Haotian Wang
ASTRA: Automated Synthesis of agentic Trajectories and Reinforcement Arenas
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as tool-augmented agents for multi-step decision making, yet training robust tool-using agents remains challenging. Existing methods still require manual intervention, depend on non-verifiable simulated environments, rely exclusively on either supervised fine-tuning (SFT) or reinforcement learning (RL), and struggle with stable long-horizon, multi-turn learning. To address these challenges, we introduce ASTRA, a fully automated end-to-end framework for training tool-augmented language model agents via scalable data synthesis and verifiable reinforcement learning. ASTRA integrates two complementary components. First, a pipeline that leverages the static topology of tool-call graphs synthesizes diverse, structurally grounded trajectories, instilling broad and transferable tool-use competence. Second, an environment synthesis framework that captures the rich, compositional topology of human semantic reasoning converts decomposed question-answer traces into independent, code-executable, and rule-verifiable environments, enabling deterministic multi-turn RL. Based on this method, we develop a unified training methodology that integrates SFT with online RL using trajectory-level rewards to balance task completion and interaction efficiency. Experiments on multiple agentic tool-use benchmarks demonstrate that ASTRA-trained models achieve state-of-the-art performance at comparable scales, approaching closed-source systems while preserving core reasoning ability. We release the full pipelines, environments, and trained models at https://github.com/LianjiaTech/astra.
Integrated Sensing and Semantic Communication with Adaptive Source-Channel Coding
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Semantic communication has emerged as a new paradigm to facilitate the performance of integrated sensing and communication systems in 6G. However, most of the existing works mainly focus on sensing data compression to reduce the subsequent communication overheads, without considering the integrated transmission framework for both the SemCom and sensing tasks. This paper proposes an adaptive source-channel coding and beamforming design framework for integrated sensing and SemCom systems by jointly optimizing the coding rate for SemCom task and the transmit beamforming for both the SemCom and sensing tasks. Specifically, an end-to-end semantic distortion function is approximated by deriving an upper bound composing of source and channel coding induced components, and then a hybrid Cramér-Rao bound (HCRB) is also derived for target position under imperfect time synchronization. To facilitate the joint optimization, a distortion minimization problem is formulated by considering the HCRB threshold, channel uses, and power budget. Subsequently, an alternative optimization algorithm composed of successive convex approximation and fractional programming is proposed to address this problem by decoupling it into two subproblems for coding rate and beamforming designs, respectively. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed scheme outperforms the conventional deep joint source-channel coding -water filling-zero forcing benchmark.
Coordinated Pandemic Control with Large Language Model Agents as Policymaking Assistants
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Effective pandemic control requires timely and coordinated policymaking across administrative regions that are intrinsically interdependent. However, human-driven responses are often fragmented and reactive, with policies formulated in isolation and adjusted only after outbreaks escalate, undermining proactive intervention and global pandemic mitigation. To address this challenge, here we propose a large language model (LLM) multi-agent policymaking framework that supports coordinated and proactive pandemic control across regions. Within our framework, each administrative region is assigned an LLM agent as an AI policymaking assistant. The agent reasons over region-specific epidemiological dynamics while communicating with other agents to account for cross-regional interdependencies. By integrating real-world data, a pandemic evolution simulator, and structured inter-agent communication, our framework enables agents to jointly explore counterfactual intervention scenarios and synthesize coordinated policy decisions through a closed-loop simulation process. We validate the proposed framework using state-level COVID-19 data from the United States between April and December 2020, together with real-world mobility records and observed policy interventions. Compared with real-world pandemic outcomes, our approach reduces cumulative infections and deaths by up to 63.7% and 40.1%, respectively, at the individual state level, and by 39.0% and 27.0%, respectively, when aggregated across states. These results demonstrate that LLM multi-agent systems can enable more effective pandemic control with coordinated policymaking...
Effective Online 3D Bin Packing with Lookahead Parcels Using Monte Carlo Tree Search
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Online 3D Bin Packing (3D-BP) with robotic arms is crucial for reducing transportation and labor costs in modern logistics. While Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has shown strong performance, it often fails to adapt to real-world short-term distribution shifts, which arise as different batches of goods arrive sequentially, causing performance drops. We argue that the short-term lookahead information available in modern logistics systems is key to mitigating this issue, especially during distribution shifts. We formulate online 3D-BP with lookahead parcels as a Model Predictive Control (MPC) problem and adapt the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) framework to solve it. Our framework employs a dynamic exploration prior that automatically balances a learned RL policy and a robust random policy based on the lookahead characteristics. Additionally, we design an auxiliary reward to penalize long-term spatial waste from individual placements. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving over 10\% gains under distributional shifts, 4\% average improvement in online deployment, and up to more than 8\% in the best case--demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework.
Detecting Unobserved Confounders: A Kernelized Regression Approach
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Detecting unobserved confounders is crucial for reliable causal inference in observational studies. Existing methods require either linearity assumptions or multiple heterogeneous environments, limiting applicability to nonlinear single-environment settings. To bridge this gap, we propose Kernel Regression Confounder Detection (KRCD), a novel method for detecting unobserved confounding in nonlinear observational data under single-environment conditions. KRCD leverages reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces to model complex dependencies. By comparing standard and higherorder kernel regressions, we derive a test statistic whose significant deviation from zero indicates unobserved confounding. Theoretically, we prove two key results: First, in infinite samples, regression coefficients coincide if and only if no unobserved confounders exist. Second, finite-sample differences converge to zero-mean Gaussian distributions with tractable variance. Extensive experiments on synthetic benchmarks and the Twins dataset demonstrate that KRCD not only outperforms existing baselines but also achieves superior computational efficiency.
REST: Diffusion-based Real-time End-to-end Streaming Talking Head Generation via ID-Context Caching and Asynchronous Streaming Distillation
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have significantly advanced the field of talking head generation. However, the slow inference speeds and non-autoregressive paradigms severely constrain the application of diffusion-based THG models. In this study, we propose REST, the first diffusion-based, real-time, end-to-end streaming audio-driven talking head generation framework. To support real-time end-to-end generation, a compact video latent space is first learned through high spatiotemporal VAE compression. Additionally, to enable autoregressive streaming within the compact video latent space, we introduce an ID-Context Cache mechanism, which integrates ID-Sink and Context-Cache principles to key-value caching for maintaining temporal consistency and identity coherence during long-time streaming generation. Furthermore, an Asynchronous Streaming Distillation (ASD) training strategy is proposed to mitigate error accumulation in autoregressive generation and enhance temporal consistency, which leverages a non-streaming teacher with an asynchronous noise schedule to supervise the training of the streaming student model. REST bridges the gap between autoregressive and diffusion-based approaches, demonstrating substantial value for applications requiring real-time talking head generation. Experimental results demonstrate that REST outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both generation speed and overall performance.
Breaking the Gradient Barrier: Unveiling Large Language Models for Strategic Classification
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Strategic classification~(SC) explores how individuals or entities modify their features strategically to achieve favorable classification outcomes. However, existing SC methods, which are largely based on linear models or shallow neural networks, face significant limitations in terms of scalability and capacity when applied to real-world datasets with significantly increasing scale, especially in financial services and the internet sector. In this paper, we investigate how to leverage large language models to design a more scalable and efficient SC framework, especially in the case of growing individuals engaged with decision-making processes. Specifically, we introduce GLIM, a gradient-free SC method grounded in in-context learning. During the feed-forward process of self-attention, GLIM implicitly simulates the typical bi-level optimization process of SC, including both the feature manipulation and decision rule optimization. Without fine-tuning the LLMs, our proposed GLIM enjoys the advantage of cost-effective adaptation in dynamic strategic environments. Theoretically, we prove GLIM can support pre-trained LLMs to adapt to a broad range of strategic manipulations. We validate our approach through experiments with a collection of pre-trained LLMs on real-world and synthetic datasets in financial and internet domains, demonstrating that our GLIM exhibits both robustness and efficiency, and offering an effective solution for large-scale SC tasks.
BaseReward: A Strong Baseline for Multimodal Reward Model
Sep 19, 2025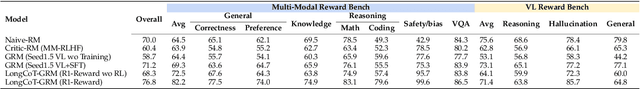



Abstract:The rapid advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has made aligning them with human preferences a critical challenge. Reward Models (RMs) are a core technology for achieving this goal, but a systematic guide for building state-of-the-art Multimodal Reward Models (MRMs) is currently lacking in both academia and industry. Through exhaustive experimental analysis, this paper aims to provide a clear ``recipe'' for constructing high-performance MRMs. We systematically investigate every crucial component in the MRM development pipeline, including \textit{reward modeling paradigms} (e.g., Naive-RM, Critic-based RM, and Generative RM), \textit{reward head architecture}, \textit{training strategies}, \textit{data curation} (covering over ten multimodal and text-only preference datasets), \textit{backbone model} and \textit{model scale}, and \textit{ensemble methods}. Based on these experimental insights, we introduce \textbf{BaseReward}, a powerful and efficient baseline for multimodal reward modeling. BaseReward adopts a simple yet effective architecture, built upon a {Qwen2.5-VL} backbone, featuring an optimized two-layer reward head, and is trained on a carefully curated mixture of high-quality multimodal and text-only preference data. Our results show that BaseReward establishes a new SOTA on major benchmarks such as MM-RLHF-Reward Bench, VL-Reward Bench, and Multimodal Reward Bench, outperforming previous models. Furthermore, to validate its practical utility beyond static benchmarks, we integrate BaseReward into a real-world reinforcement learning pipeline, successfully enhancing an MLLM's performance across various perception, reasoning, and conversational tasks. This work not only delivers a top-tier MRM but, more importantly, provides the community with a clear, empirically-backed guide for developing robust reward models for the next generation of MLLMs.
PacGDC: Label-Efficient Generalizable Depth Completion with Projection Ambiguity and Consistency
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Generalizable depth completion enables the acquisition of dense metric depth maps for unseen environments, offering robust perception capabilities for various downstream tasks. However, training such models typically requires large-scale datasets with metric depth labels, which are often labor-intensive to collect. This paper presents PacGDC, a label-efficient technique that enhances data diversity with minimal annotation effort for generalizable depth completion. PacGDC builds on novel insights into inherent ambiguities and consistencies in object shapes and positions during 2D-to-3D projection, allowing the synthesis of numerous pseudo geometries for the same visual scene. This process greatly broadens available geometries by manipulating scene scales of the corresponding depth maps. To leverage this property, we propose a new data synthesis pipeline that uses multiple depth foundation models as scale manipulators. These models robustly provide pseudo depth labels with varied scene scales, affecting both local objects and global layouts, while ensuring projection consistency that supports generalization. To further diversify geometries, we incorporate interpolation and relocation strategies, as well as unlabeled images, extending the data coverage beyond the individual use of foundation models. Extensive experiments show that PacGDC achieves remarkable generalizability across multiple benchmarks, excelling in diverse scene semantics/scales and depth sparsity/patterns under both zero-shot and few-shot settings. Code: https://github.com/Wang-xjtu/PacGDC.
MME-VideoOCR: Evaluating OCR-Based Capabilities of Multimodal LLMs in Video Scenarios
May 27, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved considerable accuracy in Optical Character Recognition (OCR) from static images. However, their efficacy in video OCR is significantly diminished due to factors such as motion blur, temporal variations, and visual effects inherent in video content. To provide clearer guidance for training practical MLLMs, we introduce the MME-VideoOCR benchmark, which encompasses a comprehensive range of video OCR application scenarios. MME-VideoOCR features 10 task categories comprising 25 individual tasks and spans 44 diverse scenarios. These tasks extend beyond text recognition to incorporate deeper comprehension and reasoning of textual content within videos. The benchmark consists of 1,464 videos with varying resolutions, aspect ratios, and durations, along with 2,000 meticulously curated, manually annotated question-answer pairs. We evaluate 18 state-of-the-art MLLMs on MME-VideoOCR, revealing that even the best-performing model (Gemini-2.5 Pro) achieves an accuracy of only 73.7%. Fine-grained analysis indicates that while existing MLLMs demonstrate strong performance on tasks where relevant texts are contained within a single or few frames, they exhibit limited capability in effectively handling tasks that demand holistic video comprehension. These limitations are especially evident in scenarios that require spatio-temporal reasoning, cross-frame information integration, or resistance to language prior bias. Our findings also highlight the importance of high-resolution visual input and sufficient temporal coverage for reliable OCR in dynamic video scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge