Andy Wong
RovoDev Code Reviewer: A Large-Scale Online Evaluation of LLM-based Code Review Automation at Atlassian
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs)-powered code review automation has the potential to transform code review workflows. Despite the advances of LLM-powered code review comment generation approaches, several practical challenges remain for designing enterprise-grade code review automation tools. In particular, this paper aims at answering the practical question: how can we design a review-guided, context-aware, quality-checked code review comment generation without fine-tuning? In this paper, we present RovoDev Code Reviewer, an enterprise-grade LLM-based code review automation tool designed and deployed at scale within Atlassian's development ecosystem with seamless integration into Atlassian's Bitbucket. Through the offline, online, user feedback evaluations over a one-year period, we conclude that RovoDev Code Reviewer is (1) effective in generating code review comments that could lead to code resolution for 38.70% (i.e., comments that triggered code changes in the subsequent commits); and (2) offers the promise of accelerating feedback cycles (i.e., decreasing the PR cycle time by 30.8%), alleviating reviewer workload (i.e., reducing the number of human-written comments by 35.6%), and improving overall software quality (i.e., finding errors with actionable suggestions).
RLSR: Reinforcement Learning with Supervised Reward Outperforms SFT in Instruction Following
Oct 16, 2025



Abstract:After the pretraining stage of LLMs, techniques such as SFT, RLHF, RLVR, and RFT are applied to enhance instruction-following ability, mitigate undesired responses, improve reasoning capability and enable efficient domain adaptation with minimal data. SFT relies on the next-token prediction objective to strengthen instruction following in a base model using a large corpus of human-labeled responses. In contrast, RFT employs a RL-based approach to adapt fine-tuned reasoning models to specific domains with limited supervision. Inspired by RFT, we propose replacing SFT with RLSR to leverage the extensive SFT dataset in an RL framework, thereby improving the base model's instruction-following ability. In RLSR, the base model generates multiple responses for each prompt, and reward scores are computed as the cosine similarity in the semantic embedding space between the generated and human-labeled responses. RLSR can be utilized in multiple ways. It can directly replace SFT, achieving superior performance on instruction-following benchmarks-for example, RLSR (SB) on Qwen-7B (INFINITY) achieved an AlpacaEval win rate of 26.34%, surpassing SFT's 21.01%. Furthermore, combining SFT and RLSR further enhances downstream task performance; Qwen-7B (INFINITY) achieved a win rate of 30.73% when trained with SFT + RLSR.
Facilitating Long Context Understanding via Supervised Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled them to process increasingly longer sequences, ranging from 2K to 2M tokens and even beyond. However, simply extending the input sequence length does not necessarily lead to effective long-context understanding. In this study, we integrate Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning into LLMs in a supervised manner to facilitate effective long-context understanding. To achieve this, we introduce LongFinanceQA, a synthetic dataset in the financial domain designed to improve long-context reasoning. Unlike existing long-context synthetic data, LongFinanceQA includes intermediate CoT reasoning before the final conclusion, which encourages LLMs to perform explicit reasoning, improving accuracy and interpretability in long-context understanding. To generate synthetic CoT reasoning, we propose Property-driven Agentic Inference (PAI), an agentic framework that simulates human-like reasoning steps, including property extraction, retrieval, and summarization. We evaluate PAI's reasoning capabilities by assessing GPT-4o-mini w/ PAI on the Loong benchmark, outperforming standard GPT-4o-mini by 20.0%. Furthermore, we fine-tune LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct on LongFinanceQA, achieving a 24.6% gain on Loong's financial subset.
Systematic Evaluation of LLM-as-a-Judge in LLM Alignment Tasks: Explainable Metrics and Diverse Prompt Templates
Aug 23, 2024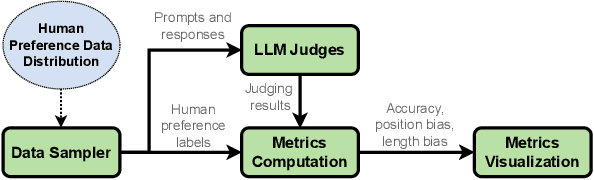
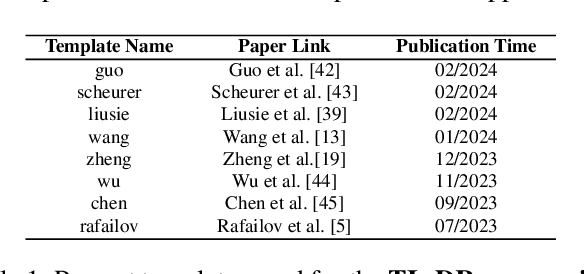
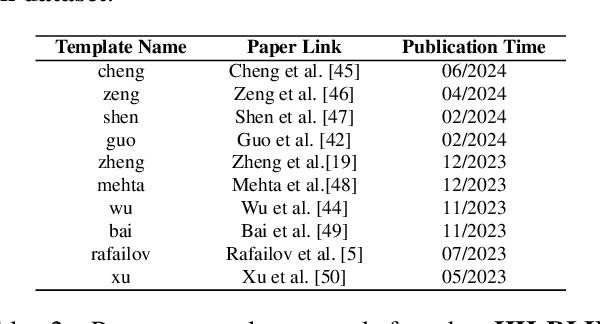
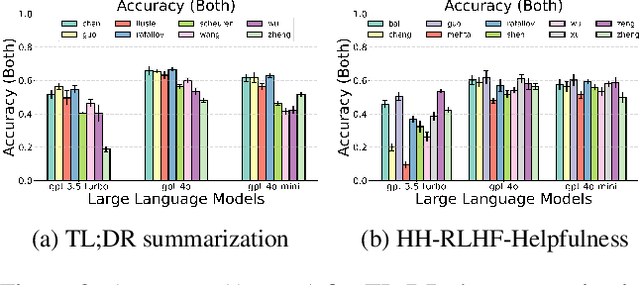
Abstract:Alignment approaches such as RLHF and DPO are actively investigated to align large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. Commercial large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 have been recently employed to evaluate and compare different LLM alignment approaches. These models act as surrogates for human evaluators due to their promising abilities to approximate human preferences with remarkably faster feedback and lower costs. This methodology is referred to as LLM-as-a-judge. However, concerns regarding its reliability have emerged, attributed to LLM judges' biases and inconsistent decision-making. Previous research has sought to develop robust evaluation frameworks for assessing the reliability of LLM judges and their alignment with human preferences. However, the employed evaluation metrics often lack adequate explainability and fail to address the internal inconsistency of LLMs. Additionally, existing studies inadequately explore the impact of various prompt templates when applying LLM-as-a-judge methods, which leads to potentially inconsistent comparisons between different alignment algorithms. In this work, we systematically evaluate LLM judges on alignment tasks (e.g. summarization) by defining evaluation metrics with improved theoretical interpretability and disentangling reliability metrics with LLM internal inconsistency. We develop a framework to evaluate, compare, and visualize the reliability and alignment of LLM judges to provide informative observations that help choose LLM judges for alignment tasks. Our results indicate a significant impact of prompt templates on LLM judge performance, as well as a mediocre alignment level between the tested LLM judges and human evaluators.
SAGE-NDVI: A Stereotype-Breaking Evaluation Metric for Remote Sensing Image Dehazing Using Satellite-to-Ground NDVI Knowledge
Jun 09, 2023Abstract:Image dehazing is a meaningful low-level computer vision task and can be applied to a variety of contexts. In our industrial deployment scenario based on remote sensing (RS) images, the quality of image dehazing directly affects the grade of our crop identification and growth monitoring products. However, the widely used peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM) provide ambiguous visual interpretation. In this paper, we design a new objective metric for RS image dehazing evaluation. Our proposed metric leverages a ground-based phenology observation resource to calculate the vegetation index error between RS and ground images at a hazy date. Extensive experiments validate that our metric appropriately evaluates different dehazing models and is in line with human visual perception.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge