recent approaches adopt invariant learning techniques from the out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization field, which seek to establish stable prediction methods across environments. However, the applicability of these invariant assumptions to graph data remains unverified, and such methods often lack solid theoretical support. In this work, we introduce the Topology-Aware Dynamic Reweighting (TAR) framework, which dynamically adjusts sample weights through gradient flow in the geometric Wasserstein space during training. Instead of relying on strict invariance assumptions, we prove that our method is able to provide distributional robustness, thereby enhancing the out-of-distribution generalization performance on graph data. By leveraging the inherent graph structure, TAR effectively addresses distribution shifts. Our framework's superiority is demonstrated through standard testing on four graph OOD datasets and three class-imbalanced node classification datasets, exhibiting marked improvements over existing methods.
ST-LDM: A Universal Framework for Text-Grounded Object Generation in Real Images
Mar 15, 2024
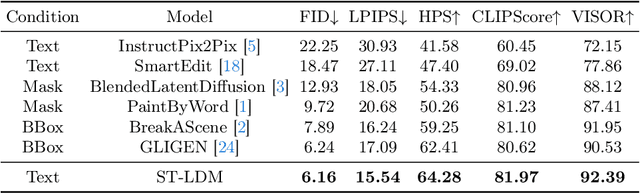
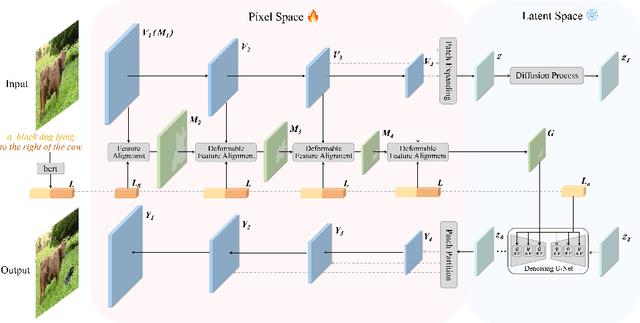
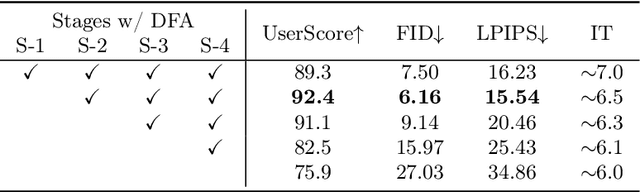
Abstract:We present a novel image editing scenario termed Text-grounded Object Generation (TOG), defined as generating a new object in the real image spatially conditioned by textual descriptions. Existing diffusion models exhibit limitations of spatial perception in complex real-world scenes, relying on additional modalities to enforce constraints, and TOG imposes heightened challenges on scene comprehension under the weak supervision of linguistic information. We propose a universal framework ST-LDM based on Swin-Transformer, which can be integrated into any latent diffusion model with training-free backward guidance. ST-LDM encompasses a global-perceptual autoencoder with adaptable compression scales and hierarchical visual features, parallel with deformable multimodal transformer to generate region-wise guidance for the subsequent denoising process. We transcend the limitation of traditional attention mechanisms that only focus on existing visual features by introducing deformable feature alignment to hierarchically refine spatial positioning fused with multi-scale visual and linguistic information. Extensive Experiments demonstrate that our model enhances the localization of attention mechanisms while preserving the generative capabilities inherent to diffusion models.
Rethinking Referring Object Removal
Mar 14, 2024
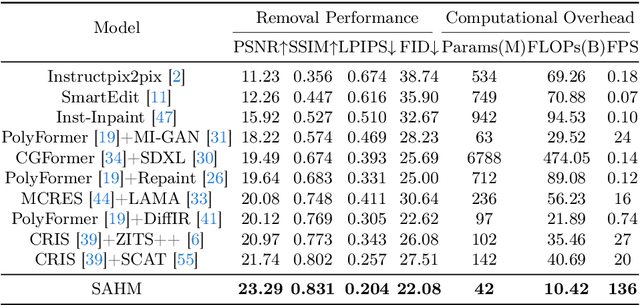


Abstract:Referring object removal refers to removing the specific object in an image referred by natural language expressions and filling the missing region with reasonable semantics. To address this task, we construct the ComCOCO, a synthetic dataset consisting of 136,495 referring expressions for 34,615 objects in 23,951 image pairs. Each pair contains an image with referring expressions and the ground truth after elimination. We further propose an end-to-end syntax-aware hybrid mapping network with an encoding-decoding structure. Linguistic features are hierarchically extracted at the syntactic level and fused in the downsampling process of visual features with multi-head attention. The feature-aligned pyramid network is leveraged to generate segmentation masks and replace internal pixels with region affinity learned from external semantics in high-level feature maps. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms diffusion models and two-stage methods which process the segmentation and inpainting task separately by a significant margin.
Multiscale Low-Frequency Memory Network for Improved Feature Extraction in Convolutional Neural Networks
Mar 13, 2024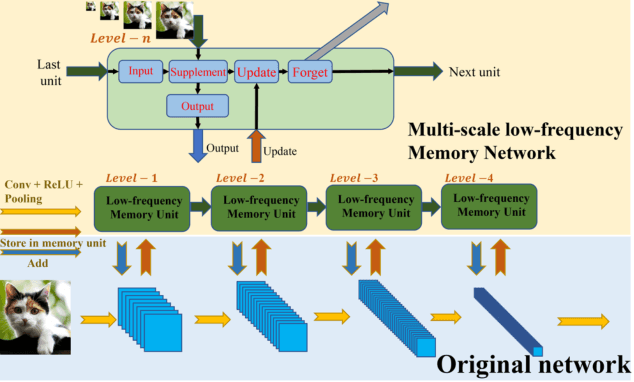
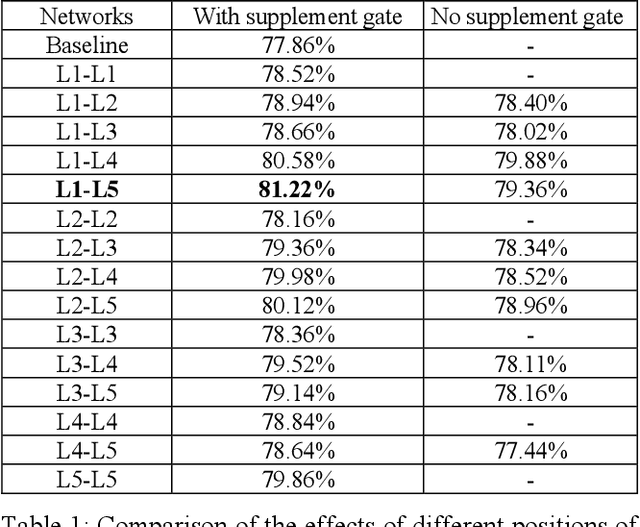
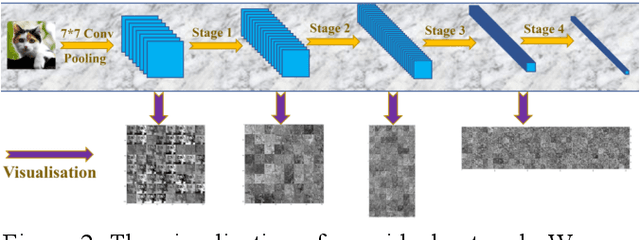
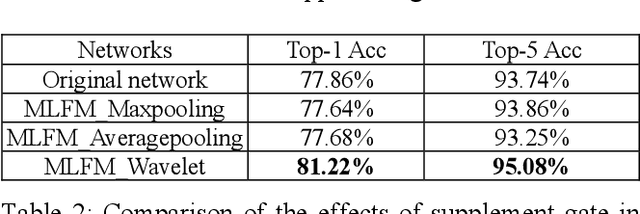
Abstract:Deep learning and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have driven major transformations in diverse research areas. However, their limitations in handling low-frequency information present obstacles in certain tasks like interpreting global structures or managing smooth transition images. Despite the promising performance of transformer structures in numerous tasks, their intricate optimization complexities highlight the persistent need for refined CNN enhancements using limited resources. Responding to these complexities, we introduce a novel framework, the Multiscale Low-Frequency Memory (MLFM) Network, with the goal to harness the full potential of CNNs while keeping their complexity unchanged. The MLFM efficiently preserves low-frequency information, enhancing performance in targeted computer vision tasks. Central to our MLFM is the Low-Frequency Memory Unit (LFMU), which stores various low-frequency data and forms a parallel channel to the core network. A key advantage of MLFM is its seamless compatibility with various prevalent networks, requiring no alterations to their original core structure. Testing on ImageNet demonstrated substantial accuracy improvements in multiple 2D CNNs, including ResNet, MobileNet, EfficientNet, and ConvNeXt. Furthermore, we showcase MLFM's versatility beyond traditional image classification by successfully integrating it into image-to-image translation tasks, specifically in semantic segmentation networks like FCN and U-Net. In conclusion, our work signifies a pivotal stride in the journey of optimizing the efficacy and efficiency of CNNs with limited resources. This research builds upon the existing CNN foundations and paves the way for future advancements in computer vision. Our codes are available at https://github.com/AlphaWuSeu/ MLFM.
An Optimization-based Baseline for Rigid 2D/3D Registration Applied to Spine Surgical Navigation Using CMA-ES
Feb 08, 2024
Abstract:A robust and efficient optimization-based 2D/3D registration framework is crucial for the navigation system of orthopedic surgical robots. It can provide precise position information of surgical instruments and implants during surgery. While artificial intelligence technology has advanced rapidly in recent years, traditional optimization-based registration methods remain indispensable in the field of 2D/3D registration.he exceptional precision of this method enables it to be considered as a post-processing step of the learning-based methods, thereby offering a reliable assurance for registration. In this paper, we present a coarse-to-fine registration framework based on the CMA-ES algorithm. We conducted intensive testing of our method using data from different parts of the spine. The results shows the effectiveness of the proposed framework on real orthopedic spine surgery clinical data. This work can be viewed as an additional extension that complements the optimization-based methods employed in our previous studies.
Fully Differentiable Correlation-driven 2D/3D Registration for X-ray to CT Image Fusion
Feb 04, 2024


Abstract:Image-based rigid 2D/3D registration is a critical technique for fluoroscopic guided surgical interventions. In recent years, some learning-based fully differentiable methods have produced beneficial outcomes while the process of feature extraction and gradient flow transmission still lack controllability and interpretability. To alleviate these problems, in this work, we propose a novel fully differentiable correlation-driven network using a dual-branch CNN-transformer encoder which enables the network to extract and separate low-frequency global features from high-frequency local features. A correlation-driven loss is further proposed for low-frequency feature and high-frequency feature decomposition based on embedded information. Besides, a training strategy that learns to approximate a convex-shape similarity function is applied in our work. We test our approach on a in-house datasetand show that it outperforms both existing fully differentiable learning-based registration approaches and the conventional optimization-based baseline.
SpineCLUE: Automatic Vertebrae Identification Using Contrastive Learning and Uncertainty Estimation
Jan 14, 2024Abstract:Vertebrae identification in arbitrary fields-of-view plays a crucial role in diagnosing spine disease. Most spine CT contain only local regions, such as the neck, chest, and abdomen. Therefore, identification should not depend on specific vertebrae or a particular number of vertebrae being visible. Existing methods at the spine-level are unable to meet this challenge. In this paper, we propose a three-stage method to address the challenges in 3D CT vertebrae identification at vertebrae-level. By sequentially performing the tasks of vertebrae localization, segmentation, and identification, the anatomical prior information of the vertebrae is effectively utilized throughout the process. Specifically, we introduce a dual-factor density clustering algorithm to acquire localization information for individual vertebra, thereby facilitating subsequent segmentation and identification processes. In addition, to tackle the issue of interclass similarity and intra-class variability, we pre-train our identification network by using a supervised contrastive learning method. To further optimize the identification results, we estimated the uncertainty of the classification network and utilized the message fusion module to combine the uncertainty scores, while aggregating global information about the spine. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on the VerSe19 and VerSe20 challenge benchmarks. Additionally, our approach demonstrates outstanding generalization performance on an collected dataset containing a wide range of abnormal cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge