Lu Fan
Accelerating Generative Recommendation via Simple Categorical User Sequence Compression
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Although generative recommenders demonstrate improved performance with longer sequences, their real-time deployment is hindered by substantial computational costs. To address this challenge, we propose a simple yet effective method for compressing long-term user histories by leveraging inherent item categorical features, thereby preserving user interests while enhancing efficiency. Experiments on two large-scale datasets demonstrate that, compared to the influential HSTU model, our approach achieves up to a 6x reduction in computational cost and up to 39% higher accuracy at comparable cost (i.e., similar sequence length).
PAC: Pronunciation-Aware Contextualized Large Language Model-based Automatic Speech Recognition
Sep 16, 2025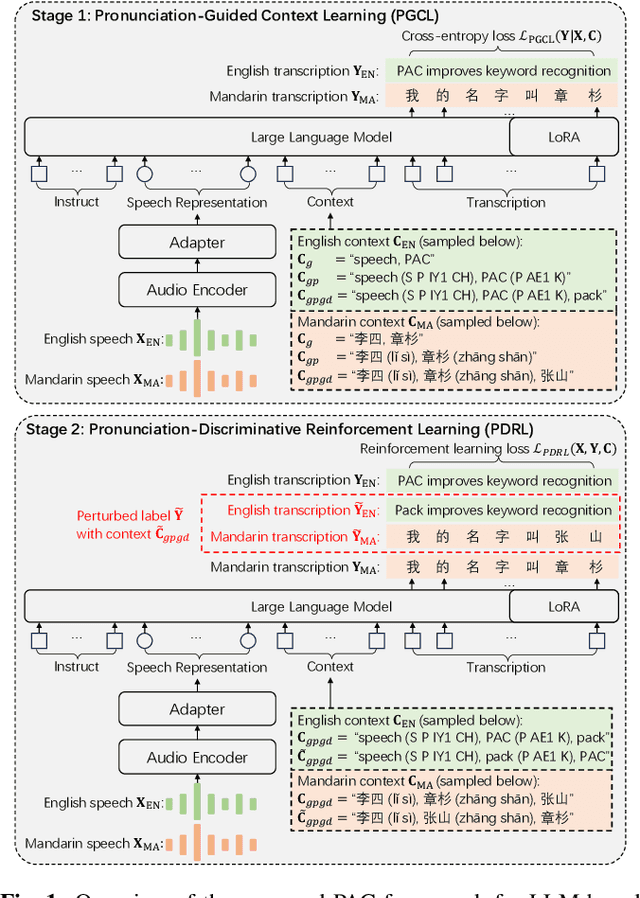
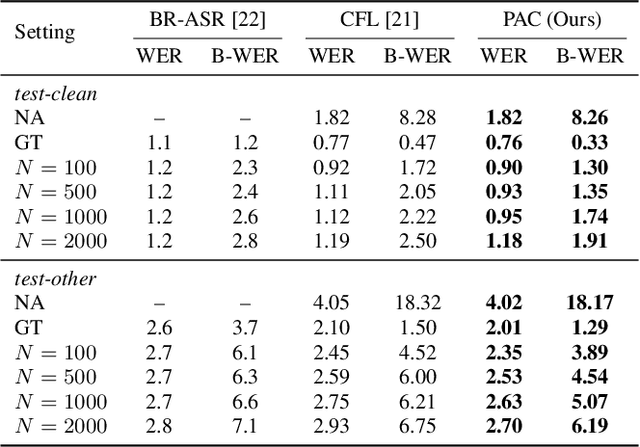
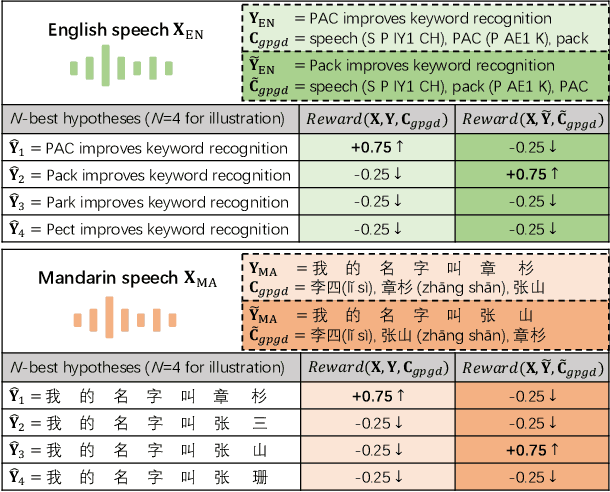
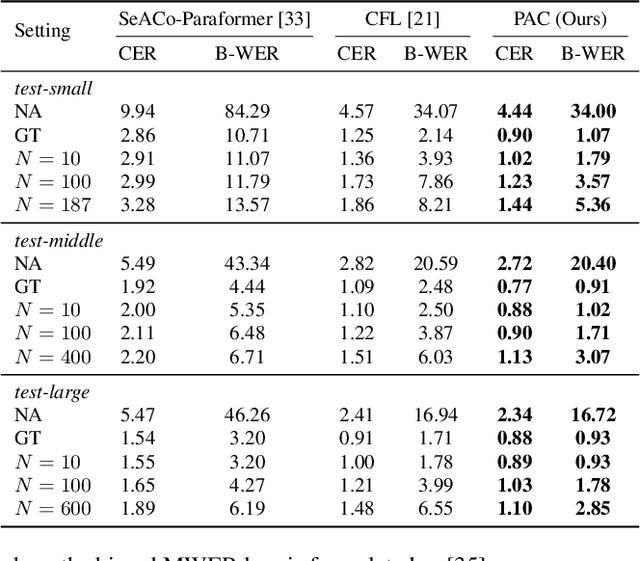
Abstract:This paper presents a Pronunciation-Aware Contextualized (PAC) framework to address two key challenges in Large Language Model (LLM)-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems: effective pronunciation modeling and robust homophone discrimination. Both are essential for raw or long-tail word recognition. The proposed approach adopts a two-stage learning paradigm. First, we introduce a pronunciation-guided context learning method. It employs an interleaved grapheme-phoneme context modeling strategy that incorporates grapheme-only distractors, encouraging the model to leverage phonemic cues for accurate recognition. Then, we propose a pronunciation-discriminative reinforcement learning method with perturbed label sampling to further enhance the model\'s ability to distinguish contextualized homophones. Experimental results on the public English Librispeech and Mandarin AISHELL-1 datasets indicate that PAC: (1) reduces relative Word Error Rate (WER) by 30.2% and 53.8% compared to pre-trained LLM-based ASR models, and (2) achieves 31.8% and 60.5% relative reductions in biased WER for long-tail words compared to strong baselines, respectively.
LANID: LLM-assisted New Intent Discovery
Mar 31, 2025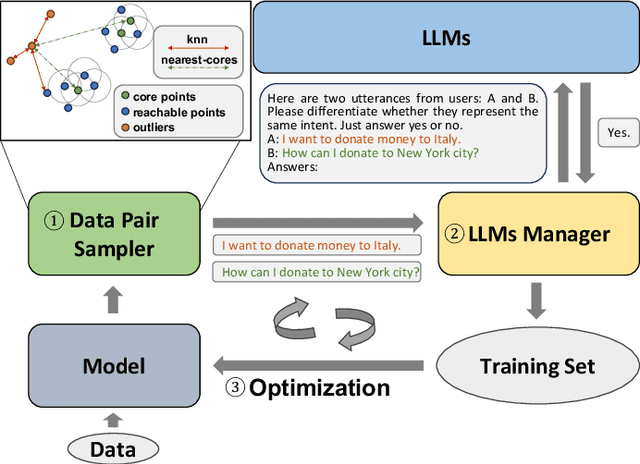
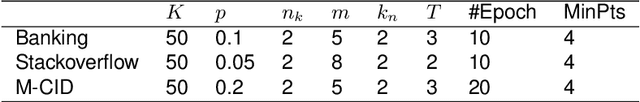
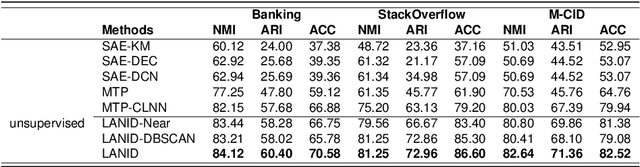
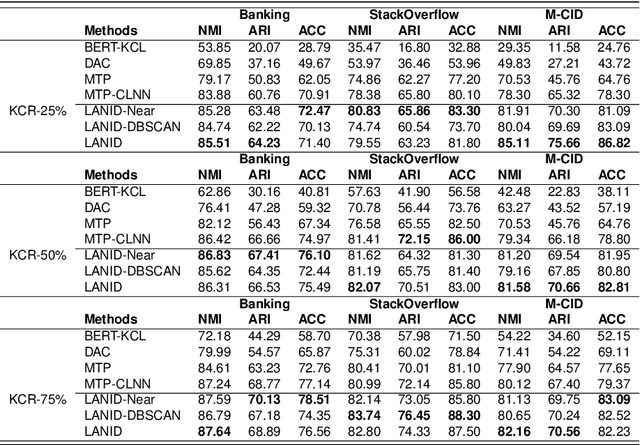
Abstract:Task-oriented Dialogue Systems (TODS) often face the challenge of encountering new intents. New Intent Discovery (NID) is a crucial task that aims to identify these novel intents while maintaining the capability to recognize existing ones. Previous efforts to adapt TODS to new intents have struggled with inadequate semantic representation or have depended on external knowledge, which is often not scalable or flexible. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong zero-shot capabilities; however, their scale can be impractical for real-world applications that involve extensive queries. To address the limitations of existing NID methods by leveraging LLMs, we propose LANID, a framework that enhances the semantic representation of lightweight NID encoders with the guidance of LLMs. Specifically, LANID employs the $K$-nearest neighbors and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) algorithms to sample selective utterance pairs from the training set. It then queries an LLM to ascertain the relationships between these pairs. The data produced from this process is utilized to design a contrastive fine-tuning task, which is then used to train a small encoder with a contrastive triplet loss. Our experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method across three distinct NID datasets, surpassing strong baselines in both unsupervised and semi-supervised settings. Our code is available at https://github.com/floatSDSDS/LANID.
Benchmarking LLMs in Recommendation Tasks: A Comparative Evaluation with Conventional Recommenders
Mar 07, 2025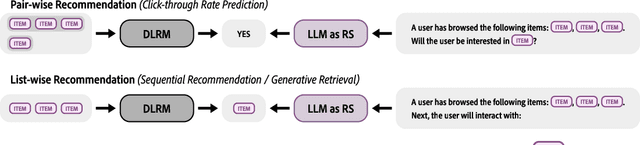
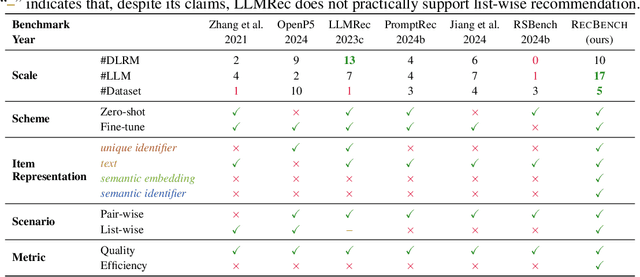
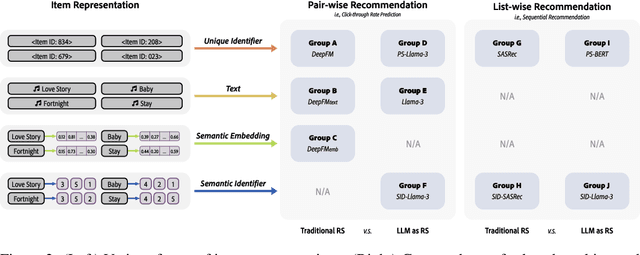
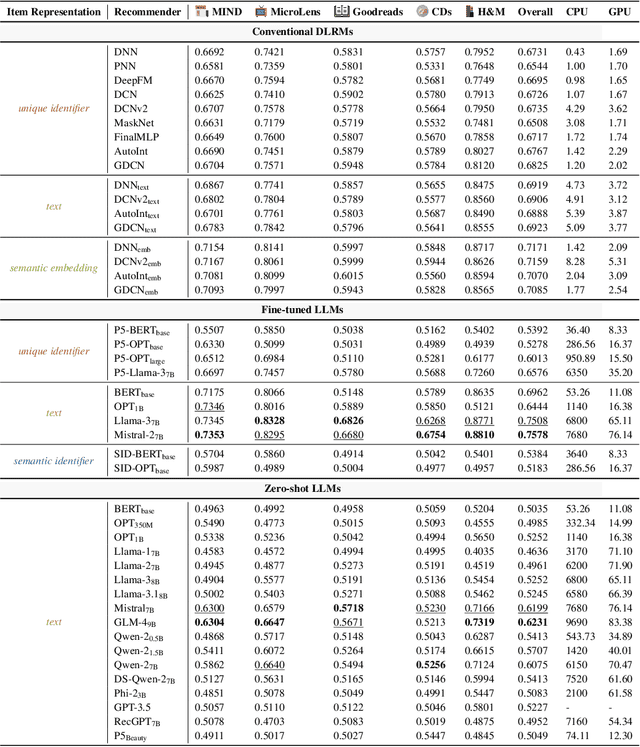
Abstract:In recent years, integrating large language models (LLMs) into recommender systems has created new opportunities for improving recommendation quality. However, a comprehensive benchmark is needed to thoroughly evaluate and compare the recommendation capabilities of LLMs with traditional recommender systems. In this paper, we introduce RecBench, which systematically investigates various item representation forms (including unique identifier, text, semantic embedding, and semantic identifier) and evaluates two primary recommendation tasks, i.e., click-through rate prediction (CTR) and sequential recommendation (SeqRec). Our extensive experiments cover up to 17 large models and are conducted across five diverse datasets from fashion, news, video, books, and music domains. Our findings indicate that LLM-based recommenders outperform conventional recommenders, achieving up to a 5% AUC improvement in the CTR scenario and up to a 170% NDCG@10 improvement in the SeqRec scenario. However, these substantial performance gains come at the expense of significantly reduced inference efficiency, rendering the LLM-as-RS paradigm impractical for real-time recommendation environments. We aim for our findings to inspire future research, including recommendation-specific model acceleration methods. We will release our code, data, configurations, and platform to enable other researchers to reproduce and build upon our experimental results.
UME: Upcycling Mixture-of-Experts for Scalable and Efficient Automatic Speech Recognition
Dec 23, 2024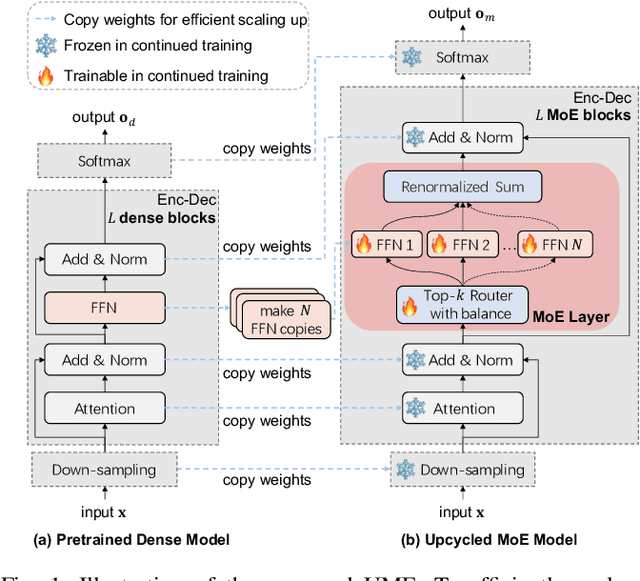
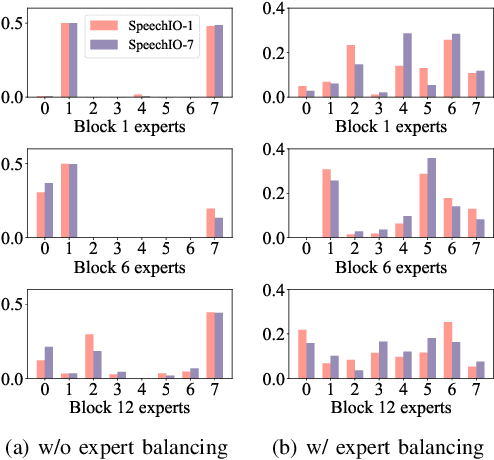
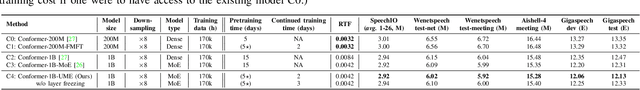
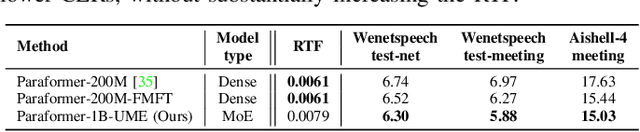
Abstract:Recent advancements in scaling up models have significantly improved performance in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) tasks. However, training large ASR models from scratch remains costly. To address this issue, we introduce UME, a novel method that efficiently Upcycles pretrained dense ASR checkpoints into larger Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures. Initially, feed-forward networks are converted into MoE layers. By reusing the pretrained weights, we establish a robust foundation for the expanded model, significantly reducing optimization time. Then, layer freezing and expert balancing strategies are employed to continue training the model, further enhancing performance. Experiments on a mixture of 170k-hour Mandarin and English datasets show that UME: 1) surpasses the pretrained baseline by a margin of 11.9% relative error rate reduction while maintaining comparable latency; 2) reduces training time by up to 86.7% and achieves superior accuracy compared to training models of the same size from scratch.
Legommenders: A Comprehensive Content-Based Recommendation Library with LLM Support
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:We present Legommenders, a unique library designed for content-based recommendation that enables the joint training of content encoders alongside behavior and interaction modules, thereby facilitating the seamless integration of content understanding directly into the recommendation pipeline. Legommenders allows researchers to effortlessly create and analyze over 1,000 distinct models across 15 diverse datasets. Further, it supports the incorporation of contemporary large language models, both as feature encoder and data generator, offering a robust platform for developing state-of-the-art recommendation models and enabling more personalized and effective content delivery.
STORE: Streamlining Semantic Tokenization and Generative Recommendation with A Single LLM
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:Traditional recommendation models often rely on unique item identifiers (IDs) to distinguish between items, which can hinder their ability to effectively leverage item content information and generalize to long-tail or cold-start items. Recently, semantic tokenization has been proposed as a promising solution that aims to tokenize each item's semantic representation into a sequence of discrete tokens. In this way, it preserves the item's semantics within these tokens and ensures that semantically similar items are represented by similar tokens. These semantic tokens have become fundamental in training generative recommendation models. However, existing generative recommendation methods typically involve multiple sub-models for embedding, quantization, and recommendation, leading to an overly complex system. In this paper, we propose to streamline the semantic tokenization and generative recommendation process with a unified framework, dubbed STORE, which leverages a single large language model (LLM) for both tasks. Specifically, we formulate semantic tokenization as a text-to-token task and generative recommendation as a token-to-token task, supplemented by a token-to-text reconstruction task and a text-to-token auxiliary task. All these tasks are framed in a generative manner and trained using a single LLM backbone. Extensive experiments have been conducted to validate the effectiveness of our STORE framework across various recommendation tasks and datasets. We will release the source code and configurations for reproducible research.
Neural2Speech: A Transfer Learning Framework for Neural-Driven Speech Reconstruction
Oct 07, 2023Abstract:Reconstructing natural speech from neural activity is vital for enabling direct communication via brain-computer interfaces. Previous efforts have explored the conversion of neural recordings into speech using complex deep neural network (DNN) models trained on extensive neural recording data, which is resource-intensive under regular clinical constraints. However, achieving satisfactory performance in reconstructing speech from limited-scale neural recordings has been challenging, mainly due to the complexity of speech representations and the neural data constraints. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel transfer learning framework for neural-driven speech reconstruction, called Neural2Speech, which consists of two distinct training phases. First, a speech autoencoder is pre-trained on readily available speech corpora to decode speech waveforms from the encoded speech representations. Second, a lightweight adaptor is trained on the small-scale neural recordings to align the neural activity and the speech representation for decoding. Remarkably, our proposed Neural2Speech demonstrates the feasibility of neural-driven speech reconstruction even with only 20 minutes of intracranial data, which significantly outperforms existing baseline methods in terms of speech fidelity and intelligibility.
Do self-supervised speech and language models extract similar representations as human brain?
Oct 07, 2023



Abstract:Speech and language models trained through self-supervised learning (SSL) demonstrate strong alignment with brain activity during speech and language perception. However, given their distinct training modalities, it remains unclear whether they correlate with the same neural aspects. We directly address this question by evaluating the brain prediction performance of two representative SSL models, Wav2Vec2.0 and GPT-2, designed for speech and language tasks. Our findings reveal that both models accurately predict speech responses in the auditory cortex, with a significant correlation between their brain predictions. Notably, shared speech contextual information between Wav2Vec2.0 and GPT-2 accounts for the majority of explained variance in brain activity, surpassing static semantic and lower-level acoustic-phonetic information. These results underscore the convergence of speech contextual representations in SSL models and their alignment with the neural network underlying speech perception, offering valuable insights into both SSL models and the neural basis of speech and language processing.
Leveraging Label Information for Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Sep 05, 2023Abstract:Multimodal emotion recognition (MER) aims to detect the emotional status of a given expression by combining the speech and text information. Intuitively, label information should be capable of helping the model locate the salient tokens/frames relevant to the specific emotion, which finally facilitates the MER task. Inspired by this, we propose a novel approach for MER by leveraging label information. Specifically, we first obtain the representative label embeddings for both text and speech modalities, then learn the label-enhanced text/speech representations for each utterance via label-token and label-frame interactions. Finally, we devise a novel label-guided attentive fusion module to fuse the label-aware text and speech representations for emotion classification. Extensive experiments were conducted on the public IEMOCAP dataset, and experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach outperforms existing baselines and achieves new state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge