Boyuan Jiang
Kling-Omni Technical Report
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:We present Kling-Omni, a generalist generative framework designed to synthesize high-fidelity videos directly from multimodal visual language inputs. Adopting an end-to-end perspective, Kling-Omni bridges the functional separation among diverse video generation, editing, and intelligent reasoning tasks, integrating them into a holistic system. Unlike disjointed pipeline approaches, Kling-Omni supports a diverse range of user inputs, including text instructions, reference images, and video contexts, processing them into a unified multimodal representation to deliver cinematic-quality and highly-intelligent video content creation. To support these capabilities, we constructed a comprehensive data system that serves as the foundation for multimodal video creation. The framework is further empowered by efficient large-scale pre-training strategies and infrastructure optimizations for inference. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that Kling-Omni demonstrates exceptional capabilities in in-context generation, reasoning-based editing, and multimodal instruction following. Moving beyond a content creation tool, we believe Kling-Omni is a pivotal advancement toward multimodal world simulators capable of perceiving, reasoning, generating and interacting with the dynamic and complex worlds.
KlingAvatar 2.0 Technical Report
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Avatar video generation models have achieved remarkable progress in recent years. However, prior work exhibits limited efficiency in generating long-duration high-resolution videos, suffering from temporal drifting, quality degradation, and weak prompt following as video length increases. To address these challenges, we propose KlingAvatar 2.0, a spatio-temporal cascade framework that performs upscaling in both spatial resolution and temporal dimension. The framework first generates low-resolution blueprint video keyframes that capture global semantics and motion, and then refines them into high-resolution, temporally coherent sub-clips using a first-last frame strategy, while retaining smooth temporal transitions in long-form videos. To enhance cross-modal instruction fusion and alignment in extended videos, we introduce a Co-Reasoning Director composed of three modality-specific large language model (LLM) experts. These experts reason about modality priorities and infer underlying user intent, converting inputs into detailed storylines through multi-turn dialogue. A Negative Director further refines negative prompts to improve instruction alignment. Building on these components, we extend the framework to support ID-specific multi-character control. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model effectively addresses the challenges of efficient, multimodally aligned long-form high-resolution video generation, delivering enhanced visual clarity, realistic lip-teeth rendering with accurate lip synchronization, strong identity preservation, and coherent multimodal instruction following.
Mitigating the Noise Shift for Denoising Generative Models via Noise Awareness Guidance
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Existing denoising generative models rely on solving discretized reverse-time SDEs or ODEs. In this paper, we identify a long-overlooked yet pervasive issue in this family of models: a misalignment between the pre-defined noise level and the actual noise level encoded in intermediate states during sampling. We refer to this misalignment as noise shift. Through empirical analysis, we demonstrate that noise shift is widespread in modern diffusion models and exhibits a systematic bias, leading to sub-optimal generation due to both out-of-distribution generalization and inaccurate denoising updates. To address this problem, we propose Noise Awareness Guidance (NAG), a simple yet effective correction method that explicitly steers sampling trajectories to remain consistent with the pre-defined noise schedule. We further introduce a classifier-free variant of NAG, which jointly trains a noise-conditional and a noise-unconditional model via noise-condition dropout, thereby eliminating the need for external classifiers. Extensive experiments, including ImageNet generation and various supervised fine-tuning tasks, show that NAG consistently mitigates noise shift and substantially improves the generation quality of mainstream diffusion models.
Score Augmentation for Diffusion Models
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in generative modeling. However, this study confirms the existence of overfitting in diffusion model training, particularly in data-limited regimes. To address this challenge, we propose Score Augmentation (ScoreAug), a novel data augmentation framework specifically designed for diffusion models. Unlike conventional augmentation approaches that operate on clean data, ScoreAug applies transformations to noisy data, aligning with the inherent denoising mechanism of diffusion. Crucially, ScoreAug further requires the denoiser to predict the augmentation of the original target. This design establishes an equivariant learning objective, enabling the denoiser to learn scores across varied denoising spaces, thereby realizing what we term score augmentation. We also theoretically analyze the relationship between scores in different spaces under general transformations. In experiments, we extensively validate ScoreAug on multiple benchmarks including CIFAR-10, FFHQ, AFHQv2, and ImageNet, with results demonstrating significant performance improvements over baselines. Notably, ScoreAug effectively mitigates overfitting across diverse scenarios, such as varying data scales and model capacities, while exhibiting stable convergence properties. Another advantage of ScoreAug over standard data augmentation lies in its ability to circumvent data leakage issues under certain conditions. Furthermore, we show that ScoreAug can be synergistically combined with traditional data augmentation techniques to achieve additional performance gains.
VFRTok: Variable Frame Rates Video Tokenizer with Duration-Proportional Information Assumption
May 17, 2025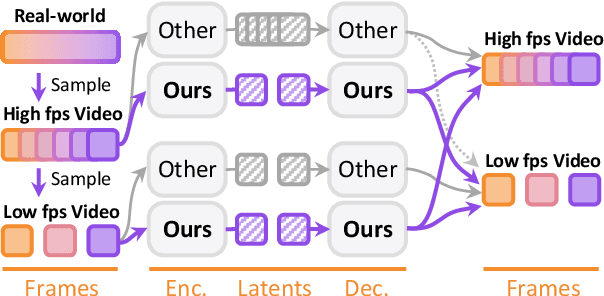
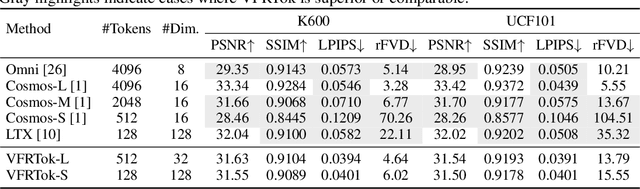
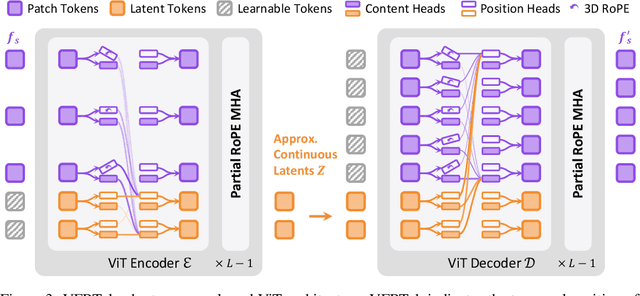
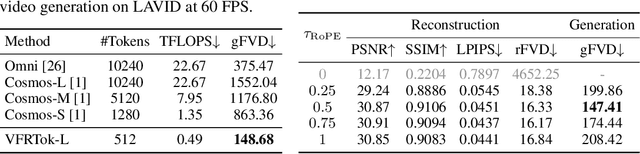
Abstract:Modern video generation frameworks based on Latent Diffusion Models suffer from inefficiencies in tokenization due to the Frame-Proportional Information Assumption. Existing tokenizers provide fixed temporal compression rates, causing the computational cost of the diffusion model to scale linearly with the frame rate. The paper proposes the Duration-Proportional Information Assumption: the upper bound on the information capacity of a video is proportional to the duration rather than the number of frames. Based on this insight, the paper introduces VFRTok, a Transformer-based video tokenizer, that enables variable frame rate encoding and decoding through asymmetric frame rate training between the encoder and decoder. Furthermore, the paper proposes Partial Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE) to decouple position and content modeling, which groups correlated patches into unified tokens. The Partial RoPE effectively improves content-awareness, enhancing the video generation capability. Benefiting from the compact and continuous spatio-temporal representation, VFRTok achieves competitive reconstruction quality and state-of-the-art generation fidelity while using only 1/8 tokens compared to existing tokenizers.
CrossVTON: Mimicking the Logic Reasoning on Cross-category Virtual Try-on guided by Tri-zone Priors
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Despite remarkable progress in image-based virtual try-on systems, generating realistic and robust fitting images for cross-category virtual try-on remains a challenging task. The primary difficulty arises from the absence of human-like reasoning, which involves addressing size mismatches between garments and models while recognizing and leveraging the distinct functionalities of various regions within the model images. To address this issue, we draw inspiration from human cognitive processes and disentangle the complex reasoning required for cross-category try-on into a structured framework. This framework systematically decomposes the model image into three distinct regions: try-on, reconstruction, and imagination zones. Each zone plays a specific role in accommodating the garment and facilitating realistic synthesis. To endow the model with robust reasoning capabilities for cross-category scenarios, we propose an iterative data constructor. This constructor encompasses diverse scenarios, including intra-category try-on, any-to-dress transformations (replacing any garment category with a dress), and dress-to-any transformations (replacing a dress with another garment category). Utilizing the generated dataset, we introduce a tri-zone priors generator that intelligently predicts the try-on, reconstruction, and imagination zones by analyzing how the input garment is expected to align with the model image. Guided by these tri-zone priors, our proposed method, CrossVTON, achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing baselines in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Notably, it demonstrates superior capability in handling cross-category virtual try-on, meeting the complex demands of real-world applications.
DynamicControl: Adaptive Condition Selection for Improved Text-to-Image Generation
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:To enhance the controllability of text-to-image diffusion models, current ControlNet-like models have explored various control signals to dictate image attributes. However, existing methods either handle conditions inefficiently or use a fixed number of conditions, which does not fully address the complexity of multiple conditions and their potential conflicts. This underscores the need for innovative approaches to manage multiple conditions effectively for more reliable and detailed image synthesis. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework, DynamicControl, which supports dynamic combinations of diverse control signals, allowing adaptive selection of different numbers and types of conditions. Our approach begins with a double-cycle controller that generates an initial real score sorting for all input conditions by leveraging pre-trained conditional generation models and discriminative models. This controller evaluates the similarity between extracted conditions and input conditions, as well as the pixel-level similarity with the source image. Then, we integrate a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to build an efficient condition evaluator. This evaluator optimizes the ordering of conditions based on the double-cycle controller's score ranking. Our method jointly optimizes MLLMs and diffusion models, utilizing MLLMs' reasoning capabilities to facilitate multi-condition text-to-image (T2I) tasks. The final sorted conditions are fed into a parallel multi-control adapter, which learns feature maps from dynamic visual conditions and integrates them to modulate ControlNet, thereby enhancing control over generated images. Through both quantitative and qualitative comparisons, DynamicControl demonstrates its superiority over existing methods in terms of controllability, generation quality and composability under various conditional controls.
Unveil Inversion and Invariance in Flow Transformer for Versatile Image Editing
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Leveraging the large generative prior of the flow transformer for tuning-free image editing requires authentic inversion to project the image into the model's domain and a flexible invariance control mechanism to preserve non-target contents. However, the prevailing diffusion inversion performs deficiently in flow-based models, and the invariance control cannot reconcile diverse rigid and non-rigid editing tasks. To address these, we systematically analyze the \textbf{inversion and invariance} control based on the flow transformer. Specifically, we unveil that the Euler inversion shares a similar structure to DDIM yet is more susceptible to the approximation error. Thus, we propose a two-stage inversion to first refine the velocity estimation and then compensate for the leftover error, which pivots closely to the model prior and benefits editing. Meanwhile, we propose the invariance control that manipulates the text features within the adaptive layer normalization, connecting the changes in the text prompt to image semantics. This mechanism can simultaneously preserve the non-target contents while allowing rigid and non-rigid manipulation, enabling a wide range of editing types such as visual text, quantity, facial expression, etc. Experiments on versatile scenarios validate that our framework achieves flexible and accurate editing, unlocking the potential of the flow transformer for versatile image editing.
FitDiT: Advancing the Authentic Garment Details for High-fidelity Virtual Try-on
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Although image-based virtual try-on has made considerable progress, emerging approaches still encounter challenges in producing high-fidelity and robust fitting images across diverse scenarios. These methods often struggle with issues such as texture-aware maintenance and size-aware fitting, which hinder their overall effectiveness. To address these limitations, we propose a novel garment perception enhancement technique, termed FitDiT, designed for high-fidelity virtual try-on using Diffusion Transformers (DiT) allocating more parameters and attention to high-resolution features. First, to further improve texture-aware maintenance, we introduce a garment texture extractor that incorporates garment priors evolution to fine-tune garment feature, facilitating to better capture rich details such as stripes, patterns, and text. Additionally, we introduce frequency-domain learning by customizing a frequency distance loss to enhance high-frequency garment details. To tackle the size-aware fitting issue, we employ a dilated-relaxed mask strategy that adapts to the correct length of garments, preventing the generation of garments that fill the entire mask area during cross-category try-on. Equipped with the above design, FitDiT surpasses all baselines in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. It excels in producing well-fitting garments with photorealistic and intricate details, while also achieving competitive inference times of 4.57 seconds for a single 1024x768 image after DiT structure slimming, outperforming existing methods.
VIVID-10M: A Dataset and Baseline for Versatile and Interactive Video Local Editing
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion-based image editing models have made remarkable progress in recent years. However, achieving high-quality video editing remains a significant challenge. One major hurdle is the absence of open-source, large-scale video editing datasets based on real-world data, as constructing such datasets is both time-consuming and costly. Moreover, video data requires a significantly larger number of tokens for representation, which substantially increases the training costs for video editing models. Lastly, current video editing models offer limited interactivity, often making it difficult for users to express their editing requirements effectively in a single attempt. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a dataset VIVID-10M and a baseline model VIVID. VIVID-10M is the first large-scale hybrid image-video local editing dataset aimed at reducing data construction and model training costs, which comprises 9.7M samples that encompass a wide range of video editing tasks. VIVID is a Versatile and Interactive VIdeo local eDiting model trained on VIVID-10M, which supports entity addition, modification, and deletion. At its core, a keyframe-guided interactive video editing mechanism is proposed, enabling users to iteratively edit keyframes and propagate it to other frames, thereby reducing latency in achieving desired outcomes. Extensive experimental evaluations show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in video local editing, surpassing baseline methods in both automated metrics and user studies. The VIVID-10M dataset and the VIVID editing model will be available at \url{https://inkosizhong.github.io/VIVID/}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge