Bo Sun
Make It Long, Keep It Fast: End-to-End 10k-Sequence Modeling at Billion Scale on Douyin
Nov 08, 2025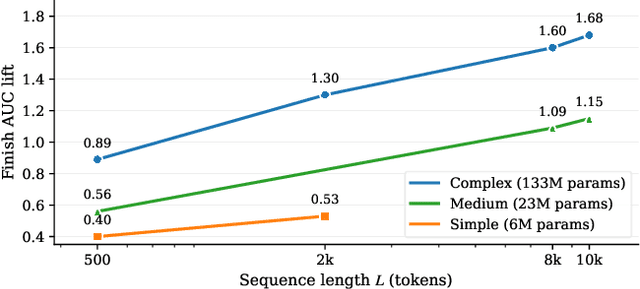
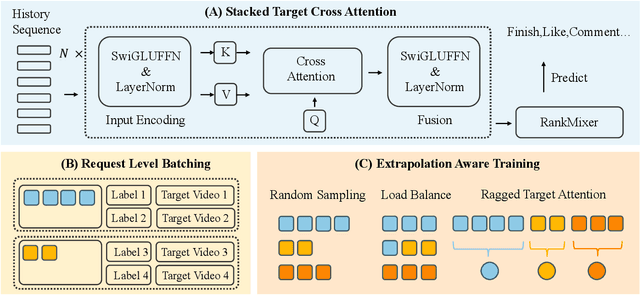

Abstract:Short-video recommenders such as Douyin must exploit extremely long user histories without breaking latency or cost budgets. We present an end-to-end system that scales long-sequence modeling to 10k-length histories in production. First, we introduce Stacked Target-to-History Cross Attention (STCA), which replaces history self-attention with stacked cross-attention from the target to the history, reducing complexity from quadratic to linear in sequence length and enabling efficient end-to-end training. Second, we propose Request Level Batching (RLB), a user-centric batching scheme that aggregates multiple targets for the same user/request to share the user-side encoding, substantially lowering sequence-related storage, communication, and compute without changing the learning objective. Third, we design a length-extrapolative training strategy -- train on shorter windows, infer on much longer ones -- so the model generalizes to 10k histories without additional training cost. Across offline and online experiments, we observe predictable, monotonic gains as we scale history length and model capacity, mirroring the scaling law behavior observed in large language models. Deployed at full traffic on Douyin, our system delivers significant improvements on key engagement metrics while meeting production latency, demonstrating a practical path to scaling end-to-end long-sequence recommendation to the 10k regime.
DPRF: A Generalizable Dynamic Persona Refinement Framework for Optimizing Behavior Alignment Between Personalized LLM Role-Playing Agents and Humans
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:The emerging large language model role-playing agents (LLM RPAs) aim to simulate individual human behaviors, but the persona fidelity is often undermined by manually-created profiles (e.g., cherry-picked information and personality characteristics) without validating the alignment with the target individuals. To address this limitation, our work introduces the Dynamic Persona Refinement Framework (DPRF).DPRF aims to optimize the alignment of LLM RPAs' behaviors with those of target individuals by iteratively identifying the cognitive divergence, either through free-form or theory-grounded, structured analysis, between generated behaviors and human ground truth, and refining the persona profile to mitigate these divergences.We evaluate DPRF with five LLMs on four diverse behavior-prediction scenarios: formal debates, social media posts with mental health issues, public interviews, and movie reviews.DPRF can consistently improve behavioral alignment considerably over baseline personas and generalizes across models and scenarios.Our work provides a robust methodology for creating high-fidelity persona profiles and enhancing the validity of downstream applications, such as user simulation, social studies, and personalized AI.
SceneCrafter: Controllable Multi-View Driving Scene Editing
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Simulation is crucial for developing and evaluating autonomous vehicle (AV) systems. Recent literature builds on a new generation of generative models to synthesize highly realistic images for full-stack simulation. However, purely synthetically generated scenes are not grounded in reality and have difficulty in inspiring confidence in the relevance of its outcomes. Editing models, on the other hand, leverage source scenes from real driving logs, and enable the simulation of different traffic layouts, behaviors, and operating conditions such as weather and time of day. While image editing is an established topic in computer vision, it presents fresh sets of challenges in driving simulation: (1) the need for cross-camera 3D consistency, (2) learning ``empty street" priors from driving data with foreground occlusions, and (3) obtaining paired image tuples of varied editing conditions while preserving consistent layout and geometry. To address these challenges, we propose SceneCrafter, a versatile editor for realistic 3D-consistent manipulation of driving scenes captured from multiple cameras. We build on recent advancements in multi-view diffusion models, using a fully controllable framework that scales seamlessly to multi-modality conditions like weather, time of day, agent boxes and high-definition maps. To generate paired data for supervising the editing model, we propose a novel framework on top of Prompt-to-Prompt to generate geometrically consistent synthetic paired data with global edits. We also introduce an alpha-blending framework to synthesize data with local edits, leveraging a model trained on empty street priors through novel masked training and multi-view repaint paradigm. SceneCrafter demonstrates powerful editing capabilities and achieves state-of-the-art realism, controllability, 3D consistency, and scene editing quality compared to existing baselines.
OPeRA: A Dataset of Observation, Persona, Rationale, and Action for Evaluating LLMs on Human Online Shopping Behavior Simulation
Jun 05, 2025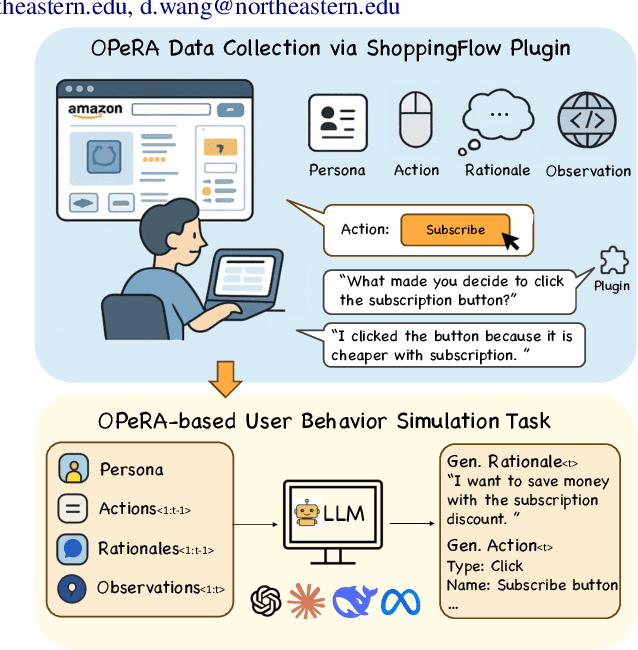
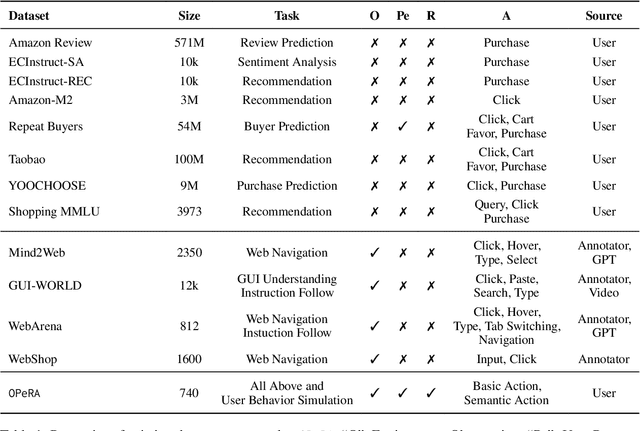
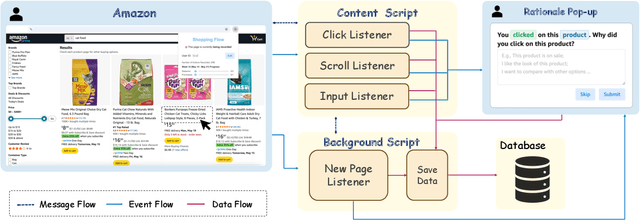
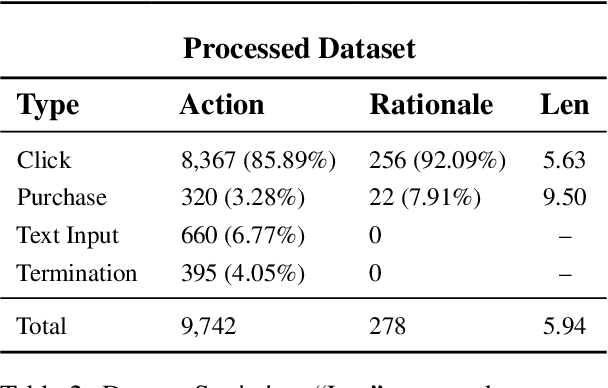
Abstract:Can large language models (LLMs) accurately simulate the next web action of a specific user? While LLMs have shown promising capabilities in generating ``believable'' human behaviors, evaluating their ability to mimic real user behaviors remains an open challenge, largely due to the lack of high-quality, publicly available datasets that capture both the observable actions and the internal reasoning of an actual human user. To address this gap, we introduce OPERA, a novel dataset of Observation, Persona, Rationale, and Action collected from real human participants during online shopping sessions. OPERA is the first public dataset that comprehensively captures: user personas, browser observations, fine-grained web actions, and self-reported just-in-time rationales. We developed both an online questionnaire and a custom browser plugin to gather this dataset with high fidelity. Using OPERA, we establish the first benchmark to evaluate how well current LLMs can predict a specific user's next action and rationale with a given persona and <observation, action, rationale> history. This dataset lays the groundwork for future research into LLM agents that aim to act as personalized digital twins for human.
MoCha: Towards Movie-Grade Talking Character Synthesis
Mar 30, 2025
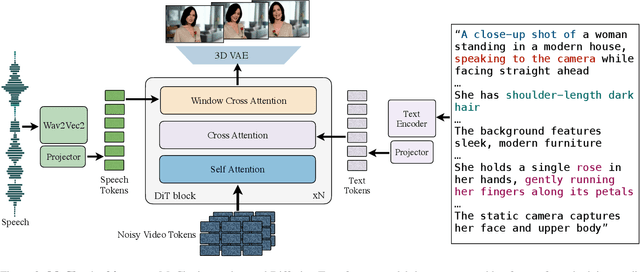
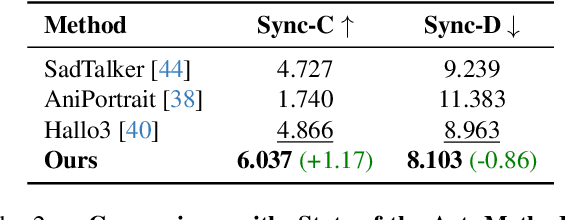
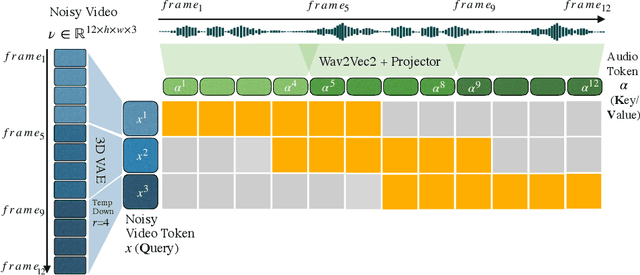
Abstract:Recent advancements in video generation have achieved impressive motion realism, yet they often overlook character-driven storytelling, a crucial task for automated film, animation generation. We introduce Talking Characters, a more realistic task to generate talking character animations directly from speech and text. Unlike talking head, Talking Characters aims at generating the full portrait of one or more characters beyond the facial region. In this paper, we propose MoCha, the first of its kind to generate talking characters. To ensure precise synchronization between video and speech, we propose a speech-video window attention mechanism that effectively aligns speech and video tokens. To address the scarcity of large-scale speech-labeled video datasets, we introduce a joint training strategy that leverages both speech-labeled and text-labeled video data, significantly improving generalization across diverse character actions. We also design structured prompt templates with character tags, enabling, for the first time, multi-character conversation with turn-based dialogue-allowing AI-generated characters to engage in context-aware conversations with cinematic coherence. Extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, including human preference studies and benchmark comparisons, demonstrate that MoCha sets a new standard for AI-generated cinematic storytelling, achieving superior realism, expressiveness, controllability and generalization.
Knowing When to Stop Matters: A Unified Algorithm for Online Conversion under Horizon Uncertainty
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:This paper investigates the online conversion problem, which involves sequentially trading a divisible resource (e.g., energy) under dynamically changing prices to maximize profit. A key challenge in online conversion is managing decisions under horizon uncertainty, where the duration of trading is either known, revealed partway, or entirely unknown. We propose a unified algorithm that achieves optimal competitive guarantees across these horizon models, accounting for practical constraints such as box constraints, which limit the maximum allowable trade per step. Additionally, we extend the algorithm to a learning-augmented version, leveraging horizon predictions to adaptively balance performance: achieving near-optimal results when predictions are accurate while maintaining strong guarantees when predictions are unreliable. These results advance the understanding of online conversion under various degrees of horizon uncertainty and provide more practical strategies to address real world constraints.
Glissando-Net: Deep sinGLe vIew category level poSe eStimation ANd 3D recOnstruction
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:We present a deep learning model, dubbed Glissando-Net, to simultaneously estimate the pose and reconstruct the 3D shape of objects at the category level from a single RGB image. Previous works predominantly focused on either estimating poses(often at the instance level), or reconstructing shapes, but not both. Glissando-Net is composed of two auto-encoders that are jointly trained, one for RGB images and the other for point clouds. We embrace two key design choices in Glissando-Net to achieve a more accurate prediction of the 3D shape and pose of the object given a single RGB image as input. First, we augment the feature maps of the point cloud encoder and decoder with transformed feature maps from the image decoder, enabling effective 2D-3D interaction in both training and prediction. Second, we predict both the 3D shape and pose of the object in the decoder stage. This way, we better utilize the information in the 3D point clouds presented only in the training stage to train the network for more accurate prediction. We jointly train the two encoder-decoders for RGB and point cloud data to learn how to pass latent features to the point cloud decoder during inference. In testing, the encoder of the 3D point cloud is discarded. The design of Glissando-Net is inspired by codeSLAM. Unlike codeSLAM, which targets 3D reconstruction of scenes, we focus on pose estimation and shape reconstruction of objects, and directly predict the object pose and a pose invariant 3D reconstruction without the need of the code optimization step. Extensive experiments, involving both ablation studies and comparison with competing methods, demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed method, and compare favorably with the state-of-the-art.
PPLNs: Parametric Piecewise Linear Networks for Event-Based Temporal Modeling and Beyond
Sep 29, 2024



Abstract:We present Parametric Piecewise Linear Networks (PPLNs) for temporal vision inference. Motivated by the neuromorphic principles that regulate biological neural behaviors, PPLNs are ideal for processing data captured by event cameras, which are built to simulate neural activities in the human retina. We discuss how to represent the membrane potential of an artificial neuron by a parametric piecewise linear function with learnable coefficients. This design echoes the idea of building deep models from learnable parametric functions recently popularized by Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs). Experiments demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of PPLNs in event-based and image-based vision applications, including steering prediction, human pose estimation, and motion deblurring. The source code of our implementation is available at https://github.com/chensong1995/PPLN.
CarbonClipper: Optimal Algorithms for Carbon-Aware Spatiotemporal Workload Management
Aug 14, 2024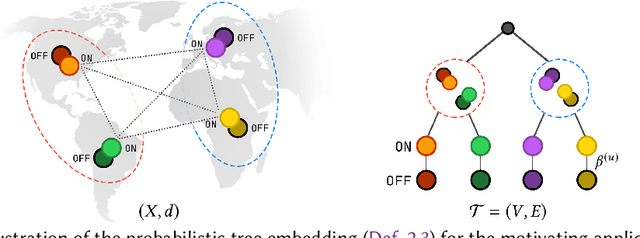
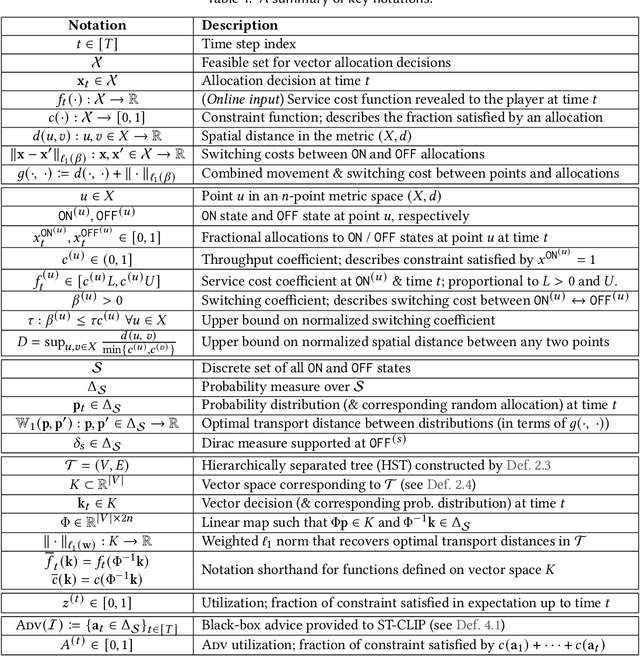
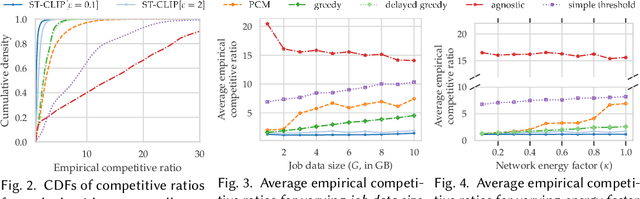
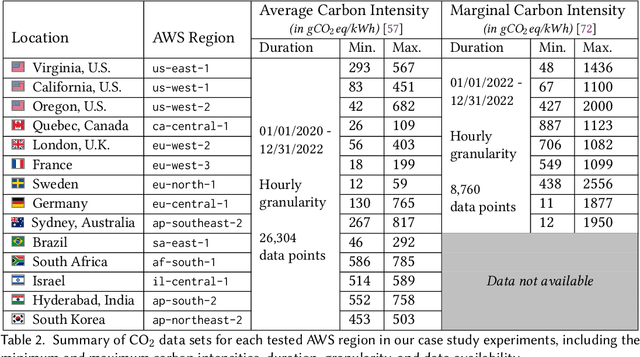
Abstract:We study carbon-aware spatiotemporal workload management, which seeks to address the growing environmental impact of data centers. We formalize this as an online problem called spatiotemporal online allocation with deadline constraints ($\mathsf{SOAD}$), in which an online player completes a workload (e.g., a batch compute job) by moving and scheduling the workload across a network subject to a deadline $T$. At each time step, a service cost function is revealed, representing, e.g., the carbon intensity of servicing a workload at each location, and the player must irrevocably decide the current allocation. Furthermore, whenever the player moves the allocation, it incurs a movement cost defined by a metric space $(X,d)$ that captures, e.g., the overhead of migrating a compute job. $\mathsf{SOAD}$ formalizes the open problem of combining general metrics and deadline constraints in the online algorithms literature, unifying problems such as metrical task systems and online search. We propose a competitive algorithm for $\mathsf{SOAD}$ along with a matching lower bound that proves it is optimal. Our main algorithm, ${\rm C{\scriptsize ARBON}C{\scriptsize LIPPER}}$, is a learning-augmented algorithm that takes advantage of predictions (e.g., carbon intensity forecasts) and achieves an optimal consistency-robustness trade-off. We evaluate our proposed algorithms for carbon-aware spatiotemporal workload management on a simulated global data center network, showing that ${\rm C{\scriptsize ARBON}C{\scriptsize LIPPER}}$ significantly improves performance compared to baseline methods and delivers meaningful carbon reductions.
Competitive Algorithms for Online Knapsack with Succinct Predictions
Jun 26, 2024


Abstract:In the online knapsack problem, the goal is to pack items arriving online with different values and weights into a capacity-limited knapsack to maximize the total value of the accepted items. We study \textit{learning-augmented} algorithms for this problem, which aim to use machine-learned predictions to move beyond pessimistic worst-case guarantees. Existing learning-augmented algorithms for online knapsack consider relatively complicated prediction models that give an algorithm substantial information about the input, such as the total weight of items at each value. In practice, such predictions can be error-sensitive and difficult to learn. Motivated by this limitation, we introduce a family of learning-augmented algorithms for online knapsack that use \emph{succinct predictions}. In particular, the machine-learned prediction given to the algorithm is just a single value or interval that estimates the minimum value of any item accepted by an offline optimal solution. By leveraging a relaxation to online \emph{fractional} knapsack, we design algorithms that can leverage such succinct predictions in both the trusted setting (i.e., with perfect prediction) and the untrusted setting, where we prove that a simple meta-algorithm achieves a nearly optimal consistency-robustness trade-off. Empirically, we show that our algorithms significantly outperform baselines that do not use predictions and often outperform algorithms based on more complex prediction models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge