Jiahao Wang
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
Embedding Perturbation may Better Reflect the Uncertainty in LLM Reasoning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language Models (LLMs) have achieved significant breakthroughs across diverse domains; however, they can still produce unreliable or misleading outputs. For responsible LLM application, Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) techniques are used to estimate a model's uncertainty about its outputs, indicating the likelihood that those outputs may be problematic. For LLM reasoning tasks, it is essential to estimate the uncertainty not only for the final answer, but also for the intermediate steps of the reasoning, as this can enable more fine-grained and targeted interventions. In this study, we explore what UQ metrics better reflect the LLM's ``intermediate uncertainty''during reasoning. Our study reveals that an LLMs' incorrect reasoning steps tend to contain tokens which are highly sensitive to the perturbations on the preceding token embeddings. In this way, incorrect (uncertain) intermediate steps can be readily identified using this sensitivity score as guidance in practice. In our experiments, we show such perturbation-based metric achieves stronger uncertainty quantification performance compared with baseline methods such as token (generation) probability and token entropy. Besides, different from approaches that rely on multiple sampling, the perturbation-based metrics offer better simplicity and efficiency.
LINA: Linear Autoregressive Image Generative Models with Continuous Tokens
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive models with continuous tokens form a promising paradigm for visual generation, especially for text-to-image (T2I) synthesis, but they suffer from high computational cost. We study how to design compute-efficient linear attention within this framework. Specifically, we conduct a systematic empirical analysis of scaling behavior with respect to parameter counts under different design choices, focusing on (1) normalization paradigms in linear attention (division-based vs. subtraction-based) and (2) depthwise convolution for locality augmentation. Our results show that although subtraction-based normalization is effective for image classification, division-based normalization scales better for linear generative transformers. In addition, incorporating convolution for locality modeling plays a crucial role in autoregressive generation, consistent with findings in diffusion models. We further extend gating mechanisms, commonly used in causal linear attention, to the bidirectional setting and propose a KV gate. By introducing data-independent learnable parameters to the key and value states, the KV gate assigns token-wise memory weights, enabling flexible memory management similar to forget gates in language models. Based on these findings, we present LINA, a simple and compute-efficient T2I model built entirely on linear attention, capable of generating high-fidelity 1024x1024 images from user instructions. LINA achieves competitive performance on both class-conditional and T2I benchmarks, obtaining 2.18 FID on ImageNet (about 1.4B parameters) and 0.74 on GenEval (about 1.5B parameters). A single linear attention module reduces FLOPs by about 61 percent compared to softmax attention. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/techmonsterwang/LINA.
From Prefix Cache to Fusion RAG Cache: Accelerating LLM Inference in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation enhances Large Language Models by integrating external knowledge, which reduces hallucinations but increases prompt length. This increase leads to higher computational costs and longer Time to First Token (TTFT). To mitigate this issue, existing solutions aim to reuse the preprocessed KV cache of each retrieved chunk to accelerate RAG. However, the lack of cross-chunk contextual information leads to a significant drop in generation quality, leaving the potential benefits of KV cache reuse largely unfulfilled. The challenge lies in how to reuse the precomputed KV cache of chunks while preserving generation quality. We propose FusionRAG, a novel inference framework that optimizes both the preprocessing and reprocessing stages of RAG. In the offline preprocessing stage, we embed information from other related text chunks into each chunk, while in the online reprocessing stage, we recompute the KV cache for tokens that the model focuses on. As a result, we achieve a better trade-off between generation quality and efficiency. According to our experiments, FusionRAG significantly improves generation quality at the same recomputation ratio compared to previous state-of-the-art solutions. By recomputing fewer than 15% of the tokens, FusionRAG achieves up to 70% higher normalized F1 scores than baselines and reduces TTFT by 2.66x-9.39x compared to Full Attention.
Efficient Protein Optimization via Structure-aware Hamiltonian Dynamics
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The ability to engineer optimized protein variants has transformative potential for biotechnology and medicine. Prior sequence-based optimization methods struggle with the high-dimensional complexities due to the epistasis effect and the disregard for structural constraints. To address this, we propose HADES, a Bayesian optimization method utilizing Hamiltonian dynamics to efficiently sample from a structure-aware approximated posterior. Leveraging momentum and uncertainty in the simulated physical movements, HADES enables rapid transition of proposals toward promising areas. A position discretization procedure is introduced to propose discrete protein sequences from such a continuous state system. The posterior surrogate is powered by a two-stage encoder-decoder framework to determine the structure and function relationships between mutant neighbors, consequently learning a smoothed landscape to sample from. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in in-silico evaluations across most metrics. Remarkably, our approach offers a unique advantage by leveraging the mutual constraints between protein structure and sequence, facilitating the design of protein sequences with similar structures and optimized properties. The code and data are publicly available at https://github.com/GENTEL-lab/HADES.
Interpretable Probability Estimation with LLMs via Shapley Reconstruction
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate potential to estimate the probability of uncertain events, by leveraging their extensive knowledge and reasoning capabilities. This ability can be applied to support intelligent decision-making across diverse fields, such as financial forecasting and preventive healthcare. However, directly prompting LLMs for probability estimation faces significant challenges: their outputs are often noisy, and the underlying predicting process is opaque. In this paper, we propose PRISM: Probability Reconstruction via Shapley Measures, a framework that brings transparency and precision to LLM-based probability estimation. PRISM decomposes an LLM's prediction by quantifying the marginal contribution of each input factor using Shapley values. These factor-level contributions are then aggregated to reconstruct a calibrated final estimate. In our experiments, we demonstrate PRISM improves predictive accuracy over direct prompting and other baselines, across multiple domains including finance, healthcare, and agriculture. Beyond performance, PRISM provides a transparent prediction pipeline: our case studies visualize how individual factors shape the final estimate, helping build trust in LLM-based decision support systems.
CellMamba: Adaptive Mamba for Accurate and Efficient Cell Detection
Dec 25, 2025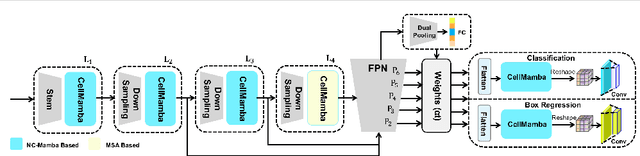
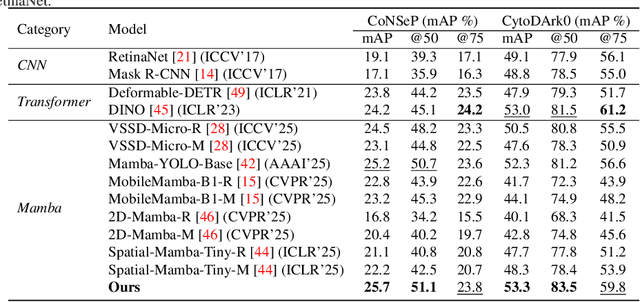
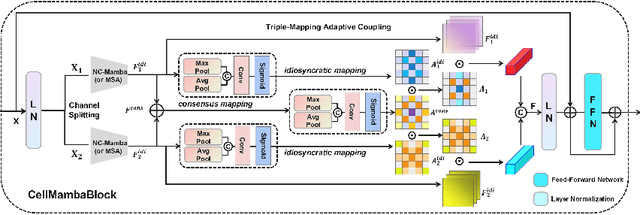
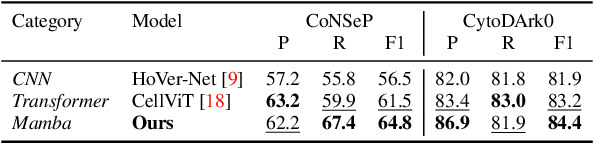
Abstract:Cell detection in pathological images presents unique challenges due to densely packed objects, subtle inter-class differences, and severe background clutter. In this paper, we propose CellMamba, a lightweight and accurate one-stage detector tailored for fine-grained biomedical instance detection. Built upon a VSSD backbone, CellMamba integrates CellMamba Blocks, which couple either NC-Mamba or Multi-Head Self-Attention (MSA) with a novel Triple-Mapping Adaptive Coupling (TMAC) module. TMAC enhances spatial discriminability by splitting channels into two parallel branches, equipped with dual idiosyncratic and one consensus attention map, adaptively fused to preserve local sensitivity and global consistency. Furthermore, we design an Adaptive Mamba Head that fuses multi-scale features via learnable weights for robust detection under varying object sizes. Extensive experiments on two public datasets-CoNSeP and CytoDArk0-demonstrate that CellMamba outperforms both CNN-based, Transformer-based, and Mamba-based baselines in accuracy, while significantly reducing model size and inference latency. Our results validate CellMamba as an efficient and effective solution for high-resolution cell detection.
T2AV-Compass: Towards Unified Evaluation for Text-to-Audio-Video Generation
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Text-to-Audio-Video (T2AV) generation aims to synthesize temporally coherent video and semantically synchronized audio from natural language, yet its evaluation remains fragmented, often relying on unimodal metrics or narrowly scoped benchmarks that fail to capture cross-modal alignment, instruction following, and perceptual realism under complex prompts. To address this limitation, we present T2AV-Compass, a unified benchmark for comprehensive evaluation of T2AV systems, consisting of 500 diverse and complex prompts constructed via a taxonomy-driven pipeline to ensure semantic richness and physical plausibility. Besides, T2AV-Compass introduces a dual-level evaluation framework that integrates objective signal-level metrics for video quality, audio quality, and cross-modal alignment with a subjective MLLM-as-a-Judge protocol for instruction following and realism assessment. Extensive evaluation of 11 representative T2AVsystems reveals that even the strongest models fall substantially short of human-level realism and cross-modal consistency, with persistent failures in audio realism, fine-grained synchronization, instruction following, etc. These results indicate significant improvement room for future models and highlight the value of T2AV-Compass as a challenging and diagnostic testbed for advancing text-to-audio-video generation.
EchoMotion: Unified Human Video and Motion Generation via Dual-Modality Diffusion Transformer
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Video generation models have advanced significantly, yet they still struggle to synthesize complex human movements due to the high degrees of freedom in human articulation. This limitation stems from the intrinsic constraints of pixel-only training objectives, which inherently bias models toward appearance fidelity at the expense of learning underlying kinematic principles. To address this, we introduce EchoMotion, a framework designed to model the joint distribution of appearance and human motion, thereby improving the quality of complex human action video generation. EchoMotion extends the DiT (Diffusion Transformer) framework with a dual-branch architecture that jointly processes tokens concatenated from different modalities. Furthermore, we propose MVS-RoPE (Motion-Video Syncronized RoPE), which offers unified 3D positional encoding for both video and motion tokens. By providing a synchronized coordinate system for the dual-modal latent sequence, MVS-RoPE establishes an inductive bias that fosters temporal alignment between the two modalities. We also propose a Motion-Video Two-Stage Training Strategy. This strategy enables the model to perform both the joint generation of complex human action videos and their corresponding motion sequences, as well as versatile cross-modal conditional generation tasks. To facilitate the training of a model with these capabilities, we construct HuMoVe, a large-scale dataset of approximately 80,000 high-quality, human-centric video-motion pairs. Our findings reveal that explicitly representing human motion is complementary to appearance, significantly boosting the coherence and plausibility of human-centric video generation.
Can We Predict the Next Question? A Collaborative Filtering Approach to Modeling User Behavior
Nov 17, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have excelled in language understanding and generation, powering advanced dialogue and recommendation systems. However, a significant limitation persists: these systems often model user preferences statically, failing to capture the dynamic and sequential nature of interactive behaviors. The sequence of a user's historical questions provides a rich, implicit signal of evolving interests and cognitive patterns, yet leveraging this temporal data for predictive tasks remains challenging due to the inherent disconnect between language modeling and behavioral sequence modeling. To bridge this gap, we propose a Collaborative Filtering-enhanced Question Prediction (CFQP) framework. CFQP dynamically models evolving user-question interactions by integrating personalized memory modules with graph-based preference propagation. This dual mechanism allows the system to adaptively learn from user-specific histories while refining predictions through collaborative signals from similar users. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach effectively generates agents that mimic real-user questioning patterns, highlighting its potential for building proactive and adaptive dialogue systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge