Gang Hua
Wormpex AI Research
CoIn3D: Revisiting Configuration-Invariant Multi-Camera 3D Object Detection
Mar 05, 2026Abstract:Multi-camera 3D object detection (MC3D) has attracted increasing attention with the growing deployment of multi-sensor physical agents, such as robots and autonomous vehicles. However, MC3D models still struggle to generalize to unseen platforms with new multi-camera configurations. Current solutions simply employ a meta-camera for unified representation but lack comprehensive consideration. In this paper, we revisit this issue and identify that the devil lies in spatial prior discrepancies across source and target configurations, including different intrinsics, extrinsics, and array layouts. To address this, we propose CoIn3D, a generalizable MC3D framework that enables strong transferability from source configurations to unseen target ones. CoIn3D explicitly incorporates all identified spatial priors into both feature embedding and image observation through spatial-aware feature modulation (SFM) and camera-aware data augmentation (CDA), respectively. SFM enriches feature space by integrating four spatial representations, such as focal length, ground depth, ground gradient, and Plücker coordinate. CDA improves observation diversity under various configurations via a training-free dynamic novel-view image synthesis scheme. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CoIn3D achieves strong cross-configuration performance on landmark datasets such as NuScenes, Waymo, and Lyft, under three dominant MC3D paradigms represented by BEVDepth, BEVFormer, and PETR.
Object-Scene-Camera Decomposition and Recomposition for Data-Efficient Monocular 3D Object Detection
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Monocular 3D object detection (M3OD) is intrinsically ill-posed, hence training a high-performance deep learning based M3OD model requires a humongous amount of labeled data with complicated visual variation from diverse scenes, variety of objects and camera poses.However, we observe that, due to strong human bias, the three independent entities, i.e., object, scene, and camera pose, are always tightly entangled when an image is captured to construct training data. More specifically, specific 3D objects are always captured in particular scenes with fixed camera poses, and hence lacks necessary diversity. Such tight entanglement induces the challenging issues of insufficient utilization and overfitting to uniform training data. To mitigate this, we propose an online object-scene-camera decomposition and recomposition data manipulation scheme to more efficiently exploit the training data. We first fully decompose training images into textured 3D object point models and background scenes in an efficient computation and storage manner. We then continuously recompose new training images in each epoch by inserting the 3D objects into the freespace of the background scenes, and rendering them with perturbed camera poses from textured 3D point representation. In this way, the refreshed training data in all epochs can cover the full spectrum of independent object, scene, and camera pose combinations. This scheme can serve as a plug-and-play component to boost M3OD models, working flexibly with both fully and sparsely supervised settings. In the sparsely-supervised setting, objects closest to the ego-camera for all instances are sparsely annotated. We then can flexibly increase the annotated objects to control annotation cost. For validation, our method is widely applied to five representative M3OD models and evaluated on both the KITTI and the more complicated Waymo datasets.
Adaptive Uncertainty-Aware Tree Search for Robust Reasoning
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Inference-time reasoning scaling has significantly advanced the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in complex problem-solving. A prevalent approach involves external search guided by Process Reward Models (PRMs). However, a fundamental limitation of this framework is the epistemic uncertainty of PRMs when evaluating reasoning paths that deviate from their training distribution. In this work, we conduct a systematic analysis of this challenge. We first provide empirical evidence that PRMs exhibit high uncertainty and unreliable scoring on out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. We then establish a theoretical framework proving that while standard search incurs linear regret accumulation, an uncertainty-aware strategy can achieve sublinear regret. Motivated by these findings, we propose Uncertainty-Aware Tree Search (UATS), a unified method that estimates uncertainty via Monte Carlo Dropout and dynamically allocates compute budget using a reinforcement learning-based controller. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach effectively mitigates the impact of OOD errors.
MLLM Machine Unlearning via Visual Knowledge Distillation
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Recently, machine unlearning approaches have been proposed to remove sensitive information from well-trained large models. However, most existing methods are tailored for LLMs, while MLLM-oriented unlearning remains at its early stage. Inspired by recent studies exploring the internal mechanisms of MLLMs, we propose to disentangle the visual and textual knowledge embedded within MLLMs and introduce a dedicated approach to selectively erase target visual knowledge while preserving textual knowledge. Unlike previous unlearning methods that rely on output-level supervision, our approach introduces a Visual Knowledge Distillation (VKD) scheme, which leverages intermediate visual representations within the MLLM as supervision signals. This design substantially enhances both unlearning effectiveness and model utility. Moreover, since our method only fine-tunes the visual components of the MLLM, it offers significant efficiency advantages. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art unlearning methods in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency. Moreover, we are the first to evaluate the robustness of MLLM unlearning against relearning attacks.
UniLayDiff: A Unified Diffusion Transformer for Content-Aware Layout Generation
Dec 09, 2025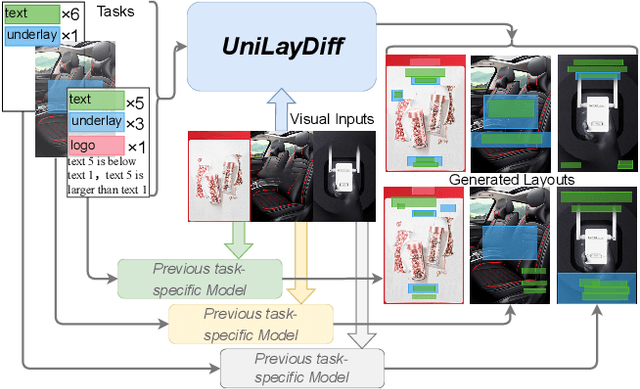
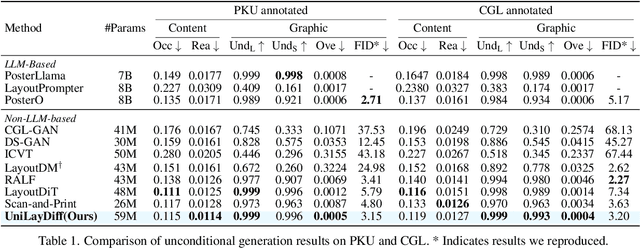
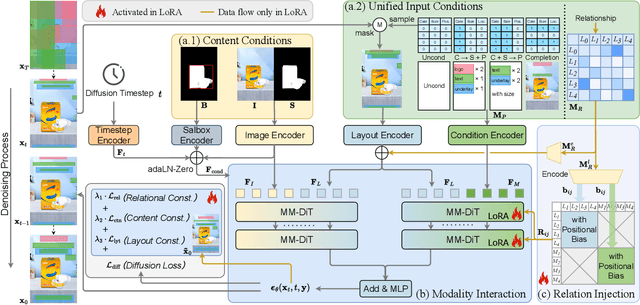
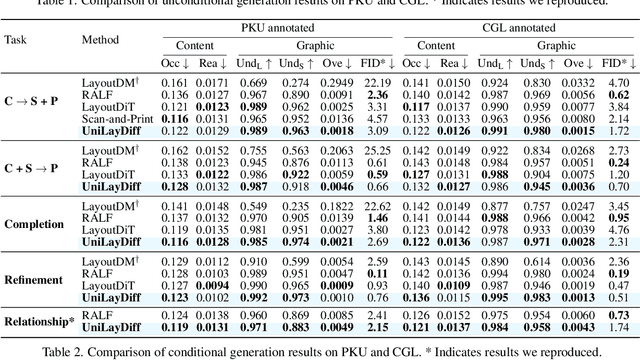
Abstract:Content-aware layout generation is a critical task in graphic design automation, focused on creating visually appealing arrangements of elements that seamlessly blend with a given background image. The variety of real-world applications makes it highly challenging to develop a single model capable of unifying the diverse range of input-constrained generation sub-tasks, such as those conditioned by element types, sizes, or their relationships. Current methods either address only a subset of these tasks or necessitate separate model parameters for different conditions, failing to offer a truly unified solution. In this paper, we propose UniLayDiff: a Unified Diffusion Transformer, that for the first time, addresses various content-aware layout generation tasks with a single, end-to-end trainable model. Specifically, we treat layout constraints as a distinct modality and employ Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformer framework to capture the complex interplay between the background image, layout elements, and diverse constraints. Moreover, we integrate relation constraints through fine-tuning the model with LoRA after pretraining the model on other tasks. Such a schema not only achieves unified conditional generation but also enhances overall layout quality. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniLayDiff achieves state-of-the-art performance across from unconditional to various conditional generation tasks and, to the best of our knowledge, is the first model to unify the full range of content-aware layout generation tasks.
ATLAS: Actor-Critic Task-Completion with Look-ahead Action Simulation
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:We observe that current state-of-the-art web-agents are unable to effectively adapt to new environments without neural network fine-tuning, without which they produce inefficient execution plans due to a lack of awareness of the structure and dynamics of the new environment. To address this limitation, we introduce ATLAS (Actor-Critic Task-completion with Look-ahead Action Simulation), a memory-augmented agent that is able to make plans grounded in a model of the environment by simulating the consequences of those actions in cognitive space. Our agent starts by building a "cognitive map" by performing a lightweight curiosity driven exploration of the environment. The planner proposes candidate actions; the simulator predicts their consequences in cognitive space; a critic analyzes the options to select the best roll-out and update the original plan; and a browser executor performs the chosen action. On the WebArena-Lite Benchmark, we achieve a 63% success rate compared to 53.9% success rate for the previously published state-of-the-art. Unlike previous systems, our modular architecture requires no website-specific LLM fine-tuning. Ablations show sizable drops without the world-model, hierarchical planner, and look-ahead-based replanner confirming their complementary roles within the design of our system
Hacking Hallucinations of MLLMs with Causal Sufficiency and Necessity
Aug 06, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across vision-language tasks. However, they may suffer from hallucinations--generating outputs that are semantically inconsistent with the input image or text. Through causal analyses, we find that: (i) hallucinations with omission may arise from the failure to adequately capture essential causal factors, and (ii) hallucinations with fabrication are likely caused by the model being misled by non-causal cues. To address these challenges, we propose a novel reinforcement learning framework guided by causal completeness, which jointly considers both causal sufficiency and causal necessity of tokens. Specifically, we evaluate each token's standalone contribution and counterfactual indispensability to define a token-level causal completeness reward. This reward is used to construct a causally informed advantage function within the GRPO optimization framework, encouraging the model to focus on tokens that are both causally sufficient and necessary for accurate generation. Experimental results across various benchmark datasets and tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, which effectively mitigates hallucinations in MLLMs.
Reward Model Generalization for Compute-Aware Test-Time Reasoning
May 23, 2025Abstract:External test-time reasoning enhances large language models (LLMs) by decoupling generation and selection. At inference time, the model generates multiple reasoning paths, and an auxiliary process reward model (PRM) is used to score and select the best one. A central challenge in this setting is test-time compute optimality (TCO), i.e., how to maximize answer accuracy under a fixed inference budget. In this work, we establish a theoretical framework to analyze how the generalization error of the PRM affects compute efficiency and reasoning performance. Leveraging PAC-Bayes theory, we derive generalization bounds and show that a lower generalization error of PRM leads to fewer samples required to find correct answers. Motivated by this analysis, we propose Compute-Aware Tree Search (CATS), an actor-critic framework that dynamically controls search behavior. The actor outputs sampling hyperparameters based on reward distributions and sparsity statistics, while the critic estimates their utility to guide budget allocation. Experiments on the MATH and AIME benchmarks with various LLMs and PRMs demonstrate that CATS consistently outperforms other external TTS methods, validating our theoretical predictions.
Componential Prompt-Knowledge Alignment for Domain Incremental Learning
May 07, 2025Abstract:Domain Incremental Learning (DIL) aims to learn from non-stationary data streams across domains while retaining and utilizing past knowledge. Although prompt-based methods effectively store multi-domain knowledge in prompt parameters and obtain advanced performance through cross-domain prompt fusion, we reveal an intrinsic limitation: component-wise misalignment between domain-specific prompts leads to conflicting knowledge integration and degraded predictions. This arises from the random positioning of knowledge components within prompts, where irrelevant component fusion introduces interference.To address this, we propose Componential Prompt-Knowledge Alignment (KA-Prompt), a novel prompt-based DIL method that introduces component-aware prompt-knowledge alignment during training, significantly improving both the learning and inference capacity of the model. KA-Prompt operates in two phases: (1) Initial Componential Structure Configuring, where a set of old prompts containing knowledge relevant to the new domain are mined via greedy search, which is then exploited to initialize new prompts to achieve reusable knowledge transfer and establish intrinsic alignment between new and old prompts. (2) Online Alignment Preservation, which dynamically identifies the target old prompts and applies adaptive componential consistency constraints as new prompts evolve. Extensive experiments on DIL benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our KA-Prompt. Our source code is available at https://github.com/zhoujiahuan1991/ICML2025-KA-Prompt
Token Coordinated Prompt Attention is Needed for Visual Prompting
May 05, 2025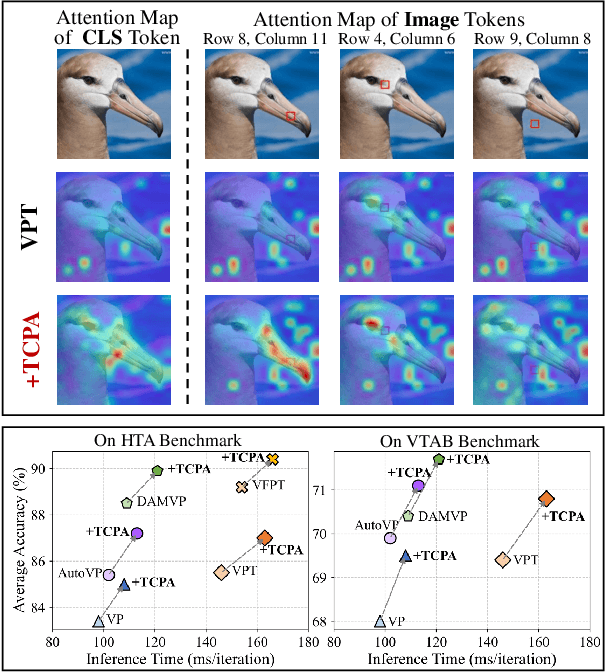
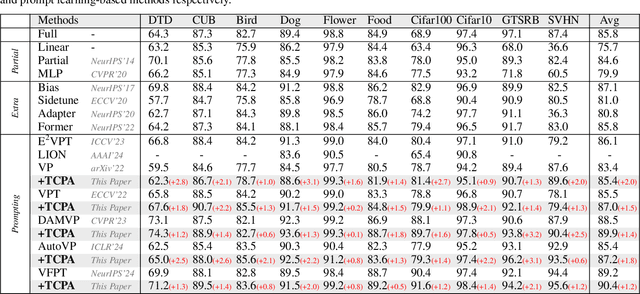
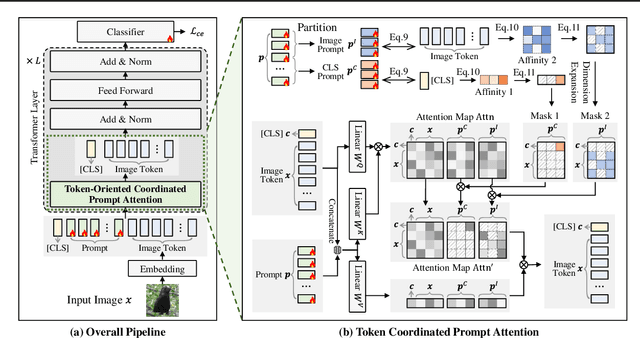
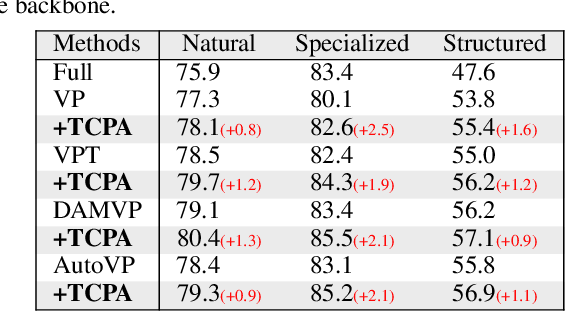
Abstract:Visual prompting techniques are widely used to efficiently fine-tune pretrained Vision Transformers (ViT) by learning a small set of shared prompts for all tokens. However, existing methods overlook the unique roles of different tokens in conveying discriminative information and interact with all tokens using the same prompts, thereby limiting the representational capacity of ViT. This often leads to indistinguishable and biased prompt-extracted features, hindering performance. To address this issue, we propose a plug-and-play Token Coordinated Prompt Attention (TCPA) module, which assigns specific coordinated prompts to different tokens for attention-based interactions. Firstly, recognizing the distinct functions of CLS and image tokens-global information aggregation and local feature extraction, we disentangle the prompts into CLS Prompts and Image Prompts, which interact exclusively with CLS tokens and image tokens through attention mechanisms. This enhances their respective discriminative abilities. Furthermore, as different image tokens correspond to distinct image patches and contain diverse information, we employ a matching function to automatically assign coordinated prompts to individual tokens. This enables more precise attention interactions, improving the diversity and representational capacity of the extracted features. Extensive experiments across various benchmarks demonstrate that TCPA significantly enhances the diversity and discriminative power of the extracted features. The code is available at https://github.com/zhoujiahuan1991/ICML2025-TCPA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge