Haoning Zhang
MoNET: Tackle State Momentum via Noise-Enhanced Training for Dialogue State Tracking
Nov 11, 2022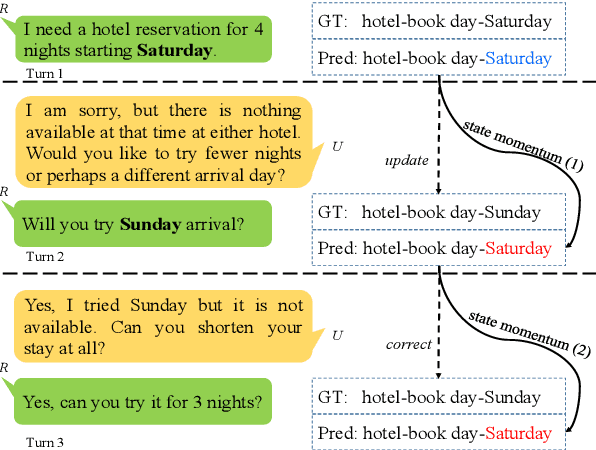
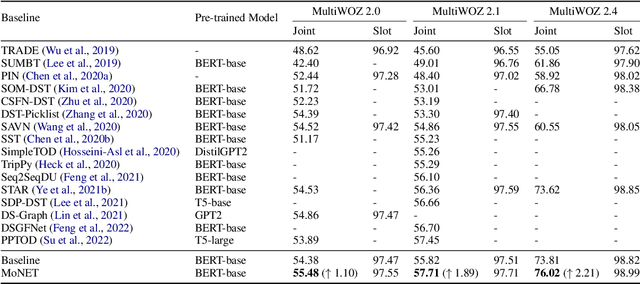
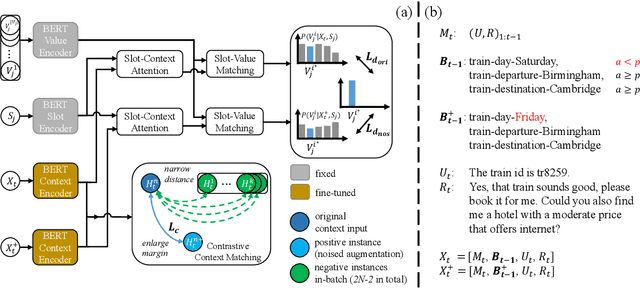
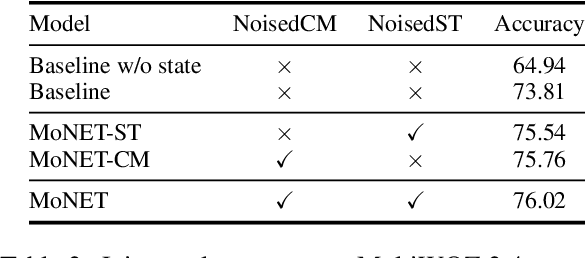
Abstract:Dialogue state tracking (DST) aims to convert the dialogue history into dialogue states which consist of slot-value pairs. As condensed structural information memorizing all history information, the dialogue state in the last turn is typically adopted as the input for predicting the current state by DST models. However, these models tend to keep the predicted slot values unchanged, which is defined as state momentum in this paper. Specifically, the models struggle to update slot values that need to be changed and correct wrongly predicted slot values in the last turn. To this end, we propose MoNET to tackle state momentum via noise-enhanced training. First, the previous state of each turn in the training data is noised via replacing some of its slot values. Then, the noised previous state is used as the input to learn to predict the current state, improving the model's ability to update and correct slot values. Furthermore, a contrastive context matching framework is designed to narrow the representation distance between a state and its corresponding noised variant, which reduces the impact of noised state and makes the model better understand the dialogue history. Experimental results on MultiWOZ datasets show that MoNET outperforms previous DST methods. Ablations and analysis verify the effectiveness of MoNET in alleviating state momentum and improving anti-noise ability.
CSS: Combining Self-training and Self-supervised Learning for Few-shot Dialogue State Tracking
Oct 11, 2022
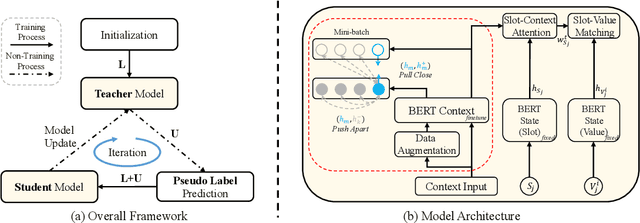
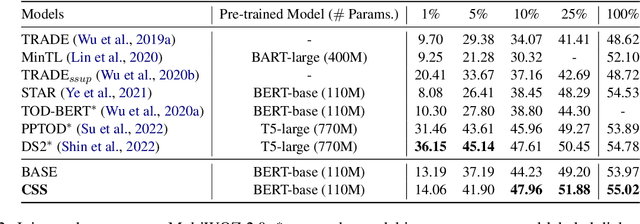
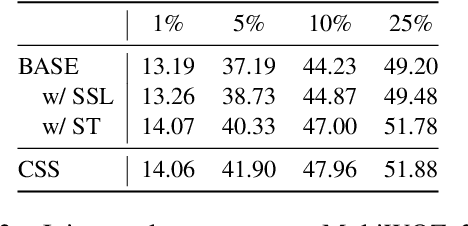
Abstract:Few-shot dialogue state tracking (DST) is a realistic problem that trains the DST model with limited labeled data. Existing few-shot methods mainly transfer knowledge learned from external labeled dialogue data (e.g., from question answering, dialogue summarization, machine reading comprehension tasks, etc.) into DST, whereas collecting a large amount of external labeled data is laborious, and the external data may not effectively contribute to the DST-specific task. In this paper, we propose a few-shot DST framework called CSS, which Combines Self-training and Self-supervised learning methods. The unlabeled data of the DST task is incorporated into the self-training iterations, where the pseudo labels are predicted by a DST model trained on limited labeled data in advance. Besides, a contrastive self-supervised method is used to learn better representations, where the data is augmented by the dropout operation to train the model. Experimental results on the MultiWOZ dataset show that our proposed CSS achieves competitive performance in several few-shot scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge