Yikun Li
SecureAgentBench: Benchmarking Secure Code Generation under Realistic Vulnerability Scenarios
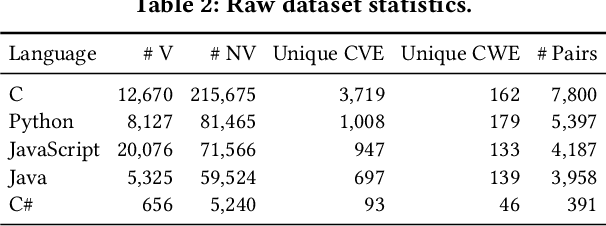
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM) powered code agents are rapidly transforming software engineering by automating tasks such as testing, debugging, and repairing, yet the security risks of their generated code have become a critical concern. Existing benchmarks have offered valuable insights but remain insufficient: they often overlook the genuine context in which vulnerabilities were introduced or adopt narrow evaluation protocols that fail to capture either functional correctness or newly introduced vulnerabilities. We therefore introduce SecureAgentBench, a benchmark of 105 coding tasks designed to rigorously evaluate code agents' capabilities in secure code generation. Each task includes (i) realistic task settings that require multi-file edits in large repositories, (ii) aligned contexts based on real-world open-source vulnerabilities with precisely identified introduction points, and (iii) comprehensive evaluation that combines functionality testing, vulnerability checking through proof-of-concept exploits, and detection of newly introduced vulnerabilities using static analysis. We evaluate three representative agents (SWE-agent, OpenHands, and Aider) with three state-of-the-art LLMs (Claude 3.7 Sonnet, GPT-4.1, and DeepSeek-V3.1). Results show that (i) current agents struggle to produce secure code, as even the best-performing one, SWE-agent supported by DeepSeek-V3.1, achieves merely 15.2% correct-and-secure solutions, (ii) some agents produce functionally correct code but still introduce vulnerabilities, including new ones not previously recorded, and (iii) adding explicit security instructions for agents does not significantly improve secure coding, underscoring the need for further research. These findings establish SecureAgentBench as a rigorous benchmark for secure code generation and a step toward more reliable software development with LLMs.
Compact Varactor-Integrated RIS for Wideband and Continuously Tunable Beamforming
May 08, 2025Abstract:This letter presents a novel Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) that features a low-profile structure, wide operating bandwidth, and continuous phase control. By incorporating a middle patch layer without introducing an additional air gap, the proposed design maintains a thin form factor, while achieving a smooth 310{\deg} phase shift over 10\% bandwidth at 6.1 GHz with excellent reflection. A fabricated 10*10 RIS array exhibits stable performance, enabling precise beam control across a 600 MHz bandwidth. These results highlight the potential of the proposed low-profile, wideband RIS with continuous phase tuning for next-generation wireless communication systems.
R2Vul: Learning to Reason about Software Vulnerabilities with Reinforcement Learning and Structured Reasoning Distillation
Apr 07, 2025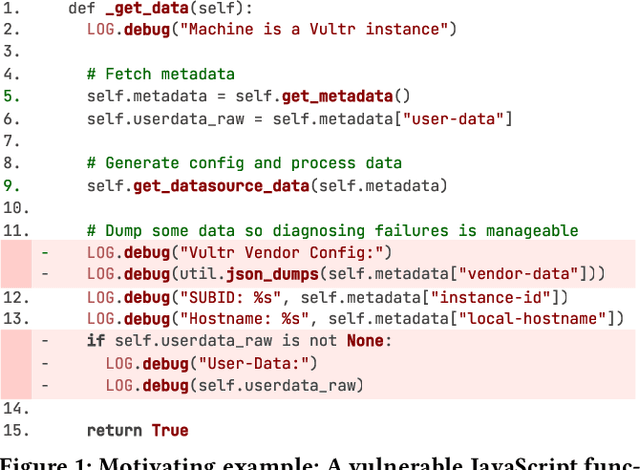


Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown promising performance in software vulnerability detection (SVD), yet their reasoning capabilities remain unreliable. Existing approaches relying on chain-of-thought (CoT) struggle to provide relevant and actionable security assessments. Additionally, effective SVD requires not only generating coherent reasoning but also differentiating between well-founded and misleading yet plausible security assessments, an aspect overlooked in prior work. To this end, we introduce R2Vul, a novel approach that distills structured reasoning into small LLMs using reinforcement learning from AI feedback (RLAIF). Through RLAIF, R2Vul enables LLMs to produce structured, security-aware reasoning that is actionable and reliable while explicitly learning to distinguish valid assessments from misleading ones. We evaluate R2Vul across five languages against SAST tools, CoT, instruction tuning, and classification-based baselines. Our results show that R2Vul with structured reasoning distillation enables a 1.5B student LLM to rival larger models while improving generalization to out-of-distribution vulnerabilities. Beyond model improvements, we contribute a large-scale, multilingual preference dataset featuring structured reasoning to support future research in SVD.
DynamicID: Zero-Shot Multi-ID Image Personalization with Flexible Facial Editability
Mar 09, 2025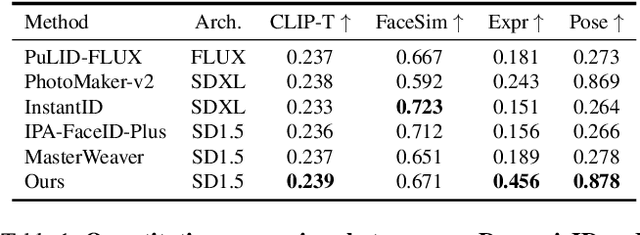
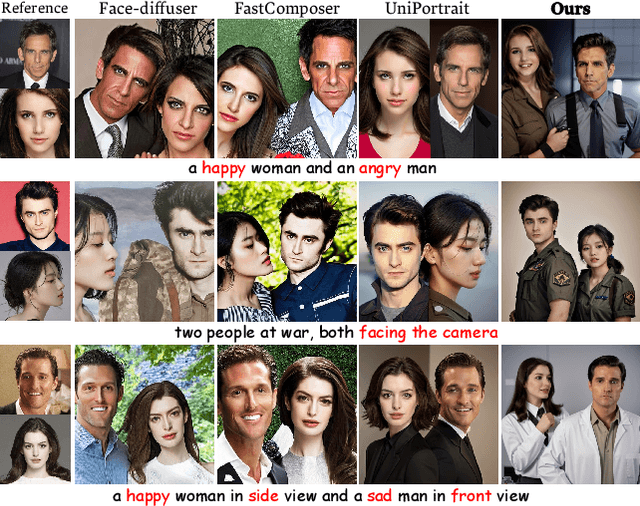
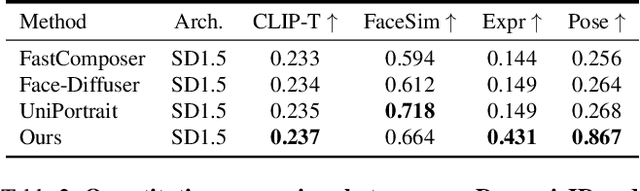
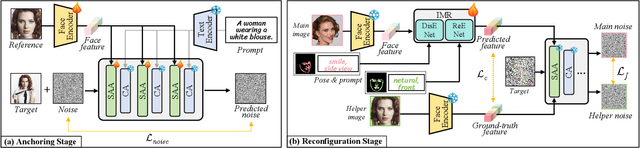
Abstract:Recent advancements in text-to-image generation have spurred interest in personalized human image generation, which aims to create novel images featuring specific human identities as reference images indicate. Although existing methods achieve high-fidelity identity preservation, they often struggle with limited multi-ID usability and inadequate facial editability. We present DynamicID, a tuning-free framework supported by a dual-stage training paradigm that inherently facilitates both single-ID and multi-ID personalized generation with high fidelity and flexible facial editability. Our key innovations include: 1) Semantic-Activated Attention (SAA), which employs query-level activation gating to minimize disruption to the original model when injecting ID features and achieve multi-ID personalization without requiring multi-ID samples during training. 2) Identity-Motion Reconfigurator (IMR), which leverages contrastive learning to effectively disentangle and re-entangle facial motion and identity features, thereby enabling flexible facial editing. Additionally, we have developed a curated VariFace-10k facial dataset, comprising 10k unique individuals, each represented by 35 distinct facial images. Experimental results demonstrate that DynamicID outperforms state-of-the-art methods in identity fidelity, facial editability, and multi-ID personalization capability.
Automatically Estimating the Effort Required to Repay Self-Admitted Technical Debt
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:Technical debt refers to the consequences of sub-optimal decisions made during software development that prioritize short-term benefits over long-term maintainability. Self-Admitted Technical Debt (SATD) is a specific form of technical debt, explicitly documented by developers within software artifacts such as source code comments and commit messages. As SATD can hinder software development and maintenance, it is crucial to address and prioritize it effectively. However, current methodologies lack the ability to automatically estimate the repayment effort of SATD based on its textual descriptions. To address this limitation, we propose a novel approach for automatically estimating SATD repayment effort, utilizing a comprehensive dataset comprising 341,740 SATD items from 2,568,728 commits across 1,060 Apache repositories. Our findings show that different types of SATD require varying levels of repayment effort, with code/design, requirement, and test debt demanding greater effort compared to non-SATD items, while documentation debt requires less. We introduce and evaluate machine learning methodologies, particularly BERT and TextCNN, which outperforms classic machine learning methods and the naive baseline in estimating repayment effort. Additionally, we summarize keywords associated with varying levels of repayment effort that occur during SATD repayment. Our contributions aim to enhance the prioritization of SATD repayment effort and resource allocation efficiency, ultimately benefiting software development and maintainability.
Automatically Identifying Relations Between Self-Admitted Technical Debt Across Different Sources
Mar 13, 2023Abstract:Self-Admitted Technical Debt or SATD can be found in various sources, such as source code comments, commit messages, issue tracking systems, and pull requests. Previous research has established the existence of relations between SATD items in different sources; such relations can be useful for investigating and improving SATD management. However, there is currently a lack of approaches for automatically detecting these SATD relations. To address this, we proposed and evaluated approaches for automatically identifying SATD relations across different sources. Our findings show that our approach outperforms baseline approaches by a large margin, achieving an average F1-score of 0.829 in identifying relations between SATD items. Moreover, we explored the characteristics of SATD relations in 103 open-source projects and describe nine major cases in which related SATD is documented in a second source, and give a quantitative overview of 26 kinds of relations.
Automatic Identification of Self-Admitted Technical Debt from Different Sources
Feb 04, 2022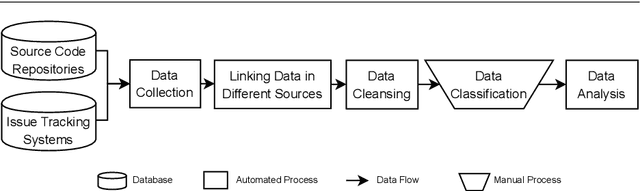
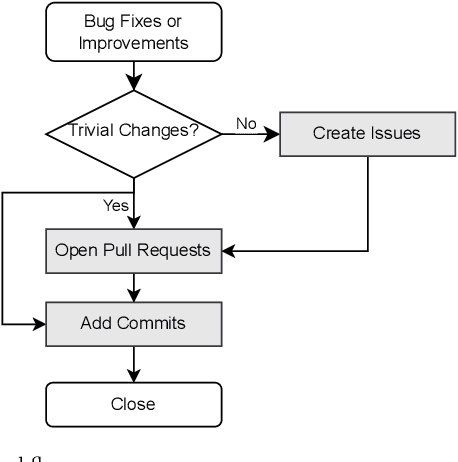
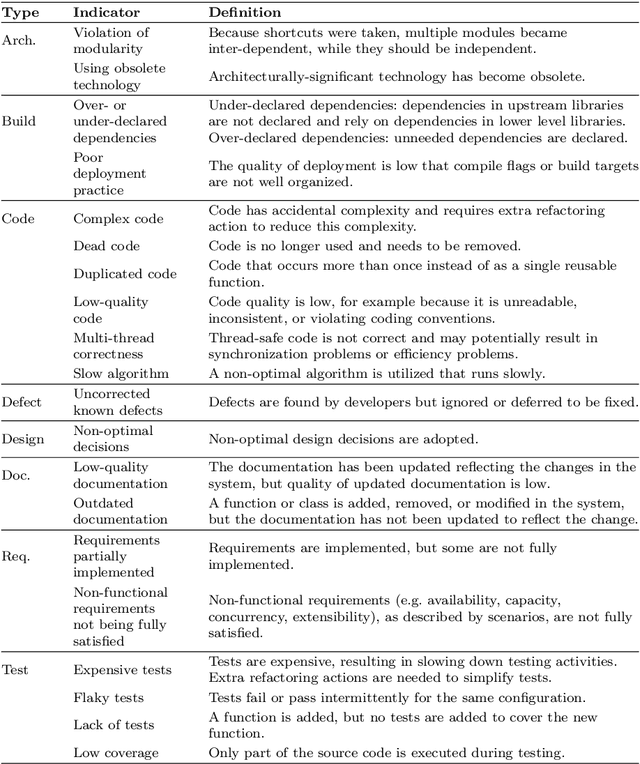
Abstract:Technical debt is a metaphor describing the situation that long-term benefits (e.g., maintainability and evolvability of software) are traded for short-term goals. When technical debt is admitted explicitly by developers in software artifacts (e.g., code comments or issue tracking systems), it is termed as Self-Admitted Technical Debt or SATD. Technical debt could be admitted in different sources, such as source code comments, issue tracking systems, pull requests, and commit messages. However, there is no approach proposed for identifying SATD from different sources. Thus, in this paper, we propose an approach for automatically identifying SATD from different sources (i.e., source code comments, issue trackers, commit messages, and pull requests).
Identifying Self-Admitted Technical Debt in Issue Tracking Systems using Machine Learning
Feb 04, 2022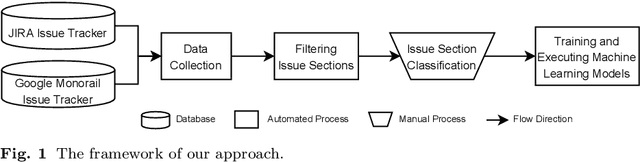



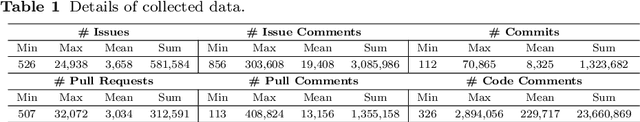
Abstract:Technical debt is a metaphor indicating sub-optimal solutions implemented for short-term benefits by sacrificing the long-term maintainability and evolvability of software. A special type of technical debt is explicitly admitted by software engineers (e.g. using a TODO comment); this is called Self-Admitted Technical Debt or SATD. Most work on automatically identifying SATD focuses on source code comments. In addition to source code comments, issue tracking systems have shown to be another rich source of SATD, but there are no approaches specifically for automatically identifying SATD in issues. In this paper, we first create a training dataset by collecting and manually analyzing 4,200 issues (that break down to 23,180 sections of issues) from seven open-source projects (i.e., Camel, Chromium, Gerrit, Hadoop, HBase, Impala, and Thrift) using two popular issue tracking systems (i.e., Jira and Google Monorail). We then propose and optimize an approach for automatically identifying SATD in issue tracking systems using machine learning. Our findings indicate that: 1) our approach outperforms baseline approaches by a wide margin with regard to the F1-score; 2) transferring knowledge from suitable datasets can improve the predictive performance of our approach; 3) extracted SATD keywords are intuitive and potentially indicating types and indicators of SATD; 4) projects using different issue tracking systems have less common SATD keywords compared to projects using the same issue tracking system; 5) a small amount of training data is needed to achieve good accuracy.
Learning to Grasp 3D Objects using Deep Residual U-Nets
Feb 10, 2020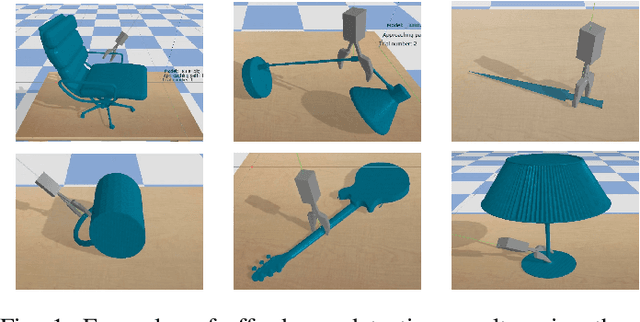
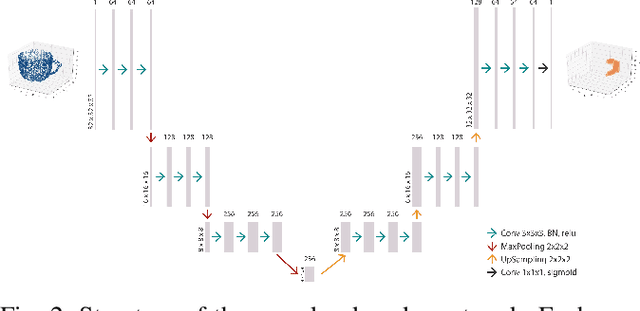
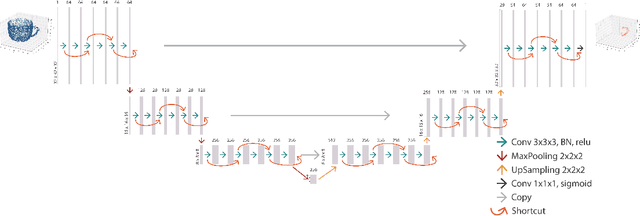
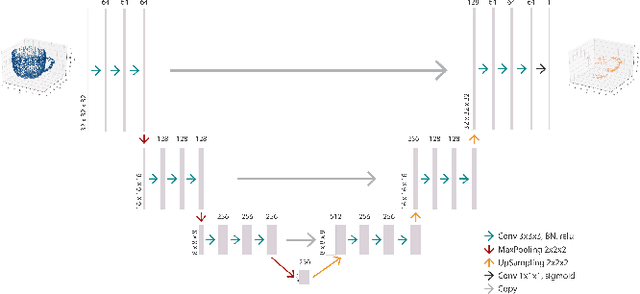
Abstract:Affordance detection is one of the challenging tasks in robotics because it must predict the grasp configuration for the object of interest in real-time to enable the robot to interact with the environment. In this paper, we present a new deep learning approach to detect object affordances for a given 3D object. The method trains a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to learn a set of grasping features from RGB-D images. We named our approach \emph{Res-U-Net} since the architecture of the network is designed based on U-Net structure and residual network-styled blocks. It devised to be robust and efficient to compute and use. A set of experiments has been performed to assess the performance of the proposed approach regarding grasp success rate on simulated robotic scenarios. Experiments validate the promising performance of the proposed architecture on a subset of ShapeNetCore dataset and simulated robot scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge