Jingyang Lin
Unleashing Hour-Scale Video Training for Long Video-Language Understanding
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Recent long-form video-language understanding benchmarks have driven progress in video large multimodal models (Video-LMMs). However, the scarcity of well-annotated long videos has left the training of hour-long Video-LLMs underexplored. To close this gap, we present VideoMarathon, a large-scale hour-long video instruction-following dataset. This dataset includes around 9,700 hours of long videos sourced from diverse domains, ranging from 3 to 60 minutes per video. Specifically, it contains 3.3M high-quality QA pairs, spanning six fundamental topics: temporality, spatiality, object, action, scene, and event. Compared to existing video instruction datasets, VideoMarathon significantly extends training video durations up to 1 hour, and supports 22 diverse tasks requiring both short- and long-term video comprehension. Building on VideoMarathon, we propose Hour-LLaVA, a powerful and efficient Video-LMM for hour-scale video-language modeling. It enables hour-long video training and inference at 1-FPS sampling by leveraging a memory augmentation module, which adaptively integrates user question-relevant and spatiotemporal-informative semantics from a cached full video context. In our experiments, Hour-LLaVA achieves the best performance on multiple long video-language benchmarks, demonstrating the high quality of the VideoMarathon dataset and the superiority of the Hour-LLaVA model.
Facilitating Long Context Understanding via Supervised Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled them to process increasingly longer sequences, ranging from 2K to 2M tokens and even beyond. However, simply extending the input sequence length does not necessarily lead to effective long-context understanding. In this study, we integrate Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning into LLMs in a supervised manner to facilitate effective long-context understanding. To achieve this, we introduce LongFinanceQA, a synthetic dataset in the financial domain designed to improve long-context reasoning. Unlike existing long-context synthetic data, LongFinanceQA includes intermediate CoT reasoning before the final conclusion, which encourages LLMs to perform explicit reasoning, improving accuracy and interpretability in long-context understanding. To generate synthetic CoT reasoning, we propose Property-driven Agentic Inference (PAI), an agentic framework that simulates human-like reasoning steps, including property extraction, retrieval, and summarization. We evaluate PAI's reasoning capabilities by assessing GPT-4o-mini w/ PAI on the Loong benchmark, outperforming standard GPT-4o-mini by 20.0%. Furthermore, we fine-tune LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct on LongFinanceQA, achieving a 24.6% gain on Loong's financial subset.
Grounding Partially-Defined Events in Multimodal Data
Oct 07, 2024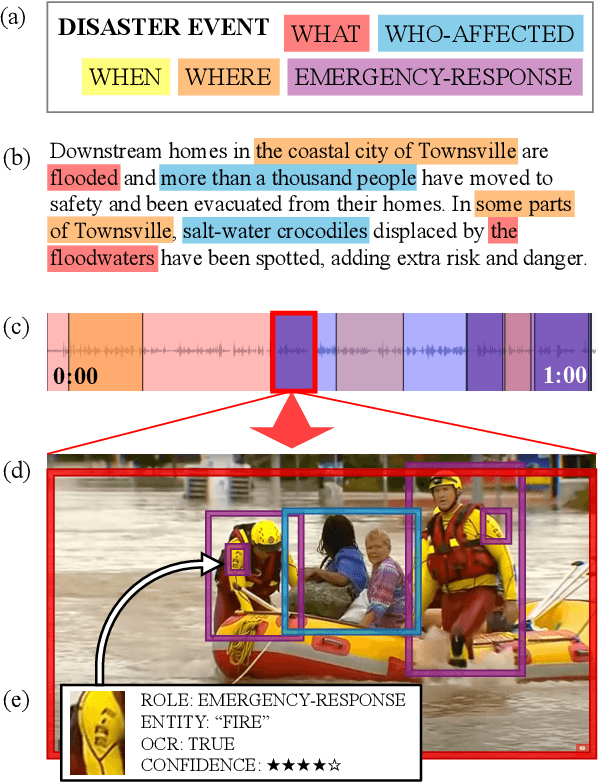
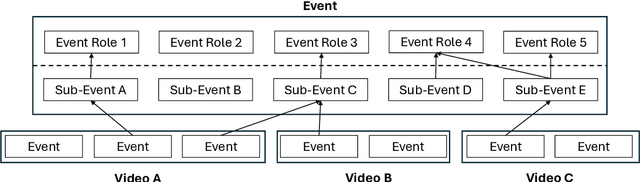
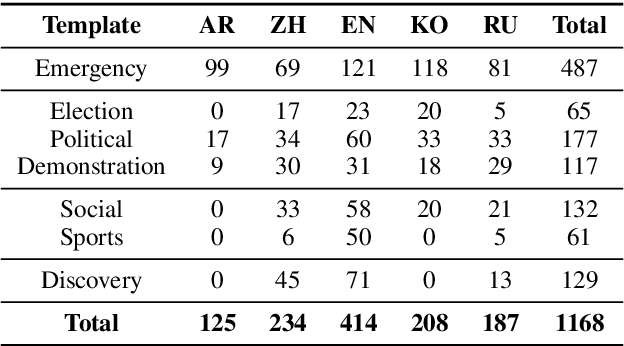
Abstract:How are we able to learn about complex current events just from short snippets of video? While natural language enables straightforward ways to represent under-specified, partially observable events, visual data does not facilitate analogous methods and, consequently, introduces unique challenges in event understanding. With the growing prevalence of vision-capable AI agents, these systems must be able to model events from collections of unstructured video data. To tackle robust event modeling in multimodal settings, we introduce a multimodal formulation for partially-defined events and cast the extraction of these events as a three-stage span retrieval task. We propose a corresponding benchmark for this task, MultiVENT-G, that consists of 14.5 hours of densely annotated current event videos and 1,168 text documents, containing 22.8K labeled event-centric entities. We propose a collection of LLM-driven approaches to the task of multimodal event analysis, and evaluate them on MultiVENT-G. Results illustrate the challenges that abstract event understanding poses and demonstrates promise in event-centric video-language systems.
Systematic Evaluation of LLM-as-a-Judge in LLM Alignment Tasks: Explainable Metrics and Diverse Prompt Templates
Aug 23, 2024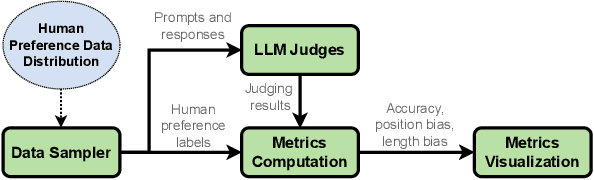
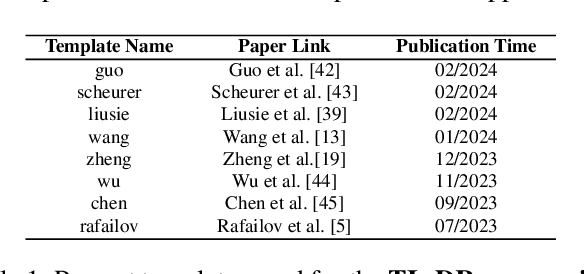
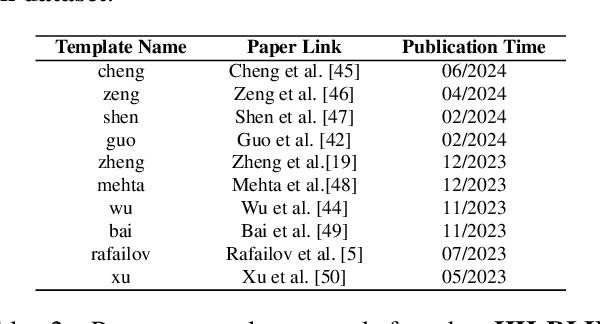
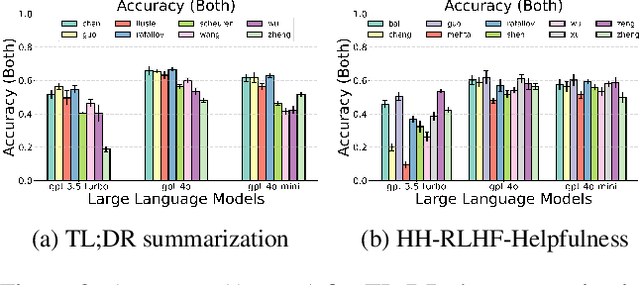
Abstract:Alignment approaches such as RLHF and DPO are actively investigated to align large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. Commercial large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 have been recently employed to evaluate and compare different LLM alignment approaches. These models act as surrogates for human evaluators due to their promising abilities to approximate human preferences with remarkably faster feedback and lower costs. This methodology is referred to as LLM-as-a-judge. However, concerns regarding its reliability have emerged, attributed to LLM judges' biases and inconsistent decision-making. Previous research has sought to develop robust evaluation frameworks for assessing the reliability of LLM judges and their alignment with human preferences. However, the employed evaluation metrics often lack adequate explainability and fail to address the internal inconsistency of LLMs. Additionally, existing studies inadequately explore the impact of various prompt templates when applying LLM-as-a-judge methods, which leads to potentially inconsistent comparisons between different alignment algorithms. In this work, we systematically evaluate LLM judges on alignment tasks (e.g. summarization) by defining evaluation metrics with improved theoretical interpretability and disentangling reliability metrics with LLM internal inconsistency. We develop a framework to evaluate, compare, and visualize the reliability and alignment of LLM judges to provide informative observations that help choose LLM judges for alignment tasks. Our results indicate a significant impact of prompt templates on LLM judge performance, as well as a mediocre alignment level between the tested LLM judges and human evaluators.
CT-GLIP: 3D Grounded Language-Image Pretraining with CT Scans and Radiology Reports for Full-Body Scenarios
Apr 29, 2024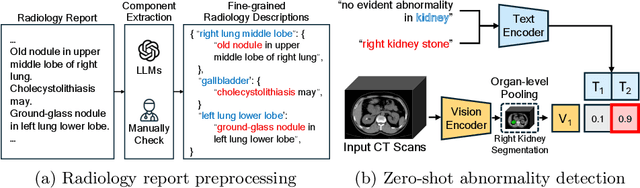
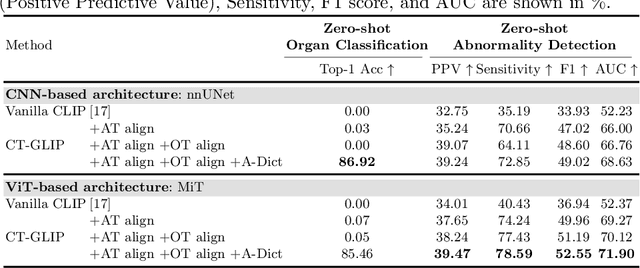
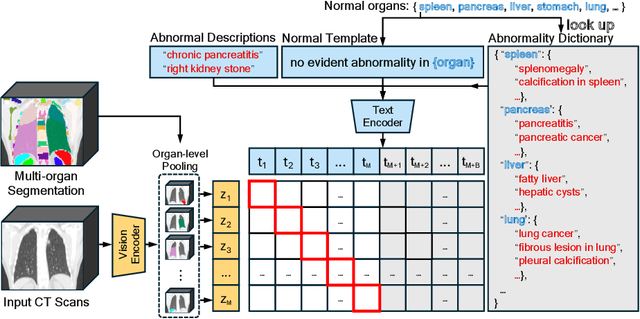
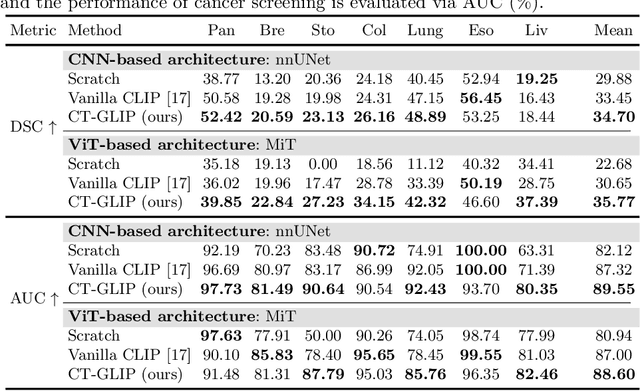
Abstract:Medical Vision-Language Pretraining (Med-VLP) establishes a connection between visual content from medical images and the relevant textual descriptions. Existing Med-VLP methods primarily focus on 2D images depicting a single body part, notably chest X-rays. In this paper, we extend the scope of Med-VLP to encompass 3D images, specifically targeting full-body scenarios, by using a multimodal dataset of CT images and reports. Compared with the 2D counterpart, 3D VLP is required to effectively capture essential semantics from significantly sparser representation in 3D imaging. In this paper, we introduce CT-GLIP (Grounded Language-Image Pretraining with CT scans), a novel method that constructs organ-level image-text pairs to enhance multimodal contrastive learning, aligning grounded visual features with precise diagnostic text. Additionally, we developed an abnormality dictionary to augment contrastive learning with diverse contrastive pairs. Our method, trained on a multimodal CT dataset comprising 44,011 organ-level vision-text pairs from 17,702 patients across 104 organs, demonstrates it can identify organs and abnormalities in a zero-shot manner using natural languages. The performance of CT-GLIP is validated on a separate test set of 1,130 patients, focusing on the 16 most frequent abnormalities across 7 organs. The experimental results show our model's superior performance over the standard CLIP framework across zero-shot and fine-tuning scenarios, using both CNN and ViT architectures.
Video Understanding with Large Language Models: A Survey
Jan 04, 2024


Abstract:With the burgeoning growth of online video platforms and the escalating volume of video content, the demand for proficient video understanding tools has intensified markedly. Given the remarkable capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in language and multimodal tasks, this survey provides a detailed overview of the recent advancements in video understanding harnessing the power of LLMs (Vid-LLMs). The emergent capabilities of Vid-LLMs are surprisingly advanced, particularly their ability for open-ended spatial-temporal reasoning combined with commonsense knowledge, suggesting a promising path for future video understanding. We examine the unique characteristics and capabilities of Vid-LLMs, categorizing the approaches into four main types: LLM-based Video Agents, Vid-LLMs Pretraining, Vid-LLMs Instruction Tuning, and Hybrid Methods. Furthermore, this survey presents a comprehensive study of the tasks, datasets, and evaluation methodologies for Vid-LLMs. Additionally, it explores the expansive applications of Vid-LLMs across various domains, highlighting their remarkable scalability and versatility in real-world video understanding challenges. Finally, it summarizes the limitations of existing Vid-LLMs and outlines directions for future research. For more information, readers are recommended to visit the repository at https://github.com/yunlong10/Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding.
Predicting Adverse Neonatal Outcomes for Preterm Neonates with Multi-Task Learning
Mar 28, 2023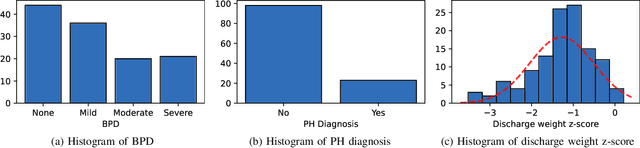
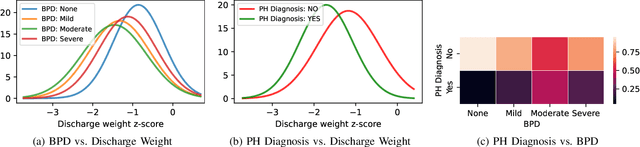
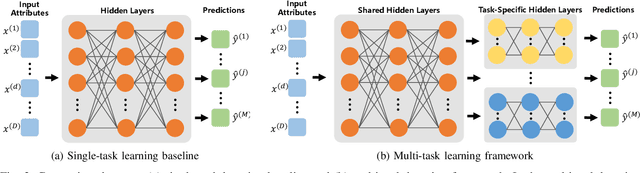
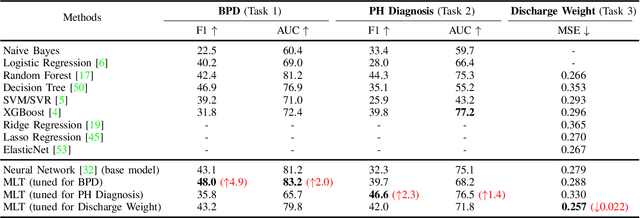
Abstract:Diagnosis of adverse neonatal outcomes is crucial for preterm survival since it enables doctors to provide timely treatment. Machine learning (ML) algorithms have been demonstrated to be effective in predicting adverse neonatal outcomes. However, most previous ML-based methods have only focused on predicting a single outcome, ignoring the potential correlations between different outcomes, and potentially leading to suboptimal results and overfitting issues. In this work, we first analyze the correlations between three adverse neonatal outcomes and then formulate the diagnosis of multiple neonatal outcomes as a multi-task learning (MTL) problem. We then propose an MTL framework to jointly predict multiple adverse neonatal outcomes. In particular, the MTL framework contains shared hidden layers and multiple task-specific branches. Extensive experiments have been conducted using Electronic Health Records (EHRs) from 121 preterm neonates. Empirical results demonstrate the effectiveness of the MTL framework. Furthermore, the feature importance is analyzed for each neonatal outcome, providing insights into model interpretability.
VideoXum: Cross-modal Visual and Textural Summarization of Videos
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:Video summarization aims to distill the most important information from a source video to produce either an abridged clip or a textual narrative. Traditionally, different methods have been proposed depending on whether the output is a video or text, thus ignoring the correlation between the two semantically related tasks of visual summarization and textual summarization. We propose a new joint video and text summarization task. The goal is to generate both a shortened video clip along with the corresponding textual summary from a long video, collectively referred to as a cross-modal summary. The generated shortened video clip and text narratives should be semantically well aligned. To this end, we first build a large-scale human-annotated dataset -- VideoXum (X refers to different modalities). The dataset is reannotated based on ActivityNet. After we filter out the videos that do not meet the length requirements, 14,001 long videos remain in our new dataset. Each video in our reannotated dataset has human-annotated video summaries and the corresponding narrative summaries. We then design a novel end-to-end model -- VTSUM-BILP to address the challenges of our proposed task. Moreover, we propose a new metric called VT-CLIPScore to help evaluate the semantic consistency of cross-modality summary. The proposed model achieves promising performance on this new task and establishes a benchmark for future research.
Out-of-Distribution Detection with Hilbert-Schmidt Independence Optimization
Sep 26, 2022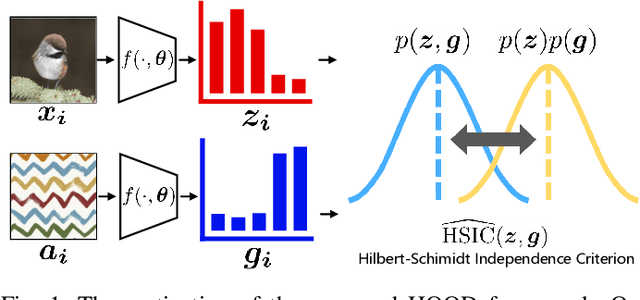
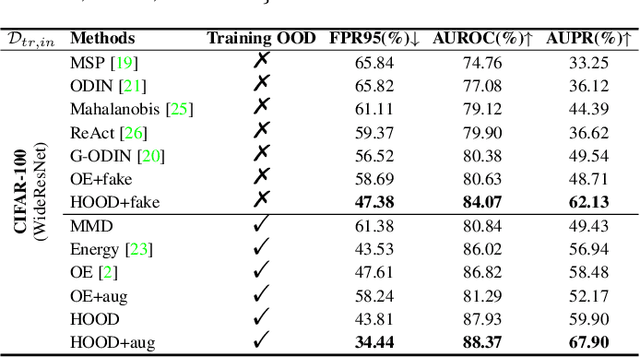
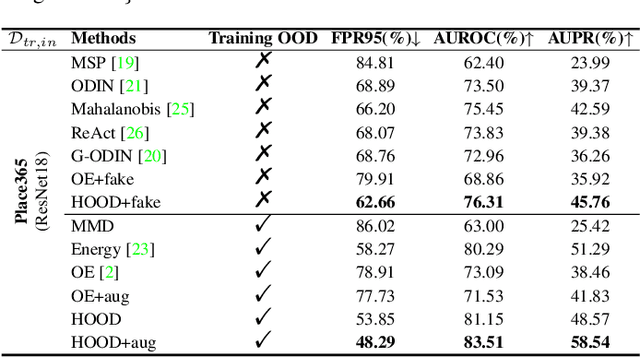
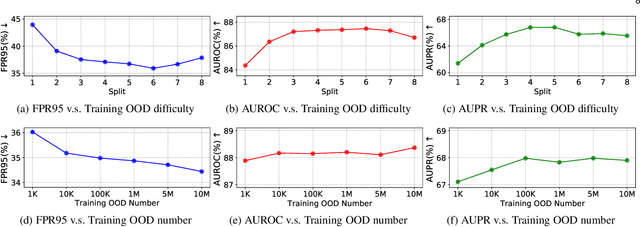
Abstract:Outlier detection tasks have been playing a critical role in AI safety. There has been a great challenge to deal with this task. Observations show that deep neural network classifiers usually tend to incorrectly classify out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs into in-distribution classes with high confidence. Existing works attempt to solve the problem by explicitly imposing uncertainty on classifiers when OOD inputs are exposed to the classifier during training. In this paper, we propose an alternative probabilistic paradigm that is both practically useful and theoretically viable for the OOD detection tasks. Particularly, we impose statistical independence between inlier and outlier data during training, in order to ensure that inlier data reveals little information about OOD data to the deep estimator during training. Specifically, we estimate the statistical dependence between inlier and outlier data through the Hilbert-Schmidt Independence Criterion (HSIC), and we penalize such metric during training. We also associate our approach with a novel statistical test during the inference time coupled with our principled motivation. Empirical results show that our method is effective and robust for OOD detection on various benchmarks. In comparison to SOTA models, our approach achieves significant improvement regarding FPR95, AUROC, and AUPR metrics. Code is available: \url{https://github.com/jylins/hood}.
Improving Self-supervised Learning with Automated Unsupervised Outlier Arbitration
Dec 15, 2021
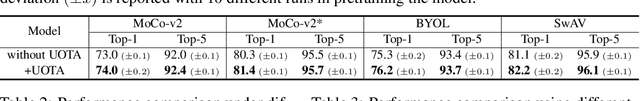
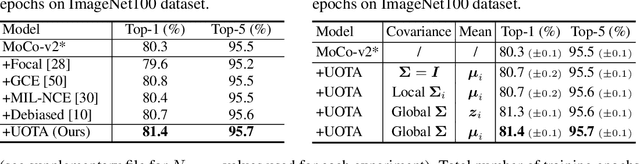
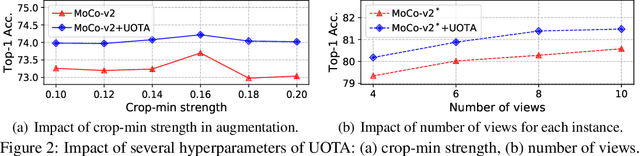
Abstract:Our work reveals a structured shortcoming of the existing mainstream self-supervised learning methods. Whereas self-supervised learning frameworks usually take the prevailing perfect instance level invariance hypothesis for granted, we carefully investigate the pitfalls behind. Particularly, we argue that the existing augmentation pipeline for generating multiple positive views naturally introduces out-of-distribution (OOD) samples that undermine the learning of the downstream tasks. Generating diverse positive augmentations on the input does not always pay off in benefiting downstream tasks. To overcome this inherent deficiency, we introduce a lightweight latent variable model UOTA, targeting the view sampling issue for self-supervised learning. UOTA adaptively searches for the most important sampling region to produce views, and provides viable choice for outlier-robust self-supervised learning approaches. Our method directly generalizes to many mainstream self-supervised learning approaches, regardless of the loss's nature contrastive or not. We empirically show UOTA's advantage over the state-of-the-art self-supervised paradigms with evident margin, which well justifies the existence of the OOD sample issue embedded in the existing approaches. Especially, we theoretically prove that the merits of the proposal boil down to guaranteed estimator variance and bias reduction. Code is available: at https://github.com/ssl-codelab/uota.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge