Qiuhao Zeng
A Study of Adaptive Modeling Towards Robust Generalization
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) increasingly support reasoning over biomolecular structures, but most existing approaches remain modality-specific and rely on either sequence-style encodings or fixed-length connector tokens for structural inputs. These designs can under-expose explicit geometric cues and impose rigid fusion bottlenecks, leading to over-compression and poor token allocation as structural complexity grows. We present a unified all-atom framework that grounds language reasoning in geometric information while adaptively scaling structural tokens. The method first constructs variable-size structural patches on molecular graphs using an instruction-conditioned gating policy, enabling complexity-aware allocation of query tokens. It then refines the resulting patch tokens via cross-attention with modality embeddings and injects geometry-informed tokens into the language model to improve structure grounding and reduce structural hallucinations. Across diverse all-atom benchmarks, the proposed approach yields consistent gains in heterogeneous structure-grounded reasoning. An anonymized implementation is provided in the supplementary material.
Entropy-Guided Dynamic Tokens for Graph-LLM Alignment in Molecular Understanding
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Molecular understanding is central to advancing areas such as scientific discovery, yet Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to understand molecular graphs effectively. Existing graph-LLM bridges often adapt the Q-Former-style connector with fixed-length static tokens, which is originally designed for vision tasks. These designs overlook stereochemistry and substructural context and typically require costly LLM-backbone fine-tuning, limiting efficiency and generalization. We introduce EDT-Former, an Entropy-guided Dynamic Token Transformer that generates tokens aligned with informative molecular patches, thereby preserving both local and global structural features for molecular graph understanding. Beyond prior approaches, EDT-Former enables alignment between frozen graph encoders and LLMs without tuning the LLM backbone (excluding the embedding layer), resulting in computationally efficient finetuning, and achieves stateof-the-art results on MoleculeQA, Molecule-oriented Mol-Instructions, and property prediction benchmarks (TDC, MoleculeNet), underscoring its effectiveness for scalable and generalizable multimodal molecular understanding
Scaling-Aware Adapter for Structure-Grounded LLM Reasoning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are enabling reasoning over biomolecular structures, yet existing methods remain modality-specific and typically compress structural inputs through sequence-based tokenization or fixed-length query connectors. Such architectures either omit the geometric groundings requisite for mitigating structural hallucinations or impose inflexible modality fusion bottlenecks that concurrently over-compress and suboptimally allocate structural tokens, thereby impeding the realization of generalized all-atom reasoning. We introduce Cuttlefish, a unified all-atom LLM that grounds language reasoning in geometric cues while scaling modality tokens with structural complexity. First, Scaling-Aware Patching leverages an instruction-conditioned gating mechanism to generate variable-size patches over structural graphs, adaptively scaling the query token budget with structural complexity to mitigate fixed-length connector bottlenecks. Second, Geometry Grounding Adapter refines these adaptive tokens via cross-attention to modality embeddings and injects the resulting modality tokens into the LLM, exposing explicit geometric cues to reduce structural hallucination. Experiments across diverse all-atom benchmarks demonstrate that Cuttlefish achieves superior performance in heterogeneous structure-grounded reasoning. Code is available at the project repository.
Investigating the Multilingual Calibration Effects of Language Model Instruction-Tuning
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Ensuring that deep learning models are well-calibrated in terms of their predictive uncertainty is essential in maintaining their trustworthiness and reliability, yet despite increasing advances in foundation model research, the relationship between such large language models (LLMs) and their calibration remains an open area of research. In this work, we look at a critical gap in the calibration of LLMs within multilingual settings, in an attempt to better understand how the data scarcity can potentially lead to different calibration effects and how commonly used techniques can apply in these settings. Our analysis on two multilingual benchmarks, over 29 and 42 languages respectively, reveals that even in low-resource languages, model confidence can increase significantly after instruction-tuning on high-resource language SFT datasets. However, improvements in accuracy are marginal or non-existent, resulting in mis-calibration, highlighting a critical shortcoming of standard SFT for multilingual languages. Furthermore, we observe that the use of label smoothing to be a reasonable method alleviate this concern, again without any need for low-resource SFT data, maintaining better calibration across all languages. Overall, this highlights the importance of multilingual considerations for both training and tuning LLMs in order to improve their reliability and fairness in downstream use.
Toward Better Generalization in Few-Shot Learning through the Meta-Component Combination
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:In few-shot learning, classifiers are expected to generalize to unseen classes given only a small number of instances of each new class. One of the popular solutions to few-shot learning is metric-based meta-learning. However, it highly depends on the deep metric learned on seen classes, which may overfit to seen classes and fail to generalize well on unseen classes. To improve the generalization, we explore the substructures of classifiers and propose a novel meta-learning algorithm to learn each classifier as a combination of meta-components. Meta-components are learned across meta-learning episodes on seen classes and disentangled by imposing an orthogonal regularizer to promote its diversity and capture various shared substructures among different classifiers. Extensive experiments on few-shot benchmark tasks show superior performances of the proposed method.
Calibrated Language Models and How to Find Them with Label Smoothing
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in natural language processing (NLP) have opened up greater opportunities to enable fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) to behave as more powerful interactive agents through improved instruction-following ability. However, understanding how this impacts confidence calibration for reliable model output has not been researched in full. In this work, we examine various open-sourced LLMs, identifying significant calibration degradation after instruction tuning in each. Seeking a practical solution, we look towards label smoothing, which has been shown as an effective method to regularize for overconfident predictions but has yet to be widely adopted in the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) of LLMs. We first provide insight as to why label smoothing is sufficient to maintain calibration throughout the SFT process. However, settings remain where the effectiveness of smoothing is severely diminished, in particular the case of large vocabulary LLMs (LV-LLMs). We posit the cause to stem from the ability to become over-confident, which has a direct relationship with the hidden size and vocabulary size, and justify this theoretically and experimentally. Finally, we address an outstanding issue regarding the memory footprint of the cross-entropy loss computation in the label smoothed loss setting, designing a customized kernel to dramatically reduce memory consumption without sacrificing speed or performance in comparison to existing solutions for non-smoothed losses.
Homophily Enhanced Graph Domain Adaptation
May 26, 2025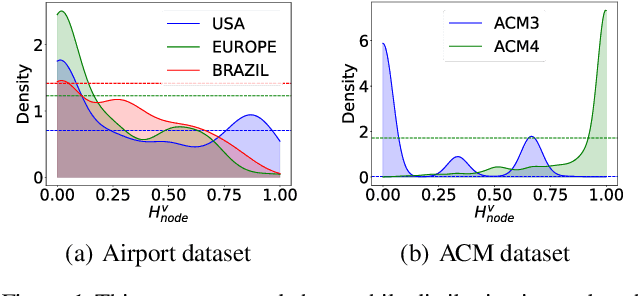



Abstract:Graph Domain Adaptation (GDA) transfers knowledge from labeled source graphs to unlabeled target graphs, addressing the challenge of label scarcity. In this paper, we highlight the significance of graph homophily, a pivotal factor for graph domain alignment, which, however, has long been overlooked in existing approaches. Specifically, our analysis first reveals that homophily discrepancies exist in benchmarks. Moreover, we also show that homophily discrepancies degrade GDA performance from both empirical and theoretical aspects, which further underscores the importance of homophily alignment in GDA. Inspired by this finding, we propose a novel homophily alignment algorithm that employs mixed filters to smooth graph signals, thereby effectively capturing and mitigating homophily discrepancies between graphs. Experimental results on a variety of benchmarks verify the effectiveness of our method.
ZETA: Leveraging Z-order Curves for Efficient Top-k Attention
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Over recent years, the Transformer has become a fundamental building block for sequence modeling architectures. Yet at its core is the use of self-attention, whose memory and computational cost grow quadratically with the sequence length $N$, rendering it prohibitively expensive for long sequences. A promising approach is top-$k$ attention, which selects only the $k$ most relevant tokens and achieves performance comparable to vanilla self-attention while significantly reducing space and computational demands. However, causal masks require the current query token to only attend to past tokens, preventing the existing top-$k$ attention method from efficiently searching for the most relevant tokens in parallel, thereby limiting training efficiency. In this work, we propose ZETA, leveraging \textbf{Z}-Order Curves for \textbf{E}fficient \textbf{T}op-$k$ \textbf{A}ttention, to enable parallel querying of past tokens for entire sequences. % in both space and time complexity of $\mathcal{O}(N \log N)$. We first theoretically show that the choice of key and query dimensions involves a trade-off between the curse of dimensionality and the preservation of relative distances after projection. In light of this insight, we propose reducing the dimensionality of keys and queries in contrast to values and further leverage $Z$-order curves to map low-dimensional keys and queries into \emph{one}-dimensional space, which permits parallel sorting, thereby largely improving the efficiency for top-$k$ token selection. Experimental results demonstrate that ZETA matches the performance of standard attention on the synthetic \textsc{Multi-Query Associative Recall} task and outperforms attention and its variants on \textsc{Long Range Arena} and \textsc{WikiText-103} language modeling.
Generalizing across Temporal Domains with Koopman Operators
Feb 15, 2024



Abstract:In the field of domain generalization, the task of constructing a predictive model capable of generalizing to a target domain without access to target data remains challenging. This problem becomes further complicated when considering evolving dynamics between domains. While various approaches have been proposed to address this issue, a comprehensive understanding of the underlying generalization theory is still lacking. In this study, we contribute novel theoretic results that aligning conditional distribution leads to the reduction of generalization bounds. Our analysis serves as a key motivation for solving the Temporal Domain Generalization (TDG) problem through the application of Koopman Neural Operators, resulting in Temporal Koopman Networks (TKNets). By employing Koopman Operators, we effectively address the time-evolving distributions encountered in TDG using the principles of Koopman theory, where measurement functions are sought to establish linear transition relations between evolving domains. Through empirical evaluations conducted on synthetic and real-world datasets, we validate the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
Foresee What You Will Learn: Data Augmentation for Domain Generalization in Non-Stationary Environments
Jan 19, 2023Abstract:Existing domain generalization aims to learn a generalizable model to perform well even on unseen domains. For many real-world machine learning applications, the data distribution often shifts gradually along domain indices. For example, a self-driving car with a vision system drives from dawn to dusk, with the sky darkening gradually. Therefore, the system must be able to adapt to changes in ambient illumination and continue to drive safely on the road. In this paper, we formulate such problems as Evolving Domain Generalization, where a model aims to generalize well on a target domain by discovering and leveraging the evolving pattern of the environment. We then propose Directional Domain Augmentation (DDA), which simulates the unseen target features by mapping source data as augmentations through a domain transformer. Specifically, we formulate DDA as a bi-level optimization problem and solve it through a novel meta-learning approach in the representation space. We evaluate the proposed method on both synthetic datasets and realworld datasets, and empirical results show that our approach can outperform other existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge