Weizhan Zhang
SegEarth-R2: Towards Comprehensive Language-guided Segmentation for Remote Sensing Images
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Effectively grounding complex language to pixels in remote sensing (RS) images is a critical challenge for applications like disaster response and environmental monitoring. Current models can parse simple, single-target commands but fail when presented with complex geospatial scenarios, e.g., segmenting objects at various granularities, executing multi-target instructions, and interpreting implicit user intent. To drive progress against these failures, we present LaSeRS, the first large-scale dataset built for comprehensive training and evaluation across four critical dimensions of language-guided segmentation: hierarchical granularity, target multiplicity, reasoning requirements, and linguistic variability. By capturing these dimensions, LaSeRS moves beyond simple commands, providing a benchmark for complex geospatial reasoning. This addresses a critical gap: existing datasets oversimplify, leading to sensitivity-prone real-world models. We also propose SegEarth-R2, an MLLM architecture designed for comprehensive language-guided segmentation in RS, which directly confronts these challenges. The model's effectiveness stems from two key improvements: (1) a spatial attention supervision mechanism specifically handles the localization of small objects and their components, and (2) a flexible and efficient segmentation query mechanism that handles both single-target and multi-target scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that our SegEarth-R2 achieves outstanding performance on LaSeRS and other benchmarks, establishing a powerful baseline for the next generation of geospatial segmentation. All data and code will be released at https://github.com/earth-insights/SegEarth-R2.
MVGSR: Multi-View Consistent 3D Gaussian Super-Resolution via Epipolar Guidance
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Scenes reconstructed by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) trained on low-resolution (LR) images are unsuitable for high-resolution (HR) rendering. Consequently, a 3DGS super-resolution (SR) method is needed to bridge LR inputs and HR rendering. Early 3DGS SR methods rely on single-image SR networks, which lack cross-view consistency and fail to fuse complementary information across views. More recent video-based SR approaches attempt to address this limitation but require strictly sequential frames, limiting their applicability to unstructured multi-view datasets. In this work, we introduce Multi-View Consistent 3D Gaussian Splatting Super-Resolution (MVGSR), a framework that focuses on integrating multi-view information for 3DGS rendering with high-frequency details and enhanced consistency. We first propose an Auxiliary View Selection Method based on camera poses, making our method adaptable for arbitrarily organized multi-view datasets without the need of temporal continuity or data reordering. Furthermore, we introduce, for the first time, an epipolar-constrained multi-view attention mechanism into 3DGS SR, which serves as the core of our proposed multi-view SR network. This design enables the model to selectively aggregate consistent information from auxiliary views, enhancing the geometric consistency and detail fidelity of 3DGS representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on both object-centric and scene-level 3DGS SR benchmarks.
HGS: Hybrid Gaussian Splatting with Static-Dynamic Decomposition for Compact Dynamic View Synthesis
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Dynamic novel view synthesis (NVS) is essential for creating immersive experiences. Existing approaches have advanced dynamic NVS by introducing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with implicit deformation fields or indiscriminately assigned time-varying parameters, surpassing NeRF-based methods. However, due to excessive model complexity and parameter redundancy, they incur large model sizes and slow rendering speeds, making them inefficient for real-time applications, particularly on resource-constrained devices. To obtain a more efficient model with fewer redundant parameters, in this paper, we propose Hybrid Gaussian Splatting (HGS), a compact and efficient framework explicitly designed to disentangle static and dynamic regions of a scene within a unified representation. The core innovation of HGS lies in our Static-Dynamic Decomposition (SDD) strategy, which leverages Radial Basis Function (RBF) modeling for Gaussian primitives. Specifically, for dynamic regions, we employ time-dependent RBFs to effectively capture temporal variations and handle abrupt scene changes, while for static regions, we reduce redundancy by sharing temporally invariant parameters. Additionally, we introduce a two-stage training strategy tailored for explicit models to enhance temporal coherence at static-dynamic boundaries. Experimental results demonstrate that our method reduces model size by up to 98% and achieves real-time rendering at up to 125 FPS at 4K resolution on a single RTX 3090 GPU. It further sustains 160 FPS at 1352 * 1014 on an RTX 3050 and has been integrated into the VR system. Moreover, HGS achieves comparable rendering quality to state-of-the-art methods while providing significantly improved visual fidelity for high-frequency details and abrupt scene changes.
ZoomEarth: Active Perception for Ultra-High-Resolution Geospatial Vision-Language Tasks
Nov 15, 2025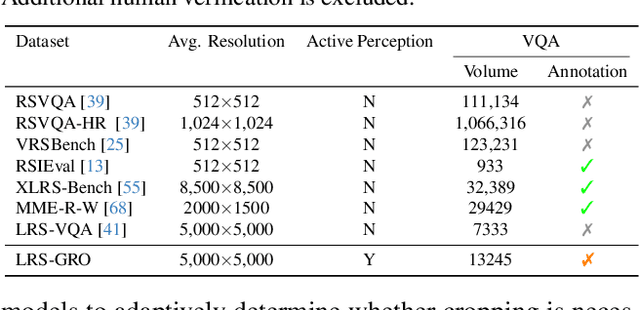
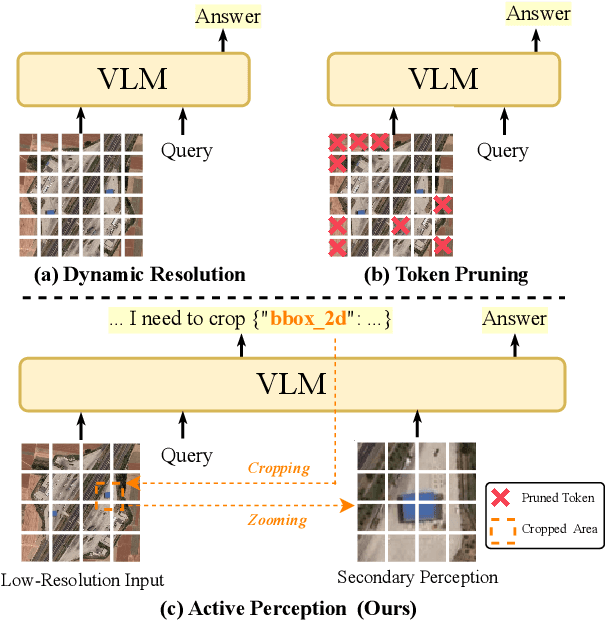
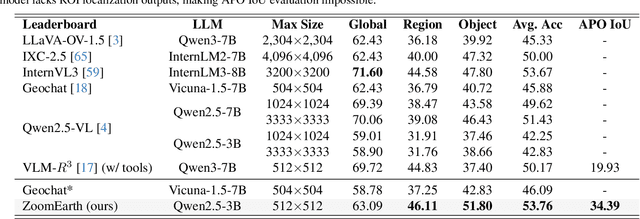
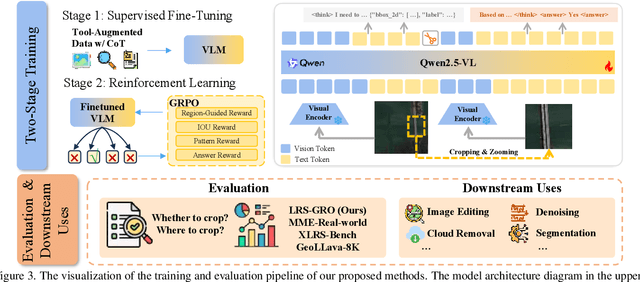
Abstract:Ultra-high-resolution (UHR) remote sensing (RS) images offer rich fine-grained information but also present challenges in effective processing. Existing dynamic resolution and token pruning methods are constrained by a passive perception paradigm, suffering from increased redundancy when obtaining finer visual inputs. In this work, we explore a new active perception paradigm that enables models to revisit information-rich regions. First, we present LRS-GRO, a large-scale benchmark dataset tailored for active perception in UHR RS processing, encompassing 17 question types across global, region, and object levels, annotated via a semi-automatic pipeline. Building on LRS-GRO, we propose ZoomEarth, an adaptive cropping-zooming framework with a novel Region-Guided reward that provides fine-grained guidance. Trained via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), ZoomEarth achieves state-of-the-art performance on LRS-GRO and, in the zero-shot setting, on three public UHR remote sensing benchmarks. Furthermore, ZoomEarth can be seamlessly integrated with downstream models for tasks such as cloud removal, denoising, segmentation, and image editing through simple tool interfaces, demonstrating strong versatility and extensibility.
InfoSAM: Fine-Tuning the Segment Anything Model from An Information-Theoretic Perspective
May 28, 2025Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM), a vision foundation model, exhibits impressive zero-shot capabilities in general tasks but struggles in specialized domains. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is a promising approach to unleash the potential of SAM in novel scenarios. However, existing PEFT methods for SAM neglect the domain-invariant relations encoded in the pre-trained model. To bridge this gap, we propose InfoSAM, an information-theoretic approach that enhances SAM fine-tuning by distilling and preserving its pre-trained segmentation knowledge. Specifically, we formulate the knowledge transfer process as two novel mutual information-based objectives: (i) to compress the domain-invariant relation extracted from pre-trained SAM, excluding pseudo-invariant information as possible, and (ii) to maximize mutual information between the relational knowledge learned by the teacher (pre-trained SAM) and the student (fine-tuned model). The proposed InfoSAM establishes a robust distillation framework for PEFT of SAM. Extensive experiments across diverse benchmarks validate InfoSAM's effectiveness in improving SAM family's performance on real-world tasks, demonstrating its adaptability and superiority in handling specialized scenarios.
DynamicID: Zero-Shot Multi-ID Image Personalization with Flexible Facial Editability
Mar 09, 2025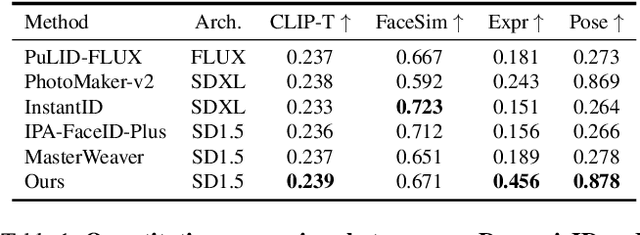
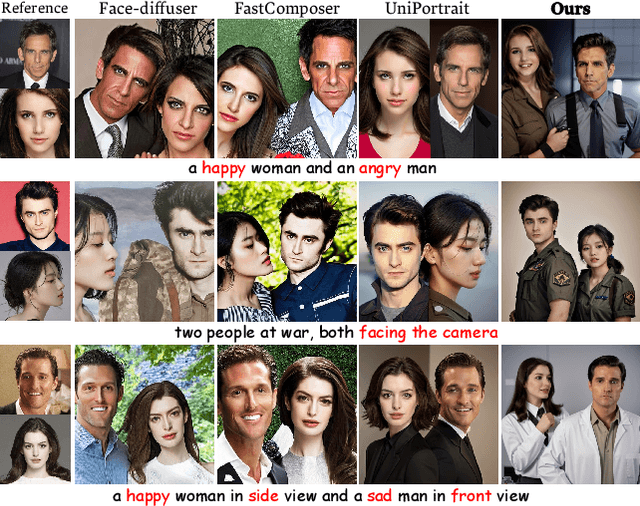
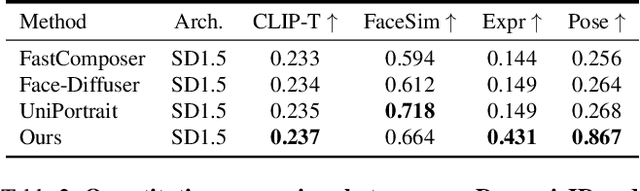
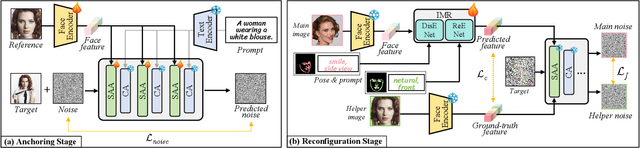
Abstract:Recent advancements in text-to-image generation have spurred interest in personalized human image generation, which aims to create novel images featuring specific human identities as reference images indicate. Although existing methods achieve high-fidelity identity preservation, they often struggle with limited multi-ID usability and inadequate facial editability. We present DynamicID, a tuning-free framework supported by a dual-stage training paradigm that inherently facilitates both single-ID and multi-ID personalized generation with high fidelity and flexible facial editability. Our key innovations include: 1) Semantic-Activated Attention (SAA), which employs query-level activation gating to minimize disruption to the original model when injecting ID features and achieve multi-ID personalization without requiring multi-ID samples during training. 2) Identity-Motion Reconfigurator (IMR), which leverages contrastive learning to effectively disentangle and re-entangle facial motion and identity features, thereby enabling flexible facial editing. Additionally, we have developed a curated VariFace-10k facial dataset, comprising 10k unique individuals, each represented by 35 distinct facial images. Experimental results demonstrate that DynamicID outperforms state-of-the-art methods in identity fidelity, facial editability, and multi-ID personalization capability.
Towards the Generalization of Multi-view Learning: An Information-theoretical Analysis
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Multiview learning has drawn widespread attention for its efficacy in leveraging cross-view consensus and complementarity information to achieve a comprehensive representation of data. While multi-view learning has undergone vigorous development and achieved remarkable success, the theoretical understanding of its generalization behavior remains elusive. This paper aims to bridge this gap by developing information-theoretic generalization bounds for multi-view learning, with a particular focus on multi-view reconstruction and classification tasks. Our bounds underscore the importance of capturing both consensus and complementary information from multiple different views to achieve maximally disentangled representations. These results also indicate that applying the multi-view information bottleneck regularizer is beneficial for satisfactory generalization performance. Additionally, we derive novel data-dependent bounds under both leave-one-out and supersample settings, yielding computational tractable and tighter bounds. In the interpolating regime, we further establish the fast-rate bound for multi-view learning, exhibiting a faster convergence rate compared to conventional square-root bounds. Numerical results indicate a strong correlation between the true generalization gap and the derived bounds across various learning scenarios.
Towards Sharper Information-theoretic Generalization Bounds for Meta-Learning
Jan 26, 2025
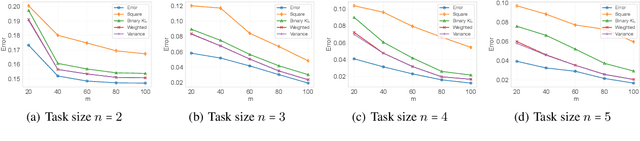

Abstract:In recent years, information-theoretic generalization bounds have emerged as a promising approach for analyzing the generalization capabilities of meta-learning algorithms. However, existing results are confined to two-step bounds, failing to provide a sharper characterization of the meta-generalization gap that simultaneously accounts for environment-level and task-level dependencies. This paper addresses this fundamental limitation by establishing novel single-step information-theoretic bounds for meta-learning. Our bounds exhibit substantial advantages over prior MI- and CMI-based bounds, especially in terms of tightness, scaling behavior associated with sampled tasks and samples per task, and computational tractability. Furthermore, we provide novel theoretical insights into the generalization behavior of two classes of noise and iterative meta-learning algorithms via gradient covariance analysis, where the meta-learner uses either the entire meta-training data (e.g., Reptile), or separate training and test data within the task (e.g., model agnostic meta-learning (MAML)). Numerical results validate the effectiveness of the derived bounds in capturing the generalization dynamics of meta-learning.
Accelerating Non-Maximum Suppression: A Graph Theory Perspective
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Non-maximum suppression (NMS) is an indispensable post-processing step in object detection. With the continuous optimization of network models, NMS has become the ``last mile'' to enhance the efficiency of object detection. This paper systematically analyzes NMS from a graph theory perspective for the first time, revealing its intrinsic structure. Consequently, we propose two optimization methods, namely QSI-NMS and BOE-NMS. The former is a fast recursive divide-and-conquer algorithm with negligible mAP loss, and its extended version (eQSI-NMS) achieves optimal complexity of $\mathcal{O}(n\log n)$. The latter, concentrating on the locality of NMS, achieves an optimization at a constant level without an mAP loss penalty. Moreover, to facilitate rapid evaluation of NMS methods for researchers, we introduce NMS-Bench, the first benchmark designed to comprehensively assess various NMS methods. Taking the YOLOv8-N model on MS COCO 2017 as the benchmark setup, our method QSI-NMS provides $6.2\times$ speed of original NMS on the benchmark, with a $0.1\%$ decrease in mAP. The optimal eQSI-NMS, with only a $0.3\%$ mAP decrease, achieves $10.7\times$ speed. Meanwhile, BOE-NMS exhibits $5.1\times$ speed with no compromise in mAP.
SpotActor: Training-Free Layout-Controlled Consistent Image Generation
Sep 07, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models significantly enhance the efficiency of artistic creation with high-fidelity image generation. However, in typical application scenarios like comic book production, they can neither place each subject into its expected spot nor maintain the consistent appearance of each subject across images. For these issues, we pioneer a novel task, Layout-to-Consistent-Image (L2CI) generation, which produces consistent and compositional images in accordance with the given layout conditions and text prompts. To accomplish this challenging task, we present a new formalization of dual energy guidance with optimization in a dual semantic-latent space and thus propose a training-free pipeline, SpotActor, which features a layout-conditioned backward update stage and a consistent forward sampling stage. In the backward stage, we innovate a nuanced layout energy function to mimic the attention activations with a sigmoid-like objective. While in the forward stage, we design Regional Interconnection Self-Attention (RISA) and Semantic Fusion Cross-Attention (SFCA) mechanisms that allow mutual interactions across images. To evaluate the performance, we present ActorBench, a specified benchmark with hundreds of reasonable prompt-box pairs stemming from object detection datasets. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The results prove that SpotActor fulfills the expectations of this task and showcases the potential for practical applications with superior layout alignment, subject consistency, prompt conformity and background diversity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge