Yusheng Su
Instella: Fully Open Language Models with Stellar Performance
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance across a wide range of tasks, yet the majority of high-performing models remain closed-source or partially open, limiting transparency and reproducibility. In this work, we introduce Instella, a family of fully open three billion parameter language models trained entirely on openly available data and codebase. Powered by AMD Instinct MI300X GPUs, Instella is developed through large-scale pre-training, general-purpose instruction tuning, and alignment with human preferences. Despite using substantially fewer pre-training tokens than many contemporaries, Instella achieves state-of-the-art results among fully open models and is competitive with leading open-weight models of comparable size. We further release two specialized variants: Instella-Long, capable of handling context lengths up to 128K tokens, and Instella-Math, a reasoning-focused model enhanced through supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning on mathematical tasks. Together, these contributions establish Instella as a transparent, performant, and versatile alternative for the community, advancing the goal of open and reproducible language modeling research.
Instella-T2I: Pushing the Limits of 1D Discrete Latent Space Image Generation
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Image tokenization plays a critical role in reducing the computational demands of modeling high-resolution images, significantly improving the efficiency of image and multimodal understanding and generation. Recent advances in 1D latent spaces have reduced the number of tokens required by eliminating the need for a 2D grid structure. In this paper, we further advance compact discrete image representation by introducing 1D binary image latents. By representing each image as a sequence of binary vectors, rather than using traditional one-hot codebook tokens, our approach preserves high-resolution details while maintaining the compactness of 1D latents. To the best of our knowledge, our text-to-image models are the first to achieve competitive performance in both diffusion and auto-regressive generation using just 128 discrete tokens for images up to 1024x1024, demonstrating up to a 32-fold reduction in token numbers compared to standard VQ-VAEs. The proposed 1D binary latent space, coupled with simple model architectures, achieves marked improvements in speed training and inference speed. Our text-to-image models allow for a global batch size of 4096 on a single GPU node with 8 AMD MI300X GPUs, and the training can be completed within 200 GPU days. Our models achieve competitive performance compared to modern image generation models without any in-house private training data or post-training refinements, offering a scalable and efficient alternative to conventional tokenization methods.
Unleashing Hour-Scale Video Training for Long Video-Language Understanding
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Recent long-form video-language understanding benchmarks have driven progress in video large multimodal models (Video-LMMs). However, the scarcity of well-annotated long videos has left the training of hour-long Video-LLMs underexplored. To close this gap, we present VideoMarathon, a large-scale hour-long video instruction-following dataset. This dataset includes around 9,700 hours of long videos sourced from diverse domains, ranging from 3 to 60 minutes per video. Specifically, it contains 3.3M high-quality QA pairs, spanning six fundamental topics: temporality, spatiality, object, action, scene, and event. Compared to existing video instruction datasets, VideoMarathon significantly extends training video durations up to 1 hour, and supports 22 diverse tasks requiring both short- and long-term video comprehension. Building on VideoMarathon, we propose Hour-LLaVA, a powerful and efficient Video-LMM for hour-scale video-language modeling. It enables hour-long video training and inference at 1-FPS sampling by leveraging a memory augmentation module, which adaptively integrates user question-relevant and spatiotemporal-informative semantics from a cached full video context. In our experiments, Hour-LLaVA achieves the best performance on multiple long video-language benchmarks, demonstrating the high quality of the VideoMarathon dataset and the superiority of the Hour-LLaVA model.
MOVi: Training-free Text-conditioned Multi-Object Video Generation
May 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion-based text-to-video (T2V) models have demonstrated remarkable progress, but these models still face challenges in generating videos with multiple objects. Most models struggle with accurately capturing complex object interactions, often treating some objects as static background elements and limiting their movement. In addition, they often fail to generate multiple distinct objects as specified in the prompt, resulting in incorrect generations or mixed features across objects. In this paper, we present a novel training-free approach for multi-object video generation that leverages the open world knowledge of diffusion models and large language models (LLMs). We use an LLM as the ``director'' of object trajectories, and apply the trajectories through noise re-initialization to achieve precise control of realistic movements. We further refine the generation process by manipulating the attention mechanism to better capture object-specific features and motion patterns, and prevent cross-object feature interference. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our training free approach in significantly enhancing the multi-object generation capabilities of existing video diffusion models, resulting in 42% absolute improvement in motion dynamics and object generation accuracy, while also maintaining high fidelity and motion smoothness.
KeyVID: Keyframe-Aware Video Diffusion for Audio-Synchronized Visual Animation
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:Generating video from various conditions, such as text, image, and audio, enables both spatial and temporal control, leading to high-quality generation results. Videos with dramatic motions often require a higher frame rate to ensure smooth motion. Currently, most audio-to-visual animation models use uniformly sampled frames from video clips. However, these uniformly sampled frames fail to capture significant key moments in dramatic motions at low frame rates and require significantly more memory when increasing the number of frames directly. In this paper, we propose KeyVID, a keyframe-aware audio-to-visual animation framework that significantly improves the generation quality for key moments in audio signals while maintaining computation efficiency. Given an image and an audio input, we first localize keyframe time steps from the audio. Then, we use a keyframe generator to generate the corresponding visual keyframes. Finally, we generate all intermediate frames using the motion interpolator. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that KeyVID significantly improves audio-video synchronization and video quality across multiple datasets, particularly for highly dynamic motions. The code is released in https://github.com/XingruiWang/KeyVID.
Self-Taught Agentic Long Context Understanding
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Answering complex, long-context questions remains a major challenge for large language models (LLMs) as it requires effective question clarifications and context retrieval. We propose Agentic Long-Context Understanding (AgenticLU), a framework designed to enhance an LLM's understanding of such queries by integrating targeted self-clarification with contextual grounding within an agentic workflow. At the core of AgenticLU is Chain-of-Clarifications (CoC), where models refine their understanding through self-generated clarification questions and corresponding contextual groundings. By scaling inference as a tree search where each node represents a CoC step, we achieve 97.8% answer recall on NarrativeQA with a search depth of up to three and a branching factor of eight. To amortize the high cost of this search process to training, we leverage the preference pairs for each step obtained by the CoC workflow and perform two-stage model finetuning: (1) supervised finetuning to learn effective decomposition strategies, and (2) direct preference optimization to enhance reasoning quality. This enables AgenticLU models to generate clarifications and retrieve relevant context effectively and efficiently in a single inference pass. Extensive experiments across seven long-context tasks demonstrate that AgenticLU significantly outperforms state-of-the-art prompting methods and specialized long-context LLMs, achieving robust multi-hop reasoning while sustaining consistent performance as context length grows.
Agent Laboratory: Using LLM Agents as Research Assistants
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Historically, scientific discovery has been a lengthy and costly process, demanding substantial time and resources from initial conception to final results. To accelerate scientific discovery, reduce research costs, and improve research quality, we introduce Agent Laboratory, an autonomous LLM-based framework capable of completing the entire research process. This framework accepts a human-provided research idea and progresses through three stages--literature review, experimentation, and report writing to produce comprehensive research outputs, including a code repository and a research report, while enabling users to provide feedback and guidance at each stage. We deploy Agent Laboratory with various state-of-the-art LLMs and invite multiple researchers to assess its quality by participating in a survey, providing human feedback to guide the research process, and then evaluate the final paper. We found that: (1) Agent Laboratory driven by o1-preview generates the best research outcomes; (2) The generated machine learning code is able to achieve state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods; (3) Human involvement, providing feedback at each stage, significantly improves the overall quality of research; (4) Agent Laboratory significantly reduces research expenses, achieving an 84% decrease compared to previous autonomous research methods. We hope Agent Laboratory enables researchers to allocate more effort toward creative ideation rather than low-level coding and writing, ultimately accelerating scientific discovery.
Beyond Natural Language: LLMs Leveraging Alternative Formats for Enhanced Reasoning and Communication
Feb 28, 2024
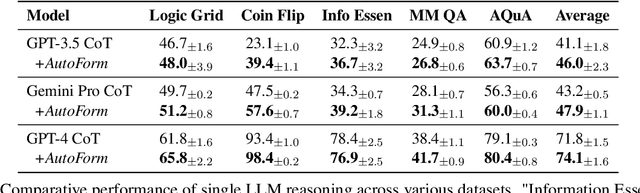

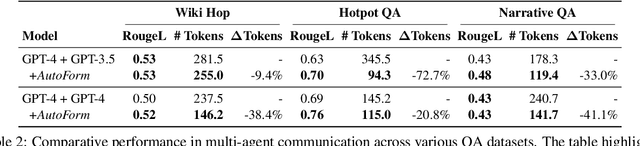
Abstract:Natural language (NL) has long been the predominant format for human cognition and communication, and by extension, has been similarly pivotal in the development and application of Large Language Models (LLMs). Yet, besides NL, LLMs have seen various non-NL formats during pre-training, such as code and logical expression. NL's status as the optimal format for LLMs, particularly in single-LLM reasoning and multi-agent communication, has not been thoroughly examined. In this work, we challenge the default use of NL by exploring the utility of non-NL formats in these contexts. We show that allowing LLMs to autonomously select the most suitable format before reasoning or communicating leads to a 3.3 to 5.7\% improvement in reasoning efficiency for different LLMs, and up to a 72.7\% reduction in token usage in multi-agent communication, all while maintaining communicative effectiveness. Our comprehensive analysis further reveals that LLMs can devise a format from limited task instructions and that the devised format is effectively transferable across different LLMs. Intriguingly, the structured communication format decided by LLMs exhibits notable parallels with established agent communication languages, suggesting a natural evolution towards efficient, structured communication in agent communication. Our code is released at \url{https://github.com/thunlp/AutoForm}.
Confidence Matters: Revisiting Intrinsic Self-Correction Capabilities of Large Language Models
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:The recent success of Large Language Models (LLMs) has catalyzed an increasing interest in their self-correction capabilities. This paper presents a comprehensive investigation into the intrinsic self-correction of LLMs, attempting to address the ongoing debate about its feasibility. Our research has identified an important latent factor - the "confidence" of LLMs - during the self-correction process. Overlooking this factor may cause the models to over-criticize themselves, resulting in unreliable conclusions regarding the efficacy of self-correction. We have experimentally observed that LLMs possess the capability to understand the "confidence" in their own responses. It motivates us to develop an "If-or-Else" (IoE) prompting framework, designed to guide LLMs in assessing their own "confidence", facilitating intrinsic self-corrections. We conduct extensive experiments and demonstrate that our IoE-based Prompt can achieve a consistent improvement regarding the accuracy of self-corrected responses over the initial answers. Our study not only sheds light on the underlying factors affecting self-correction in LLMs, but also introduces a practical framework that utilizes the IoE prompting principle to efficiently improve self-correction capabilities with "confidence". The code is available at https://github.com/MBZUAI-CLeaR/IoE-Prompting.git.
AgentVerse: Facilitating Multi-Agent Collaboration and Exploring Emergent Behaviors in Agents
Aug 21, 2023



Abstract:Autonomous agents empowered by Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone significant improvements, enabling them to generalize across a broad spectrum of tasks. However, in real-world scenarios, cooperation among individuals is often required to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of task accomplishment. Hence, inspired by human group dynamics, we propose a multi-agent framework \framework that can collaboratively and dynamically adjust its composition as a greater-than-the-sum-of-its-parts system. Our experiments demonstrate that \framework framework can effectively deploy multi-agent groups that outperform a single agent. Furthermore, we delve into the emergence of social behaviors among individual agents within a group during collaborative task accomplishment. In view of these behaviors, we discuss some possible strategies to leverage positive ones and mitigate negative ones for improving the collaborative potential of multi-agent groups. Our codes for \framework will soon be released at \url{https://github.com/OpenBMB/AgentVerse}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge