Jiang Liu
Waseda University
Reliable Use of Lemmas via Eligibility Reasoning and Section$-$Aware Reinforcement Learning
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Recent large language models (LLMs) perform strongly on mathematical benchmarks yet often misapply lemmas, importing conclusions without validating assumptions. We formalize lemma$-$judging as a structured prediction task: given a statement and a candidate lemma, the model must output a precondition check and a conclusion$-$utility check, from which a usefulness decision is derived. We present RULES, which encodes this specification via a two$-$section output and trains with reinforcement learning plus section$-$aware loss masking to assign penalty to the section responsible for errors. Training and evaluation draw on diverse natural language and formal proof corpora; robustness is assessed with a held$-$out perturbation suite; and end$-$to$-$end evaluation spans competition$-$style, perturbation$-$aligned, and theorem$-$based problems across various LLMs. Results show consistent in$-$domain gains over both a vanilla model and a single$-$label RL baseline, larger improvements on applicability$-$breaking perturbations, and parity or modest gains on end$-$to$-$end tasks; ablations indicate that the two$-$section outputs and section$-$aware reinforcement are both necessary for robustness.
CD4LM: Consistency Distillation and aDaptive Decoding for Diffusion Language Models
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive large language models achieve strong results on many benchmarks, but decoding remains fundamentally latency-limited by sequential dependence on previously generated tokens. Diffusion language models (DLMs) promise parallel generation but suffer from a fundamental static-to-dynamic misalignment: Training optimizes local transitions under fixed schedules, whereas efficient inference requires adaptive "long-jump" refinements through unseen states. Our goal is to enable highly parallel decoding for DLMs with low number of function evaluations while preserving generation quality. To achieve this, we propose CD4LM, a framework that decouples training from inference via Discrete-Space Consistency Distillation (DSCD) and Confidence-Adaptive Decoding (CAD). Unlike standard objectives, DSCD trains a student to be trajectory-invariant, mapping diverse noisy states directly to the clean distribution. This intrinsic robustness enables CAD to dynamically allocate compute resources based on token confidence, aggressively skipping steps without the quality collapse typical of heuristic acceleration. On GSM8K, CD4LM matches the LLaDA baseline with a 5.18x wall-clock speedup; across code and math benchmarks, it strictly dominates the accuracy-efficiency Pareto frontier, achieving a 3.62x mean speedup while improving average accuracy. Code is available at https://github.com/yihao-liang/CDLM
Pathology Context Recalibration Network for Ocular Disease Recognition
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Pathology context and expert experience play significant roles in clinical ocular disease diagnosis. Although deep neural networks (DNNs) have good ocular disease recognition results, they often ignore exploring the clinical pathology context and expert experience priors to improve ocular disease recognition performance and decision-making interpretability. To this end, we first develop a novel Pathology Recalibration Module (PRM) to leverage the potential of pathology context prior via the combination of the well-designed pixel-wise context compression operator and pathology distribution concentration operator; then this paper applies a novel expert prior Guidance Adapter (EPGA) to further highlight significant pixel-wise representation regions by fully mining the expert experience prior. By incorporating PRM and EPGA into the modern DNN, the PCRNet is constructed for automated ocular disease recognition. Additionally, we introduce an Integrated Loss (IL) to boost the ocular disease recognition performance of PCRNet by considering the effects of sample-wise loss distributions and training label frequencies. The extensive experiments on three ocular disease datasets demonstrate the superiority of PCRNet with IL over state-of-the-art attention-based networks and advanced loss methods. Further visualization analysis explains the inherent behavior of PRM and EPGA that affects the decision-making process of DNNs.
* The article has been accepted for publication at Machine Intelligence Research (MIR)
VOIC: Visible-Occluded Decoupling for Monocular 3D Semantic Scene Completion
Dec 22, 2025



Abstract:Camera-based 3D Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) is a critical task for autonomous driving and robotic scene understanding. It aims to infer a complete 3D volumetric representation of both semantics and geometry from a single image. Existing methods typically focus on end-to-end 2D-to-3D feature lifting and voxel completion. However, they often overlook the interference between high-confidence visible-region perception and low-confidence occluded-region reasoning caused by single-image input, which can lead to feature dilution and error propagation. To address these challenges, we introduce an offline Visible Region Label Extraction (VRLE) strategy that explicitly separates and extracts voxel-level supervision for visible regions from dense 3D ground truth. This strategy purifies the supervisory space for two complementary sub-tasks: visible-region perception and occluded-region reasoning. Building on this idea, we propose the Visible-Occluded Interactive Completion Network (VOIC), a novel dual-decoder framework that explicitly decouples SSC into visible-region semantic perception and occluded-region scene completion. VOIC first constructs a base 3D voxel representation by fusing image features with depth-derived occupancy. The visible decoder focuses on generating high-fidelity geometric and semantic priors, while the occlusion decoder leverages these priors together with cross-modal interaction to perform coherent global scene reasoning. Extensive experiments on the SemanticKITTI and SSCBench-KITTI360 benchmarks demonstrate that VOIC outperforms existing monocular SSC methods in both geometric completion and semantic segmentation accuracy, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Event Extraction in Large Language Model
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) and multimodal LLMs are changing event extraction (EE): prompting and generation can often produce structured outputs in zero shot or few shot settings. Yet LLM based pipelines face deployment gaps, including hallucinations under weak constraints, fragile temporal and causal linking over long contexts and across documents, and limited long horizon knowledge management within a bounded context window. We argue that EE should be viewed as a system component that provides a cognitive scaffold for LLM centered solutions. Event schemas and slot constraints create interfaces for grounding and verification; event centric structures act as controlled intermediate representations for stepwise reasoning; event links support relation aware retrieval with graph based RAG; and event stores offer updatable episodic and agent memory beyond the context window. This survey covers EE in text and multimodal settings, organizing tasks and taxonomy, tracing method evolution from rule based and neural models to instruction driven and generative frameworks, and summarizing formulations, decoding strategies, architectures, representations, datasets, and evaluation. We also review cross lingual, low resource, and domain specific settings, and highlight open challenges and future directions for reliable event centric systems. Finally, we outline open challenges and future directions that are central to the LLM era, aiming to evolve EE from static extraction into a structurally reliable, agent ready perception and memory layer for open world systems.
Plasticine: A Traceable Diffusion Model for Medical Image Translation
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Domain gaps arising from variations in imaging devices and population distributions pose significant challenges for machine learning in medical image analysis. Existing image-to-image translation methods primarily aim to learn mappings between domains, often generating diverse synthetic data with variations in anatomical scale and shape, but they usually overlook spatial correspondence during the translation process. For clinical applications, traceability, defined as the ability to provide pixel-level correspondences between original and translated images, is equally important. This property enhances clinical interpretability but has been largely overlooked in previous approaches. To address this gap, we propose Plasticine, which is, to the best of our knowledge, the first end-to-end image-to-image translation framework explicitly designed with traceability as a core objective. Our method combines intensity translation and spatial transformation within a denoising diffusion framework. This design enables the generation of synthetic images with interpretable intensity transitions and spatially coherent deformations, supporting pixel-wise traceability throughout the translation process.
A Lightweight Transfer Learning-Based State-of-Health Monitoring with Application to Lithium-ion Batteries in Autonomous Air Vehicles
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Accurate and rapid state-of-health (SOH) monitoring plays an important role in indicating energy information for lithium-ion battery-powered portable mobile devices. To confront their variable working conditions, transfer learning (TL) emerges as a promising technique for leveraging knowledge from data-rich source working conditions, significantly reducing the training data required for SOH monitoring from target working conditions. However, traditional TL-based SOH monitoring is infeasible when applied in portable mobile devices since substantial computational resources are consumed during the TL stage and unexpectedly reduce the working endurance. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a lightweight TL-based SOH monitoring approach with constructive incremental transfer learning (CITL). First, taking advantage of the unlabeled data in the target domain, a semi-supervised TL mechanism is proposed to minimize the monitoring residual in a constructive way, through iteratively adding network nodes in the CITL. Second, the cross-domain learning ability of node parameters for CITL is comprehensively guaranteed through structural risk minimization, transfer mismatching minimization, and manifold consistency maximization. Moreover, the convergence analysis of the CITL is given, theoretically guaranteeing the efficacy of TL performance and network compactness. Finally, the proposed approach is verified through extensive experiments with a realistic autonomous air vehicles (AAV) battery dataset collected from dozens of flight missions. Specifically, the CITL outperforms SS-TCA, MMD-LSTM-DA, DDAN, BO-CNN-TL, and AS$^3$LSTM, in SOH estimation by 83.73%, 61.15%, 28.24%, 87.70%, and 57.34%, respectively, as evaluated using the index root mean square error.
Instella: Fully Open Language Models with Stellar Performance
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance across a wide range of tasks, yet the majority of high-performing models remain closed-source or partially open, limiting transparency and reproducibility. In this work, we introduce Instella, a family of fully open three billion parameter language models trained entirely on openly available data and codebase. Powered by AMD Instinct MI300X GPUs, Instella is developed through large-scale pre-training, general-purpose instruction tuning, and alignment with human preferences. Despite using substantially fewer pre-training tokens than many contemporaries, Instella achieves state-of-the-art results among fully open models and is competitive with leading open-weight models of comparable size. We further release two specialized variants: Instella-Long, capable of handling context lengths up to 128K tokens, and Instella-Math, a reasoning-focused model enhanced through supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning on mathematical tasks. Together, these contributions establish Instella as a transparent, performant, and versatile alternative for the community, advancing the goal of open and reproducible language modeling research.
Learning from Online Videos at Inference Time for Computer-Use Agents
Nov 06, 2025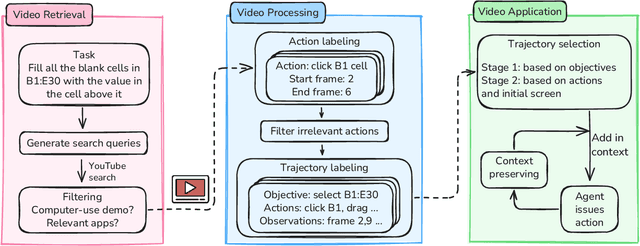

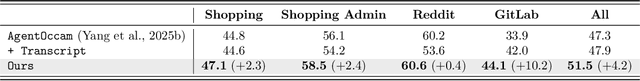

Abstract:Computer-use agents can operate computers and automate laborious tasks, but despite recent rapid progress, they still lag behind human users, especially when tasks require domain-specific procedural knowledge about particular applications, platforms, and multi-step workflows. Humans can bridge this gap by watching video tutorials: we search, skim, and selectively imitate short segments that match our current subgoal. In this paper, we study how to enable computer-use agents to learn from online videos at inference time effectively. We propose a framework that retrieves and filters tutorial videos, converts them into structured demonstration trajectories, and dynamically selects trajectories as in-context guidance during execution. Particularly, using a VLM, we infer UI actions, segment videos into short subsequences of actions, and assign each subsequence a textual objective. At inference time, a two-stage selection mechanism dynamically chooses a single trajectory to add in context at each step, focusing the agent on the most helpful local guidance for its next decision. Experiments on two widely used benchmarks show that our framework consistently outperforms strong base agents and variants that use only textual tutorials or transcripts. Analyses highlight the importance of trajectory segmentation and selection, action filtering, and visual information, suggesting that abundant online videos can be systematically distilled into actionable guidance that improves computer-use agents at inference time. Our code is available at https://github.com/UCSB-NLP-Chang/video_demo.
Adaptive Confidence-Wise Loss for Improved Lens Structure Segmentation in AS-OCT
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Precise lens structure segmentation is essential for the design of intraocular lenses (IOLs) in cataract surgery. Existing deep segmentation networks typically weight all pixels equally under cross-entropy (CE) loss, overlooking the fact that sub-regions of lens structures are inhomogeneous (e.g., some regions perform better than others) and that boundary regions often suffer from poor segmentation calibration at the pixel level. Clinically, experts annotate different sub-regions of lens structures with varying confidence levels, considering factors such as sub-region proportions, ambiguous boundaries, and lens structure shapes. Motivated by this observation, we propose an Adaptive Confidence-Wise (ACW) loss to group each lens structure sub-region into different confidence sub-regions via a confidence threshold from the unique region aspect, aiming to exploit the potential of expert annotation confidence prior. Specifically, ACW clusters each target region into low-confidence and high-confidence groups and then applies a region-weighted loss to reweigh each confidence group. Moreover, we design an adaptive confidence threshold optimization algorithm to adjust the confidence threshold of ACW dynamically. Additionally, to better quantify the miscalibration errors in boundary region segmentation, we propose a new metric, termed Boundary Expected Calibration Error (BECE). Extensive experiments on a clinical lens structure AS-OCT dataset and other multi-structure datasets demonstrate that our ACW significantly outperforms competitive segmentation loss methods across different deep segmentation networks (e.g., MedSAM). Notably, our method surpasses CE with 6.13% IoU gain, 4.33% DSC increase, and 4.79% BECE reduction in lens structure segmentation under U-Net. The code of this paper is available at https://github.com/XiaoLing12138/Adaptive-Confidence-Wise-Loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge