Haci Ilhan
Deep Learning-Enabled Signal Detection for MIMO-OTFS-Based 6G and Future Wireless Networks
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation stands out as a promising waveform for sixth generation (6G) and beyond wireless communication systems, offering superior performance over conventional methods, particularly in high-mobility scenarios and dispersive channel conditions. Recent research has demonstrated that the reduced computational complexity of deep learning (DL)-based signal detection (SD) methods constitutes a compelling alternative to conventional techniques. In this study, low-complexity DL-based SD methods are proposed for a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)-OTFS system and examined under Nakagami-$m$ channel conditions. The symbols obtained from the receiver antennas are combined using maximum ratio combining (MRC) and detected with the help of a DL-based detector implemented with multi-layer perceptron (MLP), convolutional neural network (CNN), and residual network (ResNet). Complexity analysis reveals that the MLP architecture offers significantly lower computational complexity compared to CNN, ResNet, and classical methods such as maximum likelihood detection (MLD). Furthermore, numerical analyses have shown that the proposed DL-based detectors, despite their low complexity, achieve comparable bit error rate (BER) performance to that of a high-performance MLD under various system conditions.
A Comprehensive Survey of Channel Estimation Techniques for OTFS in 6G and Beyond Wireless Networks
Dec 15, 2025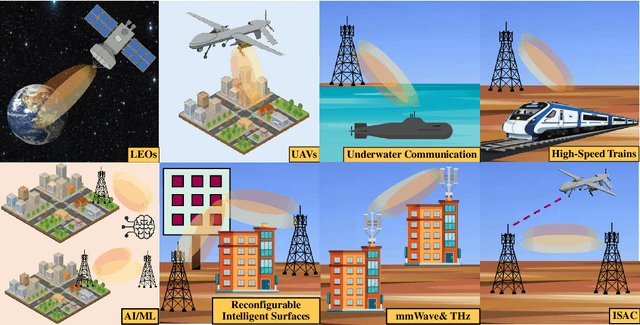
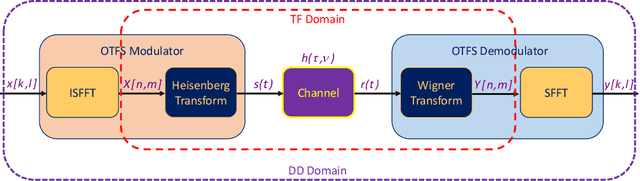
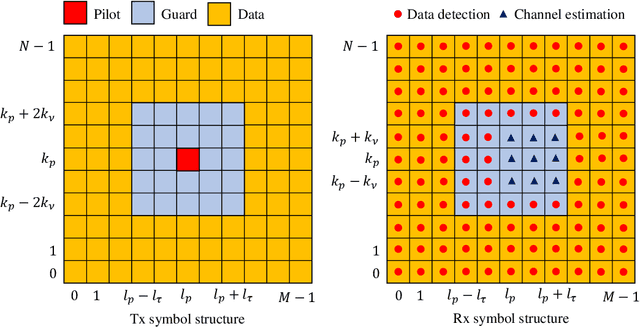
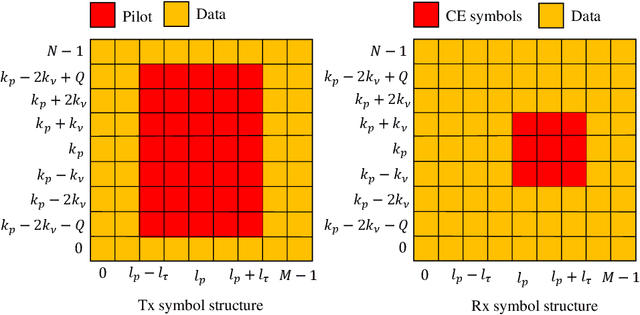
Abstract:Orthogonal time-frequency space (OTFS) modulation has emerged as a powerful wireless communication technology that is specifically designed to address the challenges of high-mobility scenarios and significant Doppler effects. Unlike conventional modulation schemes that operate in the time-frequency (TF) domain, OTFS projects signals to the delay-Doppler (DD) domain, where wireless channels exhibit sparse and quasi-static characteristics. This fundamental transformation enables superior channel estimation (CE) performance in challenging propagation environments characterized by high-mobility, severe multipath effects, and rapidly time-varying channel conditions. This article provides a systematic examination of CE techniques for OTFS systems, covering the extensive research landscape from foundational methods to cutting-edge approaches. We present a detailed analysis of DD and TF domain CE techniques presented in the literature, including separate pilot, embedded pilot, and superimposed pilot approaches. The article encompasses various algorithmic frameworks including Bayesian learning, matching pursuit-based techniques, message passing algorithms, deep learning (DL)-based methods, and recent CE approaches. Additionally, we explore joint CE and signal detection (SD) strategies, the integration of OTFS with next-generation wireless systems including massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO), millimeter wave (mmWave) communications, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), and integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems. Critical implementation challenges are presented, including leakage suppression, inter-Doppler interference mitigation, impulsive noise handling, signaling overhead reduction, guard space requirements, peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) management, beam squint effects, and hardware impairments.
Space-Time Coded RIS-Assisted Wireless Systems with Practical Reflection Models: Error Rate Analysis and Negative Moment-Based Optimization with Saddle Point Approximation
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:RIS-assisted communication has recently attracted significant attention for enhancing wireless performance in challenging environments, making accurate error analysis under practical hardware constraints crucial for future multi-antenna systems. This paper presents a theoretical framework for SER analysis of RIS-assisted multiple antenna systems employing OSTBC under practical reflection models with amplitude-dependent and quantized phase responses. By exploiting the Gramian structure of the cascaded channel f, we derive exact MGF expressions of the nonzero eigenvalue of f'f for small RIS sizes. For large-scale RIS deployments, where closed-form analysis becomes intractable, we employ Saddle Point Approximation to approximate the eigenvalue distribution. Using these results, we derive unified SER expressions using exact and SPA-based MGF formulations, applicable to arbitrary RIS sizes, phase configuration, and both identical and non-identical amplitude responses. Extensive Monte Carlo simulations confirm the accuracy of the proposed SER expressions, demonstrating very close agreement for all configurations.
Joint Phase Shift Optimization and Precoder Selection for RIS-Assisted 5G NR MIMO Systems
May 29, 2025Abstract:By intelligently reconfiguring wireless propagation environment, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) can enhance signal quality, suppress interference, and improve channel conditions, thereby serving as a powerful complement to multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) architectures. However, jointly optimizing the RIS phase shifts and the MIMO transmit precoder in 5G and beyond networks remains largely unexplored. This paper addresses this gap by proposing a singular value ($\lambda$)-based RIS optimization strategy, where the phase shifts are configured to maximize the dominant singular values of the cascaded channel matrix, and the corresponding singular vectors are utilized for MIMO transmit precoding. The proposed precoder selection does not require mutual information computation across subbands, thereby reducing time complexity. To solve the $\lambda$-based optimization problem, maximum cross-swapping algorithm (MCA) is applied while an effective rank-based method is utilized for benchmarking purposes. The simulation results show that the proposed precoder selection method consistently outperforms the conventional approach under $\lambda$-based RIS optimization.
Bit Error Rate and Performance Analysis of Multi-User OTFS under Nakagami-m Fading for 6G and Beyond Networks
May 26, 2025Abstract:Orthogonal Time-Frequency Space modulation stands out as a promising waveform for 6G and beyond wireless communication systems, offering superior performance over conventional methods, particularly in high-mobility scenarios and dispersive channel conditions. Error performance analysis remains crucial for accurately characterizing the reliability of wireless communication systems under practical constraints. In this paper, we systematically investigate the bit error rate performance of OTFS modulation over Nakagami-m fading channels in both single-user and multi-user scenarios. In analytical approaches, mathematical frameworks are employed for distinct receiver configurations: the Single-input Single-output scenario leverages Erlang probability density function of squared-Nakagami variables to derive closed-form BER expressions, while the Single-input Multiple-output case applies moment matching techniques with Gamma approximation to model multiple user interference, subsequently yielding Signal-to-interference-plus-noise Ratio characterizations through Meijer-G functions. This study examines single-path and multi-path channel conditions, evaluating the relationship between path multiplicity and error performance metrics while considering various fading intensities through Nakagami-m fading parameters. The derived closed-form BER expressions are validated through maximum likelihood detection based Monte Carlo simulations, demonstrating strong correlation between analytical and numerical results across various SNR regions. Furthermore, comparative benchmark evaluations against conventional orthogonal frequency division multiplexing with MLD reveal that OTFS consistently achieves superior error performance in high-mobility scenarios. In multipath fading environments, OTFS achieves superior diversity gain compared to conventional OFDM, which refers to enhanced error performance.
A New OTFS-Based Index Modulation System for 6G and Beyond: OTFS-Based Code Index Modulation
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes the orthogonal time frequency space-based code index modulation (OTFS-CIM) scheme, a novel wireless communication system that combines OTFS modulation, which enhances error performance in high-mobility Rayleigh channels, with CIM technique, which improves spectral and energy efficiency, within a single-input multiple-output (SIMO) architecture. The proposed system is evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations for various system parameters. Results show that increasing the modulation order degrades performance, while more receive antennas enhance it. Comparative analyses of error performance, throughput, spectral efficiency, and energy saving demonstrate that OTFS-CIM outperforms traditional OTFS and OTFS-based spatial modulation (OTFS-SM) systems. Also, the proposed OTFS-CIM system outperforms benchmark systems in many performance metrics under high-mobility scenarios, making it a strong candidate for sixth generation (6G) and beyond.
Orthogonal Time-Frequency Space (OTFS) Aided Media-Based Modulation System For 6G and Beyond Wireless Communications Networks
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a new orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS)-based index modulation system called OTFS-aided media-based modulation (MBM) scheme (OTFS-MBM), which is a promising technique for high-mobility wireless communication systems. The OTFS technique transforms information into the delay-Doppler domain, providing robustness against channel variations, while the MBM system utilizes controllable radio frequency (RF) mirrors to enhance spectral efficiency. The combination of these two techniques offers improved bit error rate (BER) performance compared to conventional OTFS and OTFS-based spatial modulation (OTFS-SM) systems. The proposed system is evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations over high-mobility Rayleigh channels for various system parameters. Comparative throughput, spectral efficiency, and energy efficiency analyses are presented, and it is shown that OTFS-MBM outperforms traditional OTFS and OTFS-SM techniques. The proposed OTFS-MBM scheme stands out as a viable solution for sixth generation (6G) and next-generation wireless networks, enabling reliable communication in dynamic wireless environments.
Deep-Learning Based Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Intervehicular Communication
May 21, 2023



Abstract:This letter proposes a novel deep neural network (DNN) assisted cooperative reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) scheme and a DNN-based symbol detection model for intervehicular communication over cascaded Nakagami-m fading channels. In the considered realistic channel model, the channel links between moving nodes are modeled as cascaded Nakagami-m channels, and the links involving any stationary node are modeled as Nakagami-m fading channels, where all nodes between source and destination are realized with RIS-based relays. The performances of the proposed models are evaluated and compared with the conventional methods in terms of bit error rates (BER). It is exhibited that the DNN-based systems show near-identical performance with low system complexity.
Space-Time Block Coded Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Based Received Spatial Modulation
Mar 28, 2022


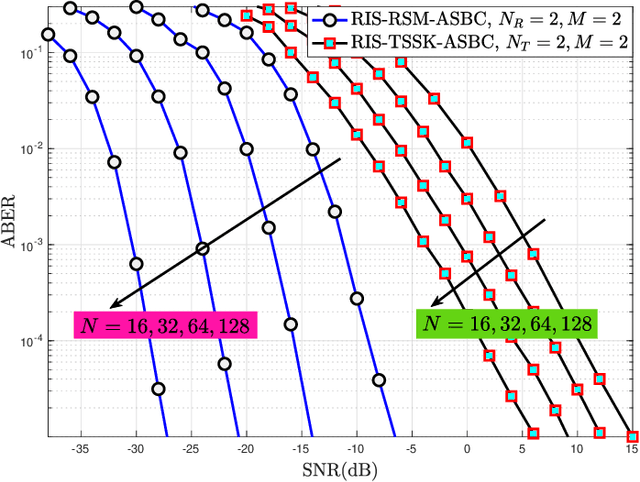
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) structures reflect the incident signals by adjusting phase adaptively according to the channel condition where doing transmission in order to increase signal quality at the receiver. Besides, the spatial modulation (SM) technique is a possible candidate for future energy-efficient wireless communications due to providing better throughput, low-cost implementation and good error performance. Also, Alamouti's space-time block coding (ASBC) is an important space and time coding technique in terms of diversity gain and simplified ML detection. In this paper, we proposed the RIS assisted received spatial modulation (RSM) scheme with ASBC, namely RIS-RSM-ASBC. The termed RIS is portioned by two parts in the proposed system model. Each one is utilized as an access point (AP) to transmit its Alamouti coded information while reflecting passive signals to the selected received antenna. The optimal maximum likelihood (ML) detector is designed for the proposed RIS-RSM-ASBC scheme. Extensive computer simulations are conducted to corroborate theoretical derivations. Results show that RIS-RSM-ASBC system is highly reliable and provides data rate enhancement in contrast to conventional RIS assisted transmit SM (RIS-TSM), RIS assisted transmit quadrature SM (RIS-TQSM), RIS assisted received SM (RIS-RSM), RIS assisted transmit space shift keying with ASBC (RIS-TSSK-ASBC) and RIS-TSSK-VBLAST schemes.
Deep-Learning Assisted Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Cooperative Communications
Jan 25, 2022Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) are software-controlled passive devices to reflect incoming signals from the source ($S$) to destination ($D$), just like a relay ($R$) with optimum signal strength, improving the performance of wireless communication networks. The configurable nature of the RIS can provide network designers the flexibility to use in a stand-alone or cooperative configuration with many advantages over conventional networks. In this paper, two new deep neural networks (DNN) assisted cooperative RIS models, namely DNN$_R$\:-\:CRIS and DNN$_{R, D}$\:-\:CRIS, are proposed for cooperative communications. In these two models, the potential of RIS deployment as a relaying element in a next-generation cooperative network is investigated using deep learning (DL) techniques as a tool for optimizing the RIS. To reduce maximum likelihood (ML) complexity at the $D$, unlike the DNN$_R$\:-\:CRIS, in the DNN$_{R, D}$\:-\:CRIS model, a new DNN based symbol detection method is presented for the same network model. For a different number of relays and receiver configurations, bit error rate (BER) performance results of the proposed DNN$_R$\:-\:CRIS, DNN$_{R, D}$\:-\:CRIS models and traditional cooperative RIS (CRIS) scheme (without DNN) are presented for a multi-relay cooperative communication scenario with path loss effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge