Wenwen Qiang
Closing the Loop: A Control-Theoretic Framework for Provably Stable Time Series Forecasting with LLMs
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently shown exceptional potential in time series forecasting, leveraging their inherent sequential reasoning capabilities to model complex temporal dynamics. However, existing approaches typically employ a naive autoregressive generation strategy. We identify a critical theoretical flaw in this paradigm: during inference, the model operates in an open-loop manner, consuming its own generated outputs recursively. This leads to inevitable error accumulation (exposure bias), where minor early deviations cascade into significant trajectory drift over long horizons. In this paper, we reformulate autoregressive forecasting through the lens of control theory, proposing \textbf{F-LLM} (Feedback-driven LLM), a novel closed-loop framework. Unlike standard methods that passively propagate errors, F-LLM actively stabilizes the trajectory via a learnable residual estimator (Observer) and a feedback controller. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical guarantee that our closed-loop mechanism ensures uniformly bounded error, provided the base model satisfies a local Lipschitz constraint. Extensive experiments demonstrate that F-LLM significantly mitigates error propagation, achieving good performance on time series benchmarks.
Towards Generalizable Reasoning: Group Causal Counterfactual Policy Optimization for LLM Reasoning
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at complex tasks with advances in reasoning capabilities. However, existing reward mechanisms remain tightly coupled to final correctness and pay little attention to the underlying reasoning process: trajectories with sound reasoning but wrong answers receive low credit, while lucky guesses with flawed logic may be highly rewarded, affecting reasoning generalization. From a causal perspective, we interpret multi-candidate reasoning for a fixed question as a family of counterfactual experiments with theoretical supports. Building on this, we propose Group Causal Counterfactual Policy Optimization to explicitly train LLMs to learn generalizable reasoning patterns. It proposes an episodic causal counterfactual reward that jointly captures (i) robustness, encouraging the answer distribution induced by a reasoning step to remain stable under counterfactual perturbations; and (ii) effectiveness, enforcing sufficient variability so that the learned reasoning strategy can transfer across questions. We then construct token-level advantages from this reward and optimize the policy, encouraging LLMs to favor reasoning patterns that are process-valid and counterfactually robust. Extensive experiments on diverse benchmarks demonstrate its advantages.
Adaptive Uncertainty-Aware Tree Search for Robust Reasoning
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Inference-time reasoning scaling has significantly advanced the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in complex problem-solving. A prevalent approach involves external search guided by Process Reward Models (PRMs). However, a fundamental limitation of this framework is the epistemic uncertainty of PRMs when evaluating reasoning paths that deviate from their training distribution. In this work, we conduct a systematic analysis of this challenge. We first provide empirical evidence that PRMs exhibit high uncertainty and unreliable scoring on out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. We then establish a theoretical framework proving that while standard search incurs linear regret accumulation, an uncertainty-aware strategy can achieve sublinear regret. Motivated by these findings, we propose Uncertainty-Aware Tree Search (UATS), a unified method that estimates uncertainty via Monte Carlo Dropout and dynamically allocates compute budget using a reinforcement learning-based controller. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach effectively mitigates the impact of OOD errors.
On the Plasticity and Stability for Post-Training Large Language Models
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Training stability remains a critical bottleneck for Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), often manifesting as a trade-off between reasoning plasticity and general capability retention. We identify a root cause as the geometric conflict between plasticity and stability gradients, which leads to destructive interference. Crucially, we argue that deterministic projection methods are suboptimal for GRPO as they overlook the intrinsic stochasticity of group-based gradient estimates. To address this, we propose Probabilistic Conflict Resolution (PCR), a Bayesian framework that models gradients as random variables. PCR dynamically arbitrates conflicts via an uncertainty-aware ``soft projection'' mechanism, optimizing the signal-to-noise ratio. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PCR significantly smooths the training trajectory and achieves superior performance in various reasoning tasks.
Causal Front-Door Adjustment for Robust Jailbreak Attacks on LLMs
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Safety alignment mechanisms in Large Language Models (LLMs) often operate as latent internal states, obscuring the model's inherent capabilities. Building on this observation, we model the safety mechanism as an unobserved confounder from a causal perspective. Then, we propose the \textbf{C}ausal \textbf{F}ront-Door \textbf{A}djustment \textbf{A}ttack ({\textbf{CFA}}$^2$) to jailbreak LLM, which is a framework that leverages Pearl's Front-Door Criterion to sever the confounding associations for robust jailbreaking. Specifically, we employ Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) to physically strip defense-related features, isolating the core task intent. We further reduce computationally expensive marginalization to a deterministic intervention with low inference complexity. Experiments demonstrate that {CFA}$^2$ achieves state-of-the-art attack success rates while offering a mechanistic interpretation of the jailbreaking process.
Enhancing Large Language Models for Time-Series Forecasting via Vector-Injected In-Context Learning
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:The World Wide Web needs reliable predictive capabilities to respond to changes in user behavior and usage patterns. Time series forecasting (TSF) is a key means to achieve this goal. In recent years, the large language models (LLMs) for TSF (LLM4TSF) have achieved good performance. However, there is a significant difference between pretraining corpora and time series data, making it hard to guarantee forecasting quality when directly applying LLMs to TSF; fine-tuning LLMs can mitigate this issue, but often incurs substantial computational overhead. Thus, LLM4TSF faces a dual challenge of prediction performance and compute overhead. To address this, we aim to explore a method for improving the forecasting performance of LLM4TSF while freezing all LLM parameters to reduce computational overhead. Inspired by in-context learning (ICL), we propose LVICL. LVICL uses our vector-injected ICL to inject example information into a frozen LLM, eliciting its in-context learning ability and thereby enhancing its performance on the example-related task (i.e., TSF). Specifically, we first use the LLM together with a learnable context vector adapter to extract a context vector from multiple examples adaptively. This vector contains compressed, example-related information. Subsequently, during the forward pass, we inject this vector into every layer of the LLM to improve forecasting performance. Compared with conventional ICL that adds examples into the prompt, our vector-injected ICL does not increase prompt length; moreover, adaptively deriving a context vector from examples suppresses components harmful to forecasting, thereby improving model performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Exploring Transferability of Self-Supervised Learning by Task Conflict Calibration
Nov 16, 2025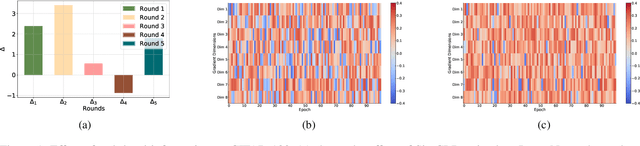
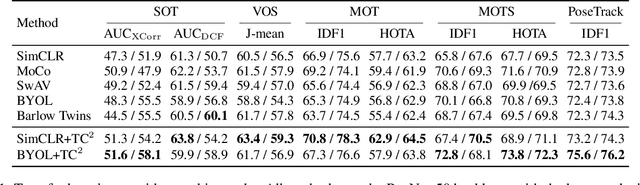
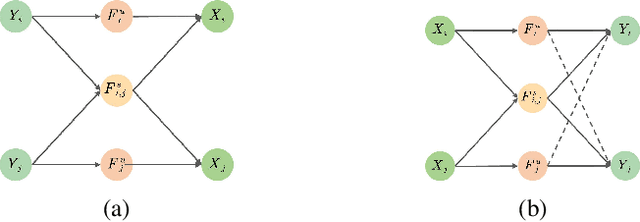
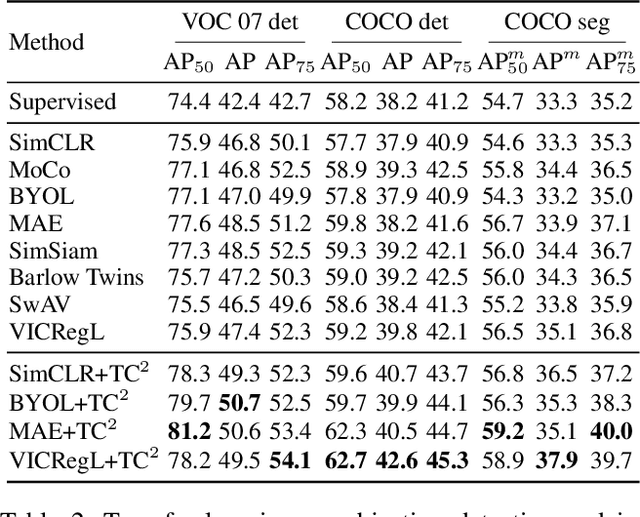
Abstract:In this paper, we explore the transferability of SSL by addressing two central questions: (i) what is the representation transferability of SSL, and (ii) how can we effectively model this transferability? Transferability is defined as the ability of a representation learned from one task to support the objective of another. Inspired by the meta-learning paradigm, we construct multiple SSL tasks within each training batch to support explicitly modeling transferability. Based on empirical evidence and causal analysis, we find that although introducing task-level information improves transferability, it is still hindered by task conflict. To address this issue, we propose a Task Conflict Calibration (TC$^2$) method to alleviate the impact of task conflict. Specifically, it first splits batches to create multiple SSL tasks, infusing task-level information. Next, it uses a factor extraction network to produce causal generative factors for all tasks and a weight extraction network to assign dedicated weights to each sample, employing data reconstruction, orthogonality, and sparsity to ensure effectiveness. Finally, TC$^2$ calibrates sample representations during SSL training and integrates into the pipeline via a two-stage bi-level optimization framework to boost the transferability of learned representations. Experimental results on multiple downstream tasks demonstrate that our method consistently improves the transferability of SSL models.
Group Causal Policy Optimization for Post-Training Large Language Models
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have broadened their applicability across diverse tasks, yet specialized domains still require targeted post training. Among existing methods, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) stands out for its efficiency, leveraging groupwise relative rewards while avoiding costly value function learning. However, GRPO treats candidate responses as independent, overlooking semantic interactions such as complementarity and contradiction. To address this challenge, we first introduce a Structural Causal Model (SCM) that reveals hidden dependencies among candidate responses induced by conditioning on a final integrated output forming a collider structure. Then, our causal analysis leads to two insights: (1) projecting responses onto a causally informed subspace improves prediction quality, and (2) this projection yields a better baseline than query only conditioning. Building on these insights, we propose Group Causal Policy Optimization (GCPO), which integrates causal structure into optimization through two key components: a causally informed reward adjustment and a novel KL regularization term that aligns the policy with a causally projected reference distribution. Comprehensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that GCPO consistently surpasses existing methods, including GRPO across multiple reasoning benchmarks.
Hacking Hallucinations of MLLMs with Causal Sufficiency and Necessity
Aug 06, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across vision-language tasks. However, they may suffer from hallucinations--generating outputs that are semantically inconsistent with the input image or text. Through causal analyses, we find that: (i) hallucinations with omission may arise from the failure to adequately capture essential causal factors, and (ii) hallucinations with fabrication are likely caused by the model being misled by non-causal cues. To address these challenges, we propose a novel reinforcement learning framework guided by causal completeness, which jointly considers both causal sufficiency and causal necessity of tokens. Specifically, we evaluate each token's standalone contribution and counterfactual indispensability to define a token-level causal completeness reward. This reward is used to construct a causally informed advantage function within the GRPO optimization framework, encouraging the model to focus on tokens that are both causally sufficient and necessary for accurate generation. Experimental results across various benchmark datasets and tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, which effectively mitigates hallucinations in MLLMs.
Causal Reward Adjustment: Mitigating Reward Hacking in External Reasoning via Backdoor Correction
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:External reasoning systems combine language models with process reward models (PRMs) to select high-quality reasoning paths for complex tasks such as mathematical problem solving. However, these systems are prone to reward hacking, where high-scoring but logically incorrect paths are assigned high scores by the PRMs, leading to incorrect answers. From a causal inference perspective, we attribute this phenomenon primarily to the presence of confounding semantic features. To address it, we propose Causal Reward Adjustment (CRA), a method that mitigates reward hacking by estimating the true reward of a reasoning path. CRA trains sparse autoencoders on the PRM's internal activations to recover interpretable features, then corrects confounding by using backdoor adjustment. Experiments on math solving datasets demonstrate that CRA mitigates reward hacking and improves final accuracy, without modifying the policy model or retraining PRM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge