Miao Pan
University of Houston
Ground What You See: Hallucination-Resistant MLLMs via Caption Feedback, Diversity-Aware Sampling, and Conflict Regularization
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable success across diverse tasks, their practical deployment is severely hindered by hallucination issues, which become particularly acute during Reinforcement Learning (RL) optimization. This paper systematically analyzes the root causes of hallucinations in MLLMs under RL training, identifying three critical factors: (1) an over-reliance on chained visual reasoning, where inaccurate initial descriptions or redundant information anchor subsequent inferences to incorrect premises; (2) insufficient exploration diversity during policy optimization, leading the model to generate overly confident but erroneous outputs; and (3) destructive conflicts between training samples, where Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK) similarity causes false associations and unstable parameter updates. To address these challenges, we propose a comprehensive framework comprising three core modules. First, we enhance visual localization by introducing dedicated planning and captioning stages before the reasoning phase, employing a quality-based caption reward to ensure accurate initial anchoring. Second, to improve exploration, we categorize samples based on the mean and variance of their reward distributions, prioritizing samples with high variance to focus the model on diverse and informative data. Finally, to mitigate sample interference, we regulate NTK similarity by grouping sample pairs and applying an InfoNCE loss to push overly similar pairs apart and pull dissimilar ones closer, thereby guiding gradient interactions toward a balanced range. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly reduces hallucination rates and effectively enhances the inference accuracy of MLLMs.
Do Not Merge My Model! Safeguarding Open-Source LLMs Against Unauthorized Model Merging
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Model merging has emerged as an efficient technique for expanding large language models (LLMs) by integrating specialized expert models. However, it also introduces a new threat: model merging stealing, where free-riders exploit models through unauthorized model merging. Unfortunately, existing defense mechanisms fail to provide effective protection. Specifically, we identify three critical protection properties that existing methods fail to simultaneously satisfy: (1) proactively preventing unauthorized merging; (2) ensuring compatibility with general open-source settings; (3) achieving high security with negligible performance loss. To address the above issues, we propose MergeBarrier, a plug-and-play defense that proactively prevents unauthorized merging. The core design of MergeBarrier is to disrupt the Linear Mode Connectivity (LMC) between the protected model and its homologous counterparts, thereby eliminating the low-loss path required for effective model merging. Extensive experiments show that MergeBarrier effectively prevents model merging stealing with negligible accuracy loss.
RAGFort: Dual-Path Defense Against Proprietary Knowledge Base Extraction in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Nov 13, 2025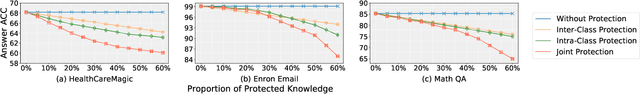
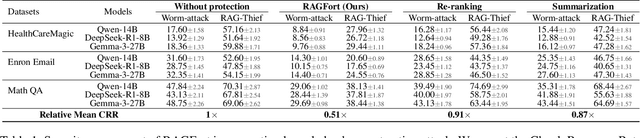
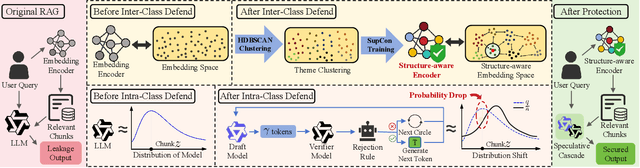
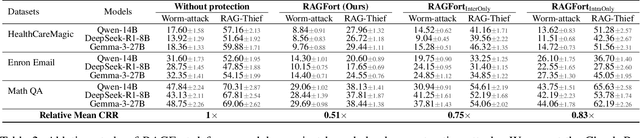
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems deployed over proprietary knowledge bases face growing threats from reconstruction attacks that aggregate model responses to replicate knowledge bases. Such attacks exploit both intra-class and inter-class paths, progressively extracting fine-grained knowledge within topics and diffusing it across semantically related ones, thereby enabling comprehensive extraction of the original knowledge base. However, existing defenses target only one path, leaving the other unprotected. We conduct a systematic exploration to assess the impact of protecting each path independently and find that joint protection is essential for effective defense. Based on this, we propose RAGFort, a structure-aware dual-module defense combining "contrastive reindexing" for inter-class isolation and "constrained cascade generation" for intra-class protection. Experiments across security, performance, and robustness confirm that RAGFort significantly reduces reconstruction success while preserving answer quality, offering comprehensive defense against knowledge base extraction attacks.
iSeal: Encrypted Fingerprinting for Reliable LLM Ownership Verification
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Given the high cost of large language model (LLM) training from scratch, safeguarding LLM intellectual property (IP) has become increasingly crucial. As the standard paradigm for IP ownership verification, LLM fingerprinting thus plays a vital role in addressing this challenge. Existing LLM fingerprinting methods verify ownership by extracting or injecting model-specific features. However, they overlook potential attacks during the verification process, leaving them ineffective when the model thief fully controls the LLM's inference process. In such settings, attackers may share prompt-response pairs to enable fingerprint unlearning or manipulate outputs to evade exact-match verification. We propose iSeal, the first fingerprinting method designed for reliable verification when the model thief controls the suspected LLM in an end-to-end manner. It injects unique features into both the model and an external module, reinforced by an error-correction mechanism and a similarity-based verification strategy. These components are resistant to verification-time attacks, including collusion-based fingerprint unlearning and response manipulation, backed by both theoretical analysis and empirical results. iSeal achieves 100 percent Fingerprint Success Rate (FSR) on 12 LLMs against more than 10 attacks, while baselines fail under unlearning and response manipulations.
EchoMark: Perceptual Acoustic Environment Transfer with Watermark-Embedded Room Impulse Response
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Acoustic Environment Matching (AEM) is the task of transferring clean audio into a target acoustic environment, enabling engaging applications such as audio dubbing and auditory immersive virtual reality (VR). Recovering similar room impulse response (RIR) directly from reverberant speech offers more accessible and flexible AEM solution. However, this capability also introduces vulnerabilities of arbitrary ``relocation" if misused by malicious user, such as facilitating advanced voice spoofing attacks or undermining the authenticity of recorded evidence. To address this issue, we propose EchoMark, the first deep learning-based AEM framework that generates perceptually similar RIRs with embedded watermark. Our design tackle the challenges posed by variable RIR characteristics, such as different durations and energy decays, by operating in the latent domain. By jointly optimizing the model with a perceptual loss for RIR reconstruction and a loss for watermark detection, EchoMark achieves both high-quality environment transfer and reliable watermark recovery. Experiments on diverse datasets validate that EchoMark achieves room acoustic parameter matching performance comparable to FiNS, the state-of-the-art RIR estimator. Furthermore, a high Mean Opinion Score (MOS) of 4.22 out of 5, watermark detection accuracy exceeding 99\%, and bit error rates (BER) below 0.3\% collectively demonstrate the effectiveness of EchoMark in preserving perceptual quality while ensuring reliable watermark embedding.
PAE MobiLLM: Privacy-Aware and Efficient LLM Fine-Tuning on the Mobile Device via Additive Side-Tuning
Jul 01, 2025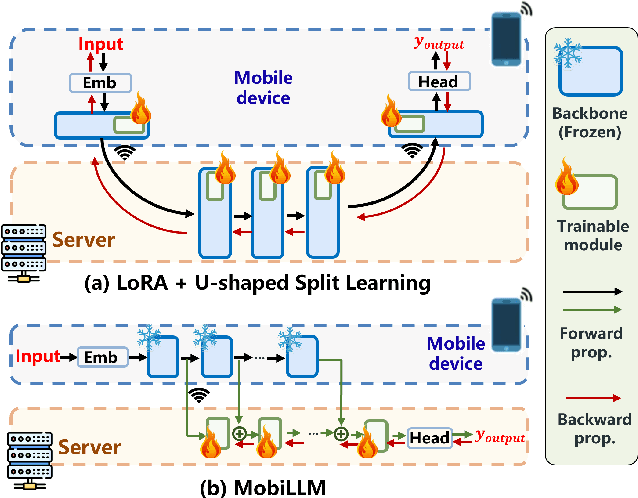
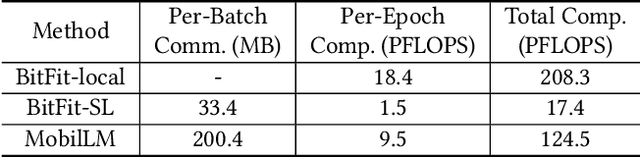
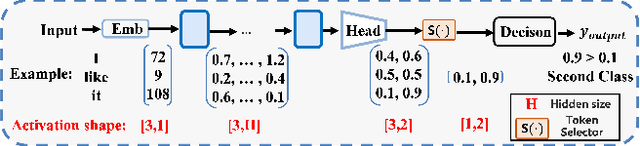
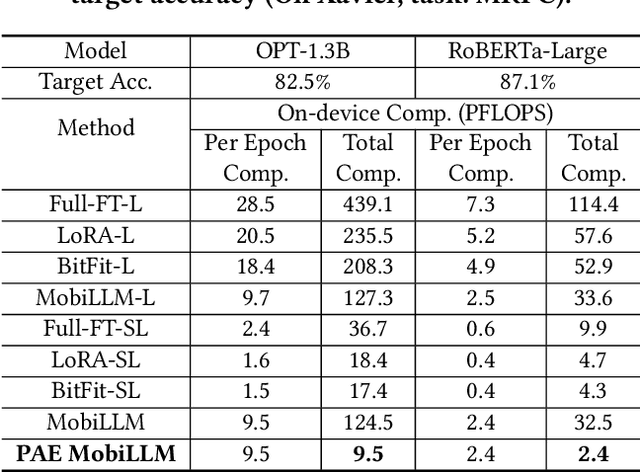
Abstract:There is a huge gap between numerous intriguing applications fostered by on-device large language model (LLM) fine-tuning (FT) from fresh mobile data and the limited resources of a mobile device. While existing server-assisted methods (e.g., split learning or side-tuning) may enable LLM FT on the local mobile device, they suffer from heavy communication burdens of activation transmissions, and may disclose data, labels or fine-tuned models to the server. To address those issues, we develop PAE MobiLLM, a privacy-aware and efficient LLM FT method which can be deployed on the mobile device via server-assisted additive side-tuning. To further accelerate FT convergence and improve computing efficiency, PAE MobiLLM integrates activation caching on the server side, which allows the server to reuse historical activations and saves the mobile device from repeatedly computing forward passes for the recurring data samples. Besides, to reduce communication cost, PAE MobiLLM develops a one-token (i.e., ``pivot'' token) activation shortcut that transmits only a single activation dimension instead of full activation matrices to guide the side network tuning. Last but not least, PAE MobiLLM introduces the additive adapter side-network design which makes the server train the adapter modules based on device-defined prediction differences rather than raw ground-truth labels. In this way, the server can only assist device-defined side-network computing, and learn nothing about data, labels or fine-tuned models.
SpeechVerifier: Robust Acoustic Fingerprint against Tampering Attacks via Watermarking
May 28, 2025Abstract:With the surge of social media, maliciously tampered public speeches, especially those from influential figures, have seriously affected social stability and public trust. Existing speech tampering detection methods remain insufficient: they either rely on external reference data or fail to be both sensitive to attacks and robust to benign operations, such as compression and resampling. To tackle these challenges, we introduce SpeechVerifer to proactively verify speech integrity using only the published speech itself, i.e., without requiring any external references. Inspired by audio fingerprinting and watermarking, SpeechVerifier can (i) effectively detect tampering attacks, (ii) be robust to benign operations and (iii) verify the integrity only based on published speeches. Briefly, SpeechVerifier utilizes multiscale feature extraction to capture speech features across different temporal resolutions. Then, it employs contrastive learning to generate fingerprints that can detect modifications at varying granularities. These fingerprints are designed to be robust to benign operations, but exhibit significant changes when malicious tampering occurs. To enable speech verification in a self-contained manner, the generated fingerprints are then embedded into the speech signal by segment-wise watermarking. Without external references, SpeechVerifier can retrieve the fingerprint from the published audio and check it with the embedded watermark to verify the integrity of the speech. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SpeechVerifier is effective in detecting tampering attacks and robust to benign operations.
Budget-Adaptive Adapter Tuning in Orthogonal Subspaces for Continual Learning in LLMs
May 28, 2025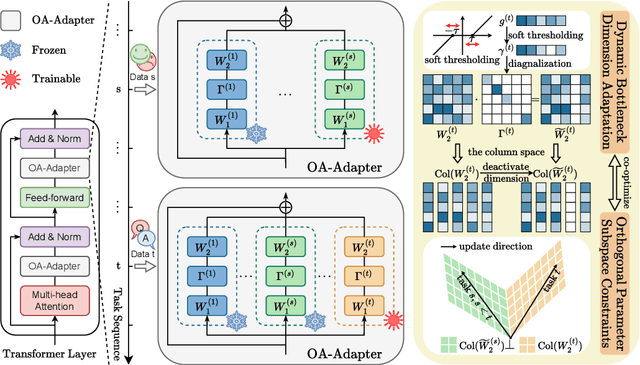
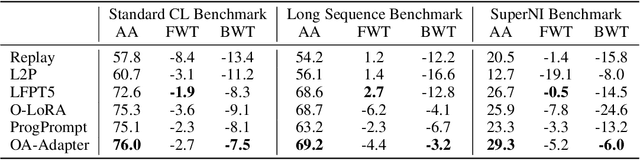
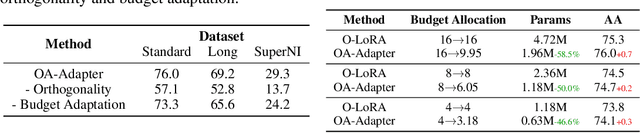
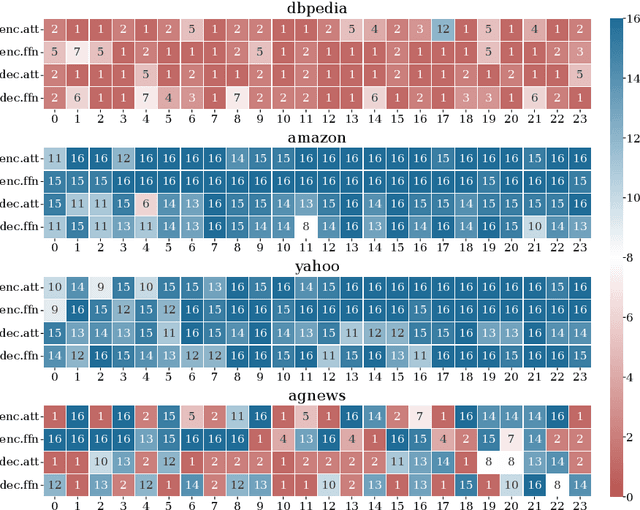
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often suffer from catastrophic forgetting in continual learning (CL) scenarios, where performance on previously learned tasks degrades severely while training on sequentially arriving tasks. Although pioneering CL approaches using orthogonal subspaces can mitigate task interference, they typically employ fixed budget allocation, neglecting the varying complexity across tasks and layers. Besides, recent budget-adaptive tuning methods for LLMs often adopt multi-stage paradigms that decouple optimization and budget allocation. Such decoupling results in potential misalignment, which hinders those approaches' practical application in CL scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose OA-Adapter, a novel parameter-efficient approach for continual learning in LLMs that unifies dynamic budget adaptation with orthogonal subspace learning in a single end-to-end training stage. Specifically, OA-Adapter introduces a dynamic bottleneck dimension adaptation mechanism that simultaneously allocates an efficient parameter budget and optimizes task objectives without misalignment. To effectively preserve previously acquired knowledge while coordinating with the dynamic budget allocation, orthogonal constraints are applied specifically between the parameter subspace of the current task and the dynamically allocated parameter subspaces of historical tasks. Experimental results on continual learning benchmarks demonstrate that OA-Adapter outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both accuracy and parameter efficiency, achieving higher average accuracy while using 58.5% fewer parameters on the standard CL benchmark.
MobiLLM: Enabling LLM Fine-Tuning on the Mobile Device via Server Assisted Side Tuning
Feb 27, 2025
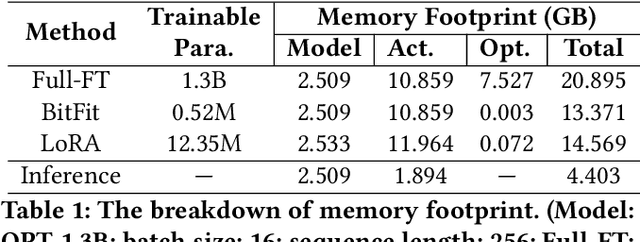
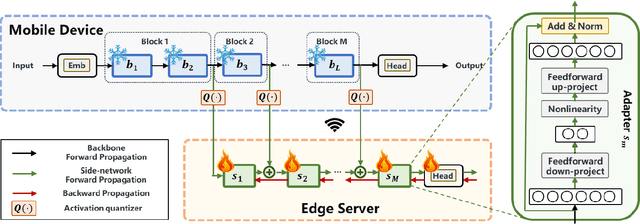
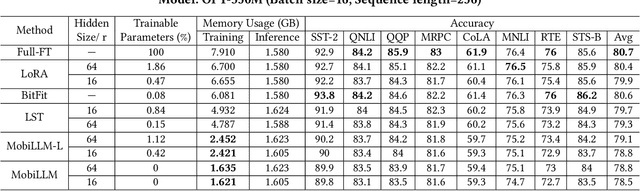
Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) at mobile devices and its potential applications never fail to fascinate. However, on-device LLM fine-tuning poses great challenges due to extremely high memory requirements and slow training speeds. Even with parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods that update only a small subset of parameters, resource-constrained mobile devices cannot afford them. In this paper, we propose MobiLLM to enable memory-efficient transformer LLM fine-tuning on a mobile device via server-assisted side-tuning. Particularly, MobiLLM allows the resource-constrained mobile device to retain merely a frozen backbone model, while offloading the memory and computation-intensive backpropagation of a trainable side-network to a high-performance server. Unlike existing fine-tuning methods that keep trainable parameters inside the frozen backbone, MobiLLM separates a set of parallel adapters from the backbone to create a backpropagation bypass, involving only one-way activation transfers from the mobile device to the server with low-width quantization during forward propagation. In this way, the data never leaves the mobile device while the device can remove backpropagation through the local backbone model and its forward propagation can be paralyzed with the server-side execution. Thus, MobiLLM preserves data privacy while significantly reducing the memory and computational burdens for LLM fine-tuning. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that MobiLLM can enable a resource-constrained mobile device, even a CPU-only one, to fine-tune LLMs and significantly reduce convergence time and memory usage.
Distributed Perception Aware Safe Leader Follower System via Control Barrier Methods
Sep 17, 2024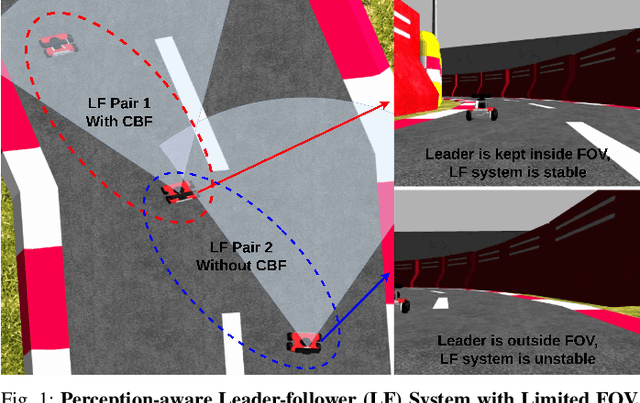
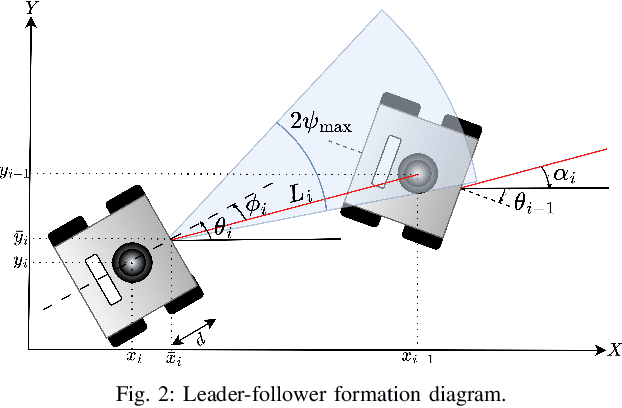
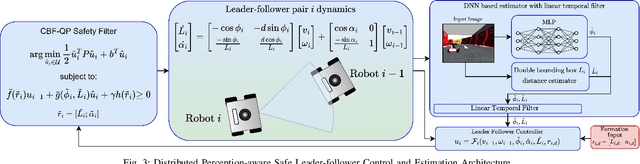
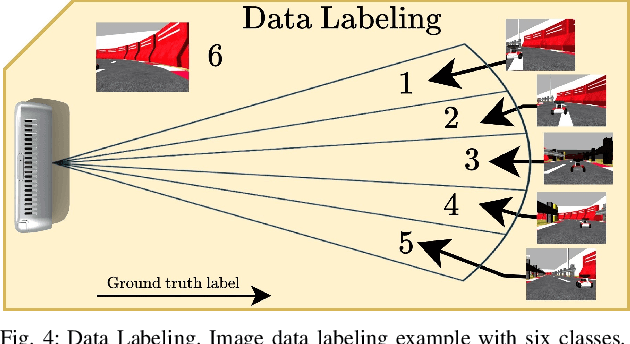
Abstract:This paper addresses a distributed leader-follower formation control problem for a group of agents, each using a body-fixed camera with a limited field of view (FOV) for state estimation. The main challenge arises from the need to coordinate the agents' movements with their cameras' FOV to maintain visibility of the leader for accurate and reliable state estimation. To address this challenge, we propose a novel perception-aware distributed leader-follower safe control scheme that incorporates FOV limits as state constraints. A Control Barrier Function (CBF) based quadratic program is employed to ensure the forward invariance of a safety set defined by these constraints. Furthermore, new neural network based and double bounding boxes based estimators, combined with temporal filters, are developed to estimate system states directly from real-time image data, providing consistent performance across various environments. Comparison results in the Gazebo simulator demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed framework in two distinct environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge